Chronic bronchitis is a progressive inflammatory process in the bronchi. Chronic bronchitis, due to mild symptoms, can develop over several years and lead to irreversible consequences. At the Yusupov Hospital, patients who show signs of the disease can undergo a comprehensive examination and receive help from qualified specialists in this field.
What it is?
What kind of bronchitis can be considered chronic? According to existing medical standards, the disease enters the chronic stage if its symptoms do not disappear for three months in a row - or they appear periodically throughout the year, but in total they take the same three months.
Chronic bronchitis is divided into certain types. In particular, a distinction is made between primary and secondary varieties.
- Primary chronic bronchitis develops from ordinary acute bronchitis. The cause of the disease can be viruses and infections, as well as hypothermia, bad habits, and poor lifestyle.
- Secondary bronchitis develops against the background of another pulmonary disease. For example, very often chronic damage to the bronchi becomes a consequence of tuberculosis, pneumonia and other ailments.
In addition, chronic bronchitis can be obstructive - and non-obstructive. What do these terms mean?
- Non-obstructive bronchitis is the easiest to treat. It is characterized by increased sputum production, cough, general weakness and other symptoms of the disease. However, its important feature is that the structure of the bronchi itself remains unchanged.
- Obstructive bronchitis is a much more unpleasant and serious disease. With it, the bronchial tree itself undergoes negative changes - so-called obstruction, degeneration and degeneration of bronchial tissue occurs. The causes of obstructive disease can be viruses, allergies, bacterial inflammation - and treating such bronchitis is much more difficult.
Of course, not every disease of the respiratory system is bronchitis. To make a diagnosis, you must consult a doctor. Diagnosis is carried out comprehensively and includes both an external examination and listening to the patient’s breathing, as well as x-rays and laboratory tests of sputum, urine and blood. Only after a comprehensive study of the medical history will the doctor be able to confidently say that the cause of poor health is precisely chronic bronchitis. Depending on the type and severity of the disease, treatment will be prescribed.
Classification
In medical practice, there are several types of bronchitis, among which there are acute forms and chronic types of the disease.
Acute bronchitis is characterized by acute inflammation of the mucous structures of the bronchi. An acute type of pathology can be:
- simple type;
- obstructive type;
- obliterating type bronchitis;
- bronchiolitis.
Simple and obstructive types of the disease are detected quite often in the adult population, replacing each other. This disease is called recurrent bronchitis. Over the course of a year, the disease appears more than 3 times.
Attention! If the disease is not completely treated, it becomes protracted, which is a risk of developing a chronic form. This diagnosis is made with periodic exacerbation of the disease for at least 2 years. With this type of disease there is a wet cough. In summer, relapses are rare.
The following types of chronic disease are distinguished:
- non-obstructive simple type, it does not interfere with breathing;
- non-obstructive with purulent discharge without changing respiratory function;
- obstructive bronchitis, which is accompanied by breathing problems;
- purulent-obstructive.
Pathogenesis
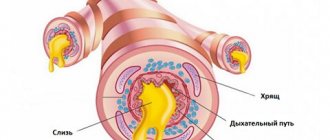
The mechanism of development of chronic bronchitis is based on damage to various parts of the local bronchopulmonary defense system: mucociliary clearance, local cellular and humoral immunity (the drainage function of the bronchi is impaired; the activity of a1-antitrypsin decreases; the production of interferon, lysozyme, IgA, pulmonary surfactant decreases; the phagocytic activity of alveolar macrophages is inhibited and neutrophils).
This leads to the development of the classic pathological triad: hypercrinia (hyperfunction of the bronchial glands with the formation of a large amount of mucus), discrinia (increased sputum viscosity due to changes in its rheological and physicochemical properties), mucostasis (stagnation of thick viscous sputum in the bronchi). These disorders contribute to the colonization of the bronchial mucosa by infectious agents and further damage to the bronchial wall.
The endoscopic picture of chronic bronchitis in the acute phase is characterized by hyperemia of the bronchial mucosa, the presence of mucopurulent or purulent secretion in the lumen of the bronchial tree, in the later stages - atrophy of the mucous membrane, sclerotic changes in the deep layers of the bronchial wall.
Against the background of inflammatory edema and infiltration, hypotonic dyskinesia of large and collapse of small bronchi, hyperplastic changes in the bronchial wall, bronchial obstruction is easily associated, which maintains respiratory hypoxia and contributes to the increase in respiratory failure in chronic bronchitis.
Strengthening the immune system
You should take care of your immunity. Although scientists today say that the antiviral effect of ascorbic acid is greatly exaggerated, in fact, vitamins are very necessary for natural protection, especially in winter. It is not even necessary to take vitamin complexes; it is enough to balance the diet by including seasonal vegetables, citrus fruits, and drinks made from dried or frozen berries.
A lot of vitamin C is found, for example, in black currants and rose hips. Also, to strengthen the immune system, it is important that the body receives enough protein, preferably of animal origin.
Reasons for development
In adults, chronic bronchitis develops due to a number of reasons. Moreover, the first manifestations of bronchitis, as well as its relapses, can be the body’s reaction to the simultaneous influence of several factors.
The main reasons for the development of chronic bronchitis in adults include:
- Smoking. The risk of developing the disease is directly proportional to the smoking experience. It is worth noting that passive smoking is no less dangerous.
- Contaminated air. People living in industrial cities are more susceptible to the disease than residents of rural areas. People who work in hazardous industries or live in areas with harsh climatic conditions are also at greater risk.
- Frequent incidence of ARVI and acute bronchitis.
- Allergic reactions.
- Infections and viruses entering the body. They are secondary causes, aggravate the course of the disease and lead to various disorders of the respiratory system and exacerbations. The onset of the inflammatory process in the bronchi is often caused by the ingestion of Haemophilus influenzae and pneumococcus.
It is also worth noting that bronchitis can develop in a person with certain predispositions (genetic and endogenous factors) to this disease. Treatment in this case will be longer.
Provoking factors
The most common cause of the development of any type of bronchitis is pathogenic microflora.
The main causative bacteria include:
- staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci.
The damaging agents of viral origin are:
- influenza virus, respiratory syncytial infection, parainfluenza, adenovirus.
Inflammatory processes are provoked by:
- the presence of viral or bacterial agents in the body;
- harmful working conditions associated with the need to be in a room with high air pollution;
- long-term smoking;
- living in poor climatic conditions.
Acute bronchitis occurs when internal infection is caused by viruses that cause colds or flu. They cannot be destroyed by drugs with antibacterial activity, so they are rarely used.
A common cause of prolonged bronchial disease is cigarette smoking. Polluted air and high concentrations of dust and toxic compounds in the environment also cause serious harm.
There are a number of factors that can significantly increase the risk of developing any type of bronchitis:
- genetic conditioning;
- living in an unfavorable climate;
- smoking.
First signs
Signs of chronic bronchitis in adults:
- persistent cough for 2 or more years in a row. It is accompanied by copious sputum and intensifies in the morning;
- feeling of weakness, fatigue, rawness behind the sternum;
- rapid breathing, dry wheezing;
- shortness of breath, fatigue during physical activity.
Exacerbation of chronic bronchitis leads to deterioration of the patient's condition. A person’s cough increases, breathing becomes difficult, and pain occurs in the chest and abdominal area. The sputum becomes purulent or mucopurulent in nature.
Treatment of annoying dry cough
Medicines for bronchitis come in different forms. For adults, tablets are most often offered for treatment, but aerosols, sprays, and syrups are also often used.
To alleviate the patient's condition in the first 3 days of the onset of the disease, to give him the opportunity not to suffer from attacks during night sleep, antitussive drugs are sometimes prescribed. They inhibit the functioning of the cough center in the brain, due to which the reflex that protects the bronchi is not so intense. Such drugs include:
- Stoptussin. It is based on butamirate dihydrogen citrate, guaifenesin. Affects nerve endings.
- Paxeladine. Based on oxeladine citrate, it affects the cough center and restores breathing.
- Bronholitin. Based on glaucine hydrobromide, ephedrine hydrochloride. Relaxes the muscles of the bronchi, acts on the cough center.
The best effect is provided by combination drugs that combine antitussive and anti-inflammatory effects. These are Sinekod, Codelac, Falimint, Bronchicum.
Symptoms of chronic bronchitis
In the very initial period of development of the inflammatory process in the bronchial mucosa, a sick adult experiences the first nonspecific signs of bronchitis - a feeling of weakness, fatigue, malaise, weakness. Headaches are possible. After a short period of time, after about 1-2 days, pain, heaviness, and a burning sensation behind the sternum appear, followed by a cough.
At the beginning it is dry, annoying, painful. Coughing is unproductive because sputum is not produced, which is why each coughing attack is accompanied by severe pain in the chest, a feeling of rawness or soreness. Sometimes the cough becomes so strong that during it headaches occur, intracranial pressure increases, and pain occurs in various muscles of the body - the abdominal wall, intercostal muscles, thigh muscles, etc.
At this moment, it is possible to increase body temperature, usually to subfebrile values, without exceeding the thermometer mark of 38 ° C. Fever may be accompanied by chills.
After 2-3 days, sputum begins to appear, which immediately alleviates the person’s suffering. A wet cough does not cause as much pain as a dry cough. Initially, the sputum is transparent and light in color. But soon the mucous sputum acquires the character of mucopurulent, which indicates that bacterial microflora has joined.
The duration of severe symptoms of bronchitis in many adults usually does not exceed 2-3 weeks, although recently there has been a tendency to lengthen the duration of the disease.
Cough may be complicated by shortness of breath if respiratory dysfunction occurs. This occurs when obstruction of the bronchi occurs due to blockage of their lumen with phlegm or due to spasm. The main symptom of obstructive bronchitis in adults is a paroxysmal cough, in which sputum is separated with great difficulty. Cyanosis of the limbs and face may appear, which is more pronounced during exhalation.
Impaired bronchial patency against the backdrop of a very long course of the disease may indicate the occurrence of a chronic process.
If the inflammatory process spreads to the smallest bronchi, then the process threatens to develop into a state of bronchiolitis or bronchopneumonia. This is indicated by an increase in body temperature to 39°C, the appearance of shortness of breath and increased breathing. If antibacterial therapy is not started promptly, a very serious complication may develop – pneumonia.
Treatment of wet cough
A wet cough is characterized by the removal of mucus from the bronchi, along with which pathological microorganisms are removed. After the 3rd day of development of the disease, antitussive medications for bronchitis cannot be used. If you combine their use with expectorants, you can lead to serious problems with the patient’s health and the development of severe complications: mucus, which is actively produced by the bronchial glands, does not come out due to inhibition of the cough center. As a result, a person will be diagnosed with total pneumonia - inflammation of the lungs over their entire area.
The following cough tablets for bronchitis are used to remove phlegm:
- Ambrobene. The active substance is ambroxol, a thinning and expectorant effect.
- Halixol. The same active ingredient.
- ACC. Based on acetylcysteine, it thins and promotes the removal of mucus.
Ambroxol and Lazlvan syrups also help in the treatment of wet cough.
Diagnostics
In the diagnosis of chronic bronchitis, it is very important to take into account the medical history (experience of smoking, work in hazardous industries, etc.), patient complaints, results of a physical examination (hard breathing, dry, wheezing, prolonged exhalation, possibly listening to moist rales of different sizes). The following laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are used:
- X-ray of the chest organs (network deformation, increased pulmonary pattern, and sometimes signs of emphysema are detected in the lungs);
- microscopy of sputum (a large number of leukocytes, grayish-yellow, greenish in color, viscous, mucopurulent in nature);
- bacteriological culture of sputum, bronchial washings;
- bronchoalveolar lavage;
- bronchography;
- bronchoscopy;
- spirometry (decrease in vital capacity of the lungs);
- pneumotachography (reduced maximum expiratory volumetric flow rate);
- general clinical blood and urine tests;
- biochemical blood test (fibrin, CRP, total protein, sialic acids, immunoglobulins).
What is the danger?
With chronic bronchitis, not only the bronchial tree suffers, but certain areas of the lungs, and even the entire body as a whole. Most often, chronic bronchitis becomes obstructive, which is why the disease is called Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, which is abbreviated as COPD. This type of disease usually occurs due to smoking or in the absence of treatment.
Changes in the lungs against the background of COPD become irreversible, so the essence of therapy is no longer to completely cure the disease, but to treat complications, symptomatic treatment, strengthen the body, and alleviate the course of this disease. If obstruction of the lungs persists for a long time, then a violation of the drainage function of all bronchi inevitably occurs. Air begins to linger in the alveoli and lung tissue. As soon as bronchospasm joins, the process of formation of pulmonary emphysema begins. As a result, pulmonary ventilation is quickly disrupted, respiratory failure develops, the cardiovascular system, nervous system and the entire body suffer.
If symptoms characteristic of COPD or smokers' cough occur, it is very important to carry out a differential diagnosis in order to timely exclude or detect diseases such as tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, bronchial asthma, and cancer, which often occur against the background of COPD.
Manufacturers of bronchitis products
To treat bronchial pathologies, you should take a comprehensive approach to the choice of drugs. Moreover, many analogue drugs are produced by several companies at once. It is difficult for the average buyer to choose, so experts suggest starting to get acquainted with trusted manufacturers. The best remedies for bronchitis were suggested by the following:
- OJSC Pharmstandard-Leksredstva (Bromhexine) is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in Russia, one of the top 5. It is an active participant in the import substitution program, creating worthy analogues to imported drugs. About 500 million packages are produced annually.
- "PRO.MED.CS Praha as" (Ambrosan) is a leading independent pharmaceutical company in the Czech Republic with its own research base. Thanks to this, she manages to create high-quality generics and her own patented medicines. The company produces 1.5 million tablets daily only. Most of them are intended for the musculoskeletal, digestive, and cardiovascular systems.
- Pharma Wernigerode Gmbh (Eucabal) is a pharmaceutical company from Germany, founded in 1903. Most of the drugs produced are presented in liquid forms - extracts, ointments, creams, gels, etc. Among them, a large share is based exclusively on natural ingredients.
- Vertex (Carbocisteine) is a well-known Russian pharmaceutical company specializing in dietary supplements and preventive medicines. The main ingredient for their creation is a medicinal herb. It takes pride of place among the fast-growing drug manufacturers in Russia.
- Europlant Fitofarm (Breast collection No. 4) is a trademark that is part of the group. She is recognized as an expert in the production and sales of herbal medicines. The herbal products produced cover most areas of medicine, offering alternative treatment.
- Krka, dd (Theotard) is an international pharmaceutical company that began its activities in 1954 in Slovenia. Engaged in the production of high-quality generics. Since 2007, it has been actively expanding its market share in Western Europe. Each product unit meets international quality standards.
- CJSC Altaivitamins (Salbutamol) is a team of professionals with many years of experience in the pharmaceutical field. It originates from the city of Biysk, where the company was founded in 1949. Then it was a vitamin and confectionery factory, and today it is a large pharmaceutical complex.
- Boehringer Ingelheim (Berodual) is a family-owned pharmaceutical company founded in Italy in 1885. Today it is one of the top 20 global drug manufacturers. There are 142 representative offices in different countries. The brand has become famous for its wide range of drugs, including those for treating animals.
- Nativa LLC (Fenoterol-Nativa) is a full-cycle pharmaceutical company with a European level of management. The manufactured products comply with GOST requirements. Specializes in the production of drugs for the treatment of socially significant diseases. Founded in 2010.
- FP "Obolenskoe" (Azithromycin) is a pharmaceutical production focused on the production of socially significant drugs. Great emphasis is placed on antiviral, antibacterial, and antiallergic agents. All products comply with international requirements and GMP and ISO standards.
- Pharmstandard (Azitrox) is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in terms of production and sales in Russia. Founded in 2003. Every year, over 1.7 billion packages of medicines for all areas of medicine are produced under this brand. There are 9 large factories scattered across the country. Participant in the import substitution program.
- Biochemie GmbH, Sandoz (Ospamox) - the Austrian company Sandoz is the owner of many large pharmaceutical enterprises, and since 1963, Biochemie GmbH. It itself is part of the Novartis group, being a leading developer of high-quality generics and biosimilars.
- OJSC "Tathimfarmpreparaty" (Erythromycin) is a Russian enterprise that produces medicines at a leading speed and volume. In this regard, it is among the top 20 countries in terms of scale of activity. Founded in 1931. Today there are two plants - a chemical and pharmaceutical plant, as well as a plant for the production of suture and surgical materials.
- CJSC "FIRN M" (Grippferon) is a biotechnology company that was founded during the Soviet Union in 1989. Today it demonstrates stable development dynamics and occupies a leading position in the production of ophthalmic drugs. Thanks to the creation of a research center, new medicines are being developed.
- APF-Trading LLC (Kipferon) is a trading company in the domestic pharmaceutical market, operating for more than 15 years. Performs wholesale sales of medicines to national distributors independently or through transport companies. It is directly related to most exclusive medicines.
Treatment at home
During remission, chronic bronchitis requires virtually no treatment, but during a relapse of the disease, a whole range of treatment procedures must be used. First on this list is drug treatment.
Without eliminating the leading causative factor—smoking cessation—no treatment will have a positive effect.
Treatment of chronic bronchitis involves a complex of means:
- An indispensable condition is the elimination of the provoking factor: quitting smoking is a prerequisite! Treatment of chronic infections of the nasopharynx - tonsillitis, sinusitis - will also slow down the progression of the disease. Unfortunately, exposure to toxic substances or dust is often of an occupational nature. Of course, not everyone can change jobs or move from a metropolis to a village.
- Antibiotics are prescribed during the period of exacerbation, when there are symptoms of intoxication and changes in blood tests. Empirically, penicillins (Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav) or 2nd generation cephalosporins (Cefuroxime, Cefaclor), macrolides (Sumamed, Rulid) or fluoroquinolones (Ciprofloxacin, Sparfloxacin) are most often prescribed. Sputum culture will help adjust treatment and select an antibiotic based on individual sensitivity.
- Expectorants . The choice is very large, and there are no studies proving the benefits of any group. Therefore, preference for any expectorant is a matter of personal taste. You can use both reflex-action drugs (potassium iodide, marshmallow, plantain, ivy extract, thyme), and sputum thinners (ACC, Mucodin), and mucoregulators (Bromhexine, Ambroxol). Drinking plenty of warm drinks, especially alkaline ones, promotes liquefaction and, therefore, better removal of mucus.
- Bronchodilators . These drugs must be taken at the first signs of bronchial obstruction - that is, when shortness of breath appears. Preference is given to inhaled forms: anticholinergics (Atrovent), beta2-agonists (Salbutamol, Salmeterol) or a combination thereof (Berodual). The usual prophylactic dose is 1-2 puffs 2-3 times a day. As an alternative to inhalers, which require certain skills (press and inhale at the same time), the bronchodilator can (and in case of bronchospasm, should) be inhaled using a nebulizer. If ineffective, a drug from the methylxanthine group is added - theophylline (Theotard 0.3 g 2 times a day or Uniphylline 0.4 g 1 time a day).
- Mechanical ways to improve bronchial drainage: chest massage, postural drainage, breathing exercises using the Strelnikova or Buteyko method. It is advisable to make these activities daily, as habitual as brushing your teeth.
- Adaptogens, vitamins and immunomodulators . Aralia, Leuzea, Eleutherococcus and ginseng, vitamins C and group B, propolis and aloe with honey are traditionally advised for patients with chronic bronchitis to take in the fall and winter to increase resistance to colds. Nowadays, bacterial immunocorrectors (Bronchovaxom, Bronchomunal) are increasingly used for the same purposes - a kind of vaccination against the most common pathogens of respiratory infections.
Of course, heredity is not in our control. But anyone can quit smoking, do gymnastics, and spend more time in the fresh air. A healthy lifestyle is better than shortness of breath and an oxygen cushion.
Antiviral drugs for the treatment of bronchitis in adults
To destroy viruses that cause the development of infectious-inflammatory disease of the bronchi, special antiviral agents are prescribed. They have several mechanisms of action:
- prevent viruses from entering healthy cells;
- destroy viral particles by blocking their reproduction or exit from infected cells;
- help strengthen a person’s own immunity.
Kipferon
An antibacterial, antichlamydial and antiviral agent is available in the form of rectal or vaginal suppositories. The drug contains two active components at once - an immunoglobulin complex preparation (ICP) and human recombined alpha-interferon. The cost of a Kipferon package of 10 suppositories is 707-746 rubles.
For bronchitis, suppositories are administered rectally (after defecation) 1-2 pieces 2 times a day. The duration of treatment is from 5 to 10 days. No side effects of the drug were recorded during treatment of patients. Kipferon is contraindicated in the presence of the following conditions:
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- individual intolerance to individual active or auxiliary components.
Grippferon
The antiviral drug is available in the form of nasal ointment or drops, nasal spray. The composition of the drug Grippferon includes recombined alpha-2 human interferon, with a volume of at least 10,000 IU per 1 ml of product. The cost of an antiviral drug varies depending on the form of release:
- nasal drops 10 ml – RUB 303-356;
- nasal spray – RUB 362-420;
- ointment with loratadine 5 grams – 240-278 rub.
For bronchitis in adults, it is preferable to use nasal drops. They are instilled into each nasal passage, 3 drops up to 6 times a day. The duration of therapy is 5-7 days. Grippferon during treatment can cause local allergic reactions - itching or burning, skin rash, redness of the mucous membranes of the nose. The medication is not recommended for use if the following contraindications exist:
- individual intolerance to interferon;
- severe forms of allergies.
Giaferon
These are rectal and vaginal suppositories with pronounced antiviral and immunostimulating properties. The active components of the drug are human recombined interferon alpha-2 (500,000 IU per 1 suppository), sodium hyalurate - 12 mg. Excipients include: paraffin, confectionery fat. The cost of a package of 10 candles is 368-402 rubles.
For infectious viral diseases, adults are prescribed Giaferon 1 suppository 1 time per day . The duration of drug therapy is 10 days. Suppositories are administered after perineal hygiene or bowel movements at night. Giaferon is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to interferons. During treatment, the following negative reactions of the body may be observed:
- chills;
- increased sweating;
- fast fatiguability;
- loss of appetite.
Inhalations for chronic bronchitis
Along with individual inhalers, there are special ultrasonic devices - nebulizers. These devices are capable of crushing liquid medications so that they can enter the smallest bronchioles along with the inhaled air. Such correct and rational use of medicinal bases makes inhalation for chronic bronchitis the main method of treatment.
The cost of a nebulizer allows almost every patient with chronic bronchitis to purchase it. This has not only therapeutic, but also economic feasibility. Indeed, the drug used during inhalation can be a drug of any group that is in a liquid state.
Namely:
- Atrovent is a bronchodilator drug of anticholinergic action. Sold in pharmacies in liquid form. For inhalation, you need to dilute 2 ml of the drug in 2 ml of physiological solution. This is a single dose;
- Berotec is a long-acting beta-adrenergic receptor agonist. For inhalation, 0.5-1.5 ml of the product is used. Must be diluted with saline solution to 4 ml;
- Ventolin is a short-acting beta-agonist. Available in special nebulae, which contain a single dose of the drug. Diluted with saline solution 1:1;
- Dioxidin is an antiseptic with a wide antibacterial spectrum of action. Used for exacerbation of chronic bacterial bronchitis. For inhalation, the drug is diluted with saline 1:4. Single dose is about 4 ml;
- Chlorophyllipt is a local antiseptic drug. The solution is prepared by diluting it with saline 1:10. A single dose of the prepared mixture is about 4 ml;
- Alkaline solutions. This can be either a ready-made soda preparation (sodium bicarbonate), or prepared at home (one teaspoon of soda per 200 ml of saline);
- Flexotide is a gluticocorticoid inhaled hormone fluticasone. Available in ready-made nebulae. For one inhalation, one nebula is needed, the contents of which are diluted with saline to 3-4 ml;
- Acetylcysteine (fluimucil) is a drug that loosens phlegm. The product is intended for inhalation, therefore it contains a ready-made diluted medicinal mixture. Single dose is about 4 ml;
- Lazolvan is a mucolytic and expectorant. Available in special bottles for inhalation administration. A single dose of the prepared solution is 3-5 ml.
The necessary drugs are simply poured into a special nebulizer receiver and inhaled after it is turned on. The frequency of administration and specific medications should be prescribed and monitored exclusively by a specialized specialist.
Antibiotic therapy
When choosing a medicine for bronchitis, especially an antibiotic, you should consult your doctor. Experts name several types of antibacterial drugs that show good activity in destroying different types of bacteria.
There are various complaints from patients: “I took an antibiotic, but it didn’t help me...”, “I’ve been taking an antibacterial drug for a week now, but there is no effect...”, “I took Ofloxacin, and I can’t leave the bathroom because of diarrhea...” and others. Such complaints indicate incorrectly selected therapy. Perhaps a person has a viral etiology of bronchitis, so antibiotics do not work. There is a possibility of using the wrong type of antibiotic that is required. Let's consider the main types of action of antibacterial drugs.
All these remedies are divided into types (series), antibacterial medicines for bronchitis and cough in adults are produced on the basis of:
- Aminopenicillins. The trade names of these drugs are Amoxilav, Arlet, Augmentin, Amoxicillin. They destroy the walls of bacteria, leading to their death. These are substances that are good for bronchitis and diseases of the ENT organs and respiratory tract. Most often, they are produced in the form of a solution or suspension.
- Cephalosporins. Known drugs are Cefazolin, Ceftriaxone, Cefex and others. This is a substance with a wide spectrum of action. Such medications are used to treat bronchitis caused by pathogens that are resistant to penicillin.
- Fluoroquinolones. They are produced under the names Ofloxacin, Moxifloxacin and others. They affect different types of bacteria, but they cannot often be used by people with poor functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, as they lead to dysbacteriosis.
- Macrolides. Known as Sumamed, Macropen and others. They prevent microbes from multiplying because they disrupt protein production in their cells.
The doctor decides which of these medications to take. It takes into account the patient’s condition and his individual characteristics of the body. He also determines the dosage and course of treatment. For complete recovery, at least 5 days of taking antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
The appropriateness of using antibiotics is also determined by a specialist. A clear sign of the need for their use is the green color in the secreted sputum.
What to do during an exacerbation?
During an exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, to enhance the therapeutic effect, it is useful to combine medications with other methods of getting rid of the disease:
- Various physiotherapy procedures that help quickly cope with chronic bronchitis not complicated by obstruction.
- A complex of physical therapy, which is allowed to be used only in the treatment of exacerbations of non-obstructive bronchitis.
- Taking vitamin preparations, especially A, group B and C, as well as various biostimulants such as aloe juice, sea buckthorn oil and propolis.
Medicines
What to take for bronchitis? Before using any medications, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Bronchodilators
To improve sputum discharge, it is necessary to use bronchi dilators. For bronchitis, adults are prescribed:
- Salbutamol;
- Eufillin;
- Theotard.
Cheaper analogues can be used. But it is better to coordinate such a prescription with your doctor.
Expectorant medications:
- Mukaltin. Helps soften mucus and facilitate its removal.
- Preparations based on thermopsis: Codelac Broncho and Thermopsol.
- Herbal products: Herbion, Bronchicum and Pertusin.
- ACC. This is a medicine that has a direct effect. Affects directly the secreted sputum. If the dose is exceeded, severe vomiting, diarrhea and heartburn may occur. You need to take these medications until the mucus is completely gone. The duration of treatment with herbs is about 3 weeks, and with pharmaceuticals - no more than two weeks.
Folk remedies
We will not consider all the recipes that can be used to cure chronic bronchitis (folk remedies are extremely varied), but will present only the most common of them.
- Honey inhalations. Just brew a spoonful of honey with several glasses of boiling water and breathe over the resulting steam. The recipe should be used only if you are not allergic to bee products. In general, honey and royal jelly are ideal immunostimulating agents that help quickly cope with infectious diseases, especially in childhood.
- Medicinal preparations (herbal) will help treat chronic bronchitis. They make a mixture of herbs: oregano, coltsfoot, plantain, licorice, thyme. Then, one tablespoon of the mixture is poured with half a liter of boiling water. Leave for three hours. Drink one third of a glass for ten days.
- Drink radish juice with honey. To do this, you need to make a hole in the vegetable and fill it halfway with natural honey. Place the radish in a cool place overnight. In the morning, a healing juice is formed in it, which allows you to quickly get rid of an old cough and signs of bronchitis.
- Horseradish 150 g, lemon – 3 pieces, grind in a meat grinder, mix. Take the gruel in the morning on an empty stomach and before bed. This treatment has a very good anti-inflammatory and expectorant effect.
- Drink half a glass of oat decoction with honey a day as a general tonic. It helps restore intestinal motility during constipation and dysbiosis. If bronchitis is to be treated with antibiotics, then you should pay special attention to this recipe.
- Take a glass of fresh lingonberry juice a day. It facilitates the discharge of sputum and strengthens the immune system.
Chronic bronchitis requires quality medical care. It is very important to start treatment on time to avoid complications. It is worth paying attention to the prevention of bronchitis: strengthening the immune system, increasing physical activity, taking multivitamins, and getting vaccinated against influenza.
Traditional medicine methods to protect health
In addition to drug treatment, traditional medicine methods also have a positive effect on the health of the whole body, stimulating the immune system, and treating coughs.
The most common recipes are herbal teas and infusions from the following plants: chamomile, calendula, linden blossom, berries and raspberry branches, coltsfoot grass, elderberry blossom.
An infusion of elecampane roots has a good expectorant effect. To prepare it, take elecampane roots, 1 tablespoon, and add 300 ml of water. This mixture is boiled over low heat for 12-15 minutes, after which it is infused for another 30-40 minutes. The infusion is taken 1 tablespoon, 3 times a day, half an hour before meals.
Syrup made from viburnum berries, ground with sugar, will help with an annoying dry cough. A delicious syrup made from turnips and honey has the same effect. To prepare it, take a homemade turnip, cut off the top like the lid, and cut out the inside to make a container for honey. Place 2 tablespoons of honey in the middle of the turnip, cover with a lid and leave overnight. Overnight, turnip juice and honey will produce a tasty and healthy syrup, which is taken 1 tablespoon 3-5 times a day.
Halotherapy
One of the most modern methods of combating chronic bronchitis is halotherapy.
The procedures are carried out in specially equipped chambers, where optimal conditions of humidity and temperature are created, and the air is thoroughly cleaned and saturated with saline solutions. With the help of halotherapy, patients can completely get rid of mild forms of the disease, and with a complex course, significant relief is achieved, thanks to which a person can do without medications for a long time.
Halotherapy
Hygiene
Hygiene rules must be observed. Viruses can persist for quite a long time not only on the skin of the hands or nasal mucosa, but even on those things in which a person goes outside. Therefore, when leaving the house, you should take wet wipes with you. And, of course, after visiting places where there are many people at the same time, you should treat your hands with antiseptic gel, rinse your nose with sea water (sprays like Aquamaris are suitable), and sometimes you can gargle.
Speaking about the simplest preventive measures, do not forget about wet cleaning. It should be regular. The apartment should be ventilated daily, even in winter.
It is very important that the air in the room is sufficiently humid. Due to the operation of central heating systems in winter, it becomes very dry, and this irritates the bronchi. Pharmacies sell special air humidifiers, but they are quite expensive, so you can use cheaper methods - for example, simply hanging a wet towel on the radiator.
Physical therapy plays an important role in the prevention of acute and prophylactic bronchitis - mainly complexes of breathing exercises. If your health allows, you should pay attention to aerobic training, which improves the functioning of the respiratory system as a whole.
Prevention
This disease responds well to complex treatment, and preventive measures will help avoid the occurrence of the disease or recurrence of relapses.
Prevention of chronic bronchitis includes the following methods:
- a balanced diet that includes vitamins and micronutrients;
- correct daily routine, you need to leave enough time for rest;
- a healthy lifestyle, consisting of complete abstinence from alcohol and smoking;
- timely treatment of diseases of the respiratory system;
- hardening;
- compliance with hygiene rules;
- daily moderate physical activity;
- constant ventilation of the room. If for some reason this is not possible, you need to monitor its humidity;
- avoiding places with large concentrations of dust or chemicals;
- premature prevention of ARVI and influenza;
- breathing exercises, about fifteen minutes a day.
In addition to publicly available methods for the prevention of chronic bronchitis, there are more global ones that are used for frequent relapses of the disease. It can be:
- change of work activity;
- climate change (you may need to move to another city or country);
- optimization of housing - exchange, insulation or renovation of an apartment.
Principles of nutrition and lifestyle
The patient's diet during treatment for bronchitis should contain a lot of proteins, vitamins and antioxidants so that the body can more easily recover from the disease. Eat fruits and vegetables, lean meat or dairy products, and calcium-rich foods daily. Temporarily exclude fried foods from the diet, but do not limit the amount and calorie content of foods in the diet - restrictions during this period lead to the fact that a person experiences a protein deficiency, and the healing process slows down. However, with pronounced symptoms of intoxication, short-term fasting can be beneficial.
It is necessary to monitor the amount of liquid consumed - drink at least three liters per day, giving preference to alkaline drinks. For respiratory diseases, it is useful to drink fruit juice, jelly, and alkaline mineral water mixed with warm milk.