The process of urination is quite intimate, the frequency and volume of which are strictly individual. But not everything always goes according to a physiological rhythm; very often women notice frequent urination, which can be accompanied by discomfort and even pain.
In most cases, when such problems arise, women are very reluctant to go to the doctor with this complaint even when the corresponding symptoms become unbearable.
But the tactic of waiting for everything to go away on its own is wrong, because this problem, which many are ashamed to talk about out loud, has a specific reason that the doctor must deal with. The reasons for frequent urination in women, both painful and painless, will be discussed in this article.
Psychology
With increased excitability of the nervous system, signals are received to empty the bladder. The main factor is stress. That is, hyperactivity is purely functional in nature, so this phenomenon is treated either with neurologist medication (sedatives) or with psychotherapy.
Doctor's advice
To narrow the diagnostic search and quickly determine the cause, before visiting a doctor, you can submit your urine for a general analysis in any laboratory. You should take the entire morning portion, having carried out hygiene procedures beforehand. During collection, women need to cover the vaginal opening with a tampon to prevent discharge containing protein from getting there and causing incorrect interpretation of the analysis. If the result obtained is normal, this will immediately rule out inflammatory diseases of the urinary system and diabetes mellitus.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist
Bladder overactivity can manifest itself in situations that a woman subjectively assesses as alarming or dangerous. In a situation of stress, when a person tries to hide external excitement (and it can be very strong), the bladder sometimes becomes a “weak link.” Recommended specialists: neurologist, psychologist or psychotherapist, preferably with a psychosomatic profile. Consulting a psychologist will help you cope with the problem.
Pathologies of internal organs and systems
The exact cause of frequent urination should be determined by a doctor, since this symptom may indicate serious, including chronic, pathologies. In this case, nocturia and pollakiuria are secondary symptoms. He appears in the background:
- diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus;
- vascular and heart diseases;
- injuries of the pelvis and internal organs;
- tumors (especially prostate).
Frequent urination is a classic symptom for people with diabetes. In diabetes insipidus, the function of the neurohypophysis, the area of the brain responsible for the release of oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone, is impaired. As a result, kidney function and urine formation are disrupted, and bladder emptying becomes more frequent. The patient drinks much more to restore the lack of fluid. With diabetes, the patient also has a constant desire to drink and defecate. During the release of urine, the patient may experience tingling and a slight burning sensation from the action of sugar.
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels often lead to nocturia. Against the background of such diseases, edema occurs, including hidden edema, which worsens during periods of physical activity. At night, swelling subsides and the body removes excess fluid. Nocturia occurs in both women and men; the patient can visit the restroom 6-8 times per night.
A prostate tumor is the cause of frequent urination in men. In this case, an adenoma is formed, which presses on the urethral canal. The normal process of urination is gradually disrupted, the amount of urine released becomes less and less, and the frequency of urges increases. In this case, the process of emptying is accompanied by pain in the urethra and lower abdomen.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Also, this symptom occurs after injuries and operations on the pelvic and abdominal organs. An increase in the frequency of urges may be painless or accompanied by pain. In such cases, symptoms and treatment are individual. As a rule, attempts are made to eliminate congenital pathologies in infancy. All of the above reasons can occur in adults and children. It is quite difficult to notice such a problem in a child, since they are characterized by frequent urination. However, if redness appears on the genitals, blood or other impurities in the urine, you need to show the child to a pediatric urologist.
Other reasons
Other reasons include:
- Features of a woman’s diet include plenty of fluid intake (especially coffee and alcohol) and diuretic products.
- Household stress (a typical case is the time shortly before taking an exam).
- Hypothermia. When the body experiences hypothermia, it compensates by urinating more frequently.
- Some medicines. Increased urination is an expected and normal side effect. A group of such drugs is called “diuretics”. Can be prescribed against edema, hypertension and in the treatment of gestosis in pregnant women.
- Neurogenic bladder. The innervation of the organ is disrupted, because of this the urge to urinate occurs even with a minimal volume of urine or is false. The pathology occurs as a result of injuries to the lumbosacral region, infectious diseases of the brain, multiple sclerosis, and severe disorders in osteochondrosis. Diagnosed and treated by a neurologist and urologist.
When changes in analyzes occur, many people panic. However, quite often the identified deviations do not correspond to reality due to incorrectly collected material for the study. If there are changes, the doctor will refer you for a retest to confirm or rule out possible pathology.
If you experience a noticeably increased urge to urinate despite no changes in your diet, contact an experienced professional immediately. Do not hesitate to tell your doctor about your problems and experiences, because health is most important.
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Rate how helpful this article was
3.7 3 people voted, average rating 3.7
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Diseases of the urinary system
Frequent urination in men and women occurs for the same reasons. The only exception is prostate adenoma, which also leads to pollakiuria. Otherwise, it leads to constant urges:
- overactive bladder;
- stones in the kidneys;
- urethritis;
- muscle weakness of the bladder walls;
- pyelonephritis;
- cystitis;
- renal failure;
- infections: chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis.
Inflammatory processes such as pyelonephritis, urethritis and cystitis are accompanied by frequent urge and pain during urination. The patient experiences a burning sensation in the urethra, and often after visiting the toilet there is a feeling of an unemptied bladder. The set of such symptoms exhausts the patient, and sometimes incontinence occurs. At the same time, the amount of urine released is very small. Symptoms intensify with hypothermia, stress, and physical exertion.
Frequent urination with an irresistible urge to urinate occurs with an overactive bladder. This pathology occurs when there is a malfunction in the peripheral nervous system, when a number of impulses are sent to the bladder. Due to involuntary contractions, a person feels a constant desire to go to the restroom. After emptying, there comes a feeling of an unfinished act. However, pain and stinging are not observed in this case.
Similar symptoms occur when the bladder wall is weak. Weakened tissues are not able to withstand the pressure of even small portions of urine, which is why you constantly want to go to the toilet. There is no pain or burning, but the patient may experience general weakness and exhaustion.
Sexually transmitted infections also cause pollakiuria, although rarely. In this case, it is quite simple to establish the cause, since in addition to frequent urges, itching, unpleasant odor, and discharge appear. During bowel movements, there may be a slight burning or tickling sensation.
How to understand that urination is impaired?
There are no strict norms for the frequency of urination; there are only conventional limits and average numbers. In this matter, everything is individual and depends on many factors.
The frequency of urges is influenced by the physiological characteristics of the body, age, changes in life and diet, drinking regimen, emotional state, and metabolic rate. Variant of the norm is 7-10 times a day. If the indicators are higher, this should alert you.
When it comes to frequent urination, we primarily mean exceeding a certain comfort threshold. Symptoms are always noticeable, the woman understands that a failure has occurred and the body is reacting to problems. This process becomes more frequent, goes beyond the usual limits and causes anxiety. You shouldn’t wait for it to go away on its own and hope that frequent urges are caused by drinking too much liquid. Everyday recurring symptoms indicate disorders in the body. The situation requires medical intervention.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you experience frequent urination, you should contact your physician, who will prescribe the necessary tests. Based on the results, he will determine which specialist doctor to refer for treatment.
Diabetes mellitus is treated by an endocrinologist, gynecological diseases are treated by a gynecologist, and in case of kidney diseases they are referred to a nephrologist. To treat frequent urination, you need to treat the disease that caused the complication.
Timely treatment will help reduce the frequency of visiting the toilet and treat complications of other diseases.
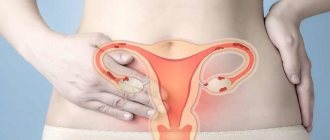
Causes of frequent urge to urinate in women
With such an unpleasant symptom as frequent urination in women, the reasons can be very different, sometimes not related to health and disease (physiological). The main causes of this phenomenon are divided into four large groups, the first place among which is occupied by pathological processes in the organs and structures of the urinary system.
Pathologies of the urinary system
A common cause of frequent urination is inflammatory urinary tract infections. Women have a natural, anatomical predisposition to these diseases, and they suffer from these problems 3 times more often than men.
- Cystitis
Frequent painful urination in women is a clear sign of cystitis. Pain when urinating is burning and cutting; after visiting the toilet, a woman is tormented by the feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder from urine, which forces her to literally sit on the toilet. At the moment the urge to urinate begins, urinary incontinence is noted (for more information about cystitis, see cystitis in women - symptoms, treatment). The character of urine initially does not change, but as the disease progresses, the urine becomes cloudy. The treatment regimen is similar to the treatment of pyelonephritis; physiotherapy (UHF, inductothermy and iontophoresis), herbal medicines are also used (see cystone for cystitis, 15 drugs for cystitis), as well as cranberry for cystitis.
- Urethritis
Frequent urination, painful at the beginning of emptying the bladder, is characteristic of urethritis. The pain is burning and accompanied by itching. The general condition of women rarely suffers, which leads to a delay in the process and late referral to doctors. Treatment of urethritis includes antibiotics and probiotics to restore the vaginal biocenosis (see list of probiotic preparations).
- Pyelonephritis
Increased urination may indicate the presence of chronic pyelonephritis. The disease manifests itself as dull, aching pain localized in the lumbar region, which intensifies in cold weather. When the pathological process worsens, the following is noted:
- a sharp rise in body temperature, up to chills - as well as weakness - nausea - impurities of blood and pus appear in the urine - progression of the disease leads to the development of arterial hypertension
Treatment of pyelonephritis is long-term and includes antibacterial therapy, antispasmodics, painkillers and herbal remedies.
- Urolithiasis disease
Frequent urination may indicate existing urolithiasis with stones localized in the bladder. The urge to urinate appears unexpectedly, sharply and is provoked by intense physical activity, occurring when running or shaking in transport. When the bladder has not yet completely emptied during urination, the urine stream may also be interrupted. Pain occurs in the lower abdomen and the area above the pubis, both at rest and during urination. Treatment of the pathology, depending on the severity of the disease and the nature of the stones, can be medicinal, physiotherapeutic or surgical, but always includes diet.
- Weakness of the muscle wall of the bladder
Manifested by frequent urination with a small volume of urine. The urge to urinate is always sudden and requires an immediate visit to the toilet. Since this pathology is congenital, therapy is aimed at strengthening the muscle tissue of the bladder with special exercises and medications.
- For overactive bladder
In this case, increased nerve signals cause a frequent urge to empty the bladder. The disease is of central origin, so treatment is aimed at interrupting the pathological excitability of the nervous system that regulates the process of urination (sedatives, muscle relaxants, etc.).
Frequent urination as a secondary sign of various pathologies of the body
- Gynecological diseases
Increased urination may be a sign of advanced uterine fibroids - a benign tumor that, due to its size, compresses the bladder. Since the disease develops gradually, dysuritic disorders are preceded for a long time by uterine bleeding, menstrual irregularities and pain in the lower abdomen. Treatment is hormonal and surgical (see uterine fibroids - symptoms and treatment).
When the uterus prolapses, associated with weakness of the ligamentous apparatus, displacement of the organs and tissues of the pelvis occurs, including the bladder. Frequent urination with incontinence indicates significant prolapse of the uterus. A woman has been bothered for a long time by painful manifestations in the lower abdomen, heavy menstruation and bleeding from the vagina. Treatment is conservative (hormones, exercise therapy) or surgical.
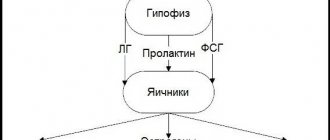
- Endocrine diseases
Frequent urge to urinate at night is often one of the first signs of diabetes in women. In addition, the woman suffers from constant thirst, itchy skin, weakness and fatigue. Treatment includes diet, drugs that lower sugar levels (if diet therapy is ineffective), insulin therapy (for an insulin-dependent form of the disease).
With diabetes insipidus, associated with dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, frequent urination occurs, and the daily volume of urine excreted increases to 5 liters. Women suffer from constant thirst, lose weight, and experience dry skin and mucous membranes. Treatment is hormonal, lifelong.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels
Frequent urination at night in women may be a sign of cardiovascular disease. If there is insufficiency of cardiac activity during active daily life, hidden swelling occurs, which disappears at night and is expressed in frequent urination. Treatment is etiological, aimed at compensating for the detected cardiac insufficiency.
Physiological reasons
If there are certain physiological reasons, a woman is bothered by frequent urination during the day, the most common of which are:
- dietary features associated with abundant fluid consumption (coffee, soda, alcohol) and foods with diuretic properties (watermelon, cranberries, melon, lingonberries, cucumber, etc.)
- stress and anxiety, in which oxygen starvation of cells leads to frequent urination
- first and third trimester of pregnancy, when increased frequency of urination is associated with the growth of the uterus and compression of the bladder
- hypothermia of the body, which causes a compensatory increase in urination;
When the underlying cause is physiological factors that cause frequent urination in women, no treatment is required. Self-elimination of the provoking situation leads to normalization of urination.
Taking medications
Increased urination, leading to frequent visits to the toilet, is also provoked by drugs from the group of diuretics, which have a therapeutic diuretic effect. These drugs are prescribed for edema, hypertension, and for the treatment of gestosis in pregnant women.
Diagnostic measures for frequent urination
When it becomes clear where to go with the emerging alarming symptoms, a new question arises that worries many patients.
How the diagnosis is carried out and the causes of the emerging deviation are identified - that’s what worries patients.
First of all, it is recommended that a representative of the fair sex undergo a urine test, as well as a gynecological smear.
These two studies allow us to exclude a fairly wide range of diseases.
For example, after assessing the composition of urine, a doctor may reject the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus if there is no glucose in the urine.
Smear examination is of great diagnostic importance.
Urine testing for STDs may not be as effective in this regard, since urine itself is not sterile.
It is possible to obtain more diagnostically significant data from a smear if it is examined correctly.
To make a diagnosis, the doctor may use microscopy, culture, PCR and other techniques.
We must not forget about the possibility of using instrumental techniques.
Ultrasound, for example, is of great importance.
With its help, you can evaluate not only the genitals, but also the system for removing urine from the body.
Frequent urination due to diseases of the genital organs
Frequent urination of women during the day may indicate not only pathologies of the urinary system, but also problems in the sexual sphere.
As doctors note, there may be several reasons for the formation of a symptom.
First of all, the doctor will always rule out fibroids.
Myoma is a benign neoplasm that develops in the uterine cavity.
In this case, the tumor can imitate pregnancy, putting pressure on the bladder, mechanically reducing its volume.
The result is predictable: as during pregnancy, a woman will visit the toilet more often than normal.
In addition to uterine fibroids, it is always worth excluding genital prolapse.
This pathology is especially common among representatives of the fair sex who have already gone through the process of childbirth.
Naturally, if the uterus prolapses, other structures located in the pelvis are displaced and may be compressed.
The bladder in this case is no exception.
The result may be the need to go to the toilet more often than normal.
It is important to remember that when the genital organs prolapse, women may urinate with blood.
Since organs can be damaged due to their normally atypical location.