Blood diagnostics is one of the most significant research methods, which doctors most often resort to in order to make an accurate diagnosis for a patient with ambiguous symptoms.
It is not always the case that people who have undergone this procedure have the opportunity to find out its results on time, for example, in a small town with only one specialist employed. Therefore, you have to resort to independent decoding, which requires knowledge of both normal indicators and basic values. Among the abbreviations that require detailed explanation is PLT.
PLT: what is it?
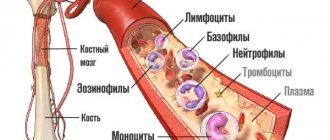
The number of platelets per unit volume of blood is designated PLT or Platelets, which is translated into Russian as plate. And not without reason, because these shaped elements have the appearance of a flat, rounded plate, devoid of a core, with several outgrowths.
The lifespan of a platelet is 10 days, after which the element is destroyed in the liver and spleen
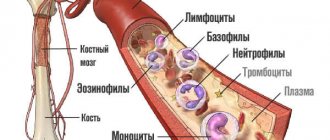
These cells are synthesized in the red bone marrow. They are responsible for:
- blood clotting and, consequently, stopping bleeding and restoration of damaged tissue areas;
- blood purification due to the removal from the bloodstream of immune complexes (killed particles of viruses and other antigens associated with antibodies) produced during inflammatory processes;
- nutrition of blood vessels, transportation of a number of biologically active substances.
Therefore, any deviations in platelet levels from the norm are a sign of disturbances in the functioning of the body.
The role of platelets in the human body:
Folk remedies
You can also adjust your platelet levels at home. Treatment with folk remedies should be under the supervision of the attending physician. Tinctures and decoctions are an addition to the main treatment; they cannot replace drug therapy.
Recipe for increasing platelets from nettle:
- nettle juice – 50 ml;
- milk – 50 ml.
Squeeze the juice from fresh nettles and add milk to it. The composition is taken 3 times a day before meals. Duration of admission – 14 days. The mixture is prepared before use; the medicine cannot be prepared for future use, it quickly loses its properties.
Chokeberry improves blood viscosity well. It is recommended to consume 50 berries every day for 3 weeks. The course of treatment cannot be extended.
Recipe for lowering platelet count with garlic:
- garlic – 1 head;
- vodka – 200 ml.
Garlic is poured with vodka and left in a dark place for a month. After a while, grind it through a sieve. Take half a teaspoon 2 times a day.
Recipe for reducing platelets with ginger:
- ginger – 30 g;
- honey – 30 g.
Ginger is crushed. Mix with honey. One spoon of the mixture is diluted in a glass of water and taken 2 times a day. If a blood test shows a deviation from the table norm in the number of platelets - an increased or decreased level - you should undergo a course of treatment. People with thrombocytopenia, regardless of age, should avoid traumatic sports.
You should also avoid alcoholic beverages, vinegar, and certain medications (Aspirin, Analgin). If your platelet count is elevated, you should follow a blood thinning diet and drink as much water as possible. It is especially important to monitor platelet levels in women during pregnancy.
Normal platelet count in blood
On average, a healthy adult contains 180–320 thousand platelets in 1 ml of blood. Occasionally, the number of these elements is assessed in relation to the number of red blood cells, using the Fonio method.
According to the Fonio method, there are normally 60–70 thousand platelets for every million red blood cells.
However, minor fluctuations in PLT can be observed under the influence of various factors:
- It’s time of day, so UAC is always taken in the morning.
- Physical activity causes an increase in platelet levels.
- Smoking leads to a decrease in PLT.
- Eating before taking the OAC - due to the fact that eating vegetables, meat products, fruits, fish, seafood, nuts and even parsley leads to an increase in PLT and, therefore, a distortion of the results. Therefore, it is always recommended to take the OAC on an empty stomach!
The level of PLT is also affected by adherence to blood sampling technique
Norm PLT in patients of different genders and ages - table
| Patient categories | PLT, 103/ml (109/l) | Patient categories | Age | PLT, 103/ml (109/l) | |
| Women | in normal condition | 180–320 | Children | newborns | 100–420 |
| 1–3 months | 180–400 | ||||
| during pregnancy | 150–380 | up to 1 year | 150–350 | ||
| during lactation | 180–320 | 1–6 years | 160–390 | ||
| during menstruation | 90–160 | 7–12 years | 160–380 | ||
| Men | 180–400 | over 12 years old | 180–320 (girls) 180–400 (boys) | ||
Research methods
Counting the number of blood platelets is part of the general (comprehensive clinical) analysis; the study is not performed separately. The content of PLT, which is abbreviated as platelets, is the main determined blood parameter. There are several ways to find out the platelet concentration and compare the result with the norm in women, and each blood test has its own advantages and disadvantages.
The following methods are used in clinical institutions:
- manual counting;
- automatic platelet detection;
- using a semi-automatic analyzer.
If pathological changes are detected, several tests are performed to confirm the diagnosis and minimize the likelihood of error. First, it is recommended to count manually (under a microscope), then use a specialized apparatus.
Using a Hematology Analyzer
The devices are semi-automatic and fully automatic (used more often). They are designed for quantitative research of blood cells.
Among the indicators characterizing platelets, the following are determined:
- concentration;
- average volume;
- volume share;
- coefficient reflecting the spread of volume values relative to the average value.
The number of cells is calculated automatically. The hematology analyzer provides a quick and accurate result (the coefficient of variation does not exceed 10%), but does not allow examining cells or detecting signs of their atypicality.
Goryaev's counting chamber
It is a simple design that involves visual platelet counting under microscopic magnification with phase contrast. A microscopic grid applied to a glass slide helps determine the number of blood platelets in a removed blood sample; the calculation is carried out using a special formula. The advantages of the technique are the ability to further study the parameters of platelets, their structure, and identify deviations in size, shape, and structure. However, the technique requires certain knowledge and skills from the laboratory doctor. An error in issuing the result of a quantitative assessment cannot be ruled out; the spread of indicators is 25-30%.
According to the Fonio method
This is a microscopic examination method. A stained blood smear is assessed. The smear is fixed with a solution that prevents the formation of a clot. Potassium salt EDTA or magnesium sulfate is used as an anticoagulant reagent. The technique involves simultaneously counting platelets and red blood cells under a microscope and calculating their ratio (in ppm).
The analysis refers to a manual counting method, helps to identify the exact (average range of 10-15%) number of blood cells and platelets, evaluate morphological features, visually determine the characteristics of platelets, including pathological formations.
Increased platelet count
An increase in the number of platelets in the blood to 400 thousand/ml or more is called thrombocytosis. This condition is typical for:
- oncological diseases, in particular liver, kidney and adrenal cancer;
- chronic inflammatory processes: colitis;
- tuberculosis;
- rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
With lymphogranulomatosis and leukemia, both thrombocytosis and thrombocytopenia can be observed.
Increased levels in children
Elevated PLT levels in children are observed when:
- disorders in the development of bone marrow, spleen or its absence;
- infectious lung diseases;
- colitis;
- anemia;
- taking medications: Aspirin;
- Reopirina;
- Biseptol.
The role of leukocytes and the norm for children of different ages
Leukocytes are the protectors of the body. They prevent various diseases in both children and adults. At an early age, their role is especially great, since with the slightest decrease in the content of blood cells, immunity can drop sharply, which will lead to the development of serious diseases. In order for the baby to develop properly and be healthy, it is necessary that the indicators of all blood cells are within normal limits.
Various blood cells perform the following functions:
- Maintaining immunity. Certain particles find and destroy pathogenic viruses that enter the body.
- Preventing inflammation. Bacteria and viruses are destroyed and eliminated using pus.
- Removing toxins. Toxic substances are inhibited by white blood cells, so they do not have time to harm the body.
- Removal of dead cells. If the deteriorating cells are not removed in time, inflammation and intoxication will begin in the body.
- Fighting allergens. The better the child’s blood picture, the less susceptible he is to developing secondary allergic reactions (that is, acquired rather than congenital allergies).
- Elimination of parasites. White blood cells secrete toxins that are harmless to the body but harmful to foreign parasitic life forms.
Obviously, if there is a lack or excess of any blood cells, the body’s functions are disrupted. If you miss the moment when a certain type of body is in deficiency or excess, the child may be at serious risk. In addition, a decrease or increase in the content of corpuscles sometimes occurs due to an already existing disease. It could even be cancer. The sooner one of the serious abnormalities is suspected, the greater the chances of successfully treating it. And the analysis of the leukocyte formula allows you to get accurate results in just a few days.
To correctly interpret test results, doctors must know the role of each group of blood cells. Below are the main functions of all white blood cells, as well as the norm for children of different age groups.
Lymphocytes
This group of blood cells is designed to protect the child’s body from the penetration and development of viruses. Lymphocytes are divided into several subtypes. Normally, their content is quite high.
Norm for different age groups (in percentage):
| Newborns | 16-31 |
| From the 5th day | 31-50 |
| After 10 days | 39-60 |
| 1-12 months | 45-60 |
| 1-4 years | 44-65 |
| 5-9 years | 35-55 |
| From 10 years | 29-45 |
Eosinophils
This indicator is the easiest to decipher, since the content varies slightly depending on age. Unlike lymphocytes, eosinophils are almost never found in the blood. However, they perform an important function: they prevent the development of allergies and eliminate parasites.
| Newborns | From 1 to 4 percent |
| 10 days-12 months | From 1 to 5 percent |
| From 1 year | From 1 to 4 percent |
Basophils
Basophils are also responsible for immune responses in the body. Their content in the blood is very small: up to 1%. In some patients it can even reach 0%, and this is considered normal. The content of basophils does not depend on age and is the same in both newborns and older children.
Neutrophils
Neutrophils are divided into three subgroups: the youngest cells, medium maturity and very mature. Young cells should normally be absent, but mature cells should be the most abundant. In addition, neutrophils are divided into band and segmented. Division is based on the shape of the nucleus. “Rods” should be from 4 to 12% immediately after birth, from the 5th day of life their number sharply decreases to 1-5%. At the age of 5 years, the child should not have more than 4% and less than 1%.
Norm of segmented neutrophils (in percent):
| Newborns | 50-70 |
| From the 5th day | 34-55 |
| 1-12 months | 17-30 |
| 1-4 years | From 20 to 35 |
| 5-9 years | From 35 to 55 |
| From 10 years | From 40 to 60 |
Monocytes
Monocytes form reliable protection against inflammation and bacteria, as they remove germs and dead cells. They can reach 15% of the total number of leukocytes. The norm depends on the age of the baby.
Table by age.
| Newborns | From 4 to 10 percent |
| From the 5th day | From 6 to 14 percent |
| 1-12 months | From 5 to 12 percent |
| 1-4 years | From 4 to 10 percent |
| 5-14 years | 4 to 6 percent |
| From 15 years old | From 3 to 7 percent |
Low PLT level
A decrease in the number of platelets in the blood to 140 thousand/ml is called thrombocytopenia and may indicate the presence of:
- blood clotting disorders;
- hypothyroidism;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- systemic connective tissue diseases: lupus erythematosus;
- scleroderma;
- dermatomyositis.
- Epstein-Barr virus;
- flu;
A decrease in platelet levels can be observed while taking certain medications, in particular Levomycetin, corticosteroids, Aspirin, Cisplatin, Busulfan, Chlorambucil and other cytostatics, which is normal.
Aspirin is often used to thin thick blood:
A decrease in the PLT level to 30 thousand/ml is considered critical, since with such a number of platelets, the likelihood of life-threatening bleeding is extremely high. Such severe thrombocytopenia is characteristic of:
- radiation sickness;
- Addison-Beermer anemia;
- Werlhof's disease.
When PLT levels are low, it is extremely important to avoid any situations that could lead to shock, as well as disruption of the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes, as this can provoke bleeding, which is difficult to stop even for experienced doctors in the hospital.
If your PLT level is low, it may be worth purchasing a soft toothbrush to prevent damage to your gums when brushing your teeth.
Decreased levels in children
A low platelet count in childhood can be a consequence of:
- development of allergic reactions to drugs;
- infectious diseases, including rubella and malaria;
- skin pathologies;
- poisoning;
- parasite infestation;
- viral infections;
- blood transfusions with reduced platelet levels.
The role of platelets in the child’s body:
PMT functions
Platelets are flat oval or round discs that do not have a nucleus. They are produced by the bone marrow and are also synthesized in small quantities in organs such as the spleen and liver.
In the body, these cells play an important role; blood clotting and restoration of damaged tissues directly depend on their concentration.
Having the ability to stick to damaged vessel walls and connect with each other, platelets form something similar to a plug. The content of blood clotting enzymes in them is the main factor that stops bleeding.
In addition, they are assigned the following functions:
- absorption of foreign particles - viruses and bacteria;
- nutrition of vascular walls;
- transportation of biological microelements.
It should be noted that these blood components are rather short-lived. They live for about 10 days, after which the body produces new cells to replace the old cells.
An increase or decrease in the level of platelets in the blood indicates the development of various pathologies in the body.
Deciphering a general blood test: what are platelets - video
Thus, PLT is an important indicator of a person's health status. Deviation from the norm may indicate the development of diseases, the treatment of which is carried out by diametrically opposed methods. Therefore, you should not self-medicate. Only a doctor can determine the exact cause by analyzing the remaining results of the OAC and the present symptoms.
- Author: Maria Voronina
A copywriter with an active lifestyle. I specialize in writing articles on medical topics. Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(13 votes, average: 4.6 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
How to decipher the result
Pathology is suspected in situations where the test result does not fall within the reference interval (normal limits). A slight deviation should not cause concern. Seek medical attention if concentrations are excessively high or low.
Many clinics have established rules that if an automatic hematology analyzer shows that an adult has a result of less than 130 or more than 550 thousand cells/μl, then to improve the diagnostic quality an additional Fonio count is performed. The results should be transferred to a doctor of the appropriate specialization. Without the participation of a clinician, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis and begin treatment.
Alarming symptoms
In order not to miss the onset of serious pathological changes, dangerous manifestations should not be ignored. Among them:
- the appearance of bruises;
- bleeding gums;
- frequent nosebleeds;
- the appearance of spider veins on the body;
- heavy and prolonged periods;
- inability to stop bleeding from minor scratches, cuts and other injuries;
- skin itching;
- tingling in the fingers and toes.
These signs are not specific. They are also typical for other diseases. However, their appearance should be a reason to consult a doctor in order to identify the cause using a test that determines platelet levels.
Downgrade methods
Antiplatelet drugs are prescribed - Ticlopidine, Clopidogrel, Aspirin. The latter drug is taken in a small dose so as not to provoke gastric bleeding. Contraindicated for children.
During pregnancy, the decrease in values is physiological and rarely needs correction. If necessary, Dipyridamole is prescribed.
Other methods
In addition to drug therapy, it is recommended to follow a diet, quit smoking, and drink alcohol. It is useful to introduce foods rich in iodine, calcium, iron, and vitamins into the diet.
From traditional medicine you can use tincture of garlic, ginger and hirudotherapy.
Recommendations
If thrombocytopenia is detected in a child, it is recommended to make some adjustments to his lifestyle:
- Minimize sports activities that can lead to injury.
- Avoid independent use of scissors, knives and other dangerous objects.
- Use laxatives as prescribed by your doctor to prevent injury to the digestive system.
Damage to the skin, mucous membranes or bleeding is a signal to immediately visit a doctor.