Pyelonephritis
Diabetes
Hepatitis
Rheumatism
17321 October 27
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable; the information below is for reference only.
Urea in the blood: indications for prescription, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and normal indicators.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Urea
When applied topically, it has a resolving, keratolytic and keratoplastic effect, and has bacteriostatic and fungistatic properties. Local application of urea in the form of a cream does not lead to its absorption into the systemic circulation and an increase in nitrogen content in the body. When taken orally or intravenously, due to the osmotic mechanism, it has a diuretic effect, dehydrating and hypotensive effect, and reduces intraocular pressure. It is not metabolized in the human body and undergoes glomerular filtration in large quantities (50–60%); not reabsorbed.
Directions for use and dosage
A solution prepared from a powder substance is administered intravenously. It is prepared immediately before use, observing the rules of asepsis. It should be taken into account that when using pre-prepared solutions, hemolysis may develop.
As a rule, a 30% solution prepared with a 10% glucose solution is used. Dissolution of the powder substance occurs with the absorption of heat. Before use, the solution must be kept until its temperature rises to room temperature.
The drug is administered intravenously at a rate of 40-60-80 drops per minute. If it is necessary to obtain maximum and rapid effect, the rate of administration is increased to 80-120 drops per minute.
The dose of Urea can vary from 0.5 to 1.5 g (on average 1 g) per 1 kg of patient’s body weight. Usually the effect occurs within 15-30 minutes and lasts 5-6 hours or more (up to 14 hours). If the effect is insufficient, it is possible to re-administer Urea with a break of 12-24 hours (no more than 2-3 injections).
With glaucoma, there is a decrease in intraocular pressure, with cerebral edema - a decrease in intracranial pressure, a decrease in the tension of the dura mater, and the appearance of pulsation.
Orally, Urea is prescribed as a 30% or 50% solution in sugar syrup at a dose of 0.75-1.5 g/kg. There is evidence that in the treatment of glaucoma, the hypotensive effect after oral administration of the drug occurs in the same time frame (after 30-45 minutes) as with intravenous drip administration. The effect on brain tissue during cerebral edema appears only a few hours after taking the drug orally.
To prevent the development of water imbalance in the first 24 hours after using the drug, it is necessary to administer intravenously 500-800 ml of an isotonic solution of glucose or sodium chloride with the addition of 0.2-0.3 g of ascorbic acid and 0.1-0.15 g of thiamine. Prescribing other diuretics simultaneously with Urea is unacceptable.
When administering the drug to patients who are unconscious or under anesthesia, a catheter should be inserted into the bladder to drain urine.
To avoid irritation and tissue necrosis, do not allow the solution to get under the skin.
When treating onychomycosis, 30% Urea ointment is used as a keratolytic agent; hyperkeratosis and ichthyosis - 10% cream.
For purulent wounds (to cleanse necrotic masses), wet dressings and irrigation with a 10% solution of the drug are used.
Use of the drug Urea
The concentration of the drug used (5% or 10%), as well as the dose of the cream, is determined individually, since they depend on the type of disease, the degree of damage and the size of the affected area. The cream is applied in a thin layer to the affected area of the skin 2 times a day. To increase the effectiveness of treatment, it is possible to use occlusive dressings; a cream with a urea concentration of 5% can be used during phonophoresis. The duration of treatment depends on the type and severity of the disease and is determined by the regression of infiltration and lichenification of the skin.
Side effects
During Urea therapy, heartburn, nausea, and vomiting may occur.
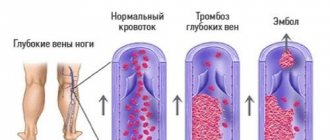
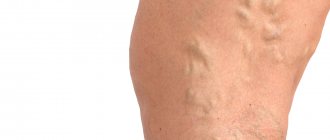
With parenteral administration - phlebitis at the injection site, venous thrombosis, subdural or subarachnoid bleeding, electrolyte imbalance, fever, palpitations, confusion, drowsiness, weakness, dizziness, headache, increased blood pressure, dry mouth, thirst.
In the first hours after administration there is a short-term increase in the concentration of residual nitrogen in the blood.
Indications for the purpose of the study
Urea in the blood is synthesized in the liver from ammonia and carbon dioxide, transported by the blood to the kidneys, there it is filtered through the glomerulus, and then excreted in the urine. Urea is an osmotically active substance, so its accumulation leads to swelling of the tissues of parenchymal organs (liver, kidneys, lungs, spleen, pancreas, thyroid gland), myocardium, central nervous system, subcutaneous tissue. An increase in urea concentration several times relative to the norm, accompanied, as a rule, by a pronounced clinical syndrome of intoxication, is called uremia.
Very often, against the background of kidney disease, simultaneously with an increase in the concentration of urea in the blood, its content in the urine decreases (a decrease in kidney function leads to an increase in urea in the blood).
The study is prescribed for coronary heart disease, systemic connective tissue diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism, systemic scleroderma, etc.), arterial hypertension (regardless of the duration of its existence), when detecting abnormalities in a general urine test during a screening study, liver disease accompanied by dysfunction (hepatitis, cirrhosis), if inflammatory or infectious diseases of the kidneys are suspected, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as before and during drug therapy, before hospitalization of the patient due to an acute illness, after dialysis sessions for evaluation their effectiveness.
The concentration of urea in the blood characterizes:
- the state of the excretory function of the kidneys, that is, their ability to excrete substances unnecessary to the body with urine;
- the condition of muscle tissue (as a result of the breakdown of protein in the muscles, urea is formed);
- liver function, where ammonia is converted to urea.
Pharmaceutical research and production enterprise
Registration number:
LP-001277
Trade name:
Uroderm.
International nonproprietary or generic name:
Urea.
Dosage form:
ointment for external use
Composition:
- Active ingredient:
urea (carbamide) (calculated as 100%) - 0.300 g. - Excipients:
emulsion wax - 0.060 g, liquid paraffin (vaseline oil) - 0.060 g, glycerol (glycerin) (in terms of 100%) - 0.100 g, glycine (aminoacetic acid) - 0.002 g, ethanol (ethyl alcohol) 95% - 0.100 g, purified water to 1.0 g.
Description:
A homogeneous white ointment with a slight odor of ammonia.
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
keratolytic agent.
ATX Code:
D11AX
Pharmacological properties
It has a keratolytic effect, softens and moisturizes the skin, increases its elasticity.
Indications for use
In the complex therapy of skin diseases accompanied by excessive keratinization: ichthyosis and ichthyosiform dermatoses, keratoderma, psoriasis, chronic eczema, Devergie's disease, follicular keratosis, hyperkeratotic forms of fungal diseases; calluses, dry skin. Used to soften the skin and remove horny layers in case of warts (before removal) and to soften the nail plates in order to facilitate their cutting and treatment for ingrown nails, onychomycosis, onychogryphosis, onychodystrophy, hard nails.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. Should not be applied to large surfaces in case of renal, hepatic or cardiovascular insufficiency.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The use of the drug is possible if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus and child. Caution must be exercised and used only on the advice of a physician. The drug should not be applied to large surfaces.
Directions for use and doses
Externally. For skin diseases accompanied by excessive keratinization (ichthyosis, ichthyosiform dermatoses, keratoderma, psoriasis, chronic eczema, Devergie's disease, follicular keratosis, calluses, dry skin), the ointment is applied to areas of accumulation of horny layers in a thin layer 2 times a day. For severe peeling, an occlusive dressing may be used. Before applying the ointment, superficial wounds, erosions, cracks, crusts, and abrasions are treated with antiseptics. Treatment is stopped after removal of the horny layers.
For hyperkeratotic forms of fungal diseases, the ointment is applied 20-30 minutes before external antifungal agents.
For warts, the ointment is applied for 2-8 hours under an adhesive plaster, then the softened part of the wart is cut off, after which it can be removed.
To facilitate trimming and treating nails with ingrown toenails, onychomycosis, onychogryphosis, onychodystrophy, and hard nails, the ointment is applied to the nails for 20-30 minutes, then they are trimmed. If the nails are significantly thickened, the ointment is applied 2 times a day, covered with an adhesive plaster, and treated after softening.
The duration of treatment for skin diseases depends on the location and severity of the process and can be several weeks. To facilitate trimming and treating nails, the ointment can be used 2-3 times a month; the duration of its use in such cases is not limited.
Side effects
When used in the acute period of a skin disease, in some cases there may be increased itching and redness of the skin at the sites of application of the drug, which requires its temporary withdrawal until the severity of the process decreases. Allergic reactions are possible.
Overdose
No cases of overdose have been reported to date.
Interaction with other drugs
The ability of urea to loosen the stratum corneum of the skin creates conditions for increased resorption of other external agents, which enhances their effect. The ointment can be alternated (morning and evening) with any other external agents, except keratolytic ones (salicylic ointment).
special instructions
Avoid contact of the drug with mucous membranes.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
The drug does not affect the ability to perform potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration of attention and speed of psychomotor reactions (including driving vehicles, working with moving mechanisms).
Release form
Ointment for external use 30%. 10, 15, 20 and 35 g in an aluminum tube. Each tube, along with instructions for medical use, is placed in a cardboard pack.
Storage conditions
At temperatures from 2 to 8°C. Keep out of the reach of children. Do not allow freezing.
Best before date
3 years. Do not use after expiration date.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
Over the counter.
The benefits and harms of urea in cosmetics
Carbonic acid diamide is used in ointments for the face, for the body, for areas with very rough skin - when caring for heels.
The compound is used to produce not only cosmetics, but also medicinal creams against psoriasis and eczema. Read about nourishing hand creams in this article.
Urea has antiseptic properties and ensures a long shelf life of the ointment. At the same time, it is not a dangerous preservative.
Diamide provides the following properties of caring compositions:
- the epidermis loses a large amount of moisture due to natural evaporation. Urea forms a hydrophobic film on the skin that retains moisture in the cells;
- urea binds water deep into the skin, providing deep-level hydration;
- urea serves as a kind of conductor for other components of the ointment;
- the compound restores the protective epithelial barrier by normalizing water balance and maintaining acidity levels. This ensures not only the softness of the skin, but also quality that is more important for the treatment of eczema: protection against pathogenic microorganisms;
- urea acts as a light acid on the upper layer of the epidermis: promotes the separation of keratinized skin flakes, removes deep impurities, softens roughness, calluses, corns;
- the substance accelerates the healing of cracks and wounds, which is actively used for scars and scars on the face;
- urea has a mild analgesic effect and is used to suppress itching and burning in psoriasis, dermatitis, and rashes.
It is quite difficult to point out the disadvantages of Urea ointment. The substance does not cause allergies - this is impossible, but it still has some restrictions on use:
- the composition should not be used in the treatment of acne in adolescents, especially with pustules, since the substance irritates inflamed skin;
- for the same reasons, you should not apply cream to your face if there are open wounds and scratches. They are quite sore and inflamed, although they heal faster.
Read about the treatment of dermatitis on the face in this material.
What is urea cream
By body moisturizer we mean a composition that includes hygroscopic ingredients. The latter are capable of holding a mass of water that significantly exceeds the mass of the molecule itself. The leader in this area is considered to be hyaluronic acid, as well as glycerin. Read about face masks with glycerin here.
Only substances that can penetrate the skin barrier can have any effect on the dermis. The rest can only affect the epidermis.
The effectiveness of urea cream is much higher than conventional formulations for the face and body. The molecule of the substance is very small and easily penetrates deep into the skin. In terms of moisture retention efficiency, urea is inferior to hyaluronic acid, but this compound breaks down much more slowly, and ultimately has a much stronger effect.
The skin on the heels quite often becomes very rough and thick, cracks and bleeds, causing a lot of discomfort. You can get rid of it only with the help of urea-based ointments. And if the substance turns out to be effective in such severe cases, then it works real miracles with the skin of the hands and face.
The creams do not use natural urea, but a compound obtained artificially. In order not to cause unpleasant associations, the substance is called urea.
This name is often indicated in the composition.
Useful properties and indications
The benefits of urea for skin are as follows:
- moisturizes and softens;
- prevents premature aging;
- rejuvenates, renews and restores skin cells;
- protects;
- accelerates the healing of various skin injuries;
- relieves the feeling of tightness;
- soothes and relieves itching;
- slightly anesthetizes;
- promotes the production of elastin, increases tone;
- smoothes wrinkles and scars;
- softens keratinized and dead particles of skin and nails (the effect is enhanced in combination with lactic acid);
- treats psoriasis, eczema and some other skin diseases.