What is a muscle spasm?
A muscle spasm is an involuntary contraction of one or more muscles. Spasms can occur in any part of the body where there are smooth muscle fibers. These are skeletal muscles (those involved in upright walking), intestines, esophagus, bronchi, uterus, as well as blood vessels and other parts of the body.
In any case, an involuntary and sharp contraction is accompanied by pain and deterioration in well-being. Sharp contractions of the blood vessels of the brain, leading to severe headaches, have a particularly negative impact on overall health.
Prevention
Angiospasm of cerebral vessels is a common transient disorder of cerebral circulation. Most often, it is caused by an irresponsible attitude towards one's own health. Therefore, in most cases, this cerebrovascular disorder can be prevented if we are not talking about congenital anomalies, various neoplasms or accidental injuries. A healthy lifestyle will help maintain normal vascular tone, first of all, quitting smoking and other bad habits. Excessive doses of alcohol and nicotine have an extremely negative effect on blood circulation.
You definitely need to move more, exercise, and walk. Physical activity has a positive effect not only on muscles and blood vessels, but also on the nervous system. This way you can avoid the unpleasant consequences of stress. All somatic, neurological, and infectious diseases must be treated in a timely manner, preventing them from becoming chronic.
Since the main causes of cerebral vasospasm are hypertension with atherosclerosis, their prevention is also mandatory. In addition to the methods listed above, you should adhere to the principles of a healthy diet. Very often, it is an unbalanced diet that leads to excess cholesterol in the blood, obesity, and arterial hypertension. You need to eat small amounts often, minimizing your intake of sugar and unhealthy fats. Complex carbohydrates, vegetables and fruits, meat, and dairy products are healthy.
Symptoms of muscle spasm
Muscle spasms manifest themselves in characteristic signs:
- A pronounced pain syndrome of an acute or aching nature.
- Feeling of tension in the affected area. Our body reflexively strives to get rid of tension, which is why we take unnatural poses. For example, when there is severe pain in the abdomen, we involuntarily bend in half to reduce the load on the abdominal muscles.
- Limitation of mobility. For example, when a leg or arm spasms, we cannot move it, and contraction of the neck muscles forces us to keep our head constantly tilted to the right or left.
The nature and intensity of pain can vary - from tolerable aching pain to unbearable pain up to loss of consciousness.
Tropicamide
Blocks receptors of the sphincter of the iris and ciliary muscle. The medicine causes temporary paralysis of accommodation. Tropicamide is prescribed for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
To relieve spasm of accommodation, the medicine is used before bedtime for 1 month. In severe cases of the disease, use 1-2 drops up to 2 times a day.
Tropicamide cannot be used with neuroleptics and antidepressants, intraocular pressure increases.
Causes of muscle spasms
What causes painful muscle contractions?
There may be several reasons for this phenomenon:
- Prolonged muscle tension.
- Unnatural body position.
- Exposure to cold.
- Nervous tension, stress.
- Metabolic disease.
- The action of certain hormones.
Most often, spasm occurs due to prolonged tension, as well as as a result of excessive physical exertion. Athletes are well familiar with involuntary contractions of the muscles of the legs, arms and back. After prolonged training with overload on a certain group of muscles, painful contraction may occur.
Usually this trouble happens to novice athletes when their running, swimming, or lifting techniques are violated. For example, track and field athletes experience calf spasms due to twisting of the foot when running.
Spasms in the arms, back and neck are a common problem in the professional world. People who are forced to sit or stand in an unnatural position due to duty often suffer from spasms.
For example, dentists who constantly hold their working arm in an elevated position above the patient experience contractions in the muscles of the neck and upper back at the beginning of their professional work. Similar problems arise for surgeons, joiners, carpenters and other workers who have to stand or sit in one position for a long time.
Stressful tension in individual muscles can also lead to spastic disorders. Prolonged mental work, as well as excitement, fear, and anxiety are usually expressed in contraction and permanent tension of the facial muscles and larynx.
Sometimes the cause of spastic pain is not external, but internal factors. For example, with a deficiency of magnesium and excess calcium in the body, convulsive contractions of the smooth muscles of the arms, legs, abdominals, and face occur.
This is due to an electrolyte imbalance in muscle tissue cells due to the influx of calcium. Replenishing magnesium deficiency automatically blocks the flow of calcium ions to the cells, causing the muscles to relax.
This is interesting! Another factor that can cause spastic syndrome is the increased production of certain hormones. Women during menstruation often suffer from pain in the lower abdomen due to strong contraction of the uterine muscles. This occurs due to increased production of the hormone prostaglandin, which also causes the uterus to contract during childbirth.
Diagnostics
The primary diagnosis is made by a therapist or neurologist based on clinical signs and their dynamics, blood pressure measurements, and information about existing diseases. After first aid is provided, a number of instrumental studies are carried out:
- MRI of the head and neck;
- angiography with the introduction of a contrast agent;
- ultrasound diagnostics of cerebral vessels;
- CT angiography;
- Dopplerography.
During diagnosis, cerebral vascular spasm is differentiated from cerebrovascular pathologies with similar symptoms. These include transient ischemic attack, strokes of both types, hydrocephalus (acutely developing with a tumor), and other liquorodynamic disorders.
Neck muscle spasm
Spasm in this part of the body occurs due to prolonged unnatural position of the head, as well as during sharp turns of the head relative to the body. Another reason why painful contraction of the neck muscles occurs is hypothermia.
T.N. lumbago, when a person feels a sudden sharp pain and cannot move, occurs when exposed to cold combined with high temperature in an open area of the body. For example, after sweating in our outerwear indoors, we unbutton our collar when going outside. The result is a spasm of the neck muscles, forcing us to see a chiropractor.
Midriacil
Midriacil blocks receptors in the sphincter of the pupil and the ciliary muscle. It causes expansion of the pupil and paralysis of the ciliary muscle. The maximum effect after using the drops occurs within 20 minutes. The drug is contraindicated in case of individual intolerance to the components, a tendency to glaucoma and at its initial stage. Eye drops are used for diagnostic purposes.
They are used in preparation for surgery, laser surgery in the prevention of synechiae.
Instructions for use:
- 1–2 drops of a 1% solution for skiascopic examination, repeat the procedure after five minutes;
- 1–2 drops 0.5% solution if fundoscopy is required.
Side effects include blurred vision, sensitivity to light, dry mouth, increased IOP, and hypotension.
Back muscle spasm
Back muscles can contract painfully for several reasons. Usually this is a long-term static voltage. For example, when we are forced to hold an object suspended for a long time, or carry heavy bags over a long distance. Lifting weights and strength exercises without prior warm-up (barbell press, dumbbell flyes) are a common cause of spasm in the upper back muscles.
The muscles of the lumbar back may be in a contracted state due to prolonged sitting. Drivers, machinists, and knowledge workers who spend many hours in front of a computer monitor often complain of aching pain and painful contraction of the lower back muscles.
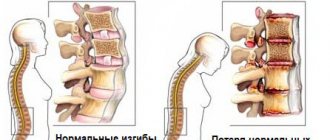
Another reason for spastic contractions of the back muscles is poor posture and curvature of the spine. When our body tries to compensate for incorrect positioning, it leads to muscle overstrain. The result is a spastic syndrome, which we often mistake for an attack of radiculitis.
Development mechanism
The basis of cerebral vascular spasm is a violation of neurohumoral regulation. Imbalance of mediators and dysfunction of calcium channels negatively affect the autonomic nervous system, which regulates vascular tone. During an attack, arteries and smaller cerebral vessels contract, and accordingly, blood flow slows down and the brain experiences oxygen starvation. As a result, characteristic symptoms appear, which can be reversible or irreversible.
In the first case, the spasm passes without consequences, in the second it is fraught with strokes, encephalopathy, and aneurysm rupture (especially in the presence of blood clots and atherosclerotic plaques).
Prolonged vasospasm during pregnancy can lead to eclampsia, a severe form of gestosis.
Leg muscle spasm
Spastic contractions of the leg muscles occur for the following reasons:
- excessive physical activity (squats, lunges) without prior warm-up;
- walking for a long time in flat-soled shoes (spastic syndrome occurs in the calf muscle);
- constantly wearing high heels;
- incorrectly selected (too tight, narrow, loose) shoes;
- injuries (dislocations, fractures), in which the body weight is transferred to one leg.
Important! Sometimes pain at a certain point in the leg occurs not due to spasm, but due to excessive irritation of the nerve. In this case, a person feels a burning sensation when touching a painful point. In this case, the help of a neurologist is necessary.
Piriformis muscle spasm
One of the most unpleasant phenomena associated with spasms is the so-called. piriformis syndrome. This muscle is responsible for lifting and turning the leg, as well as tilting the pelvis. Pain in the piriformis muscle can lead to significant limitations in mobility and walking, preventing us from moving naturally. In severe cases, numbness of the limb, pain in the knee and buttock may occur.
Facial muscle spasm
This is a fairly rare phenomenon that occurs against the background of a nervous tic of the facial muscles. The reason for this phenomenon is neurological disorders. The provoking factor is stress and nervous tension.
Typically, spastic contractions and nervous tics are accompanied by headaches, a feeling of a “mask” on the face, lack of expression in facial expressions, or, conversely, constant maintenance of a certain grimace (gloomy, surprised).
Treatment of muscle spasms
Treatment is aimed at relaxing muscles and relieving pain.
You can eliminate spastic tension in the following ways:
- exposure to heat (hot baths, sauna sessions, compresses);
- relaxing or general body massage;
- physical therapy, stretching;
- aromatherapy, acupuncture, electrophoresis;
- antispasmodic drugs.
Depending on the location of the contraction and the intensity of the pain, you can help yourself in various ways. A combination of heat and massage works well.
The ideal method for relieving muscle tension, known to athletes, is a visit to the sauna followed by a massage. Others benefit from light stretching exercises.
For spastic contractions of a neurological and psychological nature (stress, nervous tension, overwork), various relaxation methods are indicated: aromatherapy, warm baths, swimming. It is important to normalize your daily routine and increase the number of hours of sleep.
If the pain is unbearable, it is recommended to take antispasmodics orally (No-shpa, Spazmolgon, Papaverine, Papazol).
Cyclopentolate
The effect of the medication begins 30 minutes after application. The effect lasts throughout the day.
Contraindications:
- glaucoma;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- intolerance to the substances included in the composition.
The medicine should not be used by pregnant women, nursing mothers and children under 3 years of age should be used with caution.
The duration of treatment is determined by the treating doctor. Typically, the use of Cyclopentolate is not prescribed for longer than 7 days. More often the medicine is used for diagnostic purposes.