The causes of thrush are factors that influence the occurrence of the disease and contribute to the development in the human body of a favorable environment for the proliferation of fungi of the genus Candida. What is thrush and where does it come from? How can one become infected with such a disease and in what ways is it transmitted? How does the disease appear and what are the reasons for its appearance? Answers to these and many other questions can be found in the following article.
What it is?
In the normal microflora of a woman’s healthy vagina, one way or another, the Candida fungus is present in small quantities; if its quantity begins to grow rapidly, that same thrush appears. The vaginal mucosa becomes inflamed, which leads to itching, burning, heavy discharge and other symptoms of the disease, which, by the way, is not classified as a sexually transmitted disease.
The danger of thrush lies in the disturbed microflora of the vagina, which becomes an excellent place for the emergence of other infections, inflammations and diseases. If a woman is pregnant, there is a high risk of infection of the fetus. That is why treatment of vaginal candidiasis should be appropriate and timely.
Chlamydia
Chlamydial infection is very easy to distinguish from thrush. With this disease, glassy discharge appears from the urethra, most often in the morning. The color of vaginal secretion with chlamydia is yellow or greenish, and the quantity is not large.
Since chlamydia, unlike thrush, is an infection, this condition may cause an increase in body temperature, as well as signs of intoxication. The woman feels unwell, feels weak all day, may have headaches and nausea, and loses her appetite.
With mixed infection with chlamydia and other bacteria, the development of cervicitis, urethritis or cystitis is possible. Such complications are observed very rarely. In this case, the urine becomes cloudy in color, with small amounts of purulent thread-like formations or blood visible in it.
As you can see, many of the symptoms of thrush and chlamydia are similar. Therefore, they are very easy to confuse. The only sign by which a woman can independently distinguish candidiasis from chlamydia is discharge - with thrush it is curdled and white, and with chlamydia it is yellowish. You can also distinguish illnesses by the color of urine and the presence of foreign liquids in it.
But these symptoms may not always be present. In many cases, chlamydia is asymptomatic with signs of thrush. Therefore, diagnostics, blood and urine testing, as well as smears during a gynecological examination are required.
Is thrush transmitted to men?
Normally, a man’s body constantly encounters the same fungi as a woman’s. Since they are contained in the vagina of most women, the partner’s genitals in any case come into contact with the causative agent of thrush. A man can also develop candidiasis of the genital organs, which has approximately the same manifestations and causes as in women. Therefore, if a man has a reduced immune system, has diabetes mellitus or other prerequisites, then he can easily become infected with thrush. Moreover, a sexual partner can bring a large amount of fungus into a woman’s body, which will trigger the development of the disease.
Thus, thrush is transmitted to a man only if he has the prerequisites for its development and does not observe basic rules of personal hygiene. In the end, it is much easier for a man to remove all pathogens from the surface of the penis by simply washing it thoroughly, unlike a woman. And sexual intercourse itself in the presence of candidiasis is a rash action, contrary to the recommendations of doctors and is unlikely to bring pleasure
Gonorrhea
Diagnosis of gonorrhea is complicated because many people are asymptomatic. The first signs of gonorrhea are not specific; they can be confused with other pathologies. Therefore, a woman does not seek help for a long time.
Gonorrhea may begin to develop 4 days after infection if a woman has a weakened immune system. The clinical picture of gonococcal infection is very close to the signs of cystitis, cervicitis and urethritis, as well as candidiasis.
Here are the signs by which you can distinguish gonorrhea from thrush:
- purulent discharge with red streaks;
- sharp pain when urinating;
- severe hyperemia.
Both diseases quickly spread to the ovaries, causing acute inflammation. Gonorrhea can spread to internal organs if treatment is started late. But in the case of thrush, this happens much less frequently; we can say that such cases are rare.
If symptoms appear some time after unprotected sexual intercourse, it is most likely gonorrhea and the doctor diagnoses this pathology based on the presence of the listed signs. Thrush is difficult to catch during PA and does not progress as quickly as clap. Also, with candidiasis, such a pattern may not exist, because people become infected with it regardless of whether they have recently had PA or not; the main cause of thrush is reduced immunity.
Reasons for development
The attitude of thrush to infectious diseases may serve as the basis for the belief that it is transmitted from another person. In fact, there are enough Candida fungi in the body itself; they are a natural part of the bacterial environment of the intestines, oral cavity and other mucous membranes. It is important to understand that candidiasis is not the presence of these spores in the body, but rather their excess.
In a healthy body, the environment itself prevents the excessive proliferation of harmful bacteria, maintaining their normal concentration. Immunity disorders are the main factor that provokes an increase in the number of Candida albicans bacteria on the mucous membranes and their concentration in the genital area.
Provoking factors include:
- changes in the condition of the vaginal mucosa on the eve of menstruation;
- increased humidity, including from sweat or poorly dried laundry, which is an optimal environment for the development of many types of bacteria;
- changes in the acidity level of mucous membranes as a result of the use of intimate hygiene products;
- allergic reactions to bath and hygiene products used;
- allergic reactions to synthetic underwear and tampons;
- violation of the vaginal skin during sexual intercourse without sufficient natural moisture or lubrication;
- pregnancy;
- endocrine system disorders (including diabetes mellitus);
- general weakening of the immune system, as well as age-related changes in the body;
- recovery period after complex diseases or surgery;
- reactions to hormonal contraceptives, antibiotics, etc. drug treatment.
Most of the factors that provoke the development of Candida are related to weakened immunity and allergic reactions to certain substances associated with these indicators. For a long time it was read that thrush is also caused by the use of low-quality bedding and underwear. Doctors assure that underwear has no direct relation to the occurrence of thrush, but it can still provoke it indirectly. This is most often associated with a violation of normal ventilation and sweating, as its consequences. In a humid environment, the development of bacteria occurs more actively, thus, in women who wear tight synthetic underwear in hot weather, the risk of disease is indeed higher, as well as in those who violate the normal schedule of hygiene procedures.
Types of female and male infections
Women most often experience:
- vaginal candidiasis, occurs on the labia and vagina;
- cervical candidiasis, most often affects pregnant women;
- candidiasis of the mammary glands, occurs on the nipples and nipple circumference during breastfeeding.
Female thrush typically affects the vagina and vulva. In more advanced stages, the disease penetrates deeper, affecting the ovaries and cervix.
Male thrush is called urogenital candidiasis and affects the genitourinary organs. Most often it is localized on the head of the penis and is characterized by inflammation of the head and foreskin of the penis, which medicine defines as balanoposthitis.
On the Internet you can find such a type of disease as acuminate candidiasis. However, this is nothing more than another type of disease, erroneously and incorrectly named. Such a disease as genital candidiasis does not exist in nature.
Oral candidiasis
Oral thrush is a disease that affects the mouth and mucous membranes of the mouth. With this disease, white plaque is concentrated in the mouth, on the lips, gums and palate. The pharynx and tonsils are also affected. Most often, children suffer from this disease, especially under the age of one year.
Oral thrush in a baby can develop due to many reasons: infection from the mother during childbirth, weak immunity, long-term treatment with antibiotics and others. The disease in boys and girls from two to ten years of age occurs mainly due to the fact that they often put dirty hands and objects into their mouths.
Infantile thrush usually occurs easily, practically without disturbing the baby. However, in any case, at the first symptoms of the disease, the child should be shown to a pediatrician, because it can progress to a more severe stage, which is characterized by fever, anxiety and sleep disturbances.
Oral candidiasis in adults is very rare and difficult to treat.
Anal candidiasis
Anal thrush is a disease that is localized in the anus.
This type of candidiasis is characterized by:
- the presence of a whitish coating in the anus and on the stool;
- pain in the anus during defecation;
- passage of stool containing blood.
Often this disease develops against the background of rectal candidiasis. Typically, rectal thrush occurs in children, manifesting itself as redness and plaque on the butt, which causes discomfort and pain when moving. It becomes difficult to sit and walk. But it can also develop in adolescents and adults, especially if there are problems with the immune system, hygiene or nutrition.
Typically, this disease can be treated quite quickly and easily if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. When diagnosing, a specialist takes a smear from the surface of the patient’s anus, which makes it possible to accurately identify the fungal culture. After which effective treatment is prescribed, which leads to a speedy recovery.
Thrush of skin and nails
Such a disease is a rare phenomenon, usually arising as a result of exposure to endogenous or exogenous factors on the human body.
It can be:
- exposure to chemicals on the skin;
- mechanical damage to the skin and nails;
- patient's age;
- some diseases;
- severe exhaustion of the body.
This type of thrush manifests itself as redness of the skin, the appearance of a rash on the skin, as well as swelling and maceration. As a rule, the disease begins with large folds of skin: in the armpits, in the groin, between the buttocks, in the area of the mammary glands.
Candidiasis of the skin on the hands between the fingers also often develops, especially in preschool children and agricultural workers. Vaginal or genital candidiasis can also result in genital skin thrush, characterized by redness and a rash on the penis or labia (genital lips). Most often, such a rash looks like edematous-erythematous spots, pustules or papules, which, when opened, form weeping erosion.
Candidiasis on the face is quite rare and very difficult to treat. It is characterized by a small, bright red rash with clearly defined papules, located mainly in the lip area.
Infants often develop diaper candidiasis, located in the baby's perineum. There are also types of skin thrush such as bandage candidiasis and candidal folliculitis.
Thrush of the gastrointestinal tract
Thrush of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as candidiasis of internal organs in general, is a very serious disease that occurs against the background of severe suppression of the body’s immune system. This disease can also develop due to improper or insufficient treatment of fungal infections of the mucous membranes. In such cases, thrush pathogens penetrate the systemic bloodstream and spread with the blood to all internal organs of a person. Most often, this happens with long-term self-treatment of genital candidiasis, which only significantly aggravates the situation and leads to the development of such a serious disease as candidiasis of the internal organs. The most common is thrush of the gastrointestinal tract: candidiasis of the stomach, esophagus and intestines.
Symptoms of this disease are:
- frequent nausea with bouts of vomiting;
- pain in the epigastric region;
- decreased and complete loss of appetite;
- flatulence;
- general weakness of the body;
- decreased performance;
- diarrhea and other disorders of the digestive system.
With esophageal thrush, the patient often complains of difficulty swallowing, chest pain after eating, nausea and vomiting. During esophagoscopy, a whitish film of cheesy plaque can be detected on the walls of the mucous membrane of the esophagus.
Gastric thrush has a description and symptoms quite similar to gastritis. The patient suffers from constant nausea and vomiting, lack of appetite, and pain in the abdominal area. When examining vomit, a specialist can recognize particles of fungal elements, as well as a white curd film.
Candidiasis in the intestines most often occurs in young children, especially while taking antibacterial drugs. Also susceptible to this disease are women during pregnancy, the elderly, people suffering from diabetes, and HIV infection. Often the causes of candidiasis of internal organs are also long-term use of hormonal drugs, constant stressful conditions and the presence of bad habits.
Such thrush is dangerous because in advanced stages it can lead to serious and serious complications: internal bleeding, perforation of the intestines or stomach, fungal sepsis.
In especially severe cases with invasive forms, gastrointestinal thrush can lead to death.
Other types of internal thrush include candidiasis of the ears and eyes, as well as thrush in the nose.
Classification
The symptoms of candidiasis vary and depend on what type of disease we are talking about. It should be noted that many women do not even suspect that they are a carrier of the Candida fungus or suffer from a chronic form of candidiasis.
The classification of thrush in women is as follows.
- Colpitis (candidal vaginitis) - pathogenic flora is localized in the vaginal area.
- Vulvitis - yeast-like flora progresses, localizing on the external genitalia and skin.
- Vulvovaginitis is a type of disease that combines the clinical picture of vaginitis and vulvitis.
All types of thrush have similar symptoms. The tactics of therapy depend on the exact form in which the disease occurs. With thrush in women, symptoms and treatment are closely related concepts that are almost impossible to understand without the help of a doctor.
A little about the pathogen
But, as soon as the protective forces of the female body are reduced, candidal infection manifests itself in all its glory. It must be remembered that the vaginal mucosa is by no means sterile. There are many different microorganisms on it, but normally the acidic environment and local immunity of the mucous membranes lead to the fact that pathogenic cocci, Escherichia, fungi, Klebsiella, Gardnerella are present on the mucous membrane in an inactive form.
In the case of a decrease in local and general immunity, dysbiocenosis occurs in the vagina, acidity decreases, the activity of lactobacilli decreases, and alkalization of the environment occurs. The classic development of the condition is bacterial vaginosis. But in order for thrush to become active, strong alkalization is not necessary. Candida feels great even with a slight decrease in immunity. Most often, it is thrush that begins more serious inflammatory diseases of the female reproductive system. What symptoms characterize the appearance of urogenital candidiasis in women?
First signs
The following first signs of thrush in women will help make you wary and suspect the presence of the disease:
- acute burning, itching of the external genitalia, worsening in a warm environment, after taking a bath;
- redness (hyperemia) of the vagina and labia;
- copious white vaginal discharge with a cheesy consistency;
- increased pain a week before menstruation.
After this, more specific signs appear:
- curdled discharge - looks like mucus with white lumps;
- itching, burning in the vagina - do not scratch, so as not to damage the epithelium and allow the fungal infection to penetrate the bloodstream, increasing the area of inflammation of the vaginal mucosa;
- pain and discomfort when urinating - due to increased sensitivity of receptors;
- pain and burning during sex;
- slight sour smell of discharge.
Ovulation
Ovulation is the shortest stage of the menstrual cycle. During this period, hormonal changes also occur in the woman’s body, which create favorable conditions for conception.
Due to hormone surges, white, translucent discharge resembling mucus appears. This happens a few days before ovulation, and can also appear during it.
But it is important to know that against the background of changes in hormonal levels, the growth of candida is provoked, which leads to discharge like thrush.
Ovulation is characterized by the following:
- duration of discharge is no more than 3 days;
- vaginal secretion is viscous and mucous in nature;
- abdominal pain, but does not affect the condition of the urinary tract.
With thrush, the discharge can last more than 2 weeks, look like cottage cheese with grains, and are also accompanied by cramps in the abdomen and a burning sensation when urinating.
Always pay attention to the nature of the vaginal secretion. If ovulation occurs soon and the discharge is unusual, you should be wary.
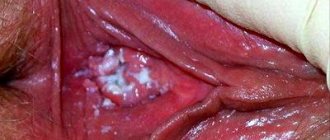
Symptoms of thrush
Thrush (see photo) does not always occur with noticeable symptoms; sometimes the disease is discovered only at a gynecologist’s appointment and comes as a surprise to the woman herself.
However, the appearance of the following signs should alert you in any case:
- Whitish rashes that quickly spread throughout the mucous membrane. They are usually noticed during hygiene procedures, such as washing. Rashes can appear on the vulva, or inside the vagina, this often happens during thrush during pregnancy.
- Itching and burning. They appear even before visible signs of the disease. These sensations do not disappear after washing.
- Pain during sexual intercourse and urination. Appears due to microcracks accompanying the disease. The skin is severely injured, so any impact causes pain.
- White cheesy discharge. Their appearance is especially noticeable on underwear, so if at some point the discharge becomes particularly large, it acquires an unpleasant odor, and there is a reason to consult a specialist.
Since thrush does not always manifest itself immediately, the best way to detect it at an early stage is through routine preventive examinations with a doctor. If the disease is detected immediately, treatment can begin before severe symptoms appear.
How can you be sure not to confuse thrush with anything else?
The easiest way to distinguish thrush from other diseases is by a coating similar to cottage cheese, sour cream or curdled milk, which is a pseudomycelium (an accumulation of false mycelium, since yeast-like fungi reproduce by spores).
It is not so easy to remove it; most often, under it, swollen, inflamed skin to the point of erosion is found. “Cottage cheese”, which gave the second name to the infection, is its most specific, always observed (including blurred course and location on the nails, hands, and armpits) sign.
What happens if thrush is not treated or if it is done incorrectly?
Thrush is like a boomerang - it can come back again and again. Candidiasis can affect the cervix, bladder and urethra. Cystitis, cervicitis, urethritis are all complications of this disease. If thrush is accompanied by sexually transmitted infections, there is a risk of inflammatory processes that can lead to infertility.
There is no need to be scared, because we are talking about cases when a woman for some reason does not go to the doctor, or independently uses medications that are not suitable for her. There are many medicines for various gynecological diseases, including vaginal suppositories, which we have already written about earlier. But not every drug is suitable. Gynecologists, if therapy occurs without visible progress, can replace one drug used with another. Not because they “sort out medications at random due to incompetence.” It’s just that the immune response of a particular organism to a particular treatment may be weak.
Severe recurrent thrush may indicate problems with immunity, then it is important to find out the reason for its decrease. There are cases (albeit infrequent) when acute thrush signaled diabetes mellitus and even HIV. But with professional and timely treatment, it proceeds without complications, and soon leaves the woman alone.
Particular attention should be paid to the treatment of thrush in women expecting a child. Firstly, their immunity is weakened and their hormonal levels change, and these are favorable conditions for the development of bacteria in the vagina. Secondly, pregnant women need to worry not only about themselves: thrush can also threaten the unborn child. While the baby is inside, candida and other fungi cannot get close to him, but during childbirth they can get into the baby’s eyes, mouth and nose. To avoid candidiasis in children, women with thrush are prescribed antifungal therapy with vaginal suppositories.
If at the time of pregnancy a woman already has an advanced stage of thrush, which has spread to internal organs, candidiasis may occur in an unborn child. Cases are very rare, but often result in premature termination of pregnancy. As for the expectant mother, she may also have a difficult time during childbirth. After all, the fungus leads to a loss of elasticity of the vaginal tissues and increases the number of ruptures. The matter, you understand, is unpleasant.
But with the right approach to treatment, complications of thrush can be avoided, and this largely depends on the woman herself.
Dysbacteriosis
It is very important to distinguish between these two diseases. After all, if a woman mistakes vaginosis for thrush and carries out treatment without consulting a doctor, the condition can only worsen.
Bacterial vaginosis is a condition in which the balance of microorganisms in the vagina is disturbed.
This disease can be distinguished by thrush in two ways. The first is an unpleasant smell, reminiscent of fish (intensifies after intercourse or after sexual intercourse), with candidiasis there is no smell at all. The second is to get tested; if you have bacterial vaginosis, the bacteria limit will be exceeded.
With bacterial vaginosis, vaginal discharge is white and thick, and with candidiasis, it is curdled. Another factor that helps distinguish diseases is swelling of the genital organs. With thrush there is, with bakvaginosis - not.
In addition, you should be aware that candidiasis can affect the development of bacterial vaginosis. That is why, after treatment for thrush, doctors advise undergoing additional examination to check the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy and to exclude other pathologies that may develop against the background of candidiasis.
To make a correct diagnosis, if the discharge looks like thrush, you need to undergo an examination, give a smear and urine test. Symptoms alone are often not enough for a doctor to confidently make the correct diagnosis.
Thrush is not a dangerous disease and can be successfully treated. However, as you can see, there are many pathologies that can be hidden under this mask, and as a result lead to complications.
Only a gynecologist is able to distinguish candidiasis from other pathologies. Therefore, if symptoms of thrush appear, you should immediately go to the hospital to prevent the development of a serious illness.
Thrush (candidiasis) occurs in women much more often than in men and, according to statistics, accounts for up to 32% of all inflammatory diseases of the genital area. In other words, every third woman with complaints of urogenital infection has symptoms of candidiasis. It is very common among the world's population: for example, half of all those living on our planet have once encountered the problem of thrush, and every fifth woman of childbearing age has a chronic form of fungal infection of the genital organs.
As for men, their risk of contracting a candidiasis infection is much lower, due to the different structure of the genital organs. But despite this, 10% of men will experience thrush in one form or another throughout their lives.
Diagnostics
The assumption about the cause of cheesy discharge and burning in the vagina requires confirmation by laboratory methods. Signs of chronic thrush can be confused with manifestations of bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis, especially if the infections develop together.
During a gynecological examination, a smear is necessarily taken from the surface of the vagina to study the composition of the discharge under a microscope and detect fungus and other types of microorganisms. A bacterial culture of the vaginal contents is done, which makes it possible to detect the size of the fungal colony and accurately determine its type. Sensitivity to antifungal agents is determined.
Using the PCR method, the genotype of infections present in the microflora is determined, and the causative agents of hidden infections (Trichomonas, Ureaplasma, Gardnerella and others) are detected.
How to treat thrush in women?
Thrush is treated mainly with tablets and suppositories; ointments and creams are also used. The drugs are divided into two groups. The first includes topical medications. With their help, gentle therapy is carried out and used for uncomplicated forms of thrush. If the disease is severe, it can be used in complex therapy with antimycotic agents.
The second group includes general action tablets that affect the entire body as a whole. Drugs of this group are used for complicated forms of candidiasis and for relapses.
Only a doctor can prescribe the drug; self-medication is dangerous!
Quick and effective treatment of thrush in women in 1 day begins with eliminating the causes of its occurrence and eliminating provoking factors. This is followed by treatment with antifungal drugs, restoration of the microflora of the vagina and intestines.
For mild and uncomplicated forms of candidiasis, the following topical drugs are used:
- Clotrimazole (Candizol, Kanesten, Candibene, Yenamazole 100, Antifungol).
- Miconazole (Gino-daktarin, Ginezon, Klion-D 100).
- Isoconazole (Gyno-travogen).
- Feticonazole (Lomexin).
- Fluomizin.
Treatment of chronic thrush includes general restorative therapy, antibiotics, and can be treated with the following drugs:
- Fluconazole and its analogues: Diflucan, Flucostat.
- Itraconazole (analogs Canditral, Irunin, Rumikoz, Itrazol, Orunit).
- Pimafucin (prescribed for the treatment and prevention of intestinal candidiasis).
- Ketocanazole (analogues of Fungavis, Oronazole, Nizoral).
In the initial stages, treatment usually goes like this:
- Clotrimazole suppositories (200 mg). The course lasts 14 days, 1 candle is consumed for each day.
- Fluconazole tablets (150 mg). Tablets are taken on the first, fourth and seventh days of treatment. Or Itroconazole tablets (200 mg): 7 days, one tablet.
- After completing the course, you can take a course of special probiotics to quickly restore the microflora.
During pregnancy
It is most difficult to treat the disease in question in the 1st trimester of pregnancy - it is during this period that the formation of all organs and systems of the child occurs. Fortunately, in the first three months of pregnancy, thrush is diagnosed very rarely - the body’s hormonal levels are still corrected by nature, and immunity remains at its usual level.
But if symptoms of candidiasis appear, the doctor will definitely prescribe the following medications:
- Pimafucin – 1 suppository per day for 6 days;
- Betadine – 1 suppository per day for 6 days in a row.
This does not mean that you need to use both drugs for treatment - the doctor will make a choice in favor of one of the listed ones.
In the 2nd and 3rd trimester, treatment can be carried out more extensively and the following antimycotic agents can be prescribed at the discretion of the gynecologist:
- Pimafucin – 6 suppositories;
- Betadine – 6 suppositories;
- Clotrimazole – 7 suppositories;
- Gyno-Pevaril – 6 suppositories;
- Vaginal applicator Ginofort – once.
Please note: treatment of thrush during pregnancy must be carried out fully. The fact is that some women stop the course of therapy immediately after the disappearance of severe symptoms - this happens on the 2-3rd day of treatment. But the absence of symptoms does not indicate complete relief from the fungal disease - after a short time, the symptoms will resume, and even more vividly.
Course of the disease
The incubation period of the disease usually lasts from two days to several weeks and even months, depending on the state of the patient’s immune system and the form of the disease:
- with latent, sluggish thrush, symptoms of the disease appear approximately on the third to fifth day after infection;
- with inflammation of the vaginal tissues accompanying candidiasis, the manifestation of the first signs of the disease is delayed for up to two weeks;
- in the case of thrush affecting the urinary tract, bladder or kidneys, symptoms of the disease may appear a month or even two after the onset of the disease,
- The incubation period of candidiasis in men ranges from five days to two months.
There are 4 degrees of development of this disease:
- A latent or latent form of the disease in which pathogenic microorganisms penetrate and establish themselves in an environment suitable for their development. This can be a significant weakening of the patient’s immunity, an exacerbation of chronic diseases, or hormonal changes in the body.
- Superficial mild form of candidiasis, which affects the surface of the mucous membranes or skin. During this period, a significant proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms occurs, which often leads to the manifestation of visible signs of the disease.
- Systemic candidiasis, in which the fungus penetrates into the deep layers of the skin and affects internal organs. This type of thrush takes a long time to treat and requires significant effort and a lot of time to recover. If treatment is not timely, it moves on to the next stage of development.
- Septic thrush caused by Candida fungus entering the systemic circulation. With the help of the circulatory system, infection of all internal organs and systems of the body occurs, which often leads to death.
In addition, thrush is classified according to the severity of the disease:
- Candida carrier. This is the initial and mildest stage of the disease. It is usually asymptomatic, and the woman may not even know that she is a carrier of the disease. The vast majority of pregnant women face this problem. This form of the disease is treated quickly and does not entail unpleasant and serious complications.
- The acute form of candidiasis is characterized by a sharp manifestation of the clinical picture of the disease. The course of the disease rapidly progresses and, in the absence of proper treatment, becomes chronic. With this form of thrush, the lymph nodes in the groin area often become inflamed, which causes even more discomfort to patients.
- A chronic form, which is characterized by periods of exacerbation during a sluggish disease. Symptoms for this type of disease are poorly expressed, but symptoms are always present. There are two types of chronic candidiasis: recurrent or recurring thrush, characterized by exacerbation of the disease after sexual intercourse or before the onset of menstruation, and persistent or sluggish thrush, which is characterized by either extinction or sudden outbreaks of symptoms of the disease.
Thrush is very often diagnosed in pregnant women. According to statistics, there is one disease in every third case. It can begin both in the early stages and in the second and third trimester. The first trimester of pregnancy is especially dangerous for this disease, since candidiasis in advanced forms can cause miscarriage. Thrush in pregnant women is a common cause of infection of the fetus. Moreover, this can happen both in utero and during the passage of the child through the birth canal.
Breastfeeding mothers may also develop this disease. Breastfeeding often causes mammary thrush, through which the baby can become infected from the mother. Moreover, if the disease is detected in the mother or in the baby, both should be treated at the same time, so that the thrush is not transmitted from one to the other and does not return again.
After ovulation, an environment favorable for the growth of the fungus is also formed. The main cause of thrush during this period is a sharp surge in progesterone, which begins to be produced just in the middle of the cycle, and promotes the adhesion and growth of the number of yeast-like fungi.
Before ovulation, a significant change in the vaginal microflora occurs, which also leads to candidiasis or thrush, which is essentially the same thing. At the same time, gynecologists claim that candidiasis affects ovulation, and therefore the ability to conceive a child, so in any case, immediate treatment is required.
During menstruation, the clinical picture of the disease looks different. In some patients, due to the development of thrush, menstruation may be delayed, in others, on the contrary, the symptoms of the disease subside.
Effective suppositories for thrush
Suppositories and vaginal tablets for the treatment of thrush are local treatments. They are prescribed when the lesions are not deep and no complications have arisen. Here is a list of the most effective remedies for thrush. The active substance is indicated in the arms.
- Pimafucin (Natamycin) is the least toxic. Can be used during pregnancy. Causes the death of various fungi. Candles are used before bedtime. They quickly relieve symptoms, but treatment must be continued for another 2-3 days after improvement. On average, the course is 3-6 days.
- Antifungol, Yenamazole 100, Candibene, Kanesten, Kanizon, (Clotrimazole) its components dissolve the Candida shell. Suppositories or vaginal tablets are inserted into the vagina once a day before bedtime. The course of treatment is 6-7 days.
- Gyno-Travogen Ovulum (Isoconazole) disrupts the permeability of the cell wall of fungi. Has antifungal and anti-inflammatory effects. Quickly eliminates itching. Used to treat forms of fungi that are resistant to other agents. A suppository (candle) is inserted deep into the vagina before bedtime once a day. The course of treatment is 3 days.
- Ginezol 7, Gino-Daktarin, Klion-D 100 (Miconazole) - destroys fungi and some bacteria. Treatment lasts 14 days. One suppository deep into the vagina before bed.
- Polygynax, Terzhinan (Nystatin) - these vaginal tablets must be moistened before insertion into the vagina. Use one before bed for 10 days.
It should be noted that minor itching and other discomfort may occur for two weeks after treatment.
Tablets for quick treatment
Treating thrush with tablets has several advantages. You will get rid of unpleasant symptoms in 1-3 days.
While treatment with suppositories, vaginal tablets and gels takes an average of a week. Taking the tablets provides comprehensive treatment of fungi in all organs. Therefore, the likelihood of thrush recurring is reduced. If the course of the disease is mild, then one drug will be enough. In another case, you will need to take several antifungal agents from different groups. To enhance the effect and relieve itching, local treatment in the form of creams or suppositories is additionally prescribed. There are several types of drugs designed to combat fungi. They have different mechanisms of action, but they all lead to the death of Candida and the destruction of their mycelium.
Here is a list of substances that destroy fungi and preparations based on them.
- Fluconazole (Diflucan, Mikosist, Medoflucon, Forkan) – a single dose of 150 mg of the drug is sufficient.
- Ketoconazole (Ketoconazole, Nizoral) – 1-2 tablets per day. Course 5 days.
- Natamycin (Pimafucin) – 1 tablet for 3-5 days.
- Miconazole (Miconazole, Micatin, Funginazole) - take 1 tablet for three days.
- Nystatin (Nystatin) – 1 tablet 4 times a day. The treatment period is 10-14 days.
These drugs should not be taken by pregnant women to treat thrush. To prevent exacerbations of candidiasis in the future, it is advisable that both sexual partners undergo treatment.
Manifestations of thrush after treatment
For the most part, with proper and timely treatment prescribed by a qualified specialist, thrush goes away without a trace, and its symptoms completely disappear.
If, after completing a course of treatment for candidiasis, the patient still has any of the symptoms characteristic of this disease, then the therapy was of poor quality and not effective enough. This could also happen as a result of self-diagnosis and self-medication, which, as a rule, lead to serious and severe consequences.
Numerous reviews from recovered patients indicate that the disease is quite treatable if the therapy is carried out by a qualified specialist. It should be understood that the sooner the patient seeks medical help, the faster his recovery will occur, and he will forever forget about such an unpleasant disease.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
How to cure uncomplicated thrush for 1 day?
Modern antifungal drugs can get rid of thrush in 1 day. In most cases, it is enough to take one capsule of Fluconazole 150 mg to destroy the fungal infection. If a woman suffers from recurrent thrush, then she will need to take one capsule once a week or a month for 6-12 months. The doctor selects the regimen individually.
For a quick recovery, it is advisable to combine systemic treatment with Fluconazole in capsules and local treatment: suppositories with antifungal and anti-inflammatory drugs, the use of creams and douching. Various pharmaceutical companies produce drugs based on Fluconazole: Diflazon, Diflucan, Mikosist, Medoflucon, Forkan, Flucostat. The active substance of these medicines disrupts the metabolic processes in fungi, which leads to their death. The medicine is well absorbed into the blood and reaches all organs, where it accumulates in the required quantity. Thus, these drugs rid the body of any diseases caused by fungi.
With vaginal candidiasis, after taking Fruconazole, a woman usually notices a significant improvement within a day. But complete recovery occurs after 3-4 days. If, a week after taking the drug, you continue to be bothered by symptoms of thrush, you should consult your doctor again.
What to do to prevent thrush from recurring?
To prevent relapse of the disease, adhere to the following measures:
- The prescription of a systemic antifungal agent is 200 mg of Itraconazole or 150 mg of Fluconazole on the first day of menstruation for 6 months.
- Vaginal suppositories for local use for 6 months, once a week.
Folk remedies
There are folk remedies against thrush, which we have already written about in detail; they are effective in the early stages of the disease, when complex therapy, including pills, is not yet required. Traditional medicine knows many different herbal medicines and more.
Douching with chamomile
Chamomile is a plant with a strong anti-inflammatory effect. It does not fight the causative agent of the disease, but relieves itching and burning and reduces inflammation. Chamomile is suitable as an aid against negative symptoms.
- Take two glasses of cold water for two tablespoons of dried plant.
- Chamomile is infused for several hours.
- The resulting infusion can be used for douching no more than three times a day.
Douching with sage
Sage is a well-known bactericidal agent with anti-inflammatory and soothing effects. It is also used for medicinal douching against thrush.
Take two liters of water for two tablespoons of dried plant and leave for several hours. Douching is carried out twice a day - morning and evening.
Soda
For thrush, douching with soda is done. You should be careful with this product; soda can negatively affect the mucous membrane; you should not make the solution too strong.
- Take no more than one teaspoon of the substance per liter of warm boiled water and mix thoroughly.
- Douching is done twice a day, in the morning and in the evening.
If only the external tissues are affected, it is enough to simply wash with this solution several times a day.
You can also take short baths based on medicinal plants; they soothe the skin and help you heal faster.
Important! Folk remedies often cause allergies, so if individual intolerance occurs, you should avoid them.
Diet and nutrition
During treatment for thrush, you should exclude some foods from your diet:
- any dishes containing large amounts of sugar;
- sweet fruits and fruit juices;
- white bread, pasta, flour products, since the starch they contain is processed by the body into glucose, a breeding ground for bacteria;
- any products with yeast, because this will only increase the number of fungi in the body.
On the contrary, yoghurts with a high content of active bacteria will come in handy. Microorganisms will be good competitors for fungi and will somewhat complicate their life. Doctors say that regular consumption of such yoghurts can reduce the risk of developing candidiasis by almost 40%. The main thing is that they are unsweetened.
Reviews from women
- Oksana, 27 years old. In winter, I had a sore throat and took antibiotics, which had a negative effect on my body. In the spring, I discovered the first signs of thrush - cheesy vaginal discharge, unpleasant itching and burning. I have had it before, so I am already being treated with a proven remedy. I drank a capsule of Pimafucin, and I forgot about the annoying candidiasis.
- Nadezhda, 30 years old. During pregnancy, due to disruptions in the hormonal system, thrush appeared. It was unpleasant, everything hurt, plus I was worried about the child. The doctor prescribed safe antifungal suppositories for five days. After they expired, the discomfort went away, I hope I will never experience it again.
- Alena, 33 years old. I have chronic recurrent candidiasis due to a weakened immune system, so I am familiar with the topic of “female thrush” firsthand. My doctor and I long ago developed a treatment regimen for exacerbations of diseases - vaginal suppositories and Diflucan in tablet form. A course for a week helps to forget about frequent relapses for about a quarter. I don’t like that the disease recurs so often, but I already have a chronic form.
Intimate life with candidiasis
Many patients are interested in questions: is it possible to have sex with candidiasis, and also whether it is possible to become pregnant with such a disease.
The fact is that untreated thrush can have a very bad effect on conception, and in some cases even lead to infertility, especially if the disease is accompanied by sexually transmitted infections.
As for sex, reviews from many patients indicate that it can only be done using barrier contraception methods. But severe, profuse thrush is accompanied by symptoms such as pain, itching and burning, from which no condom can save you. It is unlikely that such sensations will help you achieve orgasm. In this case, the advice of doctors agrees on one thing: you cannot have sex until the thrush has completely gone away, that is, until the unpleasant symptoms have completely disappeared.
Prevention
Prevention of thrush involves compliance with several simple conditions:
- Daily adequate hygiene of the genitals and regular change of underwear. You should not use aggressive perfumery products not intended for intimate hygiene - soap, gel, and so on.
- Sexual culture. Promiscuous sexual intercourse increases the chance of sexually transmitted infections, reduces local immunity and provokes dysbiosis in the vagina.
- Avoid uncontrolled self-administration of antibiotics.
- Avoid douching, as they increase the chance of injuring the vaginal mucosa and “wash away” beneficial microflora.
- Timely treatment of infectious, endocrine and allergic diseases.
- Proper nutrition and adequate physical activity as a way to maintain immunity.
Preventive measures
Following certain recommendations helps prevent the development of thrush:
- Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene using special delicate care products, regular change of linen.
- Culture of intimate life. Exclusion of casual, promiscuous sexual intercourse. They cause negative changes in local immunity and change the vaginal microflora.
- Do not use antibiotics without a doctor's prescription.
- Douching causes changes in the vaginal flora and can injure the inner lining. They are prohibited as therapeutic or preventive measures for gynecological diseases.
- In order to increase immunity, it is important to treat endocrine, allergic, and infectious diseases in a timely manner.
- Optimal sports activities and following a proper diet will provide support for the body’s protective functions.
When is it necessary to see a doctor?
You should not postpone a visit to the doctor if, with thrush, a woman has a fever, pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. Such symptoms may indicate the spread of the inflammatory process. If the color and smell of the discharge still changes, then there is a high probability of other infectious diseases.
If treatment for thrush has already been prescribed, but does not produce results within a week, then additional examination and selection of another remedy is necessary. The doctor should also be informed about the appearance of skin irritation in the genital area that occurs after starting to take anti-thrush medications.
If the disease recurs, you should not self-medicate using previous prescriptions. The doctor must do a new examination and select a more suitable drug. You cannot hope that the disease will go away on its own, especially when relapses of thrush occur frequently.
Candidiasis of the oral cavity Candidiasis of the esophagus Colpitis Cervical erosion Menopause in women Bartholinitis
Symptoms
Chronic thrush is a disease that lasts more than 2 months and progresses rapidly even when following medical recommendations.
Despite the hidden course of candidiasis, secondary manifestations in the form of compactions and irregular pigmentation can be noticed on the skin. Infiltrates, cracks, and rough folds may also form.
Chronic candidiasis is accompanied by itching in the genitals, and the disease can progress in the intestines and oral cavity.
If the form is too advanced, candidiasis can affect nearby organs, as well as the skin.