Ekaterina Smolnikova
Practicing endocrinologist (10 years of experience). He has extensive experience working in private and public clinics in Russia.
Ask a Question
Last updated - August 14, 2021 at 09:07
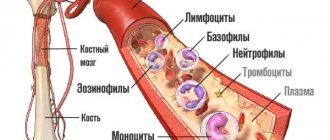
Lymphocytes, being in the body as blood cells, act as a protector of organs from aggressive pathogens. Their levels are elevated when an infection enters the body. If lymphocytes in the blood are elevated, the reasons in women can be very different: completely physiological or indicating worsening painful processes.
Norm of lymphocytes in the blood of women by age
Due to various physiological reasons, the level of these cells in the blood of the female body is different and it depends on a number of reasons:
- age;
- hormonal imbalance, pregnancy;
- the presence of a virus or bacteria in the body;
- severe injuries, fractures;
- prolonged emotional or physical stress;
- previous operations;
- chronic diseases.
There are certain norms in percentage or share, depending on the age group, specific to women.
| Age | Lymphocyte content % | Lymphocyte content units/l |
| up to 1 year | 40 – 70% | up to 9.6 billion |
| from 1 year to 5 years | 35 – 60% | up to 8 billion |
| from 5 to 10 years | 30 – 50% | up to 7 billion |
| from 10 to 15 years | 30 – 47% | up to 5.5 billion |
| from 15 to 20 years | 30 – 40% | up to 4.9 billion |
| after 20 years | 20 – 37% | up to 4.8 billion |
| after 30 years | 20 – 40% | up to 4.6 billion |
| after 40 years | 20 – 40% | up to 4.6 billion |
| after 50 years | 18 – 20% | up to 4.6 billion |
| after 60 years | 18 – 20% | up to 4.5 billion |
As follows from the table, the level of lymphocytes decreases with age, however, there are situations in which violations occur regardless of age standards.
What happens when lymphocyte levels increase
Since lymphocytes are the main defenders of the body, a sudden increase in their level in the blood may indicate the following processes:
- Infectious, bacteriological, autoimmune or viral diseases.
- Severe chronic or oncological diseases.
- Allergy.
- Strong emotional shocks.
- Disruptions in the endocrine system.
- Splenectomy.
Increased lymphocytes in the blood of women and the reasons why such changes occur are always due to the presence of a foreign “agent” and the need to fight it. Sometimes the body activates immune forces for a speedy recovery.
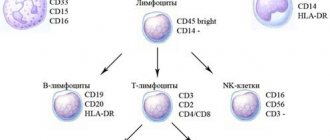
Lymphocyte cells are divided into several types, each of which performs specific functions:
- recognition of foreign antigens;
- the production of protein antibodies that begin to actively fight the disease;
- stimulation of immunity;
- control of the number of antibodies produced;
- identifying and destroying body cells other than normal, such as cancer cells.
- memorizing the structure of healthy cells in the body in order to distinguish them in the future.
All these activities are performed by B - lymphocytes, T - lymphocytes and NK - lymphocytes, thus, when their level increases in the female body, an active struggle occurs.
Symptoms of lymphocytosis
In the initial stages of increasing the level of lymphocytes in a person, no special changes or symptoms are observed.
Lymphocytosis is not a disease, but a current state of the blood, which is formed as a result of the development of pathology and indicates the work of the body’s defense system, therefore it has no specific symptoms
.
Any accompanying changes or external signs correspond to the disease that caused lymphocytosis.
It is usually accompanied by the following symptoms
:
- enlarged lymph nodes in the armpits, neck, behind the ears, and in the groin area;
- when palpated, you feel their lumpiness, the place of pressure begins to hurt, and turns red;
- temperature rises;
- some women experience increased sweating;
- severe migraines;
- you feel constant fatigue, even with moderate exercise;
- the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, constipation or diarrhea, nausea often occur;
- appetite worsens, weight loss.
To correctly find out what the growth of lymphocytes indicates, you need to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis from a doctor and pass all the prescribed tests. Untimely treatment and prolonged presence of lymphocytes outside normal limits can cause complications.
Reasons for increased lymphocytes in women
The main task of lymphocytes is to protect against infected cells or cancer cells. They (lymphocytes) have the ability to recognize and counteract dangerous antibodies in the body. An increase in the number of such protective agents in the blood is called lymphocytosis. This condition develops due to certain pathologies developing in the body of the sick patient.
Elevated lymphocytes in the blood of women, the causes of which can only be revealed through a comprehensive examination, are the main signal of the following possible diseases described below.
Genital tuberculosis
The culprit of the disease is the microbacterium tuberculosis; it is able to remain viable for a long time. Koch's wand can spread throughout the body with blood flows, and then be based in the appendages.
Once a bacterium enters the body, it can exist there for years, waiting for optimal conditions to reproduce. Decreased immunity is the most favorable time to attack the body. Settling in the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, the bacillus provokes inflammation and tissue death, and suppuration or the formation of tubercles on the mucous membranes may also appear.
Specific symptoms include:
- infertility;
- cycle disruption;
- painful periods;
- prolonged inflammation of the appendages;
- slight but persistent fever.
In combination with blood tests, urine tests and ultrasound of the pelvic organs, the gynecologist should prescribe adequate treatment and supportive care.
Brucellosis infection
Another possible reason for the sharp increase in lymphocytes in a woman’s blood is brucellosis. Infection occurs due to the penetration of microorganisms called brucellosis through the consumption of contaminated foods - meat, milk or direct contact with a sick animal.
This infection is classified as zoonotic and is based and can be transmitted to humans from:
- sheep;
- cows;
- camels;
- dogs;
- pigs;
- forest hares, deer, foxes, moose;
- goats
Thus, carriers of the disease are domestic animals and pets, wild animals, most often game. In addition to eating contaminated foods, the infection can be acquired after wearing clothes made from infected wool, through direct contact with a sick animal, or spending a long time in dog-walking areas.
Main symptoms of infection:
- short-term but high rise in body temperature.
- Enlarged lymph nodes, liver, spleen.
- Body pain and aches, loss of appetite and weakness.
- Fever, skin rashes, pain in the joints of the lower extremities.
- With a long stay in the body, the infection can affect internal organs and systems.
If the result is positive for brucellosis, the therapist will prescribe antibiotic treatment and further preventive measures.
Adrenal diseases
Increased lymphocytes in the blood of women, the causes of which may be hidden in diseases of the glands located above the kidneys, are often observed with damage to the adrenal glands and tumor formations.
Developing processes in the glands are always accompanied by such phenomena as:
- pain in the digestive system in the absence of a lesion or specific disease.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Accumulation of fat deposits in the face, neck, upper back and sternum.
- Changes in skin color, up to bluish tints and thinning to the lumen of blood vessels.
- Development of diabetes, myocardial muscle wasting, osteoporosis.
- Against the background of hormonal disorders, polyuria, nocturia, increased production of adrenaline and sudden jumps in blood pressure often occur.
The diagnosis in this case is made by an endocrinologist, after which it is necessary to immediately begin therapy.
Stress
Elevated lymphocytes in the blood of women, the causes of which lie in the stress they have experienced, can be distinguished by the following signs:
- changes in blood composition are temporary.
- The analysis was preceded by a complex operation and severe emotional shock.
- The patient's exposure to physical exhaustion or heavy exertion, hypothermia or overheating of the body.
Such conditions are temporary and pose virtually no danger throughout the entire body; the level of lymphocytes returns to normal after eliminating irritants and natural recuperation.
Hormonal imbalance
Most often, a disruption at the hormonal level can be caused by the development of such reasons as:
- Pregnancy.
- Natural processes occurring in a woman’s body associated with the monthly renewal of the endometrium of the uterus.
Increased lymphocytes in the blood occurs every month in women when their periods begin - Development of tumor pathologies of tissues and internal organs.
If lymphocytosis is detected against the background of hormone level disturbances, the cause of the failure should be established and measures should be taken to eliminate them if they pose a danger to the body.
Smoking
In the presence of long-term dependence on tobacco smoking, the composition of the blood may undergo changes due to the need of the immune system to protect itself from the harmful effects of neurotoxins. In addition to the immune system, the nervous system of a woman who smokes also suffers, and it also affects the level of pulmonary leukocytes.
Due to the regular consumption of cigarettes, conditions favorable for the development of chronic and oncological diseases develop in the body; a direct connection between smoking and atherosclerosis has been proven. Even if you quit smoking, the level of lymphocytes will return to normal for more than 3 months.
Mononucleosis
Epstein Barr virus is an infectious disease whose distinctive feature is a directed attack against B lymphocytes. These cells are able to recognize foreign cells and produce antibodies. Thus, infected lymphocytes begin to fight both against the infection and against themselves.
The most important signs that distinguish infectious mononucleosis are:
- elevated temperature;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes in the mouth, pharynx and nose.
- damage to the liver and spleen, up to rupture.
Since the causative agent of the infection belongs to viruses from the herpes family, mononucleosis is often accompanied by the development of such dangerous diseases as:
- diabetes;
- lupus erythematosus;
- articular arthritis, a characteristic feature of which is development on both parts of the body.
Against the background of acquired pathology, the composition of the blood also changes, which is reflected in an increase in the number of lymphocytes.
Whooping cough
An infectious disease characterized by inherent spasmodic coughing attacks. It is transmitted through close contact with a patient, and the causative agent is the bacterium - pertussis.
Mandatory features of the development and course of the disease are:
- cough is dry, moderate;
- rhinitis, accompanied by viscous mucus;
- with a long course of the disease, the cough worsens, becomes spasmodic, and comes in attacks;
- attacks occur mainly in the morning and evening hours.
The disease is determined by examining sputum and a smear of the pharyngeal mucosa; treatment should be prescribed after consultation with a pulmonologist and an X-ray examination.
Blood cancer
This is a fatal disease characterized by the uncontrolled proliferation of white blood cells and their accumulation in the bone marrow and blood.
This type of oncology is characterized by 2 forms:
- Leukemia.
- Lymphoma.
Characteristic features that appear during the development of cancer:
- poor blood clotting;
- increased bleeding;
- sweating at night;
- weakened immunity;
- infectious diseases that develop against the background of pathology, often becoming chronic.
- nausea, aching joints, sudden weight loss, shortness of breath.
Leukemia can occur in an acute or chronic stage; for each of them, the prognosis for the further course of the disease and the prognosis for survival are different.
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
This stage is characterized by damage to B lymphocytes; in acute leukemia, they simply do not have time to develop to the level of protective cells.
Main signs of ALL:
- chronic intoxication of the body;
- weakness, weight loss;
- increase in the size of the liver and spleen;
- decreased filtering properties of the liver;
- increased size of peripheral lymph nodes;
- decreased immunity.
Against the background of active formation of lymphoblasts, undeveloped lymphocytes, various infectious diseases and lesions of the central nervous system very often occur.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
This oncology poses a danger not only due to the nature of the development of the disease, but also due to the hidden nature of its course. It is very difficult to diagnose in the early stages and often the disease progresses and develops over a long period of time. The symptoms characteristic of the chronic form are the same as for any other form of blood cancer.
Increased lymphocytes in the blood of women, the causes of which lie precisely in the development of leukemia, are revealed by a general blood test; in addition, the pathology is characterized by a low level of platelets and red blood cells. In addition to a blood test, cerebrospinal fluid is taken, MRI, ultrasound and CT allow an assessment of the condition of the lymph node system.
Graves–Bazetov disease
This thyroid disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- sleep disturbance;
- mood swings;
- long-term depression, tearfulness;
- arrhythmia, chest pain;
- metabolic and heat exchange disorders.
Graves-Bazetov disease or diffuse toxic goiter is classified as an autoimmune disease that develops under the influence of the following factors:
- trauma to the skull and brain;
- severe psychological shock;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx.
Externally, the patient is distinguished by the presence of a goiter and damaged eyes; in addition, excessive function of the thyroid gland provokes the formation of a large amount of thyroid hormones.
Poisoning
A pathological condition in which the functioning of internal systems or individual organs of the body is disrupted due to exposure to bacteria, toxins or toxic substances.
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish the following types of poisoning:
- Food poisoning.
- Heavy metal poisoning.
- Gas poisoning.
- Overdose of medications or alcohol.
- Acids or alkalis entering the esophagus.
- Eating poisonous plants or mushrooms.
- Poisoning with other chemicals.
Typical signs of intoxication include:
- vomiting and diarrhea;
- weakness, dizziness;
- rise in temperature;
- dehydration of the body.
Any of these cases is characterized by activation of the body’s own immune system and, as a result, an increase in the number of lymphocytes in the patient’s blood.
Side effects of medications
In addition to the natural protective functions of the body, certain types of medications can also induce lymphocytosis, for example:
- Phenytoin
- Levomycetin
- Valproic acid
- Narcotic analgesics
Lymphocytosis in this case is relative in nature and occurs due to prolonged use of medication or illiterate self-medication.
Splenectomy
A surgical operation resulting in the removal of the spleen is shown in a number of cases:
- injury, organ rupture;
- pathological increase in size;
- HIV infection;
- leukemia or tumor growths in the organ cavity.
Since the spleen is an organ that takes an active part in hematopoiesis and its filtration, after its removal the body needs some time to recover. As a result, during this period the level of lymphocytes is elevated.
Oncological diseases
However, the most dangerous causes of lymphocytosis are cancers that affect the hematopoietic system. This reason also cannot be discounted. And therefore, if it is impossible to associate a symptom with some external cause, then it is recommended to undergo a thorough examination.
The most common hemato-oncological diseases in which lymphocytosis is observed are acute and chronic lymphoblastic leukemia.
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia is a serious disease of the hematopoietic system, in which immature immune cells are formed in the bone marrow that cannot perform their functions. The disease most often affects children. Along with the increase in lymphocytes, there is also a decrease in the number of red blood cells and platelets.
Why do lymphocytes increase during pregnancy?
During a normal pregnancy, the permissible level of lymphocytes remains at the level of 18 - 40%; exceeding the forty percent barrier is a pathology and indicates the development of lymphocytosis in the pregnant woman.
The main danger is that lymphocytes perceive the developing fetus as a potentially harmful object due to the presence of paternal genes; the result may be a struggle that begins, provoking rejection of the child and miscarriage.
The reasons why the level of lymphocytes in the blood of a pregnant woman may be elevated also include the presence of an infectious, viral or oncological disease; in such cases, adequate treatment is necessary.
In the absence of pathological processes, the change in the level of white blood cells occurs in the direction of decrease, since immunity during pregnancy is slightly weakened.
Diet
In this state, the body requires a full supply of essential vitamins and minerals. The doctor has the right to prescribe a medical diet as an adjuvant.
It consists of changing the diet and adding excess fiber to it (for absorption and cleansing of the intestines). Avoid foods with excess fat content, replacing it with lean meat and cereals (oatmeal). It is recommended to increase the amount of green and red vegetables, nuts, and dairy products. Fruits and vegetables containing vitamins, especially citrus fruits, help strengthen the immune system.
What test helps determine the level of lymphocytes in the blood
In order to determine the quantitative content of lymphocytes, a general biochemical blood test is performed. Before donating the material, you should prepare the body and exclude all sorts of activities that could change the composition of the blood. This applies to physical activity, drinks and food consumed, and emotional state.
On the eve of visiting the laboratory for blood collection, you should get a good night's sleep and skip breakfast. The analysis is taken from the fingertips, after which it is deciphered and the result is reported to the patient.
Preparing for the study
There are a large number of reasons why lymphocytes in the blood of women are elevated, but an increase in their number can be determined using a general blood test.
A few days before taking the sample, you should follow some rules:
- Avoid strong physical and emotional stress.
- Follow a diet that excludes fatty, sweet, smoked and salty foods, carbonated drinks, and alcohol.
- Minimize tobacco use or stop altogether.
- Stop taking medications, with the exception of vital drugs.
Immediately before the analysis:
- Light dinner 3 – 4 hours before bedtime.
- You should donate blood strictly on an empty stomach, avoid morning tea and coffee.
- Avoid massage, acupuncture, reflexology, and x-rays.
If you follow these simple recommendations, the analysis will give a reliable result.
Precautionary measures
If there is no need for bed rest, heavy physical, mental and psychological stress should be avoided. If weakness and fever are observed, it is better to go to bed rest.
To avoid additional problems, you should not self-medicate. In this way, you can spoil the test results, disrupt the picture of the disease and complicate diagnosis.
To speed up the healing process, it is recommended to exclude from the diet foods that contain salt, are heavily smoked, contain sugar, and contain excessive amounts of seasonings and spices.
How they take the analysis, how long to wait for answers
Blood is drawn from the ring finger by a medical laboratory assistant; the optimal time is considered to be the morning hours from 07:00 to 11:00. For better blood flow, the puncture site must first be slightly kneaded.
Another method is to take samples from a vein; this method is used if it is necessary to obtain a quick result. However, this method requires a blood volume of at least 5 ml, otherwise there is a danger of obtaining unreliable conclusions. Analyzes obtained in the traditional way are usually prepared in 1 to 3 days.
Decoding the analysis results
A general biochemical blood test can provide information on the quantitative composition of the main elements, and also helps to assess the level of lymphocytes. Depending on the patient's age, the therapist may conclude that white blood cell levels are high, low, or normal.
If an increased number of lymphocytes is detected, additional examinations are prescribed to identify the causes of the changes.
Lymphocyte analysis is performed under a microscope; during the test, the laboratory assistant counts the visible number of cells per 100, therefore the final value is calculated as a percentage. There is also an automatic counting of blood cells using an analyzer.
The results are recorded on a special form on which the obtained values are compared with generally accepted standards. Acceptable indicators for women differ depending on age, they are shown in the table above. Exceeding the norm by more than 10% indicates the presence of disease processes in the body.
Diagnosis of lymphocytosis
It is impossible to accurately diagnose pathology only by the number of lymphocytes. Checking the blood condition is based on a detailed blood test.
Most often these indicators are compared
:
- Leukocytes and lymphocytes
. Their mutual increase may indicate blood cancer. With tuberculosis and some other viral infections, a low leukocyte count and a high lymphocyte count are shown; - Platelets and lymphocytes
. An increase in two indicators is observed in autoimmune diseases; - Red blood cells and lymphocytes
. The synchronous growth of these bodies occurs during infection.
Treatment with drugs
Depending on the cause of lymphocytosis, the patient should be prescribed drug treatment; the following options exist:
- When an infectious pathogen is identified, antiviral and antibacterial drugs are used: Flemoklav, Amoxiclav, Ingaverin, Grippferon, Interferon.
- In case of poisoning and intestinal infection: Bifidumbacterin, Enterofuril, Enterol.
- Allergic reactions: Citrine, Zodak, nasal sprays with antihistamine effect.
- If cancer is detected, chemotherapy, leukapheresis, and bone marrow transplantation are used.
- If the reason lies in the presence of autoimmune diseases: Hydrocortisone, Traimcinolone, Dexamethasone.
- Treatment of thyrotoxicosis occurs with the help of radioactive iodine, the drugs Tyrosol, Endorm; Complete or partial removal of the thyroid gland is often practiced.
Additionally, vitamin and mineral complexes, painkillers and antipyretics can be used.
Thyrotoxicosis
One of the important functions of lymphocytes is the formation of delayed allergic reactions. That is why an increase in such cells may indicate an autoimmune process. A striking example is diffuse toxic goiter (Graves-Bazedow disease). For unknown reasons, the body begins to attack its own receptor cells, as a result of which the thyroid gland is in constant activity. Such patients are fussy, restless, and find it difficult to concentrate. There are often complaints of interruptions in heart function, shortness of breath, fever, and hand tremors. The eyes of patients with toxic goiter are wide open and sometimes seem to be coming out of their sockets.
The main laboratory sign of DTG is high values of the hormones T3 and T4 with low TSH. There is often relative and sometimes absolute lymphocytosis in the blood. The reason for the increase in lymphocytes is the excessive activity of the immune system.
Treatment of thyrotoxicosis is carried out with thyreostatics, followed by surgery or radioactive iodine therapy.
Other autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, etc.) are also combined with lymphocytosis.
Traditional medicine recipes
Among the alternative ways to reduce lymphocyte levels, there are many recipes for various situations.
Some of the most powerful natural antibiotics are:
- propolis
- honey
- garlic
- mumiyo
Garlic tincture to increase the body's immune forces:
- 200 g of fresh garlic must be chopped in any convenient way;
- pour 200 ml of the resulting raw material. alcohol;
- let it brew in a cool, dark place for 10 days.
For the best combination of ingredients, the preparation should be shaken periodically; after infusion, the resulting liquid must be filtered and left for another couple of days.
You can take this remedy 3 times a day, 2 hours after meals, starting with 1 drop for breakfast, 2 drops for lunch, 3 drops for dinner. Further according to the scheme: 4 drops - breakfast, 5 drops - lunch, 6 drops - dinner, having reached 15 drops - return in the reverse order in descending order of the number of drops after each meal.
Recipe for folk antiviral tincture from Echinacea:
- 50 - 100 g of raw materials - leaves, flowers, roots, stems, leaves, place in a glass jar;
- pour dry ingredients with 1 liter of quality vodka;
- leave in a dark place for 20 days at room temperature.
You need to take the resulting drug one tablespoon half an hour before meals three times a day. The best remedy in the fight against autoimmune disorders is coconut oil; it should be taken orally at least 4 tbsp. l. in a day.
Recipe for a decoction against the symptoms of Graves' disease:
- white licorice rhizomes – 1 tbsp. l.;
- red madder rhizomes - 1 tbsp. l.;
The resulting mixture is poured into 500 ml of hot boiled water and left for an hour; the decoction should be taken in a glass on an empty stomach.
Another effective remedy in the fight against diseases of the autoimmune system is alcohol tuning made from walnuts:
- green walnuts - 50 pieces, they should be chopped;
- Combine 250 ml of alcohol with nuts;
- leave the mixture for 60 days.
You can take the finished product one dessert spoon before each meal. Good results in the fight against lymphocytosis are obtained by drinking linden tea, blackthorn berries, and birch buds. Vitamin B17 is a powerful tool in the fight against cancer; it is found in the kernels of the seeds of apricots, cherries, bird cherries, plums, pears and apples, and almonds.
Prevention measures
- Review your diet. It should show a balance of beneficial vitamins, macro and microelements. When choosing products for the menu, preference should be given to fresh vegetables and fruits (up to 70%), lean meats, seafood, and milk derivatives.
- When choosing diets, give preference to protein.
- Spend more time outdoors. On weekends, organize outings into nature.
- Perform a simple set of exercises daily. Go to the gym, go jogging, walking or another sport.
- To strengthen the immune system, it is recommended to consume a vitamin complex. It must contain zinc and ascorbic acid.
- Maintain a drinking regime (at least 2 liters per day). During the day, in addition to purified liquid, drink green tea.
- Give up bad habits (alcohol, smoking, etc.).
- Seek medical help promptly if you have health problems.
- Carry out annual preventive examinations with specialists. Determine your health status by taking tests.
The general concept of preventive measures comes down to following the rules of a healthy lifestyle.
Forecast
Lymphocytosis can occur for various reasons, sometimes it is a signal of a common cold, and sometimes a similar phenomenon is the result of dangerous processes in a woman’s body. To make an adequate diagnosis, blood and urine tests, consultations with a therapist, oncologist and endocrinologist are used together, and ultrasound and MRI data are often used.
The causes of elevated lymphocytes in the blood of women should be identified as quickly as possible and treatment should begin. In addition to drug therapy, positive results can be achieved by simultaneously following a diet and using traditional medicine.
In most cases, a positive prognosis is given for recovery, or for a mild course of the disease, allowing you to live a full life.
Article design: Mila Friedan