Often girls develop a negative attitude towards sex after the start of sexual activity. And the reason for this is not upbringing, not moral principles, but an elementary fear of conception. In the age of the latest medical technologies, abortion is not painful, but what is the physical pain worth in comparison with mental experiences.
Not many people dare to give birth to one child after another, and they often have to terminate a pregnancy against their will. Afraid of getting pregnant, the girl looks for excuses to avoid the embrace of her husband, and the harmony of family life begins to collapse right before her eyes.
All this can be avoided if you use birth control pills correctly. Issues of contraception are successfully covered by gynecologists at SM-Clinic. They will find an individual approach to the patient and offer the optimal solution in the current situation, providing a list of remedies to choose from.
Types of birth control pills
Pharmacies offer a huge number of varieties of pills that protect against conception. It's easy to get confused in such diversity. The first thing that is important to remember: drugs are divided into two large groups:
- combined (COC);
- mini-pill.
What is the difference between these types of tablets? They differ in content and principle of operation. Each type is suitable for a certain age group and has its own contraindications. Naturally, comprehensive information on medications can only be obtained from a specialist: prepare your questions to your gynecologist.
COC: types and principle of action
COCs contain synthetic analogues of progestogen and estrogen. The drugs are divided into phase groups according to the variation of hormone-containing components:
- Monophasic. The content of the two hormones does not change per package.
- Two-phase. The amount of estrogen in each pill is the same, but the amount of progestogen varies between cycles.
- Three-phase. The package contains tablets with different hormone contents. The dose changes three times per cycle.
There is another classification of COCs: according to the quantitative indicator of active substances. There are three types of oral hormonal contraceptives:
- Microdosed. Due to the minimal hormone content, the drugs are considered as safe as possible. However, they are not suitable for everyone. This is an ideal option for young girls. It is recommended to start getting acquainted with hormonal drugs for conception with such tablets.
- Suitable tablets have a beneficial effect on appearance
Low dosage. They are optimally suited for protection in adulthood. They can be taken after childbirth (subject to cessation of lactation). The products are also indicated for young girls, but only if tablets with a microdose of hormones are not suitable for them. Such drugs also help improve appearance: if the tablets are chosen correctly, then in some cases they “work” to reduce skin greasiness and help get rid of acne and seborrhea.
- Highly dosed. Due to their high hormone content, the pills can be dangerous. They can only be used as prescribed by a doctor. This type of COC is used in the treatment of hormonal imbalances and in the treatment of “female” diseases.
How do COCs “work”? The mechanism is simple: they block ovulation by inhibiting luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones. The main function of the ovaries is also blocked, the uterine mucosa changes, and the mucus of the cervical canal thickens. Combined contraceptives “work” on all fronts. Thanks to the pills, the path of sperm is hampered, and implantation becomes impossible. This principle of action is the key to the 100% effectiveness of the tablets (of course, if the dosage regimen is not violated).
What is a mini-pill
The main difference between a mini-pill and a COC is that it contains only one hormone. The active ingredient in monocomponent tablets is progestogen. Mini-pills do not affect the entire reproductive system, but certain areas of it. Under the influence of the pills, the structure of the endometrium changes. It becomes loose, which reduces the possibility of implantation to zero. Changes also affect the cervical fluid. By the middle of the cycle, there is a noticeable decrease in the volume of mucus, its viscosity remains the same in all phases. High viscosity of the cervical fluid is necessary to create unsuitable conditions for the movement of sperm. The mini-pill can also block ovulation, but the blocking occurs only half the time. At the same time, the pills are considered effective, because even in the presence of ovulation, implantation is impossible due to various changes in the body.
Mini-pills are popular among women who have recently given birth to babies. The advantages of the drugs include their compatibility with lactation. Mini-pills give a woman who has recently become a mother the confidence that a new pregnancy will not occur until the body recovers. Mini-pills can be taken not only by breastfeeding women: the gynecologist prescribes such contraceptives if there are contraindications for taking COCs.
How to protect yourself while taking combined contraceptives
If it is difficult to quit smoking, but such a need has arisen in connection with the use of OCs, you can use auxiliary means that suppress the craving for smoking. The range of modern pharmacological products is diverse. Many of them have proven themselves well in practice. Everyone can find a convenient form of release for themselves.
Lollipops
Such drugs are available without a doctor's prescription. They contain medical nicotine. Regular consumption of pills reduces withdrawal symptoms without causing harm to the body. The active substance of an alkaloid nature in safe doses enters the blood, as a result of which the feeling of discomfort disappears.
Former smokers note their convenience due to their compact size and optimal speed of action (4-6 minutes). Women say that lollipops cope well with hunger. For females, the problem of gaining weight when quitting smoking is always relevant. The most popular in the post-Soviet countries are Nicotinette and Nicomel lollipops.
Chewing gum
Regular or nicotine-containing gum can be used. During the chewing process, nicotine from them enters the oral cavity and is absorbed through the mucous membrane and saliva. They also help fight the urge to take up a cigarette and alleviate smoking withdrawal symptoms. The dose of nicotine may vary. Nicorette elastic bands have proven themselves well.
Pills
Medicines in tablet form can be divided into three types:
- nicotine-containing (Tabex);
- antidepressants (Zyban, Brizantine);
- blockers (Champix).
Tablets of the first group act by analogy with lollipops and chewing gum. Antidepressants affect the parts of the brain responsible for the formation of smoking addiction. And the third group of drugs allows you to form an aversion to smoking by binding to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain.
Tablets for the age group “35+”
From the age of 35, the reproductive system of women begins to gradually fade away. The production of two important hormones by the ovaries - estrogen and progesterone - is reduced. After this milestone, chronic diseases worsen, the risk of thrombosis increases, and the likelihood of heart problems increases. In order not to harm your own health, you need to take a responsible approach to choosing contraceptives. It is important that the pills aimed at preventing conception are:
- The main conditions when choosing are safety and reliability
as reliable as possible;
- safe;
- with a minimum of side effects;
- with a high degree of tolerance.
Preference should be given to the latest generation drugs. Their improved formula minimizes the likelihood of side effects. Such tablets provide maximum protection against unplanned pregnancy, which is especially important after 35.
As for the dosage of hormones in drugs, women in this age category are recommended to take low-dose COCs. The fewer hormones the tablets contain, the higher their tolerance, which is important if the processes of decline of the reproductive system are started. The minimum dose of hormones after 35 is 20 mcg. This amount is contained in microdosed COCs, but they are rarely prescribed, because they are suitable for the protection of young girls. Usually, microdose tablets are used if for some reason a woman over 35 cannot choose a drug from the group of low-dose COCs.
Drugs with a high content of hormones can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor. They are often prescribed for women aged 35+. At this age, diseases of the reproductive system make themselves felt, hormones become loose. Contraception helps cope with such problems.
Reviews and opinions of doctors
Doctors recommend undergoing examination to select hormonal contraceptives. The minimum list is blood tests, a vaginal smear, a coagulogram and a biochemical study. For women who smoke, as well as those with uncontrolled diabetes, gynecologists recommend drugs without estrogen.
Janine's pills were selected together with the doctor, and it worked the second time, because... After the first drug, spotting appeared. Now there are no problems, I don’t notice any side effects.
I set a reminder to remember to take my pills. Apart from the need to take the drug at the same time every day, I don’t notice any other inconveniences.
source
Features of the selection of hormonal contraceptives
The selection of contraceptive pills should be done by a doctor. The prescription of drugs is preceded by anamnesis and various tests. This is the only way a gynecologist can determine which pills will not only be effective, but also safe. When prescribing contraceptives, the following are decisive:
- blood sugar test;
- liver enzyme test;
- assessment of blood fluid clotting;
- study of hormonal levels;
- oncocytology;
- ultrasound examination of the mammary glands and pelvis.
The determining factor is the presence of any chronic diseases. For some diseases (for example, problems with the liver, heart), hormonal pills are prohibited, while for others (endocrine diseases), on the contrary, such drugs are necessary.
If you choose contraceptives on your own, the consequences can be sad. A woman cannot objectively assess the condition of her body, hence a number of side effects: from sudden weight gain to diseases caused by hormonal imbalance.
The importance of phenotype in the selection of tablets
Not only test results are decisive when prescribing tablets. The selection of hormonal contraceptives is always carried out taking into account the constitutional and biological type of the patient. The decisive ones here are:
- Self-administration of any drugs is very dangerous for health.
skin condition;
- body hair;
- height;
- body mass;
- breast development;
- features of menstruation;
- presence/absence of PMS.
According to constitutional and biological characteristics, three groups of women are distinguished. When prescribing contraceptives, the doctor must take into account the patient’s membership in a certain group. The following phenotypes are distinguished:
- Estrogen dominance. Signs: Average/short height. Dry skin. Hair suffers from dryness. Feminine look. Prolonged menstruation, accompanied by significant discharge. The cycle consists of more than 4 weeks. Tablets: Low and high dose.
- Balanced. Traits: Average height. The chest is medium, well developed. Good skin and hair condition. Absence of premenstrual phenomena. Menstruation occurs exactly four weeks later and lasts five days. Tablets: second generation COC.
- Androgens/gestagens predominate. Signs: Tall. "Male" facial features. Underdeveloped breasts. Problem skin and oily hair. Short cycle with scanty menstruation. During the premenstrual period, severe pain in the lower abdomen is observed. Tablets: Containing an antiandrogenic component.
Some women mistakenly believe that, having determined their own phenotype, they can choose their own birth control pills. This approach to choosing hormonal contraceptives can lead to health problems. The gynecologist approaches the issue comprehensively: he takes into account the phenotype, anamnesis, and test results.
What is taken into account when choosing a method of protection?
The basis for prescribing a contraceptive is taking into account:
- gynecological pathologies;
- hormonal characteristics (irregularity of the cycle, heavy bleeding, hyperandrogenism, that is, increased hair growth on the arms, legs, face, etc.);
- medical history (number of births, pregnancies, hereditary diseases, etc.);
- results of pelvic ultrasound, tests for sexually transmitted infections, oncocytology.
A woman herself cannot form an objective picture of her health, so any method of protection other than condoms must be agreed upon with a gynecologist. To consider the option of hormonal contraception, you must visit a therapist to assess your general health, and also donate blood:
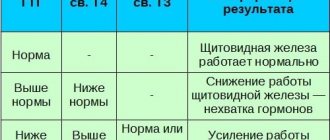
- on the level of hormones (progesterone, testosterone, prolactin, etc.), which, in turn, allows us to partially predict the body’s reaction to the substances included in the contraceptive;
- for biochemistry;
- for liver tests;
- to the level of coagulation.
Apart from condoms, all methods of contraception should be discussed with your doctor.
Principles for choosing a contraceptive
The criteria for choosing a method of contraception at any age are:
- reliability, which is assessed by the Pearl index - the lower the indicator, the more reliable the contraceptive;
- safety;
- convenience;
- minimizing side effects;
- good drug tolerance.
Due to age-related changes, in particular, exacerbation of chronic pathologies, the last two points become no less relevant than reliability and convenience.
When hormonal contraception is prohibited
Oral contraceptives, although considered the most reliable protective method against unwanted conception, are not suitable for everyone. If a woman has not stopped smoking by the age of 35, then she is strictly prohibited from taking hormonal contraceptives. Nicotine, combined with hormonal fluctuations, increases the risk of thrombosis. After thirty-five, the risk of developing heart pathologies increases, which can be facilitated by heavy smoking while taking birth control pills.
Taking hormone-containing pills is prohibited if you have:
- If you feel unwell, you should immediately consult a doctor
diabetes mellitus;
- migraine-like headaches of unknown etiology;
- liver pathologies;
- kidney diseases;
- heart diseases;
- malignant formations;
- predisposition to thrombosis.
Taking hormonal contraceptives should be stopped a month before the proposed surgery. Antibiotics reduce the effectiveness of contraception: due to changes in intestinal flora that occur while taking antibiotics, hormones are less absorbed.
Absolute contraindications to oral contraceptives
Diseases for which the use of oral contraceptives is not advisable: Gilbert's syndrome (congenital hyperbilirubinemia), bronchial asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, thyrotoxicosis, lymphogranulomatosis (symptoms, treatment), myasthenia gravis, sarcoidosis, retinitis pigmentosa, thalassemia, renal dialysis.
Absolute contraindications to combined OCs:
| Absolute contraindications to taking pure progestins:
|
At the end of the article there is a video of a TV show detailing the dangers of using OCs by any woman, since even in the absence of the contraindications listed above (the woman and the doctor may not be aware of them), a seemingly healthy woman has an extremely high risk of developing pulmonary thromboembolism and developing oncology.
Advertising campaigns from OC manufacturers convince women and doctors that reducing the amount of hormones in modern contraceptives is a progressive step and a positive thing. Any oral contraceptives, when taken for a long time, are a great EVIL for the female body, which a woman has to be convinced of much later, when the damage done to the body cannot be compensated for and lost health cannot be restored. The problem is that the effect of contraceptives is “masked” and it is almost impossible to prove that the health problems that have arisen, possible problems with further conception, oncology or pulmonary thromboembolism, or a stroke in the future could be caused by prolonged use of OCs.
Contraceptive injections
Everyone knows that hormonal contraceptives are recognized as the most effective. However, many women are confused by the need to take pills every day and follow a time schedule. If you do not follow the instructions, the guarantee will be null and void. Modern women after 35 years of age are burdened with caring for their family, building a career and engaging in self-development. In such a rhythm, it is easy to forget about taking the next pill. For these reasons, many active women choose contraceptive injections.
The action of injections is based on the same principle as oral medications. Injections also relate to hormonal protection. After the injections, ovulatory processes are suppressed, the cervix thickens, which eliminates the risk of conception. Compared to contraceptive pills, injections have a number of advantages:
- ease of use (the injection is given once every three months);
- high degree of protection due to the exclusion of force majeure;
- can be used for some female diseases (endometriosis, fibroids);
- have virtually no side effects.
Only a doctor can prescribe injections, and he also gives the injections. This method of protection is often recommended for use after 35. It is suitable for women with cardiovascular problems.
After injections, the menstrual cycle is almost always disrupted. Upon completion of adaptation, it returns to normal, but you should not use this method of protection for a long time, otherwise your period will increase. Weight gain is often observed after injections: in order not to gain weight, you will have to change your eating habits.
When choosing an injection method of contraception, you should not forget to visit the gynecological office once every six months. It is also important to regularly do oncocytology, pelvic ultrasound, and be examined by a mammologist.
Side effects of birth control drugs
Side effects are signs or conditions that develop when using contraceptives, but do not threaten women’s health. They are divided into 2 groups:
Minor side effects:
| Serious side effects:
|
In case of serious, as well as persistent minor side effects, contraception is discontinued.
Regardless of the chosen OC, a woman needs periodic assessment of her health in connection with possible side effects from taking them, namely:
- Blood pressure: measure once every 6 months
- Physical examination (breast, liver palpation, gynecological examination), urine test: 1 r/year
- Monthly breast self-examination.
It is no secret that in many developing countries, regular screening is unlikely, and there are programs (in some countries) to distribute OCs to women who do not have access to medical care. This indicates a high likelihood that OCs will be used by high-risk groups of women. Therefore, these women will have a harder time getting medical help if dangerous side effects occur.
Non-hormonal tablets
After a certain age, it is necessary to select contraceptives more carefully
After the age of 35, women often experience health problems. They make taking birth control pills with synthetic hormones impossible. However, it is important for older women to ensure reliable protection against conception, because pregnancy during this period is associated with numerous risks, and abortion can lead to irreversible consequences. New generation non-hormonal pills will come to the rescue. They belong to the group of spermicides. These tablets are intended for insertion into the vagina. This also includes gels, tampons, creams, but tablet preparations are considered the most effective.
The main component of the tablets are chemical compounds that have a negative effect on sperm. The active substances damage the sperm membrane, which leads to their death. Non-hormonal contraceptives thicken the mucus in the uterine canal, which is why sperm cannot reach their target. If particularly active sperm manage to break through the viscous liquid, they become so sluggish that fertilization is impossible.
New generation spermicides have additional protective properties. Vaginal contraceptive pills create a film on the mucous membrane through which fungus and some bacteria cannot penetrate. Non-hormonal contraception is recommended to be used in tandem with barrier protection to eliminate the likelihood of unplanned conception.
Who is suitable for vaginal tablets?
Although vaginal contraceptive pills do not contain hormones, their use must be agreed with your personal gynecologist. The components of the drug can cause allergies, so it is important to first make sure that this method of contraception is suitable in a particular case. If vaginal tablets are chosen incorrectly, itching, irritation, and allergic reactions may occur. The use of vaginal tablets to prevent pregnancy is indicated for:
- some gynecological diseases (fibroids);
- diabetes mellitus;
- contraindications to taking hormonal drugs;
- allergic reactions to latex;
- the onset of the premenopausal period.
The choice of remedy depends on the frequency of sexual intercourse
This method of contraception can be used at any age. It is optimal for women who rarely have sexual intercourse. If you have regular sex life, then for protection it is better to choose hormonal contraceptives. The use of vaginal tablets during frequent sexual intercourse can result in the development of dysbiosis.
For spermicides to “work” effectively, it is important to use them according to the instructions. You will have to plan your intimate life: the tablet must be administered immediately before contact. For a certain period of time (for each drug the time is specified in the instructions) water procedures cannot be carried out.
Types of contraceptives for women 35+
Women with regular sexual activity are more often prescribed hormonal contraceptives, which help balance hormonal levels, as well as IUDs. Installation of the IUD is recommended for women who have given birth without pathologies of the genital organs. Both methods, unlike sterilization, are reversible, which is important for women 35+ who plan to give birth again in the near future.
Forms of release of hormonal contraceptives
The most popular today are still pills as the most accessible and proven form of hormonal contraceptives.
Hormonal oral contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptive pills can be of two types:
- mini-pills with gestagens - thicken the cervical mucus and thin the endometrium, preventing the fertilized egg from settling (Pearl index - 0.5-3);
- combined oral contraceptives (COCs) containing gestagens and estrogens also suppress ovulation (Pearl index - 0.1–0.9).
The most common form of hormonal contraception is the pill.
What you need to know about COC
Based on the level of hormone content, COCs can be:
- microdosed (as a rule, prescribed to nulliparous women, as well as to those whose hormonal levels have not changed compared to young age);
- low-dose (prescribed to those giving birth with a sufficient level of their estrogen - this is exactly the most common option for women 35+);
- high-dose (recommended for women with concomitant gynecological problems).
In case of hormonal imbalance, two-phase drugs are usually prescribed, that is, with different amounts of gestagen, or three-phase drugs, with different contents of both hormones in three phases of the cycle.
How are they assigned?
When selecting a contraceptive, the doctor must also take into account the woman’s phenotype, that is, her constitutional and biological type.
Table: main phenotypes and types of hormonal contraceptives
| Phenotype | Description | Types of hormonal drugs |
| Estrogen predominant |
|
|
| Balanced |
|
|
| With androgen predominance |
| Low dosage |
Contraindications for prescribing COCs
Among the contraindications common to all COCs are:
- breastfeeding (the composition changes and the amount of milk decreases);
- suspicion of pregnancy;
- hormone-dependent diseases of the mammary glands/genital organs;
- predisposition to thrombosis;
- angina pectoris, ischemic attacks;
- liver diseases;
- pancreatitis;
- renal failure;
- diabetes;
- vaginal bleeding of unknown etiology;
- migraine;
- nicotine addiction;
- obesity.
Table: COCs most often prescribed to women 35+
| Name (hormone level/hormone concentration) | Indications for additional action (besides contraception) | Side effects |
| Janine (low dose/monophasic) |
|
|
| Regulon (low dose/monophasic) | Treatment of menstrual irregularities, dysmenorrhea and dysfunctional bleeding in the uterine cavity. |
|
| Jess (low dose/monophasic); Jess Plus with folic acid for women planning pregnancy. |
|
|
| Logest (low-dose/monophasic) |
|
|
| Yarina (low dose/monophasic) |
|
|
| Lindinet-30 (low-dose/monophasic) |
|
|
| Klaira (microdosed/three-phase) contains estrogen identical to natural, therefore it has virtually no effect on metabolic processes in the body |
|
|
| Marvelon (low dose/monophasic) |
|
|
| Tri-regol (high-dose/three-phase), the analogue is more expensive - Triquilar |
|
|
| Triziston (high-dose/three-phase) | In addition to the described effects of the drug Tri-Regol, increased stress on the vocal cords is added, and therefore is not recommended for women whose activities involve stress on this instrument. | |
| Ovidone (high dose/monophasic) | It is recommended for women with an estrogenic phenotype, since the drug contains an increased concentration of levonorgestrel, a synthetic progestogen. |
|
Hormonal oral contraceptives require compliance with the dosage schedule
When are mini-pills prescribed?
After 35 years, mini-pills are often prescribed if a woman has given birth, since such patients usually have enough of their own estrogen, and excess can cause active production of testosterone, which will provoke increased hairiness, sebum production, and the appearance of a purulent rash. In addition, excess estrogen provokes hardening of the uterine tissue, which increases the risk of developing inflammation and cancer.
Mini-pills are also indicated for smokers, since estrogen-containing drugs (COCs), while increasing blood clotting, increase the risk of thrombosis under the influence of nicotine, which triggers the mechanism of narrowing of the lumens and blockage of blood vessels.
Table: mini-pills most often prescribed to women 35+
| Name | Indications for use | Contraindications (main) | Side effects |
| Femulen | Due to the fact that the main active elements are norethindrone and levonorgestrol, they are prescribed to women with contraindications to estrogens and gestagens, during lactation and with a tendency to headaches. |
|
|
| Lactinet (cheaper analogue of Charozetta) | Appointed for:
| ||
| Exluton | Prescribed for women with high blood pressure |
Other hormonal contraceptives
Women who are not contraindicated for hormonal contraception, but who have problems with the gastrointestinal tract, as well as those who, for various reasons, cannot monitor the systematic use of the drug or take medications that can reduce the contraceptive effect of hormonal pills, may be offered other options for hormonal contraception.
Injections
The Pearl index of this product is 0.3–1.4. The essence of the action is that after administration of the drug, the hormone is collected in a special “reservoir” and from there it is released into the blood in doses. Injections are convenient for lactation, as well as for contraindications to taking estrogen, immediately after an abortion or miscarriage. But for women 35+, it is important to consider that this method of contraception can:
- promote weight gain, therefore it is contraindicated for women weighing more than 90 kg;
- cause menstrual irregularities, even amenorrhea.
If a woman is planning a pregnancy in the near future, she must remember that after completion of contraception in injection form, the effect of the drug lasts up to 3 months.
Despite the fact that the effect of injection drugs on the development of osteoporosis has not been proven, if there are risk factors for this disease, doctors recommend abandoning this method of protection, especially for women over 30.
Preparations:
- Depo-Provera (the most common in Russia and the CIS countries), the injection is given 4 times a year, it is also prescribed for breast cancer, endometrial cancer, kidney cancer and some other conditions;
- Mezigina, Cyclofem (injection given once a month);
- Net-En (injection is given once every 8 weeks).
The injection is given either in the shoulder or in the buttock, and there are two methods of administration: intramuscular and subcutaneous
Implant
Pearl index - 0.8. The essence of this method is that, using a special applicator, a capsule with a hormone that suppresses ovulation is sewn subcutaneously into the shoulder area. With the same indications as for the injection, the implant has a significant advantage for women 35+ who are not planning a pregnancy, but do not dare to take drastic measures (sterilization) for some reason: the implant provides a contraceptive effect for up to 5 years. Moreover, this method of protection is safe during lactation and reduces pain during menstruation, it is reversible, that is, the capsule can be removed at any time. However, he:
- can cause infertility, since the ovaries are exposed to prolonged exposure to a hormone that inhibits their function;
- increases the risk of disruptions in the monthly cycle;
- requires a mandatory visit to the doctor to insert and remove the capsule, since incorrect manipulation may leave a mark;
- may cause allergies.
Preparations:
- Norplant (set for 5 years);
- Norplant-2 (installed for 3 years).
Some women note that the implant is unaesthetic: the capsule can be felt under the skin
Hormonal patch and hormonal ring
These are variants of microdosed hormonal drugs, that is, after 35 they are usually prescribed to nulliparous people who have not used hormonal contraception before. The patch (Pearl index - 0.9) and the ring (Pearl index - 0.4–0.6) have the same set of contraindications and side effects, but these drugs are based on a different method of delivering the hormone into the bloodstream. The patch is applied to the abdomen (buttocks, shoulder blade, outer shoulder) once every three weeks, after which a week-long break is taken. The hormonal ring is inserted into the vagina according to the same schedule. From the patch, hormones enter through the skin, and from the ring through the mucous membrane. However, the patch may become dirty or come off without the woman noticing.
Many women put a patch on their shoulder
If inserted incorrectly, the ring may not only cause inconvenience, but also not provide the desired effect. In addition, the hormonal ring is contraindicated in case of cervical prolapse (after a difficult birth, due to excess weight, etc.), as well as in the first six months of lactation before the introduction of complementary foods, as it can affect milk volumes.
In Russia and the CIS countries, the most accessible are the Evra patch and the NuvaRing ring.
A doctor tells a woman about the rules for inserting and removing a ring.
Video: is there a risk of developing cancer when using hormonal contraception?
Intrauterine device
Pearl index - 0.8–1.9. The IUD is placed for a long period of time, which is convenient for those who have given birth and have regular sexual activity with one man. The device reliably protects against unwanted pregnancy, preventing the fertilized egg from attaching to the wall of the uterus, and has a positive effect on the body. For example, the Goldlily IUD provides an additional bactericidal effect due to the gold included in the device. Modern IUDs, in particular Mirena, do not allow this method of contraception to be classified exclusively as non-hormonal, since Mirena contains hormones that have a concomitant effect on a woman’s health. For women 35+, installation of the IUD may be contraindicated if inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, infections, cervical erosion (including after childbirth) or PCOS (as a result of age-related hormonal changes) are diagnosed. And among the consequences of using the IUD are the likelihood of increased pain during menstruation, as well as complications if it is inserted incorrectly into the uterine cavity.
Among the most popular options, in addition to Mirena, are:
- Multiload - a spiral in one size, therefore suitable for women in whom, after measuring the size of the uterus with a probe, the length of its cavity is from 6 to 9 cm, is installed for 4 years, is contraindicated for women with an allergy to copper or taking immunosuppressants;
- Koper - a feature of this spiral is a greater release of copper in the uterine cavity, which causes a stronger local reaction, is established for a period of up to 6 years;
- Goldlily - gold in the composition has a powerful bactericidal effect and prevents the occurrence of inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, is established for a period of up to 7 years;
- Juno Bio-T with Silver - prevents the formation of adhesions in the uterine cavity, protects the woman’s body from inflammatory diseases and other infectious complications associated with the presence of the spiral in the uterine cavity, is established for a period of up to 7 years;
- Nova T - thanks to its convenient T-shape, it is suitable for most women, similar to Multiload, but installed for up to 5 years.
The shape of the IUD is selected according to the characteristics of the female body: the most common shape is T-shaped, if due to the structure of the uterus it cannot be placed, then an umbrella-shaped spiral is installed, and after an abortion, a ring-shaped one is placed
Barrier contraceptives
In addition to protection against unwanted pregnancy, an important advantage of barrier contraceptives, in particular condoms and spermicides, is protection against sexually transmitted infections. Thus, condoms, when used correctly, provide up to 96% protection.
For mature women, barrier methods are usually indicated for irregular sexual activity, multiple sexual partners, as well as for the period of treatment of gynecological or other diseases for which other contraceptives cannot be used.
Preference is also given to condoms immediately after the end of lochia during lactation.
Condoms and spermicides
If we compile a conditional rating of barrier contraceptives, then the first place will go to condoms, the use of which does not require the approval of a doctor. Condoms are often recommended for couples for whom direct contact between the penis and vagina is contraindicated during the period of treatment (for example, infections). Among the most popular condoms in terms of price and quality are:
- Durex;
- Okamoto;
- LifeStyles;
- VIZIT;
- My.Size;
- Masculan.
The condom is the most famous, safe and affordable method of barrier contraception
If you are allergic to condoms, or if a woman is faced with vaginal dryness - a common problem caused by an age-related decrease in the production of hyaluronic acid, the molecules of which retain moisture in the skin and mucous membranes - spermicides are recommended, occupying the second position in the conditional rating:
- foam or jelly (Delfinon, Patentex, Emko Coromex);
- vaginal suppositories (Pharmatex, Erotex, Contratex, Patentex Oval);
- vaginal tablets (Benatex, Gynecotex, Traceptin);
- creams (Pharmatex);
- foaming tablets (Pharmatex);
- foaming suppositories (Pharmatex, Erotex);
- soluble films (Pharmatex);
- vaginal tampons (Pharmatex);
- sponges (Pharmatex).
The form of the drug is recommended by a specialist, based on convenience and the desired effect.
Spermicides may cause local allergic reactions in both partners
Diaphragm and cap
Both devices are placed on the cervix. The cap, unlike the diaphragm, can be adjusted to the length and tone of the uterus. The Pearl index at the diaphragm is 6–20, at the cap it is 9–20. The wide range of Pearl index values is determined by the factors by which it is calculated, including the correct operation of the device. Therefore, the diaphragm and cap occupy the last place in the conditional rating.
Women after childbirth will have to change the size of the devices, as the tone of the vaginal muscles changes. The diaphragm and cap are contraindicated in women with cervical erosion, with bending and prolapse of the vaginal walls.
The most popular and affordable diaphragms are:
- Ramses;
- Rantos;
- Duraflex.
The diaphragm is a rubber or latex dome-shaped cap with a flexible rim
The most famous caps on the domestic market are:
- devices manufactured by Laboratoire CC;
- FemCap.
The cap is a latex cap-shaped product, half the size of the diaphragm, placed on the cervix
Sterilization
Surgical contraception, that is, sterilization, is an irreversible way to protect against unwanted pregnancy, since during the operation (during cesarean section, through punctures or incisions on the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity - during laparoscopy or mini-laparotomy, respectively), tubal ligation is performed. Many women over 35 who do not plan to have children still do not consider sterilization due to possible complications. However, some of them, namely the probable change in hormonal levels, as well as the acceleration of the onset of menopause, are nothing more than a myth. As for manifestations of a real threat, such consequences include:
- the risk of complications during the operation, for example, an allergic reaction to anesthesia;
- the likelihood of formation of adhesions in the pelvic organs;
- the risk of an umbilical or inguinal hernia.
Sterilization is possible only when a woman is definitely not planning a pregnancy
Natural methods of birth control
These contraceptive options can be classified as “last resort” when there is no other option for protection:
- calendar method (Pearl index - 25–40), that is, a ban on sex on days when there is a high probability of becoming pregnant;
- interrupted sexual intercourse (Pearl index - 2–3), that is, removal of the penis from the vagina before ejaculation;
- lactational amenorrhea (Pearl index - 4–18) - the use of hormonal changes that occur in a woman’s body during lactation, when, under the influence of the active production of prolactin, the production of progesterone is suppressed, as a result of which the egg does not come out, the uterus does not change, and menstruation does not occur.
There are many disadvantages to natural methods of contraception. First of all, this is unreliability and lack of protection from sexually transmitted infections. The last factor is very important for women who do not have a regular sexual partner. There are also a number of disadvantages associated with a specific contraceptive option. For example, interrupted intercourse is not effective, since viable sperm may be contained in the lubricant that is released from the penis even before ejaculation. And with lactational amenorrhea, a woman must strictly adhere to the rule of feeding on demand, and without fail at night, without supplementing or feeding the baby.
For women 35+, emergency contraception is contraindicated, since high doses of hormones contained in the drugs can provoke thrombosis.
Can I use emergency contraception?
There are times when protection is necessary after the fact. Unprotected sex, a torn condom, missing birth control pills - all these factors force a woman to look for post-coital methods of contraception.
There are emergency pills. They are taken after sexual intercourse, if the risks of untimely pregnancy are high. The action of emergency contraceptive drugs is aimed at inhibiting ovulatory processes, changes in the endometrium, and rejection of the fertilized egg. Postcoital tablets contain a huge dose of hormones, so they are strictly forbidden to be considered as a regular contraceptive method. The use of emergency medications is permissible no more than twice a year.
If up to the age of 35 a woman can occasionally turn to emergency contraception, then after this age she should forget about this method. A high dose of hormones in postcoital pills is dangerous due to the possibility of blood clots, which leads to stroke and even death. After 35 years, the likelihood of developing blood clots increases significantly. Such pills are especially dangerous for women who smoke. With the disappearance of the opportunity to use emergency contraception, you need to reconsider your approach to birth control issues. As you age, it is important to choose the most reliable means, consulting your gynecologist about each.
Hormonal contraceptives and possible pregnancy
Can you get pregnant while taking birth control?
This question worries many women. Of course, pregnancy while using hormonal oral contraceptives is not excluded, but its likelihood is too low.
- First of all, unwanted pregnancy occurs when the rules for taking pills are violated (missing, irregular, taking at different times, the drug has expired).
- You should also take into account possible vomiting in case of poisoning or combined use with drugs that reduce the contraceptive effect of hormonal pills.
Is it possible to take contraceptives when pregnancy has already occurred or is suspected?
The answer to this question is negative. If pregnancy occurs after taking contraceptive drugs, it is desired, then there are no indications for its termination (interruption). You just need to stop taking the pills right away.
Intrauterine devices after 35
A popular method of contraception for women over 35 years of age is the IUD. It is inserted into the uterine cavity. The plate acts on the epithelium and prevents implantation from occurring. If there is a spiral, foam forms in the uterine cavity, which interferes with the movement of sperm.
In terms of effectiveness, this method is equal to hormonal birth control pills, but in terms of convenience it takes the lead. The economic factor also speaks in favor of the spiral: the cost of installing a plate is much lower than when taking pills regularly.
Why then do not all women get IUDs? It's easy to explain. Closer to forty years, age-related changes in the reproductive system begin to occur, in particular, the tissue of the cervix takes on a pathological appearance. This makes installation of the spiral impossible. The appropriateness of this method of contraception can only be determined by a gynecologist after a complete examination of the patient.
Surgical contraception
There are also irreversible methods of contraception.
These include sterilization. After the surgical method of contraception, the possibility of conception disappears forever. The operation is aimed at ensuring obstruction of the fallopian tubes. Women over 35 years of age turn to this method of contraception for medical reasons. There are a number of conditions in which pregnancy (ending in childbirth or abortion) is strictly prohibited: it carries risks to life. Such circumstances require one hundred percent guarantees. In other cases, the doctor will help you choose a reliable, but not radical, method of contraception.