Information about the product
Release form
The blood pressure medication Perineva is available in the form of white tablets with different contents of the main component. Round tablets contain 2 and 8 mg of perindopril, and oval tablets contain 4 mg of the substance.
Each tablet is packaged in an individual blister cell. One blister contains 10 tablets. A pack can contain 30 or 90 tablets. The kit includes instructions for using Perineva.
Composition of tablets
The main active ingredient of the tablets is Perindopril erbumine.
Additional components:
- calcium chloride hexahydrate;
- polyvinylpyrrolidone;
- lactose monohydrate;
- silica;
- magnesium stearate;
- cellulose.
Packaging of Perinev tablets
Price and terms of sale
The drug Perineva is sold in pharmacies with a prescription. The cost of Perinev's blood pressure tablets is 210 rubles for a package of 30 tablets and 1000 rubles for a package of 90 tablets. The price of Perineva depends on the amount of the main substance included in the composition.
Storage conditions
The drug for Perinev's blood pressure should be stored in a place protected from children at room temperature.
The shelf life of the medicine is 3 years from the date of manufacture. After the expiration date, tablets must be disposed of in accordance with sanitary standards.
Reviews from patients taking the drug
Doctors often prescribe the drug Perineva. Reviews from patients who took the drug are varied. But it is indispensable when a mild remedy is needed that rarely causes side effects. If you believe the instructions for use, then Perineva is exactly like that.
For example, one user writes that she has been taking Perineva for three months. A month after starting use, her blood pressure leveled off within 24 hours and did not rise above 130/80. Before this it increased every evening.
In this case, the patient was successfully selected a medicine. But it should be noted that Perineva’s treatment will not eliminate the causes of the disease, but will only dull the symptoms. Hypertension often occurs with an unhealthy lifestyle. You need to reconsider your diet, daily routine, and quit smoking.
If you look further at what patients think about Perinev tablets, reviews confirm that not everyone is happy with taking the drug. Most often this occurs due to ignorance of the features of the product. Thus, a patient with hypertension wrote that he has been treated with Perineva for the fourth month. Previously, the blood pressure level did not rise above 130/85. But recently, when the weather changed, the pressure began to rise and reach 170/110, headaches and other signs of hypertension appeared. These pills, in his opinion, do not significantly lower blood pressure. He wants to switch to another remedy, stronger.
In this case, it is necessary to undergo a serious examination, go to a doctor for a consultation and follow his recommendations. A healthy lifestyle is important. This will be the main treatment for hypertension. And medications only complement it. If you continue to move little and eat haphazardly, then in a couple of years the pressure may get out of control and no medications will help.
Here's what another user is talking about. She contacted her local physician with complaints of high blood pressure, constant headaches, and shortness of breath during exercise. The doctor prescribed treatment for Perineva. She provided the prescription in Latin to the pharmacy, where they sold her Perinev 8 mg tablets. She took Perineva for hypertension for six months according to the instructions for use. The blood pressure remained well during this time and never rose above 145/95. But I suffered from a constant cough. The doctor said to switch to another drug and add a diuretic. Now she has started treatment with another drug. How this will affect her health is still unknown.
How effective a particular drug is cannot be predicted in advance. Currently, medications for blood pressure are selected taking into account the instructions for use, trial and error, but, unfortunately, no other approach has yet been invented. Each person's body reacts differently to a particular drug.
Pharmacodynamics: increases or decreases blood pressure
Perineva for lowering blood pressure belongs to the group of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. The drug has a pronounced antihypertensive effect and is an effective cardioprotector with a vasodilator effect.
The drug contains perindopril, which inhibits the conversion of angiotensin 1 to angiotensin 2. Due to this, blood vessels dilate and blood pressure decreases.
The drug reduces the activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme, activates angiotensinogenase in the blood, and reduces the production of aldosterone. The effect of the drug extends to a decrease in the production of ACE, which leads to the normalization and activity of bradykinin, which is responsible for vasodilation of blood vessels. A decrease in ACE activity leads to increased production of the kinin-kallikrein system. This leads to the activation of prostaglandins.
Action of perindopril:
- reduces upper and lower blood pressure;
- reduces total peripheral vascular resistance;
- accelerates peripheral blood circulation;
- accelerates blood circulation in the kidneys without affecting the glomerular filtration rate.
Perindopril has no effect on increasing heart rate.
The treatment course involves taking one tablet per day
The drug reduces blood pressure 4-6 hours after taking the tablet. The drug has a prolonged effect. The pressure will not increase during the day. After 24 hours, the effect of the tablets remains 87%. In some patients, the effect after 24 hours can reach 100%. To reduce Perineva's blood pressure, it is enough to take 1 pill.
The pressure under the influence of the drug decreases gradually, which is safe for a patient with hypertension.
For a lasting hypotensive effect, it is necessary to take Perineva at high blood pressure for a month. The drug is not addictive, so there will be no withdrawal symptoms after finishing taking the blood pressure pills.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Perindopril or kinase II is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, belongs to exopeptidases and is a prodrug from which the active metabolite perindoprilat is formed. Converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II (vasoconstrictor) and destroys the vasodilator bradykinin to an inactive hectapeptide. Due to the suppression of ACE activity, the level of angiotensin II decreases, plasma renin activity increases (negative feedback of renin release is inhibited) and aldosterone secretion decreases. ACE destroys bradykinin, so suppression of this enzyme also leads to an increase in the activity of the circulating and tissue kallikrein-kinin system, while activating the prostaglandin system.
The therapeutic effect of the drug is due to the effect of the active metabolite – perindoprilate.
Perindopril lowers blood pressure (both diastolic and systolic) in the lying and standing positions. It reduces total peripheral vascular resistance (TPVR), as a result of which blood pressure (BP) decreases. At the same time, peripheral blood flow accelerates, but the heart rate (HR) does not increase. As a rule, renal blood flow also accelerates, but the glomerular filtration rate does not change. It takes 4–6 hours for the maximum hypotensive effect to develop after a single oral dose; the effect persists for 24 hours, but even after 24 hours, 87–100% of the maximum effect is still provided. Blood pressure decreases quickly. Stabilization of the hypotensive effect is observed after 1 month of regular use of Perineva and persists for a long time. Discontinuation of therapy does not cause the development of withdrawal syndrome.
The active substance reduces myocardial hypertrophy of the left ventricle. Increases the concentration of high-density lipoproteins (HDL); in patients with hyperuricemia, reduces the concentration of uric acid. With long-term use, it normalizes the myosin isoenzyme profile and reduces the severity of interstitial fibrosis.
The drug eliminates structural changes in small arteries and improves the elasticity of large arteries. By reducing pre- and post-load, it normalizes heart function. In chronic heart failure (CHF), it reduces peripheral vascular resistance, filling pressure in the right and left ventricles, increases cardiac output and cardiac index. When taking the drug in an initial daily dose of 2 mg in patients with CHF functional classes I and II according to the NYHA classification, there is no statistically significant decrease in blood pressure compared to placebo.
Pharmacokinetics
Perindopril in tablet form is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract; it takes 1 hour to achieve maximum plasma concentration. Bioavailability is about 65–70%.
About 20% of the absorbed substance is converted into the active metabolite perindoprilat. The maximum content in plasma is observed after 3–4 hours. Half-life (T1/2) – 1 hour. The volume of distribution of unbound perindoprilate is 0.2 l/kg. The connection with blood plasma proteins is insignificant, the connection with ACE is less than 30%, but depends on its concentration. Excreted by the kidneys. Does not accumulate. T1/2 of the unbound fraction is 3–5 hours; in patients with chronic heart and renal failure and the elderly, excretion is slow.
In patients with liver cirrhosis, the hepatic clearance of perindopril changes, but the total amount of metabolite formed remains unchanged, so dose adjustment of Perineva is not required.
Food reduces the conversion of perindopril to perindoprilat, thereby reducing the bioavailability of the drug.
Perindoprilat is removed by peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis (rate 70 ml/min., 1.17 ml/sec.).
For whom is it contraindicated?
Perineva for blood pressure has absolute and relative contraindications.
Absolute contraindications include:
- galactosemia;
- hypolactasia;
- glucose-galactose malabsorption;
- individual intolerance to components;
- Quincke's edema.
The medication is contraindicated in children under 18 years of age.
Children's age is a contraindication to taking the drug
Relative restrictions in use
This primarily concerns CHF in the decompensated stage. Patients with arterial hypotension should not take the medicine; only certain calculations on the part of the doctor can allow taking Perineva.
Among the relative contraindications:
- Aortic/mitral valve stenosis;
- Renovascular type hypertension;
- Obstructive cardiomyopathy (hypertrophic type);
- Cerebrovascular diseases, which include ischemia of the heart muscle, insufficiency of cerebral blood flow, and coronary insufficiency;
- CRF (creatinine clearance is taken into account);
- Bilateral stenosis of the nephroarteries or arterial stenosis of the only existing kidney, as well as post-transplant status;
- Hemodialysis using special membranes;
- Hyperkalemia, hyponatremia and hypovolemia;
- Condition after surgery;
- Connective tissue diseases - for example, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma;
- Diabetes mellitus of any type;
- Inhibition of hematopoiesis in the bone marrow associated with the use of immunosuppressants;
- The patient belongs to the Negroid race;
- Age over 65;
- Parallel therapy with allergens (desensitizing).
If the doctor who prescribes your medicine for some reason does not know about some of your diseases, current or previously, be sure to tell him about them. This happens if the patient comes to the appointment not with a medical card, but with an insert sheet. He may forget to mention this or that disease, the doctor will not take this into account, and the therapy may be incorrect (and therefore dangerous).
Relative contraindications
In case of relative contraindications, the doctor guides the patient throughout the entire course of therapy to prevent worsening of the condition. He adjusts the dosage or changes the treatment regimen for any deviations.
Relative contraindications include:
- chronic heart failure in the stage of decompensation;
- decreased blood pressure;
- aortic stenosis;
- narrowing of the left atrioventricular orifice;
- renovascular hypertension;
- hypertrophy of the ventricular walls;
- cerebrovascular disease;
- ischemia;
- blood flow deficiency syndrome;
- decreased coronary blood flow;
- chronic kidney failure;
- bilateral stenosis of the nephro arteries;
- aortic stenosis of the kidney;
- kidney transplantation;
- hemodialysis;
- increased potassium levels in the blood;
- lack of sodium;
- hypovolemia;
- condition after surgery;
- Libman-Sachs disease;
- systemic scleroderma;
- diabetes;
- aplastic anemia;
- belonging to the Negroid type;
- old age from 65 years;
- allergen therapy.
It is necessary to inform the doctor about any existing abnormalities or ailments in order to exclude a deterioration in health while taking Perinev’s blood pressure medication.
Before using the drug, you should consult your doctor
Pharmacokinetic characteristics
The medicinal composition is absorbed quite quickly from the digestive tract; it takes an hour for peak plasma levels to be reached. Biological availability – within 65-70%.
Approximately 20% of the absorbed component becomes the active metabolite perindoprilate. Its plasma maximum concentration is fixed after 3.5 hours, and the half-life is equal to an hour. The substance has an insignificant connection with blood proteins (from the plasma part), but the connection with ACE does not reach 30%, but it depends on the content of the ingredient.
Evacuation is carried out through the kidneys. Food, as scientists have proven, somewhat reduces the transformation of perindopril into perindoprilat, which reduces drug bioavailability.
Is it possible during pregnancy and lactation?
The blood pressure drug Perineva cannot be taken during gestation. If a woman finds out about pregnancy during a course of taking pills, she should immediately stop therapy and inform her doctor.
Taking the drug in the third trimester can provoke a fetotoxic effect: oligohydramnios, decreased kidney function, slow development of the skull bones.
A child taking the drug by a pregnant woman may develop congenital hypotension and renal failure.
During breastfeeding, you should stop taking the drug, since there is no data on the penetration of components into breast milk. If it is impossible to stop taking the drug, it is necessary to transfer the baby to artificial feeding.
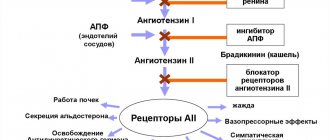
ACE inhibitors: how they work
The general scheme is as follows: angiotensin I is formed from plasma beta-globulins, including angiotensinogen, under the influence of renin. It does not affect vascular tone and remains neutral. This component is susceptible to the action of ACE (that is, angiotensin converting enzyme). In this way, the vasoactive peptide angiotensin II is formed: it has an inherent effect on vascular tone precisely due to irritation of receptors that are sensitive to angiotensin. This is how the blood vessels narrow.
Under the influence of such active angiotensin, norepinephrine and aldosterone are released, as well as antidiuretic hormone. And if the entire process described above occurs with high intensity, a person develops hypertension. And the pressure can increase to a critical level, provoking a hypertensive crisis and vascular accidents.
Therefore, doctors have developed medicinal products that control the production of angiotensin II and subsequent hormonal surges. In particular, it was possible to achieve this goal with Perinev’s blood pressure tablets.
How to take for high blood pressure and hypertension
The drug is prescribed as a monotherapy or in complex therapy. The initial daily dosage for blood pressure is 4 mg. In severe hypertension, the initial daily dose should not exceed 2 mg. Gradually the dosage can be increased to 8 mg per day.
Perinev tablets should not be taken together with diuretics. Three days before starting therapy with Perineva, you must stop drinking diuretics. If it is impossible to stop taking a diuretic, Perinev tablets are taken in the minimum dosage, which is 2 mg. When combined with diuretics, it is necessary to monitor blood counts, monitor potassium concentrations, and monitor blood pressure and kidney function.
In old age, treatment with Perineva should be started with a minimum dosage of 2 mg.
The medication is started with minimal dosages
Indications for use
According to the instructions, Perineva is intended for the treatment of arterial hypertension and chronic heart failure.
The drug is used (as part of complex therapy with indapamide) to prevent recurrent stroke in patients with a history of cerebrovascular diseases.
An ACE inhibitor is also prescribed for stable coronary heart disease (CHD) to reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications in patients who have undergone coronary revascularization and/or myocardial infarction.
Treatment regimen for other cardiovascular diseases
To prevent stroke, it is recommended to take Perinev tablets once a day, 2 mg 14 days before starting Indapamide therapy. Perinev needs to start drinking when he has high blood pressure no later than 2 weeks after the stroke.
For chronic heart failure, the patient is prescribed 2 mg of the drug per day. After 14 days, the doctor may increase the dosage to 4 mg. At the same time, the doctor may add beta blockers, Digoxin, and diuretics to therapy.
Before prescribing the drug, the doctor conducts a comprehensive examination, monitors blood pressure readings for some time, monitors the condition of the kidneys and potassium concentration.
Dosages
Depending on the diagnosis, dosages for Perinev tablets for use are selected as follows:
- hypertension - initial amount - 4 mg;
- elderly patients - from 2 mg;
- severe disturbances of cardiac activity, occurring chronically - from 2 mg;
- preventive measures to help avoid a recurrent stroke - from two milligrams;
- kidney disease - 2–4 milligrams per day.
Special instructions and recommendations
When taking Perineva for high blood pressure, you must follow the schedule. You need to take the pills at the same time. Do not break, crush, dissolve or chew the tablets. They are taken whole with a sufficient amount of drinking water.
If you miss one, you do not need to take two tablets at once, as this may cause an overdose.
Other recommendations:
- Transient hypertension will not be an indication to interrupt treatment. Taking the pills is stopped until the condition normalizes, and then therapy is continued according to the proposed regimen.
- The doctor adjusts the dosage if adverse reactions occur.
- The doctor evaluates the benefits and harms of the drug in patients with ischemia and the development of angina.
- If Quincke's edema occurs, stop taking Perinev tablets and call an ambulance.
- If jaundice occurs, stop taking the tablets. The patient is sent to a medical facility to undergo a comprehensive examination to identify pathologies in the liver.
- Taking Perinev blood pressure tablets can cause a temporary increase in blood creatinine and urea levels.
- Patients with diabetes who are taking antidiabetic agents or insulin need to monitor their blood glucose levels.
- The day before the upcoming operation, you must stop taking Perinev tablets, since anesthesia in combination with the drug can provoke a strong decrease in blood pressure.
During treatment with the drug, the patient may develop a persistent cough. This is the body's reaction to the components of the product. The cough will go away on its own after stopping the drug.
While taking Perineva, a cough may appear, which will go away with discontinuation of the drug.
What are the side effects?
Among the side effects of the drug "Perineva" there were complaints from patients that:
- dizzy and headache;
- there is noise in the ears;
- there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- there is discomfort in the digestive system;
- there are visible rashes on the skin that itch;
- asthenic syndrome manifests itself.
Blood serum tests show an increased level of urea, which stabilizes after discontinuation of the drug course.
Possible side effects
In rare cases, some patients may experience visual disturbances after taking the pills. A person sleeps poorly, his mood changes. It has been noted that arrhythmia may occur, and from the respiratory system - cough, shortness of breath.
In case of an overdose, along with renal failure, shock may occur and the rhythm of the heart may change towards speeding up or slowing down.
To remove excess doses of peridopril from the body, hemodialysis is performed.
Possible adverse reactions
Before taking the drug, you must carefully read the instructions for use of Perineva. Taking Perinev tablets can provoke the appearance of adverse reactions from the functioning of vital systems and internal organs:
- cardiovascular system: decrease in blood pressure to critical levels, angina pectoris, cardiac arrhythmia, stroke, heart attack, angitis;
- digestive system: dyspepsia, difficulty defecating, vomiting, abdominal pain, dry mouth, inflammation of the pancreas, hepatitis;
- respiratory organs: cough, dyspnea, narrowing of the bronchial lumen, rhinitis, eosinophilic pneumonia;
- nervous system: headaches, sensitivity disorders, dizziness, mood swings, sleep disturbances, disorientation in space, impaired concentration, memory impairment;
- organs of perception: ringing in the ears, blurred vision;
- musculoskeletal system: spasms, convulsions;
- genitourinary system: impotence, impaired renal function, acute kidney failure;
- circulatory system: hemolytic anemia, decreased platelet count, decreased leukocyte level, decreased neutrophil count, decreased hematocrit number, decreased hemoglobin level;
- skin: rashes, itching, nettle fever, Quincke's edema, erythema multiforme;
- laboratory indicators: excess potassium, increased creatinine, increased urea, increased bilirubin;
- other reactions: asthenia, increased sweating.
Recommended duration of use
Many users are interested in the duration of use of Perinev tablets. The duration of use of any medicinal substance, including Perinev tablets, according to the instructions for use, is prescribed only by a doctor after serious examinations and monitoring of the patient and his body’s reaction to these tablets. It can be used long-term as an antihypertensive agent: its effect lasts 24 hours, which is very convenient. According to the instructions for use, the drug is taken under regular monitoring of kidney function, the patient’s health and well-being.
Drug overdose
In case of an overdose, the patient develops characteristic symptoms:
- a strong decrease in blood pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- sinus rhythm disturbance;
- increased heart rate;
- disturbance of water-electrolyte metabolism;
- hyperventilation syndrome;
- increased feeling of anxiety;
- cough;
- vestibular disorders;
- affective shock reactions;
- renal dysfunction.
If there is a significant decrease in blood pressure, the patient should be laid horizontally, with his legs slightly elevated. It is necessary to ensure a flow of fresh air and remove tight clothing. The patient needs to compensate for the lack of blood and administer angiotensin-2 intravenously.
In case of overdose, it is necessary to monitor the performance of the heart and blood vessels, monitor the level of creatinine and electrolytes in the blood.
Overdose can lead to a sharp drop in blood pressure
Can it be combined with NSAIDs?
NSAIDs are a category of drugs with a particular frequency of use. These include anti-inflammatory and analgesic medications, which people with different indicators of physical health use relatively often. For example, people drink Nimesulide or Diclofenac for joint pain, osteochondrosis, post-traumatic pain, etc. These compounds are also used for so-called colds.
But not all patients think about whether it is possible to combine NSAIDs with other medications that are often used in courses. So, if you combine them with Perineva’s treatment, a weakening of the hypotensive effect cannot be ruled out. The level of K ions in the blood may increase, causing renal function to deteriorate. In some cases, things turn into the development of acute renal failure. If a patient has diseased kidneys, and he drinks Aspirin along with Perineva, acute renal failure is highly likely to develop.
Therefore, before taking a painkiller or anti-inflammatory pill, remember that you are taking Perineva, which does not combine well with them. And what you can take in case of a cold or joint pain, check with your doctor.
Drug interactions
Before using the blood pressure drug Perinev, you must tell your doctor about any other medications you are taking.
It is not recommended to take Perinev tablets with lithium-containing drugs, potassium-containing drugs, or diuretics.
Perineva lowers blood pressure, like other angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. The first dose of Perineva can cause a sharp drop in blood pressure. Patients with reduced circulating blood volume are especially susceptible to this. In patients with uncomplicated arterial hypertension, sudden increases in pressure are not observed.
Perineva for hypertension can provoke a sharp and strong decrease in blood pressure in patients with severe chronic heart failure who are simultaneously taking loop diuretics. Patients with this diagnosis must be constantly under the supervision of their attending physician. The doctor should carefully consider the dosage, initially prescribing the minimum values. The same recommendations are valid for patients with coronary heart disease and cerebrovascular diseases.
Compatibility with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are among the most commonly prescribed drugs. These are painkillers, anti-inflammatory, immunostimulating. Non-steroidal drugs include Nimesulide and Diclofenac, which are prescribed for pain in the joints, spine, and after injury. Non-steroidal drugs are used to treat colds, viruses, and infections.
When taking NSAIDs simultaneously with Perinev tablets, the hypotensive effect of the latter may be reduced. Taking NSAIDs provokes an increase in potassium ions in the blood serum, which leads to impaired renal function. In rare cases, acute renal failure may develop. Patients with impaired renal function are at risk.
The compatibility of drugs can be determined by a doctor
Before taking any anti-inflammatory drug, you must remember that Perinev tablets are incompatible with them. If you have a cold or other health problems, you should consult a doctor who will prescribe a drug that is safe to take in combination with Perinev tablets.
What can you combine with?
You can take Perineva for high blood pressure simultaneously with:
- nitrates;
- beta blockers;
- thrombolytic agents;
- aspirin in combination with antiplatelet agents.
Perineva
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
During pregnancy, the use of the drug is contraindicated.
If pregnancy is confirmed, Perineva® should be discontinued as soon as possible. Use in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy can cause fetotoxic effects (decreased renal function, oligohydramnios, delayed ossification of fetal skull bones) and neonatal toxic effects (renal failure, arterial hypotension, hyperkalemia). If the drug is used in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination of the fetal kidneys and skull bones. The use of Perineva® during lactation is not recommended due to the lack of data on the possibility of perindopril passing into breast milk. If it is necessary to use the drug during lactation, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Use for liver dysfunction
Patients with liver disease do not require dose adjustment. In patients with liver cirrhosis, the hepatic clearance of perindopril changes, while the total amount of perindoprilate formed does not change, and no adjustment of the dosage regimen is required.
Use for renal impairment
In patients with kidney disease, the dose of Perineva is determined depending on the degree of renal dysfunction. During treatment, the content of potassium ions and creatinine in the blood serum should be regularly monitored. Recommended doses are presented in the table.
| Creatinine clearance | Recommended dose |
| from 60 ml/min and more | 4 mg/day |
| from 30 to 60 ml/min | 2 mg/day |
| from 15 to 30 ml/min | 2 mg every other day |
| Patients on hemodialysis *(CC less than 15 ml/min) | 2 mg per day of dialysis |
*- Dialysis clearance of perindoprilate is 70 ml/min. Perineva should be taken after a dialysis session.
Use in children
Contraindicated: under 18 years of age (efficacy and safety have not been established).
Use in elderly patients
In elderly patients, the recommended starting dose is 2 mg/day. In the future, the dose can be gradually increased to 4 mg and, if necessary, to a maximum of 8 mg/day, provided that the lower dose is well tolerated.
special instructions
Stable ischemic heart disease
In patients with coronary artery disease who develop an episode of unstable angina (significant or not) during the first month of therapy with Perineva®, it is necessary to assess the benefit/risk ratio of therapy with this drug.
Arterial hypotension
When treating arterial hypertension, ACE inhibitors can cause a sharp decrease in blood pressure. In patients with uncomplicated hypertension, symptomatic hypotension rarely occurs after the first dose. The risk of excessive reduction in blood pressure is increased in patients with reduced blood volume during diuretic therapy, while following a strict salt-free diet, hemodialysis, as well as with diarrhea or vomiting, or in those suffering from severe renin-dependent arterial hypertension. Severe arterial hypotension was observed in patients with severe chronic heart failure, both in the presence of concomitant renal failure and in its absence. The most common arterial hypotension can develop in patients with more severe chronic heart failure, taking high-dose loop diuretics, as well as in the presence of hyponatremia or renal failure. In such patients, careful medical monitoring is recommended during initiation of therapy and during dosage titration. The same applies to patients with coronary artery disease or cerebrovascular diseases, in which an excessive decrease in blood pressure can lead to myocardial infarction or cerebrovascular complications.
If arterial hypotension develops, it is necessary to place the patient in a horizontal position with elevated legs, and, if necessary, administer an intravenous solution of sodium chloride to increase blood volume. Transient arterial hypotension is not a contraindication for further therapy. After restoration of blood volume and blood pressure, treatment can be continued subject to careful selection of the dose of the drug.
In some patients with chronic heart failure and normal or low blood pressure, an additional decrease in blood pressure may occur during therapy with Perineva®. This effect is expected and is usually not a reason to discontinue the drug. If arterial hypotension is accompanied by clinical manifestations, dose reduction or discontinuation of Perineva® may be required.
Aortic or mitral valve stenosis/hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
ACE inhibitors, incl. Perindopril should be prescribed with caution to patients with mitral valve stenosis and left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (aortic valve stenosis and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy).
Renal dysfunction
In patients with renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance less than 60 ml/min), the initial dose of Perineva should be adjusted according to the clinical clearance and then depending on the therapeutic response. For such patients, regular monitoring of the concentration of potassium ions and creatinine in the blood serum is necessary.
In patients with symptomatic heart failure, arterial hypotension that develops during the initial period of therapy with ACE inhibitors can lead to deterioration of renal function. Cases of acute renal failure, usually reversible, have sometimes been reported in such patients.
In some patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis or renal artery stenosis of a solitary kidney (especially in the presence of renal failure), an increase in serum concentrations of urea and creatinine was observed during therapy with ACE inhibitors, which was reversible after discontinuation of therapy. In patients with renovascular hypertension during therapy with ACE inhibitors, there is an increased risk of developing severe arterial hypotension and renal failure. Treatment of such patients should begin under close medical supervision, with small doses of the drug and with further adequate dose selection. During the first weeks of therapy with Perineva®, it is necessary to discontinue diuretics and regularly monitor renal function. In some patients with arterial hypertension in the presence of previously undetected renal failure, especially with concomitant diuretic therapy, there was a slight and temporary increase in serum urea and creatinine concentrations. In this case, it is recommended to reduce the dose of Perineva® and/or discontinue the diuretic.
Hemodialysis patients
Several cases of persistent, life-threatening anaphylactic reactions have been reported in patients undergoing dialysis using high-flux membranes and concomitantly taking ACE inhibitors. If hemodialysis is necessary, a different type of membrane must be used.
Kidney transplantation
There is no experience with the use of perindopril in patients with recent kidney transplantation.
Hypersensitivity/angioedema
Rarely in patients taking ACE inhibitors, incl. perindopril, angioedema of the face, extremities, lips, mucous membranes, tongue, glottis and/or larynx developed. This condition can develop at any time during treatment. If angioedema develops, treatment should be stopped immediately, and the patient should be under medical supervision until symptoms disappear completely. Angioedema of the lips and face usually does not require treatment; Antihistamines can be used to reduce the severity of symptoms. Angioedema of the tongue, glottis, or larynx can be fatal. If angioedema develops, it is necessary to immediately administer epinephrine (adrenaline) subcutaneously and ensure airway patency.
Patients with a history of angioedema not related to the use of ACE inhibitors have a higher risk of developing angioedema while taking an ACE inhibitor.
Anaphylactoid reactions during LDL apheresis procedure
In patients prescribed ACE inhibitors during the procedure of LDL apheresis using dextran sulfate absorption, in rare cases, an anaphylactic reaction may develop. It is recommended to temporarily discontinue the ACE inhibitor before each apheresis procedure.
Anaphylactic reactions during desensitization
In patients receiving ACE inhibitors during a course of desensitization (for example, hymenoptera venom), in very rare cases, life-threatening anaphylactic reactions may develop. It is recommended to temporarily discontinue the ACE inhibitor before each desensitization procedure.
Liver failure
During therapy with ACE inhibitors, it is sometimes possible to develop a syndrome that begins with cholestatic jaundice and then progresses to fulminant liver necrosis, sometimes with death. The mechanism of development of this syndrome is unclear. If jaundice or elevated liver enzymes occur while taking an ACE inhibitor, the ACE inhibitor should be discontinued immediately and the patient should be closely monitored. It is also necessary to conduct an appropriate examination.
Neutropenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, anemia
Cases of neutropenia/agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia and anemia have been reported in patients receiving ACE inhibitor therapy. With normal renal function in the absence of other complications, neutropenia rarely develops. Perineva® should be used with great caution in patients with systemic connective tissue diseases (for example, SLE, scleroderma), simultaneously receiving immunosuppressive therapy, allopurinol or procainamide, as well as when combining all of these factors, especially with existing renal impairment. Such patients may develop severe infections that do not respond to intensive antibiotic therapy. When carrying out therapy with Perineva® in patients with the above factors, it is recommended to periodically monitor the number of leukocytes in the blood and warn the patient about the need to inform the doctor about the appearance of any symptoms of infection.
In patients with congenital deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, isolated cases of hemolytic anemia have been reported.
Negroid race
The risk of developing angioedema in black patients is higher. Like other ACE inhibitors, perindopril is less effective in lowering blood pressure in black patients, possibly due to the higher prevalence of low-renin conditions in this population of patients with arterial hypertension.
Cough
During therapy with ACE inhibitors, a persistent, non-productive cough may develop, which stops after discontinuation of the drug. This should be taken into account in the differential diagnosis of cough.
Surgery/general anesthesia
In patients whose condition requires major surgery or anesthesia with drugs that cause hypotension, ACE inhibitors, including perindopril, may block the formation of angiotensin II with compensatory renin release. One day before surgery, therapy with ACE inhibitors must be discontinued. If the ACE inhibitor cannot be canceled, then arterial hypotension developing according to the described mechanism can be corrected by increasing the volume of blood volume.
Hyperkalemia
During therapy with ACE inhibitors, including perindopril, the concentration of potassium ions in the blood may increase in some patients. The risk of hyperkalemia is increased in patients with renal and/or heart failure, decompensated diabetes mellitus, and in patients using potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements, or other drugs that cause hyperkalemia (eg, heparin). If it is necessary to prescribe these drugs simultaneously, it is recommended to regularly monitor the potassium content in the blood serum.
Diabetes
In patients with diabetes mellitus taking oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin, blood glucose concentrations should be carefully monitored during the first few months of ACE inhibitor therapy.
Lithium
Concomitant use of lithium and perindopril is not recommended.
Potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium-containing drugs, potassium-containing foods and nutritional supplements
It is not recommended to use in combination with ACE inhibitors.
Lactose
Perineva® tablets contain lactose. Therefore, patients with hereditary galactose intolerance, lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome should not take this drug.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
It is necessary to take into account the possibility of developing arterial hypotension or dizziness, which may affect driving and working with technical equipment.
Is it possible to drive a car
Taking Perineva medication with high blood pressure can lead to a deterioration in psychomotor reactions, so it is necessary to refrain from driving vehicles during the course of treatment. The patient should refrain from performing work that requires increased concentration or complex mental processes. You cannot work with complex systems and mechanisms.
Taking the drug affects memory, concentration, causes headaches, vestibular disorders, confusion, which can lead to an accident on the road.
If adverse reactions occur in the body, you should consult a doctor who will adjust the dosage or select another method of therapeutic intervention.
Taking Perineva may affect the quality of work that requires concentration
Analogs
If the original medicine is not available in pharmacies, substitutes with similar therapeutic properties can be used.
The following medications can be used as analogues:
- Noliprel – a product based on indapamide and perindopril, which have pronounced diuretic and hypotensive properties. The drug is prescribed for hypertension and heart disease, accompanied by increased blood pressure. The drug is available in tablet form, the dosage of the components in each is 0.625 and 2.5 mg. The drug is usually used for mild forms of hypertension and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Noliprel A forte - Prestarium contains only perindopril and is available in tablet form. The medication has antihypertensive properties and significantly improves the condition of patients with hypertension.
- Enap N contains a diuretic and antihypertensive active component, but they are different. The composition contains hydrochlorothiazide, which has a diuretic effect, as well as enalapril, which lowers blood pressure. The product is considered effective, despite other active ingredients in the composition.
Analogues are also highly effective, but their use must be agreed with a doctor.