Skin demodicosis is a parasitic infestation caused by microscopic mites Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis. Despite the fact that the pathogen parasitizes the skin of healthy people (statistically, Demodex folliculorum, Demodex brevis are found in 20-80% of adults and 100% of elderly people over 70 years of age), clinical manifestations do not occur in everyone. It is believed that there are a number of predisposing factors that together lead to the disease. In some patients, the infestation can lead to a severe skin condition known as rosacea or rosacea.
Causes of demodicosis
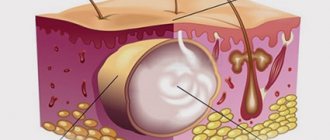
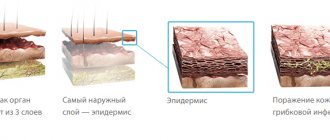
Only two species of Demodex mites parasitize human skin: Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis. The first lives in the hair follicles, the second in the sebaceous glands. Since the main food for the parasite is the components of sebum, the pathogen prefers areas of the skin with a large number of sebaceous glands. This is the area of the face, eyelids, forehead, nasolabial folds, nose. Less commonly, the parasite lives on the skin of the chest and back.
An adult D. folliculorum is about 0.3-0.4 mm long, with a worm-like translucent body consisting of two distinct segments. At the head end the parasite has 4 pairs of short segmented limbs. D. brevis is practically no different from its “relative”, with the exception of a slightly shorter body length. Ticks are not able to survive for a long time outside the body of their host.
Transmission routes – contact, contact-household. The parasite can be spread through towels, bed linen, and dirty hands.
The frequency of occurrence of Demodex folliculorum is higher than that of Demodex brevis, but the latter is distinguished by its ability to parasitize not only on the skin of the face. The parasite is equally common in both men and women.
The life cycle of the demodicosis pathogen consists of 5 phases and lasts from 14 to 18 days. Mating of males and females occurs on the surface of the skin, where the parasite rises from the sebaceous glands and hair follicles. In search of a partner, the tick is capable of moving at a speed of about 10-15 cm per hour. After fertilization, the females return to the thickness of the skin, where they lay eggs. After 60 hours, larvae emerge from them, which then turn into protonymphs and nymphs (36 and 72 hours for each stage). Nymphs, in turn, turn into adult ticks within 60 hours, capable of mating in 12-24 hours.
It was previously believed that rosacea or rosacea was caused by Demodex mites. However, extensive research has shown this theory to be untenable. Demodicosis, according to modern concepts, is a polyetiological disease in the development of which several factors are involved.
Ticks are often found on healthy people. The presence of a parasite without predisposing factors does not lead to disease. However, with immunodeficiencies, stress, vitamin deficiency, other diseases of the skin (seborrhea, acne) and the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, Itsenko-Cushing's disease), with frequent use of cosmetics, the use of medications that lead to a decrease in immunity, disturbances in the immune system entail a sharp increase in the number of ticks. On average, there are 1-2 mites per 1 square centimeter on the skin of a healthy person. In patients with clinical manifestations of demodicosis (rosacea), up to 60 parasites can live on every square centimeter of skin.
What kind of disease is this?
Demodicosis is a skin pathology that occurs due to the penetration and reproduction of the Demodex folliculorum mite in the ducts of the glands of the epidermis and mucous membranes.
This parasite has microscopic dimensions (up to 0.5 mm) and is classified as opportunistic, since it lives on approximately 90% of the Earth's inhabitants, but only 5-10% suffer from demodicosis.
That is, outbreaks of the disease do not occur in everyone and are provoked by certain factors (the state of the carrier’s body, environmental conditions).
Demodicosis in humans: photo
Mite reproduction is often provoked by:
- chronic stress, psychological trauma, psycho-emotional stress;
- poor nutrition, with a predominance of carbohydrate and fatty foods;
- passion for tanning and visiting solariums;
- love of bath procedures (steam room, sauna);
- use of inappropriate skin care products and cosmetics;
- immunodeficiency states and weakening of the body’s defenses after infections, surgical interventions, chronic ailments;
- hormonal pathologies, with disruption of the sebaceous and sweat glands;
- skin diseases.
Infection can occur through common objects (bed linen, showers, toilets, during procedures in beauty and hairdressing salons).
Demodectic mange in humans, whose treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor, is not a dangerous disease, but self-medication can lead to serious complications (a bacterial infection and the development of inflammation).
Risk factors
- Application of topical corticosteroid preparations to the skin of the face;
- Immunodeficiency conditions associated with taking drugs that suppress the immune system (systemic therapy with corticosteroids, chemotherapy) or diseases (AIDS, diabetes mellitus, Cushing's disease or syndrome);
- Cosmetics containing components that reduce the barrier function of the skin and/or are used by parasites as food;
- Dysregulation of sebum production (seborrhea, oily skin, acne);
- Age over 17-18 years;
- Genetic predisposition.
Expert opinion
- Cosmetologist
- Surgeon
Anna Avaliani
practicing cosmetologist
If one of your relatives has demodicosis, you should also be wary. Of course, there is no evidence of heredity of the pathology, but experts have noticed that in 40% of patients with this diagnosis, relatives also suffer from the disease. In addition, many people believe that demodicosis is diagnosed only in those with oily skin, but this is not true. This disease affects even dry skin types.
Aisha Baron
plastic surgeon
If you do not treat, the signs of pathology will only worsen (the disease will move from stage 1 to stage 2).
But if a person follows all the recommendations and changes his lifestyle, then it will be possible to control the symptoms. The main thing is to approach the problem comprehensively. Demodicosis is a very common disease that can be treated. To eliminate a tick, it is necessary to carry out timely diagnosis and determine the stage of the disease.
You should consult a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease so that treatment is as effective and quick as possible. Reviews about the treatment of demodex on the face, basically, carry the same message - you should start treatment on time and follow all the doctors’ instructions.
Mechanism of development of demodicosis
It is still unknown exactly how mites provoke skin inflammation. One theory says that the presence of a parasite on the skin does not lead to disease, and only with a decrease in immunity do prerequisites arise for deeper penetration of the pathogen from the hair follicles into the skin. Violation of the epithelial barrier leads to the entry of waste products of the parasite (antigens) into the surrounding tissues, which causes antigen-antibody reactions and type IV hypersensitivity reactions.
Attempts by the immune system to neutralize the pathogen lead to leukocyte infiltration of the skin and inflammation, followed by the formation of granulomas, papular or pustular rashes. The addition of a secondary infection (Bacillus oleronius, Staphylococcus epidermidis) significantly worsens the course of the disease.
In severe cases, demodicosis of the eyelids, demodicosis of the eyes, and demodicosis of the scalp, back, and chest are possible.
Features of topical medications
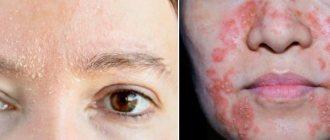
Sometimes photos of signs of demodicosis are truly amazing, since the patient’s skin can change beyond recognition, and it will be very difficult, and sometimes even impossible, to return it to its previous appearance. In many ways, everything will depend on the actions of the patient himself.
Topical medications are usually used in courses with short breaks. Thus, mild stages of pathology can be completely eliminated in one to two months. But if the disease has already begun to actively progress, then treatment may take more than one year.
Most often, for therapy, doctors recommend their patients to use various ointments for external use. Thus, drugs containing zinc, sulfur, as well as mercury or tar have an excellent therapeutic effect. Products based on these components can stop the activity of ticks.
The drugs most often prescribed to patients include the following:
- “Ichthyol” ointment;
- "Metragil";
- Sulfuric ointment;
- yellow mercury ointment;
- "Demalan" and many others.
Each of these medications is very effective. However, it is worth remembering that treatment can only be prescribed by an experienced dermatologist, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient’s body.
If the pathology begins to spread to the eyes, then additional treatment should be prescribed. It is very important to use special eye drops. Such drugs as “Armin”, “Tosmilen” and “Physostigmine” showed their best results. And in order to restore the growth of hair, eyebrows and eyelashes, it is recommended to rub burdock oil into the skin.
Classification of demodicosis
ICD-10 code: B88.0.
For practical purposes, the clinical classification of demodicosis according to forms is used:
- Erythematous form: the leading symptom is redness and swelling of the skin;
- Pustular form: resembles acne vulgaris, occurs with the formation of acne on the skin, pustules ranging in size from 0.5 to 2 mm with pronounced perifollicular inflammation;
- Mixed form.
Damage to the eyes and eyelids deserves special mention. The parasite is able to inhabit the meibomian glands - modified sebaceous glands, the mouths of which open at the edges of the eyelids.
Demodicosis of the scalp occurs when parasites spread to the scalp.
Features of demodicosis in children
Children very rarely become infected with demodicosis, even with increased oily skin. Most often in childhood, the disease occurs in the form of blepharoconjunctivitis (inflammation of the eyelids and conjunctiva of the eye), resistant to treatment with antibiotics.
conclusions
Only you are responsible for your health, so start doing it right now. If you notice even the slightest signs of demodicosis, immediately go to a dermatologist. Quickly started treatment will save you from many unpleasant consequences.
Start leading a healthy lifestyle, eat well, avoid stress, monitor your immune system, and you can protect yourself from many dangerous and unpleasant diseases. Take care of yourself and you will be free from many health problems.
Symptoms of demodicosis
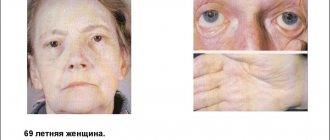
Clinically, demodicosis on the human face is similar to a severe form of acne vulgaris. The skin is thickened, moist, greasy, shiny in the light, especially in the area of the nose and cheeks. The skin color is pale gray, there is severe itching (especially at night). The pores are enlarged and secrete a large amount of sebaceous gland secretion. The primary elements of the rash are varied and consist of pustules, papules, microabscesses, acne against the background of severe erythema (redness of the skin). The vascular pattern may increase, there is severe folliculitis and sycosis. Secondary elements of the rash are scars, knots, scratches; in severe cases, cicatricial deformation of the nose is possible with an increase in its volume, making it look like a red plum (rhinophyma).
If the scalp is affected - itching, hair loss, dandruff, rash. When the eyes are affected, thickening of the eyelids, loss of eyelashes, inflammation of the conjunctiva (conjunctivitis), dry eyes due to dysfunction of the meibomian glands, and inflammation of the cornea are noted.
Prevention of pathology
Even if a person at first glance gets rid of the pathology, he needs to understand that relapses often occur with demodex. Therefore, you need to follow certain preventive rules for life:
- You need to keep your bed linen clean, and you will have to put on new pillowcases every day.
- After a person has washed, it is better to dry off with paper napkins.
- Personal items that touch the face must be kept clean and must be systematically disinfected. This applies to hats, glasses, hairpins, etc.
- It is better for men to shave with a new disposable razor each time or to constantly disinfect the razor.
- Try to use a small amount of cosmetics.
- If a person is undergoing treatment, then it is worth protecting yourself from drinking alcohol.
Treatment of demodicosis
Preparations for the treatment of demodicosis
Antibacterial drugs (metronidazole, tetracyclines, macrolides) and drugs that reduce sebum production (isotretinoin) are used as systemic agents.
Local preparations
Sulfur ointment for demodicosis is used because of its acaricidal (ability to kill ticks) and antiseptic effects. Apply to the affected areas of the skin and rub in thoroughly.
Permethrin is a more modern remedy that has a pronounced acaricidal effect. It is used topically in various pharmaceutical forms.
Ivermectin is a common acaricidal drug, widely used in the form of local (lotion, shampoo, ointment, gel) and systemic preparations (injections, tablets). Like permethrin, it causes the death of parasites due to disruption of the transmission of nerve impulses.
Esdepalletrin (Spregal) is an insecticidal drug widely used to treat parasitic diseases caused by arthropods (mites), such as demodicosis and scabies.
IMPORTANT! There are contraindications and side effects. Prescribing oral forms of drugs for demodicosis is possible only after examination and consultation with a doctor.
For demodicosis of the eyes and eyelids, use erythromycin eye drops, pilocarpine in the form of drops or gel (causes paralysis and death of the parasite).
Diagnostics
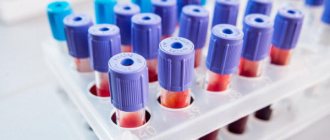
The symptoms of the disease have a number of similarities with other skin pathologies, so the most reliable method of confirming it is mite detection test
To do this, a scraping is taken from suspicious areas using a scalpel.
Before the study, patients are asked not to use soaps, gels or shampoos when caring for their face and body.
The biopsy is placed under glass and then examined in the laboratory under a microscope.
Diet for demodicosis
Increased sebum production is one of the factors that increases the risk of demodicosis. As with acne and seborrhea, a diet that limits the consumption of fats and carbohydrates can reduce the risk of occurrence and severity of clinical manifestations of demodicosis. The absence of fats and carbohydrates in the diet significantly reduces the production of sebum, which is mainly synthesized by the body from fatty acids and triglycerides.
It is recommended to adhere to a healthy diet rich in vitamins, microelements and proteins with a sharp limitation of carbohydrates and fats. Introduce vegetables, fruits, lean meats, and fish into your diet. It is necessary to exclude fatty and dairy products, delicacies, pickles, spicy dishes, and sausages. Cooking method: steaming, boiling. Any fat that enters the body will be used to synthesize sebum.
What does tick activity lead to?
Acne ironwort affects a person in several directions at once:
- By feeding on cells, microorganisms damage their structure not only mechanically, but also with chemicals contained in their saliva. The result of such activity is the appearance of inflammatory nodules, excessive keratinization of cells, and changes in skin color.
- After the death of the gland, substances are released that provoke the immune system to produce antibodies, which can result in the appearance of allergies.
- By suppressing the immune system, the gland thereby stimulates the activation of other inhabitants of the human skin belonging to the category of “opportunistic pathogens”.
Sources
- Facial dermatosis associated with Demodex: a case-control study. Ya-e Zhao, Yan Peng, Xiang-lan Wang, Li-ping Wu, Mei Wang, Hu-ling Yan, and Sheng-xiang Xiao, PMC - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/ articles/PMC3232434/
- Demodex folliculorum: Requirements for Understanding Its Role in Human Skin Disease, Albert M. Kligman, Michael S. Christensen, Journal of Investigative Dermatology https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022202X15350120
- Demodex folliculorum on the eyelash follicule of diabetic patients — https://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0004-27492011000600008
- Potential role of Demodex mites and bacteria in the induction of rosacea, Authors: Stanisław Jarmuda, Niamh O'Reilly, Ryszard Żaba, Oliwia Jakubowicz , Andrzej Szkaradkiewicz, Kevin Kavanagh https://www.microbiologyresearch.org/docserver/fulltext/jmm/ 61/11/1504_jmm048090.pdf?expires=1498579664&id=id&accname=guest&checksum=0DB2C446E2EBFAB11A0C06D324F37F47
- Human Demodex Mite: The Versatile Mite of Dermatological Importance, Parvaiz Anwar Rather and Iffat Hassan, Indian Journal of Dermatology - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3884930/
- Ocular Demodicosis (Demodex Infestation) Clinical Presentation, Manolette R Roque, MD, MBA https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1203895-clinical
- Sociodemographic characteristics and risk factor analysis of Demodex infestation, Ya-e Zhao, Na Guo, Meng Xun, Ji-ru Xu, Mei Wang, and Duo-lao Wang https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/ articles/PMC3232433/ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3232433/
- N. D. Khilkevich, M. V. Kachuk, A. P. Muzychenko, N. V. Kruk, E. L. Vetokhina DEMODECOSIS AS A DERMATOLOGICAL PROBLEM Belarusian State Medical University, Department of Skin and Venereal Diseases, Unitary Enterprise "Neovit"