Muscles are organs of the human body that are made up of muscle tissue. They allow a person to perform body movements and contract under the influence of nerve impulses. The term "myalgia" is used to describe a symptom that is expressed by muscle pain. It can be triggered by a variety of factors, which will be discussed in this article.
Myalgia occurs when moving or pressing on muscles. It can affect one or several muscles at once. Painful sensations may affect ligaments and tendons located nearby. If you want to know why the muscles in your body hurt and how to relieve muscle pain, contact the CELT Pain Clinic. Our doctors will conduct a diagnosis and find out the reason why you are experiencing discomfort. In accordance with it, treatment will be prescribed, which will definitely be effective.
At CELT you can get advice from a specialist algologist.
- Initial consultation – 4,000
- Initial consultation with the head of the Pain Clinic - 4,500
Make an appointment
Symptoms
Muscle pain may occur along with other symptoms, which vary depending on the underlying disease. For example, muscle pain that is caused by an injury may be accompanied by bruising and swelling in the area of the injury. Additional symptoms that may accompany muscle pain include:
- Depression
- Diarrhea
- Symptoms of acute respiratory illness (fever, chills, sore throat, fatigue, headache, cough)
- Impaired concentration
- Loss of appetite
- Muscle cramps
- Numbness, tingling or burning (called paresthesia)
- Problems walking
- Sleep disorders
- Swelling at the site of injury
- Sudden weight loss
- Vomit
Serious symptoms that may indicate a life-threatening condition
In some cases, muscle pain may occur in association with other symptoms that may indicate a serious or life-threatening condition, such as a heart attack or meningitis. You should immediately consult a doctor if you have any of these symptoms:
- Changes in consciousness or attention, such as loss of consciousness or sudden memory loss
- Changes in mental state, such as disturbances in perception of one's surroundings
- Chest pain radiating to the arm, shoulder, neck, or jaw
- Difficulty breathing, shortness of breath
- Inability to move any part of the body
- Impairment (loss) of vision
- Lack of urine
- Progressive weakness and numbness
- Seizure
- Stiff neck with high fever
There are acute and chronic myalgia
Acute pain is most often observed with injuries, overload, and infectious diseases. It can have different intensity - from insignificant to pronounced, and usually disappears in 2-7 days.
Chronic pain lasts for more than a month and usually indicates the development of myofascial syndrome.
There are such degrees of muscle pain::
1st degree . Local or regional pain, which manifests itself only when the muscle is applied - pressure or stretching. Upon palpation, a compaction can be detected, and in response to palpation there may be small convulsive twitches. Muscle strength is normal.
2nd degree . The pain is spontaneous, pulling, throughout the muscle; corresponding skin zones with increased pain activity are detected. Muscle strength may decrease slightly, by approximately 25%9.
3rd degree . Diffuse severe pain at rest, a whole group of muscles is involved, their strength decreases by 30% or more.
Up to contents
Cause of pain
Skeletal muscle pain is most often caused by direct trauma or injury from a muscle strain or tear. A muscle strain occurs when a few muscle fibers are damaged, while a muscle tear occurs when a large number of muscle fibers are torn. A rupture (tear) of a tendon can also lead to muscle pain. Muscles and tendons have the ability to regenerate, but if a muscle or tendon is severely ruptured, surgical restoration of the integrity of the damaged structures is required. Muscle pain can be caused by cramps resulting from overuse or abnormal nerve impulses that lead to excessive muscle contraction. In some cases, muscle pain can be a symptom of serious or life-threatening conditions such as a heart attack, meningitis, or cancer.
Traumatic causes of muscle pain
Muscle pain can be associated with any injury, including:
- Impact with a blunt object
- Muscle strain or tear
- Excessive or repetitive movements
- Nerve compression (due to disc herniation, spinal stenosis)
Neuromuscular diseases and conditions
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, Charcot disease) is a severe neuromuscular disease that causes muscle weakness and disability.
- Brain or spinal cord injury
- Dermatomyositis (a condition characterized by muscle inflammation and skin rash)
- Lyme disease (an inflammatory bacterial disease transmitted by ticks)
- Multiple sclerosis (a disease that affects the brain and spinal cord and causes weakness, coordination, balance, and other problems)
- Muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis)
- Muscle infections such as an abscess
- Parkinson's disease (a brain disease that causes poor movement and coordination)
- Polymyalgia rheumatica (a condition characterized by muscle pain and stiffness)
- Polymyositis (muscle inflammation and weakness)
- Stroke
Other possible causes of muscle pain
Muscle pain can be caused by many other diseases and conditions, including:
- Cancer
- Depression
- Fibromyalgia
- Angina or myocardial infarction
- Hypothyroidism
- Flu or other respiratory illnesses
- Kidney failure
- Electrolyte disturbances (abnormalities in potassium or calcium levels in the blood).
- Pregnancy
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Vitamin B12 or vitamin D deficiency
Medicines and substances that can cause muscle pain include:
- ACE inhibitors (used to lower blood pressure)
- Cocaine
- Statins (cholesterol-lowering drugs)
Questions that help determine the cause of muscle pain include:
- Are there other symptoms such as sore throat or fever?
- Do you feel pain in one specific area or throughout your body?
- How long does this condition last?
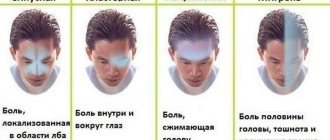
- In what parts of the body is pain localized?
- What reduces pain or increases pain?
- What medications are you currently taking or have recently taken?
Potential complications of muscle pain
Complications associated with muscle pain depend on the underlying disease or condition. For example, muscle pain associated with fibromyalgia or a degenerative disease can lead to decreased mobility and associated complications. Many skeletal muscle pains, however, respond well to treatment. However, if muscle pain is prolonged and associated with a systemic disease, it can lead to the following complications, including:
- Chronic pain
- Immobility and associated complications (such as bedsores and blood clots)
- Persistent pain resistant to treatment
- Amyotrophy
- Muscle contracture
- Permanent muscle or nerve damage (most often due to nerve compression), including paralysis.
- Decreased quality of life
Designations
Pain has several definitions. Let's look at them.
- Pain is a psychophysical state of a person, which is a reaction to stimuli associated with organic or functional disorders.
- This word also refers to the unpleasant sensation that a person experiences when experiencing any dysfunction.
- Pain also has a physical form. It manifests itself due to malfunctions in the body.
From all of the above, we can draw the following conclusion: pain is, on the one hand, the performance of a protective function, and, on the other, a phenomenon that is of a warning nature, namely, it signals an upcoming disorder in the functioning system of the human body.
What is pain? You should know that this is not only physical discomfort, but also emotional experiences. The psychological state may begin to deteriorate due to the presence of pain in the body. Against this background, problems appear in the functioning of other body systems. For example, gastrointestinal disorders, decreased immunity and loss of ability to work. A person’s sleep may also worsen and their appetite may disappear.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of muscle pain (myalgia) is primarily based on the history of the disease and symptoms. Most muscle pain is related to muscle strain (for example, due to poor posture or sedentary lifestyle) or injury (for example, sprains, bruises, or muscle soreness from sports). Instrumental research methods, such as ultrasound or X-ray, CT, MRI, help confirm or differentiate the cause of muscle pain .
Medical history (anamnesis).
The doctor will be interested in the type of pain, the location of the pain, and the intensity of the muscle pain. This information may be key to identifying the causes of leg pain. Information about the presence of muscle injuries, the presence of bruises, factors that lead to an increase or decrease in muscle pain or whether the pain is persistent, for example with a herniated disc, and the time the pain appears (day or night) is very important.
Inspection. An examination by a doctor can determine the presence of areas of pain, the presence of areas of skin discoloration, range of motion in muscles or joints, muscle strength, the presence of local tenderness in the tendon area, or identification of trigger points (for example, in fibromyalgia). In addition, reflex activity, sensitivity and other neurological tests are important to detect the presence of neurological disorders. The time of onset of muscle pain is also relevant, as, for example, with osteoporosis or ankylosing spondylitis. Alcohol or drug abuse can be a possible cause of muscle pain and information about this is important in determining the causes of muscle pain. Some medications may also have the side effect of muscle pain.
Laboratory research methods.
Blood tests can determine the presence of an inflammatory process or infections, autoimmune processes; biochemical tests can determine dysfunction of internal organs (for example, liver or kidneys).
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound). This research method allows you to visualize the presence of muscle inflammation (myositis), muscle and tendon ruptures.
Research methods such as CT or MRI are necessary to visualize problems in deep muscles where ultrasound examination is of little information or when it is necessary to visualize neurological conditions or traumatic injuries. Electrophysiological research methods (EMG or ENMG) can determine the presence of inflammatory or degenerative muscle diseases or impaired nerve conduction due to compression of nerve roots or other neurological diseases.
A muscle biopsy is usually used as a last step in diagnosing muscle diseases, and only if there are clear signs of such diseases.
Fibromyalgia
Many women after 50 years of age develop complex soft tissue damage. It's called fibromyalgia. The risk group consists of people with sleep disorders. Muscle spasms and pain are the most obvious, but not the only problem of the disease. Others include memory impairment, depression, and weather dependence. Treatment aims to relieve symptoms and includes medications and relaxation techniques.
Treatment
Treatment for muscle pain depends on the cause of the symptom. Therefore, the most important factor determining treatment tactics is making an accurate diagnosis. For example, if muscle pain is caused by taking certain medications, then in such cases it may be enough to stop taking these medications or replace them with other medications. Drug treatment for muscle pain may include NSAIDs or analgesics, and even opiates.
Acute muscle pain
For acute muscle pain that occurs after an injury, it is necessary to provide rest and unloading, and in some cases, immobilization. In addition, local cooling with ice wrapped in a towel has a good effect in such cases, which helps reduce swelling, inflammation, and pain. In addition, it is necessary to stop the exercise that led to muscle pain. Treatment of muscle injuries requires quite a lot of time, since early restoration of normal loads can lead to chronic pain syndrome and excessive scarring of muscle tissue, and in severe cases to the development of myositis ossificans.
Chronic muscle pain
Treatment for chronic pain may include heat treatments as well as other treatments such as:
- Acupuncture and acupressure
- Electrotherapy (therapy through electricity)
- Electromyostimulation
- Physiotherapy
- Exercise therapy
- Manual therapy
Systematic exercises (physical therapy) are especially relevant when the cause of chronic pain is degenerative diseases of the spine, such as osteochondrosis, spondylosis, and disc herniation.
Surgical treatment methods are used for severe traumatic muscle injuries or when there is compression of the nerve roots.
Prevention of muscle pain consists of the following rules: maintaining a healthy lifestyle, sufficient physical activity, a balanced diet, proper ergonomics of the workplace, avoiding alcohol abuse and smoking.
What to do if muscles hurt after exercise, how to treat?
The first thing to do if your muscles hurt is to stop any physical activity. It is necessary to provide the affected area of the body with complete physical rest. If the pain does not go away within 20 - 30 minutes, then you need to contact a traumatologist or chiropractor.
The fact is that muscles hurt after exercise for good reason. Unpleasant sensations are always associated with minor muscle fiber injuries. Under the influence of a pronounced contractile reaction, small fibers rupture. Accordingly, a violation of innervation and blood supply occurs.
The integrity of the fibers can be restored only with proper drainage of stagnant lymphatic fluid and relief of the inflammatory reaction. An osteopathic physician can provide effective assistance in such situations.
The second reason is the accumulation of lactic acid. To remove and utilize it, it is necessary to relieve muscle spasm, increase blood supply and the flow of lymphatic fluid. This can be done using massage and reflexology.
Before treating muscles, be sure to conduct a full differential diagnosis. Only after an accurate diagnosis can treatment begin. At home, you can recommend doing a light massage, applying heat and applying non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ointments externally (but not longer than 3 days in a row).
Thyroid problems
One of the diseases in which arm muscles ache for no reason is hypothyroidism. This is a disorder in the production of thyroid hormones. The main symptoms are weakness of the arms, puffiness of the face, and hair loss. In severe cases, swelling of the larynx may develop, leading to swollen, sore neck muscles. This condition requires urgent hormonal treatment.
Polymyalgia rheumatica
If there are disorders in the immune system, damage to all muscle groups can develop at once. This is called polymyalgia rheumatica. Its symptoms include morning stiffness, pain in the shoulders, hips, neck and other parts of the body. The causes of this condition are unknown, but more often it is inherited. Treatment of polymyalgia is long-term (up to 2 years) and consists of taking corticosteroids.
Autoimmune diseases
In some cases, the body, for unknown reasons, begins to react incorrectly to its own tissues. As a result, the functioning of all systems occurs. Such diseases are considered autoimmune. These are polymyositis, lupus, myasthenia gravis and rheumatoid arthritis. Their manifestations include muscle and joint pain. There is no cure for such ailments, and treatment is aimed at alleviating the condition.
Potassium deficiency
Minerals are required for proper muscle contraction. The main one is potassium. If this element is insufficient, all types of muscles become weak and their tone decreases. Hypokalemia is accompanied by cramps, drowsiness, and constipation. In severe cases, the whole body hurts and there is constant thirst. At the initial stage, the doctor prescribes potassium supplements, at the later stage - their intravenous administration.
Poisoning
When toxic substances enter the body, they begin to spread through the bloodstream throughout all systems and tissues. Frequent causes of poisoning are low-quality products, medications, and toxic substances. A strong immune system can quickly cope with them. If it is weakened or poisoning is accompanied by an infection, pain and aches appear in the body.
Cardiovascular disorders
Blockage of the veins through which blood flows to the muscles causes a decrease in their contractility. The cause of this is often atherosclerosis. This is the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of blood vessels. In the early stages of the disease, problems are felt only during physical activity. Without treatment, atherosclerosis can lead to lameness, so if you experience causeless pain, consult a doctor immediately.