Release form and composition
- Capsules: size No. 0, gelatin, yellow; contents – granules of almost white or white color (in blister packs of 6 pcs., 1 pack in a cardboard pack);
- Powder for the preparation of a suspension for oral administration (for children): almost white or white in color, with the smell of orange; ready-made suspension - homogeneous, white with a yellowish tint (in single-dose bags of 4.2 g, in a cardboard pack of 3 or 6 bags, a cup may be included in the kit; 100 mg/5 ml - 17 g each, 200 mg/5 ml - 25 g each in dark glass jars, in a cardboard pack 1 jar complete with a dosing spoon and dispenser or a 2-sided dosing spoon).
Composition of 1 capsule:
- Active substance: azithromycin (in dihydrate form) – 250 mg;
- Excipients: microcrystalline cellulose, calcium stearate, polyvinylpyrrolidone;
- Capsule shell composition: gelatin, propyl hydroxybenzoate, titanium dioxide, acetic acid, methylhydroxybenzoate.
Composition of 1 packet of powder:
- Active substance: azithromycin (in dihydrate form) – 50, 100 or 200 mg;
- Excipients: sucrose, sodium saccharinate, sodium citrate (sodium citrate trisubstituted), Kollidon CL-M (crospovidone), orange food flavoring.
Consumers praise Azitrus
Most of the patients to whom the medication was prescribed by a doctor are satisfied with its effect. The first reason why consumers like Azitrus is the price. As you already know, the medication is inexpensive (even if you need to purchase two packages of the drug). The second reason that makes consumers choose this medication for a child is its convenient use. You only need to take the medicine once a day. Many children have problems using any medications. But the drug "Azitrus" has a sweet orange taste. Therefore, your baby will easily drink the prepared solution. The third advantage of the medicine is its effective action. The drug begins to work immediately after administration. Thanks to its liquid consistency, it is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream, performing its main functions.
Parents of children who were prescribed this medication report that within 24 hours after taking the drug, the child’s temperature dropped and overall health improved. There are also opposing opinions. Some children, on the contrary, developed a fever after taking the antibiotic. What does this mean? Doctors say that using the medicine causes massive death of bacteria and harmful microbes. They are toxic. That is why the baby’s temperature may rise sharply on the first day of treatment. There's nothing wrong with that. Continue to give the medicine and monitor the child's condition.
Indications for use
AzitRus is used to treat infectious and inflammatory diseases of organs and systems caused by sensitive microorganisms:
- ENT organs and upper respiratory tract: sinusitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, otitis media;
- Lower respiratory tract: bronchitis, exacerbation of chronic pneumonia, bacterial infections, including those caused by atypical pneumonia pathogens;
- Skin and soft tissues: secondary infected dermatoses, impetigo, erysipelas;
- Urinary tract: urethritis (including gonorrheal);
- Female genital organs: cervicitis.
AzitRus is also used to treat the following diseases:
- Scarlet fever;
- Creeping erythema (erythema migrans) – the initial stage of Lyme disease (tick-borne borreliosis);
- Diseases of the stomach and duodenum associated with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori (as part of complex therapy).
Summarize
From the article you learned about the inexpensive antibiotic “Azitrus” (powder for children). Instructions for use, photos of the drug are presented to your attention. If after two days of using the medication your baby does not feel better, and the signs of the disease increase, this indicates the ineffectiveness of the drug. There is no need to continue treatment further. See your doctor as soon as possible. You probably need other antibiotics. This situation is often encountered by patients who have not undergone a preliminary test for the sensitivity of microorganisms. This is why it is so important to seek help from qualified doctors. After all, your baby’s health depends on them. Remember that incorrect use of antibiotics can only worsen the course of the disease. Good health to your child!
Directions for use and dosage
AzitRus should be taken orally 1 time per day 1 hour before meals or 2 hours after meals.
Recommended dosages for adults depending on indication:
- Respiratory tract infections: 500 mg/day for a 3-day course;
- Infections of the skin and soft tissues, creeping erythema: day 1 – 1000 mg, days 2-5 – 500 mg;
- Uncomplicated urethritis and/or cervicitis: 1000 mg once;
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum caused by Helicobacter pylori (as part of combination therapy): 1000 mg/day for 3 days.
Recommended doses for children:
- Infections of the respiratory tract, soft tissues and skin: on the 1st day 10 mg/kg, over the next 4 days - 5-10 mg/kg/day or 10 mg/kg 1 time per day for 3 days;
- Erythema creeping: day 1 – 20 mg/kg, days 2-5 – 10 mg/kg/day.
For children over 6 months of age, AzitRus is prescribed in the form of a suspension prepared from powder.
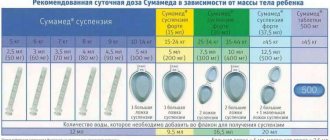
Recommended daily (single) doses of the suspension depending on the child’s body weight when using powder at a dose of 100 mg/5 ml - azithromycin (suspension):
- 5 kg – 50 mg (2.5 ml);
- 6 kg – 60 mg (3 ml);
- 7 kg – 70 mg (3.5 ml);
- 8 kg – 80 mg (4 ml);
- 9 kg – 90 mg (4.5 ml);
- 10-14 kg – 100 mg (5 ml).
Recommended daily (single) doses of the suspension depending on the child’s body weight when using powder at a dose of 200 mg/5 ml - azithromycin (suspension):
- 15-24 kg – 200 mg (5 ml);
- 25-34 kg – 300 mg (7.5 ml);
- 35-44 kg – 400 mg (10 ml);
- From 45 kg – doses for adults (from 500 to 1000 mg).
Rules for preparing a suspension for oral administration: pour a small amount of boiled and cooled water into a clean glass, pour out the contents of 1 packet and stir until a homogeneous suspension is obtained. After taking the drug, rinse the glass with clean water, dry and store in a clean, dry place.
Contraindications
- liver and/or kidney failure;
- breastfeeding period;
- age up to 6 months - for suspension; up to 3 years and/or body weight less than 25 kg – for capsules;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug or other macrolides.
The drug should be used with extreme caution in the presence of cardiac arrhythmias (due to the possible threat of prolongation of the QT interval, ventricular arrhythmias), as well as in children with severe functional disorders of the kidneys and/or liver.
During pregnancy, taking the drug is possible only if the expected benefits of therapy significantly outweigh the possible risk of complications.
Side effects
- Allergic reactions: rash, itching, urticaria, angioedema; in children – itching, urticaria, conjunctivitis;
- From the digestive system: >1% – abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea; ≤1% – melena, vomiting, flatulence, increased activity of liver transaminases, cholestatic jaundice; in children (≤1%) – changes in taste, loss of appetite, candidiasis of the oral mucosa, constipation, gastritis;
- From the urinary system: ≤1% – nephritis;
- From the central nervous system: ≤1% – headache, dizziness, drowsiness; in children (≤1%) – sleep disturbances, anxiety, hyperkinesia, neurosis, headache (in the treatment of otitis media);
- From the cardiovascular system: ≤1% – chest pain, palpitations;
- From the reproductive system: vaginal candidiasis;
- Other: photosensitivity, asthenia.
Pharmacological properties
Antibiotics with a broad spectrum of activity have a specific effect on the body. The drug helps:
- cope with pathogenic microorganisms, stop the process of their growth and reproduction;
- destroy the membrane connection between pathogenic bacteria, preventing their reproduction inside the body.
Information: azithromycin is active against a large number of pathogenic agents, leads to the death of bacteria, and is used in a course.
The drug is used in the treatment of bacterial diseases, as well as in case of complications during a viral or fungal infection.
The antibiotic has the ability to accumulate in tissues, thereby increasing the effectiveness of treatment. When taken as a course, the effectiveness of the drug increases, but after discontinuation the concentration of the active substance decreases. This happens within a day.
special instructions
AzitRus should not be taken with food.
If you miss a regular dose, the missed dose should be taken as quickly as possible, and subsequent doses should be taken at intervals of 24 hours.
When concomitantly prescribing antacids, a break of at least 2 hours should be observed between doses of the drugs.
After discontinuation of AzitRus, some patients may experience hypersensitivity reactions; in these cases, specific therapy under medical supervision is recommended.
When prescribing high doses of the drug, you can take film-coated tablets, AzitRus forte at a dose of 500 mg.
Additional information, analogues
You already know how the medicine “Azitrus” (powder) is used for children. Instructions for use and indications are presented to your attention. It is also worth considering additional information. The medication is not recommended to be used with food. This therapy may be less effective because the absorption of azithromycin slows down. If you forget to give your baby the next portion, then you should not wait for the next dose. Offer him the medicine right now, and take the next dose in a day. Do not use a double dose if you miss a dose. The drug should be taken for at least three days. With early withdrawal, resistance of microorganisms to the active substance occurs. The drug "Azitrus" has a prolonged effect. The effect of the medication is observed 2-4 days after its discontinuation. If for some reason the antibiotic “Azitrus” (for children) is not suitable for your child, the instructions for use recommend replacing the powder with another antibiotic. But this should be done only after consulting a doctor.
Structural analogues based on azithromycin include the drugs “Sumamed”, “Azithromycin”, “Azivok”, “Sumaklid” and others. If we talk about macrolides in general, then the drug “Azitrus” can be replaced with “Arvicin”, “Vilprafen”, “Klacid” and other drugs. In case of an allergic reaction and severe side effects, the medication is often replaced with cephalosporins (Cefatoxim, Suprax).
Drug interactions
- Aluminum- and magnesium-containing antacids, ethanol and food: absorption of azithromycin slows down and decreases;
- Digoxin: its concentration in the blood plasma increases;
- Ergotamine, dihydroergotamine: their toxic effect increases (dysesthesia, vasospasm);
- Triazolam: its clearance decreases and its pharmacological effect increases;
- Lincosamines: the effectiveness of azithromycin decreases;
- Tetracycline, chloramphenicol: the effect of azithromycin is enhanced;
- Indirect anticoagulants, felodipine, methylprednisolone, cycloserine and drugs subject to microsomal oxidation (oral hypoglycemic agents, ergot alkaloids, cyclosporine, bromocriptine, terfenadine, disopyramide, hexobarbital, phenytoin, valproic acid, carbamazepine, xanthine derivatives, including theophylline): their elimination slows down, plasma concentrations and toxicity increase.
Since macrolides, interacting with warfarin, enhance its anticoagulant effect, a similar effect can be expected with the simultaneous administration of AzitRus, therefore prothrombin time should be carefully monitored.
Possibility of combination with other means
Does the instructions for use allow taking the medicine “Azitrus” (for children) with other drugs? The powder is often used in combination with probiotics and antifungal drugs. Such combinations avoid side effects. Antiviral agents and immunomodulators are often prescribed. During the treatment of bronchitis and pneumonia, mucolytic compounds are used. It is not prohibited to combine such means. But there are drugs that you need to avoid during antibiotic therapy.
Medicines containing magnesium, aluminum and ethanol slow down the absorption of Azitrus. Additional antibiotics increase the toxic effect of azithromycin. At the same time, the maximum therapeutic effect is achieved. Lincosamine drugs reduce the effectiveness of the active substance.
Similar medicines
Azithromycin has no direct analogues, but there are certain antibacterial agents that can be used in the treatment of infectious diseases of various origins.
Hemomycin
Belongs to the group of macrolide antibacterial agents. The active ingredient is azithromycin. It is classified as a drug with a wide spectrum of activity.
Sumamox
Available in powder form and also in the form of a solution intended for intramuscular administration. In most cases, it is prescribed for the treatment of infectious diseases of the respiratory system: bronchitis, pneumonia.
Despite its low toxicity, AzitRus is considered relatively safe, therefore it is used in pediatrics and is well tolerated by patients. But if during therapy a person has complaints about deterioration in health, it is worth consulting with a doctor, since antibacterial therapy is always associated with certain risks.