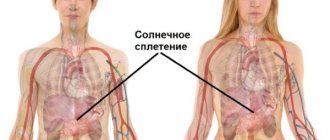
The area the size of a human fist, located midway between the end of the sternum and the navel, along the midline of the abdomen, is the projection of the largest cluster of nerves in our body - the solar plexus.
Pain in the area of the solar (celiac, splanchnitic) plexus is a serious symptom. It may indicate both diseases of the abdominal organs, to which the plexus transmits commands from the brain, and inflammation of the collection of nerves itself. The latter state is not at all safe: it “knows how” to reflexively stop a person’s breathing.
Gastritis
Pain syndrome in the solar plexus most often appears due to the inflammatory process in the gastric mucosa.
Causes of the disease
Many factors can trigger gastric inflammation. The most common :
- Helicobacter pylori infection;
- unhealthy diet (dry food, abuse of smoked food, excess spices);
- smoking;
- drinking alcohol;
- long-term treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- poisoning
Sometimes the cause of gastritis is autoimmune processes, but more often it is bad habits and poor diet.
Signs of the disease
The nature of the pain depends on the course of the disease. With acute gastritis, the pain will be severe, and with chronic gastritis, it will hurt moderately (dull pain). In addition to pain, the patient has the following symptoms :
- dyspepsia;
- flatulence;
- heartburn;
- nausea and/or vomiting;
- decreased appetite;
- belching with an unpleasant aftertaste.
In acute gastritis, the pain is severe and diarrhea often develops, while the chronic course can only be accompanied by epigastric discomfort, unpleasant belching, and loss of appetite.
Treatment
Therapy depends on the cause and severity of solar plexus pain. Patients are prescribed:
- taking sorbents (in case of poisoning);
- intravenous fluids (prevent dehydration caused by diarrhea and vomiting);
- antibiotics (destruction of Helicobacter pylori);
- antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-shpa) to reduce pain in the solar plexus.
In addition to these measures, patients are given symptomatic treatment to help eliminate vomiting, heartburn and other signs of the disease. Additionally, patients are prescribed a gentle diet.
Who will help
If there is pain inside under the solar plexus and there is a suspicion of gastritis, then you should visit a therapist or gastroenterologist.
Pathologies of the duodenum
Inflammation, erosion or atrophic processes in the duodenal mucosa negatively affect digestive function. The pain will be just below the stomach, on the right side of the solar plexus.
Causes
The development of diseases of the duodenum is provoked by:
- poor nutrition;
- smoking or alcohol abuse;
- indigestion in the stomach;
- helminthic infestations;
- metabolic disorders (gout, diabetes, diseases accompanied by the formation of stones);
- entry of an infectious pathogen.
Pathologies of the duodenum are rarely diagnosed as an independent disease. More often, atrophy or inflammation occurs as a complication of chronic gastritis.
Symptoms
It will hurt in different ways, depending on the cause and nature of the pathological process. Pain manifestations can be sharp, aching or dull. In addition to pain, a person experiences:
- nausea;
- urge to vomit;
- problems with stool;
- belching.
The source of pain is located slightly to the right of the midline between the navel and solar plexus.
Treatment
The selection of medications is carried out taking into account the provoking factor. Patients are prescribed:
Surgical treatment is used if the pathological process is accompanied by the appearance of scars, hernias or tumors that prevent the advancement of the food bolus. Then the deformed area is excised, sometimes including part of the stomach.
Who to contact
Therapeutic tactics to eliminate signs of duodenal pathologies are selected by a gastroenterologist or surgeon.
Osteochondrosis and vertebral hernias
Pathologies of the spine, accompanied by destruction of the intervertebral discs, will impair the nerve processes. In this case, the pain may radiate to the epigastric region.
Causes
Causes spinal diseases:
- dystrophy of intervertebral cartilage;
- physical inactivity;
- long-term static loads;
- back bruises.
It is typical for this type of pathology that the prevailing pain increases gradually, over several months or years.
Symptoms
Signs of the disease depend on the location and severity of compression of the nerve process. With strong compression, there will be a sharp pain in the solar plexus, and with slight compression, dull or moderate pain .
Painful discomfort can appear both above and below the epigastric region - it depends on where in the spine the injury is located.
In case of vertebral pathologies, if there is pain under the solar plexus, dyspeptic disorders may additionally occur. This is a sign that the innervation of the intestine is impaired.
Treatment
A person with spinal diseases is prescribed:
- analgesics;
- NSAIDs;
- chondroprotectors;
- anti-inflammatory ointments.
In addition, physical therapy and physiotherapy are prescribed.
Which doctor treats
You should visit an orthopedist or neurologist.
Peptic ulcer
The gradual destruction of the mucous membrane provokes the formation of ulcerations. Small injuries gradually grow and lead to deep damage to the walls of the organ. The ulcer can be localized in the stomach or duodenum.
Causes
The development of ulcers is provoked by non-compliance with diet and lack of treatment for the following pathologies:
- gastritis;
- duodenal diseases.
Where in the solar plexus it will hurt depends on the location of the ulcer. This may be the epigastric region or an area slightly lower with a slight shift to the right from the center line of the abdomen.
Symptoms
When the ulcer worsens, there is acute pain in the solar plexus. Patients describe the pain as “dagger-like” or burning. During remission the pain is moderate.
In addition to pain, the following symptoms occur:
- belching;
- heartburn;
- nausea;
- vomiting food, after which the patient feels relief;
- the appearance of cramps in the upper abdomen;
- problems with sleep (ulcer sufferers often have solar plexus pain at night);
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- atony;
- constipation (diarrhea occurs rarely).
Peptic ulcer disease is characterized by the appearance of hunger pains. This is because during prolonged fasting, digestive juices irritate the surface of the ulceration, causing painful discomfort.
Sharp pain in the solar plexus is caused by perforation of the ulcer when the contents of the organ enter the abdominal cavity.
Treatment
In case of exacerbation of a peptic ulcer, the patient is prescribed bed rest and a diet that prevents irritation of the digestive tract (mashed warm dishes without spices, with a small amount of salt).
Medicines prescribed:
- antibiotics (if there is a bacterial infection);
- acidity reducing agents;
- antispasmodics;
- medications to reduce secretory activity.
The goal of the therapy is to reduce irritation of the ulcerated area and ensure healing of the injury.
In case of perforation, surgical treatment is indicated. The affected area of the organ is excised along with the surrounding healthy tissue.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you feel acute pain in the solar plexus, and have a history of stomach or duodenal diseases, then first of all you need to visit a gastroenterologist.
OKS
Usually, with acute coronary syndrome, which occurs with myocardial infarction or severe angina, there is pain on the left behind the sternum, but this is not always the case, sometimes due to cardiac pathologies there is pain under the solar plexus.
Causes
Provoke the development of ACS:
- thrombosis of coronary vessels;
- spasms of the heart arteries.
The difference between severe angina and a heart attack is that in the first case, physiological vascular spasm occurs, which is eliminated by taking medications.
Symptoms
If pain in the solar plexus occurs due to heart disease, then this can be suspected by the following signs:
- painful discomfort decreases slightly at rest;
- after taking analgesics, the intensity of pain does not decrease;
- after using nitrates (Isoket, Nitroglycerin), the condition partially improves.
You can distinguish cardiac pain in the solar plexus from pain caused by other factors using an ECG.
Treatment
Heart disease must be treated in an intensive care unit or cardiology department. Depending on the cause and severity of the condition, patients are given:
- thrombolysis;
- blood thinning therapy;
- pain relief with narcotic analgesics.
Until the patient's condition stabilizes, the person is in the hospital.
Pancreatitis
Inflammation of pancreatic tissue is considered a dangerous disease. When it occurs, the ducts that ensure the flow of organ secretions into the small intestine are blocked and, under the influence of digestive enzymes, pathological “self-digestion” occurs.
Causes
Pancreatitis occurs due to the influence of the following factors:
- alcohol abuse;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- chronic intoxication (in those working with industrial poisons);
- poor nutrition;
- unfavorable environmental situation.
The disease can develop slowly with a gradual increase in pain in the epigastric region or acutely, when it immediately begins to hurt severely in the solar plexus.
Symptoms
The acute form or exacerbation of a chronic process is characterized by pain surrounding the solar plexus and costal arches. In addition to pain, the patient experiences:
- nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- bloating;
- bluish skin in the umbilical area;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- cardiopalmus;
- confusion.
It hurts so much that the person rushes around trying to find a comfortable position and complains that it is hard to breathe.
In the chronic form, the symptoms are mild, pain and indigestion are relieved by taking medications, but parts of the organ slowly die off.
Treatment
Therapy depends on the severity of the inflammatory process.
Spicy
If the solar plexus and under the ribs hurt, and the symptoms of pancreatitis are severe, then hospitalization in a surgical or gastroenterology department is indicated. In stationary conditions the following is carried out:
- intravenous infusions (Reopoliglyukin, Reosorbilact);
- elimination of pain and spasm (Platifillin, Ketorolac, and in case of a severe pain attack, the administration of narcotic analgesics is possible);
- stopping vomiting (Cerucal);
- preventing organ swelling (Cerucal is used);
- replenishment of enzymatic deficiency (Contriven, Trasylol);
- decreased gastric secretion (Omez);
- increasing immune strength (vitamin therapy).
In the first days after an attack, patients are shown a starvation diet, and then gentle nutrition to reduce the load on the organ.
Chronic
If the disease is accompanied by moderate symptoms, then outpatient treatment is allowed. A gentle diet low in carbohydrates and fats is prescribed. To prevent pancreatic necrosis, patients are prescribed:
- enzymes (Pancreatin, Festal);
- proton pump inhibitors to reduce acidity (Omeprazole);
- antacids.
Why else can the solar plexus hurt?
Let's look at less common causes of pain under the solar plexus:
- Intestines. When the duodenum or small intestine is inflamed, pain appears just below the solar plexus. If the pain is low, then perhaps the pathological process affects part of the large intestine.
- Wearing tight things. More often than not, women suffer from this when they choose narrow clothes. In this case, pain below the solar plexus will be associated with wearing certain clothes.
- Irritation of the nerve plexuses. Nerve plexuses are localized in the celiac region, irritation of which can be accompanied by pain. The provoking factor will be hard work or injury.
Short summary
If your solar plexus hurts, then a visit to the doctor is necessary. Let's consider when emergency medical care is needed, and when a planned visit to the clinic is possible:
- Nature of pain. If the pain is acute, then you need to call an ambulance, and if there is a nagging pain in the solar plexus and the cause is known (diet violation, exacerbation of osteochondrosis), then a scheduled visit to the clinic is indicated.
- Intensity. If the pain is severe, then immediate help is needed.
- Action of analgesics. If taking antispasmodics or painkillers is ineffective and pain in the solar plexus persists, then emergency hospitalization is necessary. The cause may be acute pancreatic necrosis or heart attack.
The causes of pain in the solar plexus can be relatively harmless (exacerbation of chronic gastritis or irritation of the nerve node during physical activity), or they can indicate a serious pathology (acute pancreatitis, heart attack). Do not ignore the pain that has arisen. Timely seeking medical help will help avoid serious complications.
Found a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter
Anatomy and physiology
The abdominal cavity begins immediately below the costal arches. It is separated from the chest by a large muscle, the diaphragm, stretched between the ribs like a tent, whose task is to ensure human breathing. There is a hole in the diaphragm. The largest artery, the aorta, passes through it from the chest cavity. Behind it, at the level of the first lumbar vertebra, there is a whole network of nerves originating from several nerve ganglia.
The main ones are the two semilunar ganglia (the so-called nerve ganglia, which are the place where, covered with a membrane, the connection of nerve endings occurs). From them, like the rays of the sun, nerves radiate to all the organs of the abdominal cavity, as well as to the diaphragm, adrenal glands and ovaries. The vast majority of them are represented by parasympathetic fibers (there are also sympathetic and sensory nerves). The appearance of this “abdominal brain” determined its name.
Pain in the solar plexus area is a dangerous symptom: it may indicate a pathology of its constituent nerve fibers. Such a violation of the conduction of impulses is fraught with “switching off” or “interruptions in the functioning” of those internal organs that receive commands from the celiac plexus. It is most dangerous if the branches leading to the diaphragm are affected - they can “switch off” breathing, which will require emergency assistance. Therefore, all you can do is, if you experience pain in the pit of your stomach, immediately seek medical help.
Causes of pain syndrome
The main causes of pain in the solar plexus can be divided into 2 groups:
- Damage to the nerve fibers themselves due to injury, bacterial or viral inflammation.
- Reactive pain due to a disease of one of the abdominal organs, to which sensory fibers from the splanchnitic plexus approach.
In the first type of pathology, the functioning of one or several organs of the cavity may be disrupted; in the second case, pain in the plexus will be a consequence of organ pathology. Only specialists with medical education can determine what was primary and what developed as a result. Below we will look at the main symptoms in order to quickly determine which doctor you need to consult.
Damage to the celiac plexus itself
These are: solar plexus injury, solaritis (neuritis) and solar plexus neuralgia.
| Injury | Neuralgia | Solarite |
What is the basis of the disease
Brief but strong stimulation
Causes
Hit with a fist, a ball in the stomach, a collision with a car, a strong belt tightening
Reactive inflammation of the plexus, occurring as a result of its location near inflamed organs: pancreas, peritoneum, tissue surrounding the stomach or pancreas.
Radiculitis, osteochondrosis, herpes zoster, intervertebral hernia.
Poisoning by poisons coming from outside (nicotine, lead, alcohol) or formed as a result of illness
Symptoms
The pain is sharp, shooting, makes you bend over while sitting and bring your legs to your stomach. Appears in fits and starts. Its localization is midway between the navel and the xiphoid process of the sternum. This is pain that radiates to the back. If the attack has just passed, it can be provoked by physical activity or emotional stress.
In addition to the acute pain of a boring nature “in the pit of the stomach,” heat is felt in this area (while the body temperature does not rise).
Sharp pain radiates to the chest cavity, lower back, and rectum. It decreases when the legs are bent and brought towards the stomach, and taking drugs like “No-shpa” or “Buscopan” has no effect on it.
The activity of internal organs is disrupted, which is accompanied by constipation or diarrhea, vomiting, belching, increased amount of urine or disturbances in the sexual sphere. There may be involuntary short-term breath holdings
What to do
Call an ambulance, take a position lying on your side, with your head raised, apply any dry cold to the lower part of the sternum
Pain in the solar plexus as a sign of internal organ disease
The fact that it is not the solar plexus itself that is affected, but pain here comes from internal organs modified by pathology, is evidenced by such signs as: the connection of the pain syndrome with eating, urination, changes in the nature of feces, and so on.
| Irritation of sensory, but not autonomic fibers of the plexus. The structure of the nerves is practically not damaged | This is damage to the plexus fibers by an infectious agent (inflammation) | |
| Compression of the plexus by prolapsed internal organs, dilation (aneurysm) of the aorta, pancreatic cyst, enlarged lymph nodes due to metastases or lymphogranulomatosis, strong protrusion of the spine forward | Inflammation of the plexus as a result of an infectious process: | |
| Visit a therapist who will help you decide on further diagnostics (that is, visiting related specialists and undergoing tests) and treatment. If you hold your breath, call an ambulance. | ||
| Main symptom | What is it, additional signs | How to check |
| Pain after eating | ||
Stomach ulcer
Nausea, belching, occasionally vomiting, bloating. It becomes easier after drinking milk or warming the sore spot.
Dependence of diagnosis on pain localization
The localization of the pain syndrome will help to roughly guide you in the search for the disease.
Localization of pain - to the left of the plexus
Pain to the left of the solar plexus can occur with one of the following pathologies:
Pain – to the right of the plexus
If the pain syndrome is located to the right of the midline connecting the sternum and the navel, this may be in favor of:
- appendicitis;
- cholecystitis;
- hepatitis A;
- cholelithiasis;
- right-sided intercostal neuralgia;
- liver tumors;
- inflammation, tumors or burns of the lower part of the esophagus;
- pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis or stone - in the left kidney.
Soreness – below the solar plexus
Pain under the solar plexus is characteristic of the following diseases:
- Genital organs (mainly in women): fallopian tubes, ovaries.
- Bladder, ureters (more often such irradiation is typical for men).
- Large intestine (colitis, sigmoiditis, proctitis)
The painful area is located above the solar plexus
Pain above the plexus is typical for:
- Diseases of the esophagus (esophagitis, tumors, erosions, burns). An additional symptom in this case will be pain when swallowing, located behind the sternum. Belching and nausea will also be noted.
- Pathologies of the pleura (pleurisy, empyema). They develop as complications of pneumonia or tuberculosis. Their connection with breathing speaks in their favor.
- Pneumonia (usually lower lobe). Typically, this pathology occurs with fever and muscle pain. If it is not treated for some time, shortness of breath and a feeling of lack of air develops.
- Heart diseases. Here, the pain is associated with anxiety or physical activity, and is alleviated by taking nitroglycerin or with long-term use of drugs such as Anaprilina, Atenolol, Nebivolol. If the pain is severe and occurs after several years of attacks that were relieved with nitroglycerin, it may be a myocardial infarction.
- Diseases of the diaphragm (most often a diaphragmatic hernia, when the abdominal organs enter the chest cavity). In this case, there may be heart rhythm disturbances and difficulty breathing after eating, especially if the person then assumes a horizontal position.
- Intercostal neuralgia. With this pathology, in the affected intercostal space you can sometimes find a blistering rash of herpes zoster or palpate the pinched vertebra by pressing on each individually. Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia will be the appearance of pain above the solar plexus on the right or left, which radiates to the left or right hand (respectively). It hurts to take a deep breath or cough. The temperature rarely rises; symptoms of intoxication (nausea, weakness, muscle or bone pain), which distinguishes this pathology from pleurisy.
Traumatic neuritis (post-traumatic neuropathy)
Traumatic neuritis (post-traumatic neuropathy)
Traumatic neuritis (post-traumatic neuropathy) is a disease of the nerve root that occurs after mechanical injury to the nerve:
- operations
- wounds, including after injection of the drug (post-injection neuritis)
- shocks and prolonged compression
- broken bones and dislocated joints
Traumatic neuritis (post-traumatic neuropathy), depending on the level and type of nerve damage, will be manifested by a variety of symptoms: movement disorders (paresis, paralysis) in a particular muscle or group of muscles, numbness, changes in sensitivity (increased, weakened or perverted).
Traumatic neuritis of the ulnar nerve due to a fracture of the ulna.
Traumatic neuritis often occurs with fractures or dislocations of bones and joints of the extremities due to their anatomical proximity. After diagnosing the level of nerve damage, treatment begins taking into account the symptoms of nerve root damage.
Traumatic neuritis (post-traumatic neuropathy), which causes persistent pain symptoms (neuralgia), or hypoesthesia (decreased sensitivity), or muscle paresis (decreased strength) requires time and patience and responds well to treatment.
Injuries to such a large nerve as the sciatic nerve are rarely complete. More often, one or the other portion of the sciatic nerve suffers more.
Diagnosis of traumatic neuritis
Neuropraxia is a disease of the peripheral nervous system, during which there is a temporary loss of motor and sensory function due to blockade of nerve conduction. Disruption of nerve impulse transmission with neuropraxia usually lasts an average of 6–8 weeks until it is completely restored.
Symptoms of damage to any peripheral nerve during traumatic neuritis consist of motor, reflex, sensory and vasomotor-secretory-trophic disorders. The examination of a patient with traumatic neuritis traditionally begins with the collection of anamnestic information.
Classical electrodiagnostics is of great importance in the system of comprehensive examination of a patient with traumatic neuritis in periods of 2 weeks and later after injury, helping to separate degenerative from non-degenerative disorders. This determines, to a certain extent, the prognosis, since closed injuries to the nerve trunks, in particular the brachial plexus, accompanied by degeneration, are always questionable regarding the completeness and quality of restoration of lost movements, especially in the distal parts of the limb.
Restoration of movements to a strength of 4–5 points after traumatic neuritis is observed only in those muscles in which classical electrodiagnostics reveal reduced electrical excitability or a reaction of partial degeneration of the nerve.
In the reaction of complete degeneration of the nerve after traumatic neuritis, restoration of movement in the muscles is not observed.
In very late periods after nerve damage due to traumatic neuritis, the detection of loss of electrical excitability of paralyzed muscles provides another reason in favor of refusing nerve surgery. Earlier than in other areas, the electrical excitability of the muscles of the dorsum of the forearm disappears. Contrary to established ideas, the small muscles of the hand often turn out to be more resistant to the ability to respond to electric stimulation.
Electromyography is a very promising research method for closed injuries of the brachial plexus, allowing to record the dynamics of changes in the neuromuscular system during the recovery process. The corresponding electromyographic curve with the appearance of previously absent action potentials in traumatic neuritis allows us to expect the restoration of movement long before the first clinical signs of this restoration.
What to do for pain in the solar plexus
If a pain syndrome occurs that, in your opinion, is similar to solaritis or solar plexus neuralgia, you urgently need a neurologist who will help restore normal conduction of the plexus nerves. If the pain is more accompanied by diarrhea, fever, urine discharge with blood or other symptoms, you need to visit a therapist who will refer you to the right specialists and prescribe the necessary tests.
The solar plexus is also called the celiac plexus, splanchnic plexus, and solar node. It is located at the top of the abdominal cavity and is the largest plexus of nerve cells located outside the boundaries of the nervous system. Therefore, pain in the solar plexus area is a serious signal, and you need to treat it with the utmost caution, not letting it take its course, hoping that everything will go away on its own.
The plexus is formed:
- Right and left celiac nodes
- Mesenteric node
- A large number of nerves radiating from it in different directions, like rays from the sun.
Therapy
Treatment of neuritis is carried out using:
- medications that normalize blood flow in the vessels;
- agents that improve nerve conduction;
- vitamin B;
- antibiotic therapy;
- interferon and gamma globulin (for viral neuritis);
- vasoconstrictor drugs;
- analgesics;
- therapeutic exercises;
- self-massage;
- dehydration medications.
Physiotherapy occupies a special place in the treatment of neuritis. The following methods are used:
- manual influence;
- UHF;
- UZ;
- pulse current;
- electrophoresis;
- mud baths;
- massage;
- exercise therapy;
- radon baths.
The nature of pain and its intensity
The nature of the pain can suggest a preliminary diagnosis. For example, severe stabbing pain in the solar plexus makes itself felt when this area is injured.
Constant aching pain accompanied by hiccups may indicate overexcitability of the nerve ganglion due to chronic inflammation in the abdominal cavity.
Pressing pain may be associated with the upward release of an internal organ into the abdominal cavity, most often the spleen. This occurs as the disease progresses, when the diseased organ increases in volume, disrupting the connection of the internal organs with the central nervous system.
To relieve pain, it is recommended to take the following body position: sit on a chair and lean forward.
Weak spot
The area of concentration of nerve nodes that interests us does not have protection in the form of a bone frame. It is protected from external influences only by muscles, but not everyone has a muscular corset developed enough to provide significant protection from mechanical influence. Impacts to this area, which are often encountered in professional sports, pose a particular danger.
Important! The solar plexus is practically not protected by anything, therefore it is one of the weakest points in the human body.
Causes that can cause pain in the solar plexus area
Neuritis (plexitis)
This is the name for damage to the solar plexus due to inflammation of the nerves that make up its structure.
The causes of the pathology may be:
- Passive lifestyle
- Excessively high physical activity
- Intestinal and chronic infections (flu, syphilis, malaria, typhoid, etc.)
- Autointoxication (fecal retention in the intestines)
- Intoxication (alcohol or nicotine poisoning)
- Hitting hard with a fist or ball while playing sports
- Osteochondrosis
- Radiculitis
- Vertebral hernia
- Shingles
- Excessive constriction of the abdomen with a belt, etc.
More typical for solar plexus neuritis:
- Pain in the middle of the line drawn between the navel and sternum
- Painful sensations are characterized by a strong paroxysmal, drilling and stabbing character.
- Brief holding of breath is possible.
- There is a feeling of fullness, heat in the abdomen
- Pain intensifies under stress, after strong physical exertion
- Taking a body position on your side, with your legs tucked to your stomach, reduces pain.
Acute pain in the solar plexus is a sign of solaritis
It is the most severe pathological condition of the solar plexus due to the development of an inflammatory process in it. Solaritis can occur when neglected, without the necessary treatment, neuritis or neuralgia of the solar plexus. There is an acute form (the first sharp pain in the solar plexus area) and a chronic form (frequent attacks).
In addition, patients note:
- Dull or pressing pain in the chest and heart
- Feeling hot at everyday, normal body temperature
- Bloating
- Discomfort throughout the body
- Heaviness in the stomach
Due to a disorder of stomach tone, the following occurs:
- Constipation
- Belching
- Appetite disturbance
- Heartburn
For treatment the following is prescribed:
- Massage
- Physiotherapy
- Therapeutic gymnastics
Digestive tract disease
The causes of pain in the solar plexus are not always related to the solar plexus itself.
For example, pain with attacks of nausea can occur due to inflammation of various digestive organs:
Injury
Sharp pain in the solar plexus can occur due to a strong blow (with a hand, foot, ball, or other object) to the chest. The pain is quite acute, there is shortness of breath and a feeling of nausea.
If the injury is not severe, the pain lasts for several minutes. For relief, just take a comfortable position and lightly massage your stomach.
Physical overexertion
Prolonged physical activity and hard work can also cause pain in the solar plexus area. The difference from previous causes of pain is that in this case no treatment is required, it is enough to reduce physical activity and rest a little.
Etiology
Neuritis is usually caused by viruses and bacteria. Bacteria penetrate into tissues during sore throats, bronchitis and other ailments. Viruses settle in the body during the progression of various viral infections - herpes, ARVI, influenza, etc. It is the pathogenic activity of microorganisms that is the main reason for the progression of the disease. But inflammation of the peripheral nerve trunk can also be provoked by some endogenous and exogenous causes.
Exogenous causes:
- intoxication of the human body with alcoholic beverages, low-quality products, and some pharmaceutical drugs;
- injuries of varying severity (post-traumatic neuritis);
- peripheral nerve compression. This can happen for the following reasons - surgery, harmful professional activity, etc.
Endogenous causes:
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- metabolic disorder;
- bearing a child;
- rheumatism;
- inflammation of the middle ear;
- heredity.
It is worth noting that often symptoms of neuritis appear after severe hypothermia. In this case, the inflammatory process most often affects the occipital, trigeminal or facial nerve.
Various localizations of pain in the solar plexus
Pain over the solar plexus
It occurs in the lower part of a person's chest, under the ribs.
The main reasons may be:
- Pathologies of the esophagus:
- Erosion
- Burns
- Tumors
- GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease)
Pain under the solar plexus
- Inflammation of the genital organs in women: ovaries, fallopian tubes. With these pathologies, pain very often spreads to the plexus area.
- Inflammation of the bladder, ureters (urethritis, cystitis)
- Inflammation of the rectum and colon (sigmoiditis, colitis, proctitis)
Pain on the right
- The bottom of the esophagus (GERD, erosions, tumors, esophagitis) may hurt due to the fact that it extends to the right of the stomach.
- Head of the pancreas
- Gallbladder (cholelithiasis, tumors, cholecystitis). Although it often hurts under the right rib.
- Right intercostal neuralgia
- Liver: tumors, cirrhosis, hepatitis, echinococcosis
Pain on the left
- Stomach (ulcer, gastritis, tumors)
- Tail of the pancreas (tumors, pancreatitis)
- Duodenum (ulcer, duodenitis, tumors)
- Left-sided intercostal neuralgia
- Ureter, left kidney (urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis, prolapsed or overly mobile kidney)
Neuropathy (neuritis) of the trigeminal nerve
The trigeminal nerve (nervus trigeminus, V pair of cranial nerves) is mixed: it consists of motor and sensory fibers. In addition, its branches contain autonomic fibers from the oculomotor, facial and glossopharyngeal nerves.
The cortical representation of the V pair of the cranial nerves is located in the lower part of the precentral gyrus.
Its motor fibers innervate the temporal, mylohyoid, anterior belly of the digastric, pterygoid and masticatory muscles, and also give branches to the tensor tympani muscle. The motor portion of the trigeminal nerve is responsible for the movements of the lower jaw up, down and to the sides.
Sensitive nerve roots on the face innervate the dorsum of the nose, the medial (inner) corner of the eye, the upper eyelid, the skin of the forehead and scalp to the coronal suture (I - orbital branch), the upper jaw with teeth, the skin of the lower eyelid, the lateral (outer) corner of the eye , upper part of the cheek and upper lip (II - maxillary branch), lower jaw with teeth, skin of the temporal region, lower part of the cheek and lower lip, ear and chin (III - mandibular branch).
Autonomic fibers approach the lacrimal and salivary glands, oral mucosa, tonsils, and gums.
Causes of trigeminal neuropathy
Dysfunction of the nervus trigeminus due to various causative factors is called neuropathy. The causes of neuropathies can be infections (tonsillitis (tonsillitis), viral hepatitis, syphilis, herpes), sinusitis, osteomyelitis, intoxication, allergic reactions, injuries, including those of an iatrogenic nature (in dental practice). Hypothermia, stress, and alcohol consumption contribute to the appearance of symptoms. Painful attacks are provoked by food intake, changes in weather conditions, and physical activity. When nerve fibers are irritated as a result of inflammation of various origins, they speak of trigeminal neuritis.
Symptoms of trigeminal neuropathy
Symptoms of trigeminal nerve neuropathy are motor and sensory disorders, in accordance with the zones of innervation of its branches. Pain (neuralgia) is aching, burning or pulsating in nature and can be localized in the chin, eye, ear, teeth of the upper and lower jaw, forehead, hair roots. The pain syndrome develops acutely or subacutely, can be short-term, accompanied by spasm of the masticatory muscles (trismus), or constant, with increasing intensity. Painful sensations are combined with numbness and paresthesia (tingling, “crawling”, etc.) of the corresponding areas of innervation.
When the mandibular nerve is damaged, the ability to lower the lower jaw is impaired and, as a result, the inability to speak and eat. Pain in the ear may be accompanied by a feeling of stuffiness, “squelching” in the ear canal when opening the mouth, or chewing. With neuritis, palpation (pressure) at the exit points of the trigeminal nerve is painful. Upon examination, a violation of sensitivity is revealed, often pain during vertical percussion (tapping) of the teeth.
Diagnosis of the disease is based on clinical data and x-ray methods.
Treatment of trigeminal neuropathy
Treatment of trigeminal neuropathy includes the prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs, B vitamins (riboflavin, thiamine, cyanocobalamin), and, if indicated, antihistamines, antibacterial and antiviral agents. To improve neurometabolic processes, drugs such as nootropil, Cerebrolysin, Actovegin, Sermion, and nicotinic acid are prescribed. A good effect is observed with physiotherapeutic influence: ultraviolet irradiation, UHF, phonopheresis with lidocaine, diathermic currents, etc. Acupuncture reflexotherapy sessions can bring relief. To relieve pain and improve general well-being, patients receive analgesics (analgin, baralgin, ketorol), sedatives (phenazepam, Corvalol, motherwort, valerian, etc.).
Treatment in most cases is carried out on an outpatient basis. If conservative therapy is ineffective and there is a need for inpatient treatment of diseases that cause neuropathy (neuralgia) of the trigeminal nerve, patients are hospitalized. If necessary, patients undergo surgery.
Diagnosis and treatment
Due to the fact that the solar plexus combines nerve impulses from many organs, pain can indicate a large number of diseases.
To determine the causes of pain in the solar plexus, use:
- Abdominal ultrasound
- MRI
- X-ray
- Laparoscopy
- Stool and urine analysis
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
- Bacteriological research
Even using the above methods, sometimes the cause of the pain cannot be immediately determined. And the underlying disease must be treated under the supervision of a doctor.