Contraceptive pills Jess Plus have proven themselves well in the hormonal contraception market.
This drug belongs to monophasic microdosed hormonal tablets.
Contraceptive Jess Plus is produced by the German company Bayer Schering Pharma AG.
The international name for Jess plus is Yaz plus (Jazz plus).
In this article we will look at a detailed description of the drug, what hormones it contains, what side effects it can cause, how to take it, etc.
IMPORTANT! The information is provided for informational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; to select OK, consult a specialist, undergo an examination and get tested.
About the tablets
Initially, I would like to say a few words about the drug itself. So, these are film-coated tablets. They have a nice pink hue and are round and biconvex. On one side you can see the letter “Z+”. The drug contains substances such as calcium levomefolate, drospirenone, and ethinyl estradiol. These are the main components, but there are also additional ones. There are 24 such tablets in a package.
There are also additional ones, there are 4 of them in a pack - they are vitamin-rich, light orange. There are a total of 28 Jess Plus tablets in the package. The reviews doctors leave about this drug inspire confidence. Many of them advise choosing these tablets precisely because they have these four vitamin tablets. By the way, they are distinguished by the placebo effect. When a girl takes the first such pill, her period should begin within a short period of time (usually one day). After the fourth tablet is taken, the next day you can open a new package of Jess Plus. Reviews from doctors show that this is another advantage of this drug. After all, there is no need to take any breaks, the body will actually not wean itself off the pills.
Compound
One tablet of COC Jess Plus contains the following active ingredients:
- Drospirenone (drospirenonum) – 3 mcg; has an antiandrogenic effect.
- Ethinyl estradiol (aethinyloestradiolum) – 20 mcg; analogue of endogenous estradiol.
- Calcium levomefolate (calcii levomefolinas) – 451 mcg; biologically active folic acid formula. This is a medicinal substance designed to eliminate folate deficiency in the female body. The presence of this component in the composition is what distinguishes Jess Plus from Jess.
In total, the blister contains 28 tablets (24 active + vitamins and 4 just vitamins).
Excipients:
- lactose monohydrate - 45.329 mg
- microcrystalline cellulose - 24.8 mg
- croscarmellose sodium - 3.2 mg
- hyprolose (5 cP) – 1.6 mg
- magnesium stearate – 1.6 mg
Action Jess Plus
- Suppress ovulation, i.e. interfere with the development and release of the egg
- Makes cervical mucus thick, making the cervix impassable for sperm
- They change the structure of the endometrium (the mucous membrane of the uterus), as a result - the fertilized egg cannot attach to the walls of the uterus
- Replenishes the lack of folate in a woman’s body
Each package of Jess Plus includes a detailed annotation.
Action
What effect does the drug “Jess Plus” have on the female body? Reviews from doctors who are specialists in this field say that these tablets are quite multifunctional. So, this is a low-dose drug, the difference from other contraceptives is the minimum amount of hormones included in its composition. The pills suppress ovulation by increasing the viscosity of the cervical substance.
The drug also normalizes and shortens the cycle, eliminating pain that a girl may experience during menstruation. It is also possible that the woman will begin to lose weight - this is also the effect of the drug. Peripheral edema will no longer bother her, her facial skin will improve (acne and oily sheen will disappear), and her hair will become beautiful. This all happens due to drospirenone. In general, tablets have a positive effect on the entire body - this is their advantage.
Folic acid as one of the advantages of a medicinal product
The reason for sympathy, as well as the explanation for the large number of positive reviews addressed to this oral contraceptive, is the presence of folic acid in its composition, which, by the way, is important in the case of planning pregnancy. Reviews from women about Jess Plus are presented below.
The intrauterine development of the fetus needs folic acid, and a deficiency of this vitamin can later manifest itself as neurological pathologies, as well as anemia in the expectant mother. For this reason, several months before the planned conception, doctors strongly recommend the use of folates, which are part of Jess Plus. Reviews from women confirm this.
Rules of application
Now it’s worth talking about how to drink Jess Plus. Instructions for use are very simple. The pack is almost a square sticker with a dosed drug. There is a blank line above the first line of tablet capsules. There you should glue a strip with the days of the week, which will run parallel to the tablets. Let's say a girl starts drinking them on Wednesday. From a set of stickers (they come with the drug), you need to choose the one where the very first day is Wednesday. And glue it onto the empty line. This is very convenient, especially for forgetful girls. This way you can control your pill intake. And from each of them there is an arrow towards the one you need to drink the next day. In general, there is no need to worry about how to use Jess Plus.
Instructions for use are not complicated - you need to take one tablet at the same time every day. If necessary, you can drink it with a small amount of water. As you can already understand, one package is enough for 28 days.
Is it possible to skip?
Under no circumstances should you skip taking Jess Plus tablets. The instructions for use state that they must be drunk daily, at the same time - with minimal deviation (it can be a little earlier or later, but the difference should not exceed 8 hours). If a pill is missed, it must be taken as soon as possible. Otherwise, the effect of the drug is reduced. It’s simple, for the desired effect to occur, the active substances must enter the body at the same time, as if replenishing the required balance. Of course, if a girl takes pills to improve the condition of her skin and hair, then missing one pill will not cause global problems. However, if the goal is protection from unwanted pregnancy, then it is better to set an alarm clock to take the drug to avoid unpleasant situations (as some do).
Its virtues
These are hormonal pills that are related to monophasic oral contraceptives with microdosing. This medicine has a number of the following advantages:
- The duration as well as the intensity of menstrual flow is reduced, which leads to less monthly blood loss.
- This medication can be prescribed for medicinal purposes against the background of certain hormonally dependent pathologies of the uterus and ovaries, such as, for example, polycystic disease and endometriosis.
- The reverse development of fibrocystic mastopathy is ensured.
- The functioning of the thyroid gland is normalized.
- The chance of developing colorectal cancer is reduced.
- The risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis is reduced.
- Various inflammatory processes in the pelvic area occur less frequently, since mucus that is viscous due to the use of hormonal contraceptives prevents the penetration of infection.
- The antiandrogenic function of drospirenone reduces oily skin and hair and eliminates acne.
- Antidiuretic hormone, along with antagonism, helps remove excess fluid from the body, resulting in weight loss, usually by two to three kilograms.
According to women's reviews, pregnancy after Jess Plus, after their discontinuation, occurs very quickly.
Reception nuances
On the first day of the menstrual cycle, you need to start drinking Jess Plus. The instructions for use recommend doing exactly this - and there will be no failures, and the drug will be absorbed better and faster. It is also unlikely that side effects will occur in this case.
But this is not the only nuance that is worth knowing about. Many girls are interested in the question of whether they can drink birth control and alcohol. Yes, you can. However, it is worth remembering some points here. Firstly, do not abuse strong drinks. Everyone knows that sometimes this results in vomiting. A pill may also come out with it. Accordingly, it will have no effect. The same applies if diarrhea occurs. In the latter case, doctors recommend taking another one - it’s better to be safe.
A few more words should be said about age restrictions. The drug “Jess Plus” does not have any of these. The instructions and reviews of girls who started taking oral contraceptives at a fairly early age (from the age of 16) confirm this. Experience shows that the drug is really good and of high quality - since no side effects were noticed (we are talking about those cases when patients first consulted with a doctor, and did not independently decide to start taking pills).
Jess Plus
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The drug is contraindicated during pregnancy.
If pregnancy is detected while taking Jess® Plus, the drug should be discontinued immediately. Data on the results of taking the drug Jess® Plus during pregnancy are limited and do not allow us to draw any conclusions about the negative impact of the drug on pregnancy, the health of the fetus and newborn child. At the same time, extensive epidemiological studies have not revealed an increased risk of developmental defects in children born to women who took COCs before pregnancy or teratogenic effects in cases of inadvertent use of COCs in early pregnancy. Specific epidemiological studies have not been conducted regarding the drug Jess® Plus. The drug is contraindicated during breastfeeding. Taking COCs can reduce the amount of breast milk and change its composition, so their use is not recommended until you stop breastfeeding. Small amounts of sex hormones and/or their metabolites may be excreted in milk, but there is no evidence of their negative effects on the health of the child.
Use for liver dysfunction
The drug is contraindicated for use in women with severe liver dysfunction.
Use for renal impairment
The drug is contraindicated for use in women with severe renal impairment and acute renal failure.
Use in children
The effectiveness and safety of Jess® Plus as a contraceptive have been studied in women of reproductive age. It is assumed that the effectiveness and safety of the drug in post-pubertal age up to 18 years are similar to those in women after 18 years. The use of the drug before menarche is not indicated.
Use in elderly patients
Jess® Plus is not used after menopause.
special instructions
If any of the conditions, diseases and risk factors listed below currently exist, the potential risks and expected benefits of using Jess® Plus should be carefully weighed in each individual case and discussed with the woman before she decides to start taking drug of this drug.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
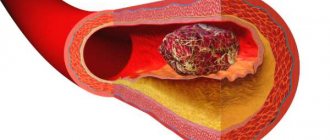
The results of epidemiological studies indicate a relationship between the use of COCs and an increased incidence of venous and arterial thrombosis and thromboembolism (such as deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular disorders) when taking combined oral contraceptives. These diseases are rare.
The risk of developing venous thromboembolism (VTE) is greatest in the first year of taking such drugs. An increased risk is present after initial use of combined oral contraceptives or resumption of use of the same or different combined oral contraceptives (after a dosing interval of 4 weeks or more). Data from a large prospective study involving 3 groups of patients suggest that this increased risk is predominantly present during the first 3 months.
The overall risk of VTE in patients taking low-dose combined oral contraceptives (<50 mcg ethinyl estradiol) is 2-3 times higher than in non-pregnant patients not taking COCs, although the risk remains lower than the risk of VTE during pregnancy and childbirth.
VTE can be life-threatening or fatal (in 1-2% of cases).
VTE, manifested as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, can occur with the use of any combined oral contraceptives.
It is extremely rare that when using combined oral contraceptives, thrombosis of other blood vessels occurs, for example, hepatic, mesenteric, renal, cerebral veins and arteries or retinal vessels. There is no consensus regarding the relationship between the occurrence of these events and the use of combined oral contraceptives.
Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis (DVT): unilateral swelling of the lower extremity or along a vein of the lower extremity, pain or discomfort in the lower extremity only in an upright position or when walking, local increase in temperature in the affected lower extremity, redness or discoloration of the skin on the lower extremity.
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism (PE): difficulty or rapid breathing; sudden cough, incl. with hemoptysis; sharp pain in the chest, which may intensify with deep inspiration; sense of anxiety; severe dizziness; fast or irregular heartbeat. Some of these symptoms (eg, shortness of breath, cough) are nonspecific and may be misinterpreted as signs of other more or less severe events (eg, respiratory tract infection).
Arterial thromboembolism can lead to stroke, vascular occlusion, or myocardial infarction.
Symptoms of a stroke: sudden weakness or loss of sensation in the face, upper or lower extremities, especially on one side of the body, sudden confusion, problems with speech and comprehension; sudden unilateral or bilateral vision loss; sudden disturbance in gait, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination; sudden, severe or prolonged headache for no apparent reason; loss of consciousness or fainting with or without an epileptic seizure.
Other signs of vascular occlusion: sudden pain, swelling and slight blue discoloration of the extremities, acute abdomen.
Symptoms of myocardial infarction: pain, discomfort, pressure, heaviness, a feeling of squeezing or fullness in the chest, arm or chest; discomfort radiating to the back, cheekbone, larynx, arm, stomach; cold sweat, nausea, vomiting or dizziness, severe weakness, anxiety or shortness of breath; fast or irregular heartbeat.
Arterial thromboembolism can be life-threatening or fatal.
The risk of developing thrombosis (venous and/or arterial) and thromboembolism increases:
- with age;
- in smokers (with increasing number of cigarettes or increasing age, the risk increases, especially in women over 35 years of age);
in the presence of:
- obesity (BMI more than 30 kg/m2);
- family history (for example, venous or arterial thromboembolism ever in close relatives or parents at a relatively young age). In the case of a hereditary or acquired predisposition, the woman should be examined by an appropriate specialist to decide on the possibility of taking the drug Jess® Plus;
- prolonged immobilization, major surgery, any operation on the lower extremities or major trauma. In these situations, it is advisable to stop using the drug Jess® Plus (in the case of a planned operation, at least four weeks before it) and not to resume taking it for two weeks after the end of immobilization;
- dyslipoproteinemia;
- arterial hypertension;
- migraine;
- heart valve diseases;
- atrial fibrillation.
The possible role of varicose veins and superficial thrombophlebitis in the development of venous thromboembolism remains controversial.
The increased risk of thromboembolism in the postpartum period should be taken into account.
Peripheral circulatory disorders may also occur in diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus, hemolytic uremic syndrome, chronic inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis) and sickle cell anemia.
An increase in the frequency and severity of migraines during use of Jess® Plus (which may precede cerebrovascular events) may be grounds for immediate discontinuation of this drug.
Biochemical indicators indicating a hereditary or acquired predisposition to venous or arterial thrombosis include the following: resistance to activated protein C, hyperhomocysteinemia, antithrombin-III deficiency, protein C deficiency, protein S deficiency, antiphospholipid antibodies (anticardiolipin antibodies, lupus anticoagulant).
When assessing the risk-benefit ratio, it should be taken into account that adequate treatment of the relevant condition may reduce the associated risk of thrombosis. It should also be taken into account that the risk of thrombosis and thromboembolism during pregnancy is higher than when taking low-dose oral contraceptives (<50 mcg ethinyl estradiol).
Tumors
The most significant risk factor for developing cervical cancer is persistent human papillomavirus infection. There are reports of a slight increase in the risk of developing cervical cancer with long-term use of COCs. However, the connection with taking COCs has not been proven. The possibility of the relationship of these data with screening for cervical diseases and with characteristics of sexual behavior (less frequent use of barrier methods of contraception) is discussed.
A meta-analysis of 54 epidemiological studies showed that there is a slightly increased relative risk of developing breast cancer diagnosed in women currently taking COCs (relative risk 1.24). The increased risk gradually disappears within 10 years of stopping these drugs. Because breast cancer is rare in women under 40 years of age, the increase in breast cancer diagnoses in women who are currently or recently taking COCs is small relative to the overall risk of breast cancer. Its connection with the use of COCs has not been proven. The observed increased risk may be a consequence of careful monitoring and earlier diagnosis of breast cancer in women using COCs. Women who have ever used COCs are diagnosed with earlier stages of breast cancer than women who have never used them.
In rare cases, during the use of COCs, the development of benign, and in extremely rare cases, malignant liver tumors was observed, which in some patients led to life-threatening intra-abdominal bleeding.
If severe abdominal pain, liver enlargement, or signs of intra-abdominal bleeding occur, this should be taken into account when making a differential diagnosis.
Tumors can be life-threatening or fatal.
Other states
Clinical studies have shown no effect of drospirenone on plasma potassium concentrations in patients with mild to moderate renal failure. However, in patients with impaired renal function and an initial potassium concentration at the upper limit of normal, the risk of developing hyperkalemia cannot be excluded while taking medications that lead to potassium retention in the body.
Women with hypertriglyceridemia (or a family history of this condition) may have an increased risk of developing pancreatitis while taking COCs.
Although slight increases in blood pressure have been described in many women taking COCs, clinically significant increases have rarely been observed. However, if a persistent, clinically significant increase in blood pressure develops while taking Jess® Plus, this drug should be discontinued and treatment of arterial hypertension should be started. The drug can be continued if normal blood pressure values are achieved with antihypertensive therapy.
The following conditions have been reported to develop or worsen both during pregnancy and while taking COCs, but their association with COC use has not been proven: jaundice and/or pruritus associated with cholestasis; formation of gallstones; porphyria; systemic lupus erythematosus: hemolytic-uremic syndrome; Sydenham's chorea; herpes during pregnancy; hearing loss associated with otosclerosis. Cases of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis have also been described with the use of COCs.
In women with hereditary forms of angioedema, exogenous estrogens may cause or worsen symptoms of angioedema.
Acute or chronic liver dysfunction may require discontinuation of Jess® Plus until liver function tests return to normal. Recurrent cholestatic jaundice, which develops for the first time during pregnancy or previous use of sex hormones, requires discontinuation of the drug Jess® Plus.
Although COCs may have an effect on insulin resistance and glucose tolerance, there is no need to change the therapeutic regimen in diabetic patients using Jess® Plus. However, women with diabetes should be closely monitored while taking this drug.
Chloasma can sometimes develop, especially in women with a history of chloasma during pregnancy. Women with a tendency to chloasma while taking Jess® Plus should avoid prolonged exposure to the sun and exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Folates may mask vitamin B12 deficiency.
Preclinical safety data
Preclinical data from routine repeated-dose toxicity, genotoxicity, carcinogenicity and reproductive toxicity studies do not indicate a particular risk to humans. However, it should be remembered that sex hormones can promote the growth of certain hormone-dependent tissues and tumors.
Preclinical data from routine studies of levomefolate calcium for repeated-dose toxicity, genotoxicity and reproductive toxicity do not indicate a particular risk to humans.
Laboratory tests
Taking Jess® Plus may affect the results of some laboratory tests, including indicators of liver, kidney, thyroid, adrenal function, the concentration of transport proteins in plasma, indicators of carbohydrate metabolism, parameters of blood coagulation and fibrinolysis. Changes usually do not go beyond normal values. Drospirenone increases plasma renin activity and aldosterone concentrations, which is associated with its antimineralocorticoid effect.
There is a theoretical possibility of increasing the concentration of potassium in the blood plasma in women receiving Jess® Plus simultaneously with other drugs that can increase the content of potassium in the blood plasma. These drugs include angiotensin II receptor antagonists, potassium-sparing diuretics, and aldosterone antagonists. However, in studies evaluating the interaction of drospirenone with ACE inhibitors or indomethacin, there was no significant difference in plasma potassium concentrations compared with placebo.
Reduced efficiency
The effectiveness of Jess® Plus may be reduced in the following cases: if you miss pills, with vomiting and diarrhea, or as a result of drug interactions.
Frequency and severity of menstrual-like bleeding
While taking Jess® Plus, irregular (acyclic) spotting and bleeding from the vagina (spotting or “breakthrough” uterine bleeding) may occur, especially during the first months of use. Therefore, any irregular bleeding should be assessed after an adaptation period of approximately 3 cycles.
If irregular bleeding recurs or develops after previous regular cycles, careful evaluation should be performed to rule out malignancy or pregnancy.
Some women may not develop withdrawal bleeding during a break in taking the pills; the drug cannot be continued until pregnancy has been ruled out.
Medical examinations
Before starting or resuming use of the drug, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the woman’s life history, family history, conduct a thorough physical examination (including measuring blood pressure, heart rate, determining the BMI index, examining the mammary glands), gynecological examination, cytological examination of the cervix (Papanicolaou test), exclude pregnancy. When resuming taking the drug Jess® Plus, the volume of additional studies and the frequency of control examinations are determined individually, but at least once every 6 months.
The woman should be warned that Jess® Plus does not protect against HIV infection and other sexually transmitted diseases.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
There have been no reported cases of adverse effects of the drug Jess® Plus on the speed of psychomotor reactions; No studies have been conducted to study the effect of the drug on the speed of psychomotor reactions.
Side effect
Well, now it’s worth touching on a not very pleasant topic regarding Jess Plus tablets. Side effects – these are the ones we will talk about. Those girls who chose them themselves are unhappy with the pills. Without a doubt, there are cases in which an independent decision (without taking tests or examining a doctor) is correct, and the drug is suitable for the girl. But this is a matter of chance. You need to know that birth control pills are very serious. Still, they affect hormonal levels. And no matter how high-quality they are, it is necessary to undergo tests so that the doctor can personally select exactly the drug that is suitable for a particular patient. Otherwise, you may experience side effects.
These are bleeding, bad discharge, nausea, vomiting, headache and discomfort in the abdomen, cycle disruption, weight gain, sudden mood swings. And this is just a small list of what a girl who has chosen Jess Plus for herself can expect. The effect of the drug is really good, but it is only for those for whom these tablets are suitable.
Indications
“Jess Plus” are hormonal tablets that are indicated for those girls who suffer from hormone-dependent fluid retention. This happens to many people, by the way. They are also great for treating moderate acne. If a girl has folate deficiency, these tablets are also created for her. And they are also indispensable if a woman suffers from a severe form of premenstrual syndrome. And finally, the most important and, in fact, the main effect, as well as a part-time indication, is contraception. In this regard, “Jess Plus” is one of the most reliable drugs in the whole world.
Contraindications
But these pills are not recommended for those girls who suffer from thrombosis (no matter what kind - arterial or venous). Ischemic attacks or angina are also contraindications. Also, if a girl often suffers from migraines, then she should not start taking these pills either. The same is true if a woman has diabetes.
There are a number of other contraindications: liver failure, tumors, hormone-dependent malignancies, bleeding from the genitals, pregnancy, etc. If any of the above is present, then you do not need to take these pills. As a matter of fact, this is another reason why you should visit a doctor before purchasing a pack of the drug.
Comments and reviews
Much has been said about Jess Plus. How to take it, whether you need to take breaks, in what cases you should abandon this idea - all this is clear. But what do the girls who have been taking these pills for months say? Almost everyone confidently claims that this is one of the best contraceptive options. Pain during menstruation disappears, and you don’t have to worry about when the next one will start. There is much less discharge and the cycle ends earlier. Plus, a nice bonus is the improved condition of facial skin and hair, as mentioned above.
In fairness, I would like to note that there are only two really good drugs that fall into the category of contraceptives. These are “Jess Plus” and “Yarina” - this information is confirmed by thousands of reviews from girls, women and doctors around the world.
Analogs
The analogues closest in their effect to Jess Plus are the drug Yarina, which contains the same gestagen, but includes a little more estrogen and microdosed drugs, for example, Logest, Microdinon and Novinet. For the listed medications, the dosage of estrogen is absolutely the same, but the progestogen ingredient is slightly different.