Salmonellosis is an acute infectious intestinal disease caused by various types of bacteria of the genus Salmonella. Salmonella affects the gastrointestinal tract and can sometimes occur with typhoid-like symptoms, less often in the form of generalized septic forms.
Medicine knows about 2 thousand serovars (varieties) of salmonella, however, in our country only 500 species provoke intestinal diseases in humans. The causative agents of salmonellosis are extremely resistant to low temperatures, as well as other manifestations of the external environment.
These bacteria can survive in animal feces for three years, in water bodies for up to four months, and in dairy products for up to 20 days. Many strains of salmonella are resistant to antibiotics, but are easily killed by chlorine-containing disinfectant solutions.
Description of the disease
The causative agent of salmonellosis is excreted in feces, after which it enters the body through the oral cavity. Most often, bacteria affect the stomach and small intestine.
People can suffer quite severely from infection due to strong susceptibility. How severely the infection affects the body depends on many different factors. This is primarily influenced by the number of pathogens that have penetrated, as well as their antigenic composition. Quite important is how strong the body’s immune system is, as well as the presence of some pathologies of the digestive system.
Pathogens
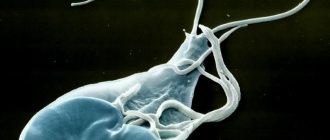
The causative agents of this infection are gram-negative enterobacteriaceae. Their distinguishing feature is that they do not form spores. The bacterium itself belongs to the genus Salmonella.
The most favorable temperature for bacteria to live is 35 degrees Celsius. They have good resistance to external factors, due to which their life cycle can be quite long depending on the environment. The pathogen is able to survive at temperatures from 7 to 45 °C.
Who is at risk?
In order for a pathogenic bacterium to enter the body through the oral-fecal route, it is enough to simply not wash your hands once after using the toilet or upon returning home from the street. It is not surprising that the question of how to treat salmonellosis worries parents most.
Children under the age of 12 are the main risk group for infection, since they most often do not follow basic rules of personal hygiene. Infants are the most susceptible to infections, since babies do not yet have time to develop strong immunity.
Causes
After Salmonella manages to penetrate the gastrointestinal tract, it ends up in the small intestine. Together with particles of epithelium, they reach the mucous membrane, where bacteria begin to multiply. As a result, inflammation of the mucous membrane and lymph nodes occurs.
The waste products of the pathogen are toxic to the human body, in which blood microcirculation is disrupted due to severe intoxication. Then the transport of ions begins and a sharp withdrawal of electrolytes and water from the body’s cells into the intestines occurs.
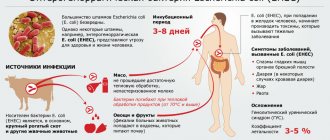
Transmission routes
There are several main routes of transmission and infection of the human body.
The most common ones are:
- Fecal-oral. The most common route of pathogen transmission. A person becomes infected by eating food contaminated with bacteria, which could have been introduced into it by an infected store clerk or catering establishment employee. Swimming in ponds or pools contaminated with salmonella can also lead to this.
- Infection can be caused by drinking raw water. This usually leads to massive infection of others.
- You can become infected with salmonellosis even with an ordinary handshake. In addition, this can happen when using someone else's personal hygiene items.
The sources of salmonella can be not only infected people. Poultry, pigs, cattle and domestic animals can carry the infection. It is noteworthy that bacteria that get into food do not in any way affect the appearance or taste of the food. This feature significantly increases the likelihood of infection. During the warm season, the highest number of infection cases occurs.
Diagnostics
Before starting treatment for an infection, the patient must undergo several different tests. It will be necessary to provide stool and blood samples for laboratory analysis.
The doctor then carefully reviews the test results to make an accurate diagnosis and confirm the infection. Also, during the research, the specialist will need to find out what exactly caused the infection. To obtain this information, samples of undigested food in the esophagus may be taken from the patient. This way you can find out which product was the carrier of the pathogen.
Incubation period
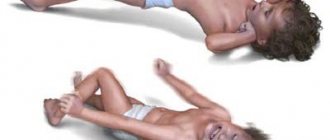
The most common incubation period is one day. The minimum period is six hours, and the longest period can reach three days. During the incubation period, patients begin to experience painful symptoms, which can also appear after ordinary food poisoning.
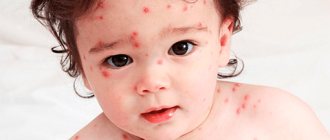
Signs of salmonellosis in an adult:
- sharp pain in the abdomen;
- flatulence;
- constant bloating;
- frequent diarrhea, accompanied by an extremely unpleasant odor;
- there is mucus in the stool;
- frequent vomiting and nausea;
- a sharp decrease in appetite, due to which the infected person practically stops eating;
- elevated temperature;
- feeling of aching in muscles and bones;
- mild neurological symptoms.
The time that has passed since infection does not affect how the disease develops. The number of symptoms will increase with the development of pathology.
Those people who experience problems with the secretion of gastric juice will be especially sensitive to the pathogen. This is due to the fact that some of the bacteria are killed by hydrochloric acid when they enter the stomach. A person who has problems with acid secretion allows more salmonella to enter the intestines, where the harmful activity of the infection subsequently begins.
First of all, bacteria attach to the mucous membrane, and then begin to penetrate its surface tissue. Not only the waste products of the pathogen are toxic, but also even dying salmonella, which also release substances dangerous to the body.
Salmonella are very well adapted to the body's immune system.
When foreign bacteria are detected, the immune system sends special cells - macrophages - to fight the pathogen. This method of protection against infection is not effective enough, since the bacterium can use macrophages to its advantage. The fact is that salmonella absorbed by protective cells may not die. Instead, they move inside macrophages throughout the body, affecting not only the intestines, but also other organs. Thus, the liver, kidneys, heart and even the brain membrane may become infected. As a result, the spread of infection beyond the gastrointestinal tract can lead to very serious complications and serious consequences.
Symptoms
Symptoms of infection may vary. It depends on the exact form in which the pathology occurs.
There are five such forms:
- gastrointestinal;
- typhus-like;
- asymptomatic;
- bacterial carriage;
- septic.
Depending on the form, the symptoms of salmonellosis manifest themselves differently.
First signs
There are the most common signs of infection that accompany most forms of salmonellosis.
These signs include:
- a sharp drop in pressure;
- cardiopalmus;
- weakness;
- headache;
- abdominal pain;
If the infection has reached the large intestine, blood may be present in the stool.
Gastrointestinal form
It is the most common form of salmonellosis. It has a very characteristic clinical picture in the form of manifestations of acute signs of intoxication of the body.
In particular, these signs are:
- cephalgia;
- febrile fever (body temperature 38-39 degrees)
- pyretic fever (body temperature 39-40 degrees);
- chills and trembling throughout the body.
The disorder of the gastrointestinal tract progresses rapidly.
There are several stages in the development of infection:
- First, the patient begins to experience severe pain in the stomach, the part of which is closest to the navel.
- After some time, the patient begins to suffer from profuse vomiting. Quite often, particles of food that are not completely digested by the stomach are observed in the vomit.
- Then the vomit becomes more watery. Sometimes an admixture of bile appears.
- Physical examination often reveals a dry tongue with a white coating.
- Diarrhea occurs with greenish-colored feces with mucous and foamy inclusions.
- The liver and spleen become enlarged.
As a rule, diarrhea stops within 3-5 days after infection. During this time, the human body can seriously suffer from dehydration. To mitigate the consequences, the patient needs to drink as much water as possible.
In addition to dehydration, diarrhea can cause other problems.
These are:
- serious metabolic disorder;
- abundant loss of mineral salts;
- the appearance of seizures;
- hypotension;
- tachycardia;
- syncope and presyncope;
- attacks of vertigo.
Complete disappearance of unpleasant symptoms usually occurs after five days. Full recovery may take two weeks.
The gastrointestinal form of salmonellosis has two degrees of severity:
- The mild form is characterized by a complete absence of elevated temperature or only a slight increase in temperature. The infected person may sometimes experience bouts of vomiting and diarrhea. Mild symptoms disappear within three days.
- The severe form differs from the mild form by a more prolonged illness, lasting five or more days. The patient has constant nausea, vomiting, a sharp decrease in blood pressure and loss of strength.
A severe form of salmonellosis is very similar in symptoms to dysentery.
Typhoid form
At the initial stages, the symptoms of infection strongly resemble the gastrointestinal form of salmonellosis, but after a while the symptoms are more reminiscent of typhoid fever. The patient has been suffering from fever and severe intoxication for a week. Sometimes patients may experience hallucinations and become delusional.
A week after infection, a red rash forms on the abdomen, which disappears after three days. The color of the tongue begins to change to gray-brown, the skin becomes paler. There is also a significant enlargement of the liver and spleen. The abdomen is constantly bloated, and there are frequent attacks of flatulence.
This form of infection is quite difficult to treat, so full recovery can be expected only after a month and a half after infection.
Septic form
The septic form of infection is a fairly rare occurrence. It affects the elderly, newborns and those suffering from weakened immune systems.
This form of infection is accompanied by:
- feverish condition;
- hyperhidrosis;
- chills;
- trembling in the body;
- development of jaundice;
- abscess of tissues and organs.
In addition, this species is the most dangerous because it has the highest risk of death. This danger is explained by the fact that suppuration forms in the tissues and internal organs, leading to the development of sepsis. It occurs in a chronic form.
Asymptomatic form
The name of this variety speaks for itself, since it has no symptoms. This feature is explained by the fact that only a small amount of bacteria enters the human body. As a result, it successfully copes with a small number of salmonella bacilli, neutralizing them completely. Thus, no harm is caused to human health.
Bacteria-carrying species
A person infected with salmonellosis may not even be aware that he is a carrier and distributor of the infection. The bacterium leaves the host’s body along with feces for three months, infecting everyone around them. In some cases, the timing of bacterial isolation may be shorter.
Typhoid-like form
Salmonellosis of this species is extremely severe and can be fatal. During the first 3 days, the patient experiences vomiting and loose stools, and the temperature rises to 38 degrees. On the 4th day the symptoms change.
Loose stools and vomiting stop, the temperature rises to 40 degrees and can last up to 30-45 days. By the end of the 1st week, a red rash appears on the abdomen, caused by high fever and an enlarged spleen and liver. It lasts for 2-3 days. The skin, due to poor liver function, acquires a yellow tint.
The disease is difficult to treat. A long feverish state brings the body to complete exhaustion. The abdomen remains enlarged throughout the entire illness due to changes in the size of the internal organs. The patient has been delirious for a long time. After recovery, lifelong immunity is developed.
Disease in pregnant women
Pregnant women are much more susceptible to infection, so the symptoms are more pronounced.
Features of the flow:
- During pregnancy, women's immunity is greatly weakened, so the body cannot properly resist the spread of infection. As a result, Salmonella bacilli freely penetrate into the blood.
- The general symptoms are much more intense, since dehydration and intoxication occur much faster.
- The infectious agent poses a particular danger to the pregnant fetus, since the cells can cross the placenta and harm the baby.
- Most pregnant women should not use almost all medications to treat the infection.
Treatment of salmonellosis in pregnant women should be safe for the child, but at the same time effective. Doctors recommend that in order to avoid serious consequences, before the fifth month of pregnancy, treatment is carried out exclusively in a medical institution under the supervision of specialists.
Is it necessary to see a doctor?
In some cases, adults can recover on their own without hospital treatment. This is quite acceptable, but only when the severity of symptoms gradually decreases and the diet is followed. In this case, the infected person’s body can cope with the disease itself.
If the patient is very often bothered by frequent vomiting and diarrhea, a visit to the doctor is required. You need to go to the infectious diseases emergency department, where you will have to undergo inpatient treatment, since it is impossible to cope with such a severe course of the disease on your own.
Also, a visit to the doctor is mandatory if the patient suspects that he has a septic form. This form of infection cannot be treated without the participation of specialists.
How is the treatment carried out?
In some cases, the disease has such a severe impact on the body that the patient may need to be hospitalized. In any case, elderly people, infants, people with weakened immune systems, food industry workers and medical workers should undergo inpatient treatment.
The therapeutic approach involves the use of diet therapy. It is aimed at completely eliminating a number of food categories from the diet.
These include products:
- spicy;
- salty;
- smoked;
- hot.
In extreme cases, antibiotic therapy is carried out, especially in a hospital setting. Patients are also prescribed medications based on saline solution, entrosorbents and probiotics.
In addition, toxic substances are removed from the body mechanically. To do this, the stomach is washed and cleansing enemas are done. Then the intake of activated carbon and other sorbents - Smecta and Enterosgel - begins. If such therapy does not bring a satisfactory result, salmonellosis is combated by intravenous administration of hemodez, sodium bicarbonate and rheopolyglucin.
Drug therapy
It is impossible to cure salmonellosis without the use of medications. Drug therapy on average lasts no more than ten days, but the duration of treatment very much depends on the general condition of the patient.
During the initial phase of treatment, it is very important to mitigate the effects of severe dehydration caused by diarrhea and vomiting. To do this, you need to use drugs that can slow down the bowels. Loperamide has the necessary properties. Manufacturers do not recommend taking it for more than five days in a row.
After the patient begins to feel a little better, oral medications or intramuscular injections are included in the treatment regimen.
Most often used as antibacterial drugs:
- Azithromycin;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Cefotaxime;
- Ceftriaxone.
To get rid of headaches, doctors often use Ibuprofen and Paracetamol.
Enzyme-containing preparations will help normalize the functioning of the digestive system.
These include:
- Festal;
- Mezim;
- Creon.
A patient who had to undergo a course of antibiotic treatment is then prescribed a course of probiotics to restore the microflora in the intestines. This is a rather lengthy process that can take several weeks.
The most effective means that cope well with this task are:
- Lactobacterin;
- Bifidumbacterin;
- Acipol.
The generalized form of infection forces the patient to take antibacterial drugs based on chloramphenicol, doxycycline or fluoroquinol. However, with this type of infection, taking antibiotics is not necessary.
Drinking regime
Preference should be given to saline solutions. In almost every pharmacy you can purchase special powders for their preparation. In particular, Regidron, Oralit and Tsitroglucosolan are suitable for this.
You can also use improvised means to prepare a suitable solution.
You can dilute one of the following products per liter of water:
- 20 grams of glucose (8 teaspoons);
- 1.5 grams of potassium chloride (sold at the pharmacy);
- 2.5 grams of soda (half a teaspoon);
- 3.5 grams of salt (teaspoon).
You can drink ordinary compote made from raisins or dried apricots. You need to drink liquid little by little, but regularly. It is advisable to take a few sips every 5-10 minutes. During the first few hours of symptoms, you need to drink 400 milliliters of fluid every hour. It is also important to drink a glass of water after each bowel movement.
Features of bacteria of the genus Salmonella
Salmonella is named after the American veterinarian researcher Daniel Elmer Salmon (1850–1914), who first isolated this bacterium from pigs. A few years later, identical bacteria were identified in material from a patient who died of enteritis.
Since then, it has become clear that salmonellosis, unlike typhoid and paratyphoid fevers, are anthropozoonoses. You can get the causative agent of salmonellosis not only from a sick person or carrier, but also through contact with a sick animal or contaminated food of animal origin.
Salmonella belongs to the family of intestinal infections, where it is classified as a separate genus Salmonella. They are bacteria with a complex antigenic and biochemical structure.
However, this does not prevent them from being quite simple microorganisms for bacteriological diagnosis. They are available for identification by routine bacteriological methods in almost every microbiological laboratory.
Salmonella are highly resistant to certain factors:
- low temperatures (can remain at freezer temperature);
- high temperatures (they die at temperatures not lower than 70 degrees Celsius);
- chemical disinfectants and antibiotics.
The last point is especially relevant for salmonella, the causative agents of nosocomial infections, the so-called hospital strains. It is known that this type of salmonella is particularly severe, possibly with fatal outcomes.
The bacterium develops resistance to disinfectants and antimicrobial therapy used in hospital settings. At the same time, it has the ability to strengthen its pathogenic properties, repeatedly circulating through weakened organisms.
These reasons lead to the fact that, when staying in hospital conditions for a long time, patients also run the risk of contracting nosocomial salmonellosis. The bacteria are difficult to treat, since salmonella mutates and develops antibacterial defense mechanisms.
Multiple resistance to antibacterial drugs is caused by several reasons:
- the wide availability of antibiotics in the pharmacy network and their use by patients without consultation with a specialist - self-medication.
- use of antibiotics in agriculture when raising animals.
- the use of antibacterial additives as food preservatives to extend shelf life.
- using antibacterial coatings to develop new packaging materials for the same purpose.
The combination of these factors with the presence of a source of infection leads to the development of salmonellosis in countries with well-developed food and other production. Products are produced in large quantities, delivered to wide store chains, from where they reach a large number of consumers.
Diet
In medical institutions, when treating salmonellosis, the patient is prescribed a special diet. It is aimed at minimizing the chemical and mechanical effects of food on damaged tissue of the intestinal mucosa. The diet also helps restore normal microflora.
A therapeutic diet differs from an ordinary diet in its energy deficiency, since the diet involves minimal consumption of foods high in proteins, fats and carbohydrates. As the patient's condition improves, the diet begins to gradually expand.
The duration of the diet is different for each patient, as it depends on a number of additional factors:
- state of the body;
- forms of infection;
- age of the infected person.
Usually, with the right diet and adequate treatment, recovery occurs within a month, leaving no complications.
Authorized Products
In case of salmonellosis, the list of foods acceptable for food is quite limited.
These include:
- varieties of fish and meat with low fat content;
- white bread crackers;
- rice, semolina and buckwheat porridge, cooked in water without the use of oil;
- dairy products;
- apples and bananas;
- fruit or vegetable puree;
- jelly and compotes.
All food must be ground or crushed as much as possible before consumption. You need to eat 4-5 times a day, but the portions should be relatively small to avoid overeating.
What is prohibited
Throughout the entire treatment period and the two-week period following the disappearance of all symptoms, many foods should be excluded from the diet.
These include:
- citrus;
- fatty fish and meats;
- smoked, fried and pickled foods;
- strong alcohol;
- tea and coffee;
- carbonated drinks;
- pearl barley, millet and oatmeal;
- vegetables with coarse fiber: cabbage, beans, radishes and radishes.
When consumed, more gastric juice is produced, and some of them have a rough effect on the intestines.
Pathogens
View of Salmonella under a microscope
The causative agent of the disease is the Salmonella bacterium. There are more than 2,000 species, and more than 200 are dangerous for chickens.
Salmonella spp. are zoonotic bacteria, for which birds, in particular, can serve as reservoirs. Most often, infections are transmitted through food or droppings; Human infection can occur through direct contact with infected individuals or indirectly through consumption of contaminated food or water.
Of all its species, the most common is Salmonella enteritidis. In 2014, Russian state supervisory authorities conducted a massive inspection of poultry farms to determine the incidence of salmonellosis. Only 40% of farms were free of infection. In other cases, the bird was infected with this dangerous bacterium.
But not all forms of bacteria are dangerous to people. Some of them cause disease only in chickens. For example, Salmonella gallinarum pulorum will not harm humans.
Treatment of this pathology is complicated by the bacteria's resistance to various environments. She lives quietly for about seven months and reproduces in reservoirs. It can be detected in tap water for 2 months. And in the litter the microbe feels great for up to 4 months. But salmonella lasts the longest time in the soil - for 12 months. More often than others, chickens become infected.
Infection also depends on the immunity of each individual individual. If you do everything to strengthen it, then even in the event of a disease, the number of infected will be much less.
Self-infection occurs through:
- food or water;
- container;
- maintenance and care items;
- bedding;
- egg shells;
- bedbugs, worms, insects and rodents.
Folk recipes
Salmonellosis can be treated in this way only if the patient simultaneously undergoes drug therapy and follows a diet. Before using traditional medicine, you need to consult a specialist.
A warm compress will help overcome stomach cramps, which often bother the patient during infection.
Required:
- pan;
- cup;
- coarse salt or cereal;
- cloth bag.
Pour salt or cereal into a frying pan and heat it up. Two cups will be enough. Afterwards, you need to pour the hot remedy into a bag and place it on the place where the patient is experiencing spasms. Cover the patient with a blanket from above and do not remove the bag from under it until it has completely cooled down. You can repeat this procedure as needed.
Infected individuals suffering from severe diarrhea in the absence of hypoglycemia are advised to abstain from all food for three days. Fasting should begin as soon as signs of illness appear.
Additionally, aromatherapy can be used, since the smell of oils can have a beneficial effect on the body, increasing its resistance to infection.
You can heat essential oils on a special lamp:
- thyme;
- sage;
- eucalyptus;
- lavender;
- ginger;
- lemon;
- orange;
- cinnamon.
If diarrhea is particularly severe, you can lubricate the stomach with an oil mixture. To do this, add a couple of drops of cypress, chamomile or sandalwood oil to ten milliliters of olive or linseed oil. Afterwards, the resulting mixture should be rubbed into the stomach with gentle circular movements.
Chamomile and calendula infusion
To strengthen the immune system and increase the body's overall resistance, you can make a decoction of chamomile or calendula. The calendula plant has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. Thanks to these features, this plant has been used in folk medicine for a long time.
For the decoction you need:
- one tablespoon of flowers;
- a glass of boiling water.
The flowers need to be poured with boiling water and allowed to brew for thirty minutes. After the decoction has cooled completely, it should be consumed 30 minutes before eating. You need to drink half a glass at a time.
Chamomile decoction is prepared in an identical way, but it must be infused for four hours. It is consumed two tablespoons four times a day after meals.
Plantain infusion
There is nothing complicated in preparing plantain infusion.
For this you will need:
- pre-chopped plant;
- a glass of boiling water.
A tablespoon of herb is poured into one glass of boiling water. The product is infused for fifteen minutes and, after complete cooling, is drunk in small sips.
Infusion of wild strawberry leaves
Wild strawberry leaves need to be chopped and dried. Then pour one tablespoon of the plant into two glasses of boiled cold water. The herb should infuse overnight. Afterwards, you need to strain the product and take half a glass four times a day.
Rehabilitation
The duration of hospital stay for patients with a localized form is about two weeks. If the patient suffers from a generalized form, the period of rehabilitation increases to one month. After two months from the end of therapy, the patient undergoes a bacteriological examination, which is repeated twice. The patient is discharged from the medical institution only if both tests show the absence of the pathogen in the body.
How to speed up recovery
One of the most important stages of recovery is the return of beneficial microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. Fermented milk products will help with this. At home, you can ferment whole milk using a hay stick. This bacterium is capable of fighting infection.
The main treatment can be supplemented with herbal medicine. Decoctions of oak, pomegranate peel and bird cherry fruits will help with this. These plants have an astringent effect. Typically, the use of these decoctions is supplemented by taking herbal infusions with anti-inflammatory properties.
Bacterial carriage
After recovery, some people remain carriers of the pathogen - salmonella is in the gastrointestinal tract, but there are no clinical manifestations of the disease. They continue to infect others, but they themselves are unaware of it. Bacterial carriage after salmonellosis occurs:
- Prolonged - the pathogen is released from 30 to 90 days.
- Chronic - it is detected from 90 to 180 days after the symptoms disappear.
- Transient - a single detection of the pathogen in the stool with a negative RNGA result (indirect hemagglutination reaction) and a normal coprocytogram.
An accurate diagnosis is established only after bacteriological examination of stool, vomit and identification of bacteria.
Possible consequences
Each intestinal infection caused by a pathogenic pathogen can pose a serious threat to human health.
Delayed or incorrect therapy can lead to the following complications:
- heart and kidney failure;
- sudden jumps in blood pressure;
- respiratory arrest;
- from the internal organs - the formation of purulent deposits;
- peritonitis;
- appendicitis;
- arthritis;
- infectious-toxic shock;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases (pancreatitis and cholecystitis).
In rare cases, advanced disease can cause inflammation and encephalopathy, reaching the brain membrane through the bloodstream. In extremely rare cases, salmonellosis can cause blood clotting problems.
Genital area
Salmonellosis can provoke a variety of problems in the functioning of the genital area due to the close location of the source of infection to the corresponding organs.
Complications and consequences of salmonellosis for the reproductive system:
- Decreased libido and sex drive . Occurs due to general intoxication and the development of combined inflammatory processes;
- Inflammation of the prostate gland . A common problem among men, which is very difficult to get rid of in the case of bacterial prostatitis. As modern medical statistics show, only in a third of cases does complex therapy achieve complete recovery of the patient and rid him of complications. The basic principles of treatment are pain relief (NSAIDs and antidepressants are used), fighting infection (fluoroquinolones, penicillins or macrolides), as well as taking adrenergic blockers (Alfuzosin, Tamsulosin) and microenemas with antiseptic solutions;
- Inflammation of the cervix . Ectopia of an infectious nature, one of the main elements of the main female genital internal organ, is amenable to complex treatment, including both conservative therapy and instrumental and surgical techniques - electrosurgery, thermocoagulation, laser destruction, chemical coagulation, etc.
Forecast
The generalized form of the disease, which is the most common, has a favorable prognosis. This is especially true in cases where the patient managed to seek help from a specialist in time. A less common form, septic, can already pose a serious threat to human health and life.
According to statistics, only 0.25% of infections lead to death. It is important to remember that after recovery, the patient will have immunity from the disease for only ten months from the moment of recovery. After this period, the person is again vulnerable to the pathogen.
Prevention
In most cases, the source of infection is animals or products obtained from animals. The rules of prevention in this case are quite simple.
These include:
- In order to protect yourself as much as possible from the disease, you need to stop eating raw meat, fish and eggs. The risk of infection is quite high, since even after several hours of cooking, salmonella may not die. When meat is thicker than 15 centimeters, the likelihood that the bacterium will survive increases significantly. Before cooking, the meat must be cut into thin slices.
- Since poultry is also quite often a carrier of the pathogen, special attention should be paid to the preparation of eggs. The duration of their cooking should not be less than six minutes. On the very surface of the shell there may be particles of bird droppings containing the pathogen. Hands should be washed thoroughly with soap after contact with the shell. There is an exception to this rule. Quail eggs are practically not susceptible to bacterial infection, so they can be eaten even raw.
- To cut raw foods, you need to use a separate knife and a cutting board. All utensils used for raw meat, poultry and fish should be washed thoroughly after use and never used for other products.
- Do not consume raw milk. You can only drink boiled or pasteurized.
- Bacteria can also live in foods that may not be related to animals. In particular, these include confectionery and baked goods, for the preparation of which contaminated eggs can be used. You should avoid buying food from street vendors.
The remaining precautionary rules are identical to ordinary hygiene rules.
They are:
- regular hand washing after walking outside or contacting animals;
- refusal to drink unboiled water;
- strengthening the immune system;
- treatment of chronic diseases that make the body more vulnerable to infection.
Due to the fact that there are many types of bacteria that lead to salmonellosis, vaccination against this disease is not done. It is impossible to make a universal vaccine that could equally effectively fight all types of pathogens. Human immunity to salmonellosis wears off quite quickly, so the resulting vaccine would not be effective for long.
Ways of transmission of salmonellosis
- The primary source of infection is considered to be farm animals - cattle, pigs, horses, sheep, as well as waterfowl, in which salmonellosis is asymptomatic. These animals are capable of excreting the pathogen in urine, feces, milk, saliva for years and be a source of infection for the person caring for them during transportation, processing and storage of carcasses. Recently, unfavorable sanitary conditions for keeping chickens have led to an increase in cases of human infection with salmonellosis through chicken eggs.
- The source of infection for a person is either a patient with salmonellosis or a bacteria carrier who has no signs of the disease. When infected from person to person, the transmission mechanism is mainly fecal-oral, that is, through dirty hands, only in rare cases through contact and household contact - when caring for the sick, in a close team, especially in a hospital or kindergarten.
- A large percentage of cases of human infection occurs through food - poultry meat, animals, fish, ready-made thermally unprocessed foods - salads, fruits, confectionery products, beer.
Infection is especially dangerous for children under one year of age, since it can lead to severe generalized forms of salmonellosis, the treatment of which in children presents serious difficulties. As a child grows, his susceptibility to salmonella decreases. Any intestinal infections have seasonal fluctuations, so epidemiological outbreaks are most often observed in the hot, warm season.
Recommendations from experts
Experts recommend that when the first signs of infection appear, immediately contact a doctor, since the consequences of a delayed visit to a doctor can be extremely serious. This is especially true for pregnant women, the elderly and children, since their disease is much more difficult to treat. Despite the fact that the peak of diseases occurs in the warm season, vigilance is necessary in any season.
From this video you can learn what salmonellosis is, its symptoms and treatment in adults.
Joints
Salmonella, as typical representatives of infectious agents, along with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and gonococcus, can cause arthritis in humans.
As modern medical statistics show, arthritis is most often diagnosed in the joints of the upper and lower extremities, less often in the hip localization.
The route of entry of the main pathogen in this case is secondary - as mentioned above, salmonella actively multiply and are localized mainly in the intestines, but with blood or lymph they enter the joint and form a new focus of infection.
Patients of the older age group are more susceptible to this process, and they also exhibit the most striking symptoms of the pathology, including:
- Intoxication with sudden onset;
- Swelling of the affected joint;
- Pain when moving;
- The increase in temperature is local at first, and when the process generalizes, general.
The principles of treatment of infectious arthritis are the main therapy for salmonellosis, joint immobilization, application of compresses, bed rest.