Release form and composition
Dosage forms of Chloramphenicol:
- tablets (in paper packages of 10 pcs., in cardboard packages of 20 pcs.);
- eye drops (in glass dropper bottles of 5 or 10 ml, 1 bottle per package);
- capsules (in cardboard packs of 20 pcs.);
- alcohol solution (in glass bottles of 25 ml);
- powder (in glass bottles of 0.5 or 1 g, 1 bottle per package);
- liniment (in tubes of 25 g, 1 tube per package);
- vaginal suppositories (in packs of 10 pcs.).
Composition of 1 tablet:
- active substance: chloramphenicol – 0.25 or 0.5 g;
- auxiliary components: calcium stearate/stearic acid, starch.
Composition of 1 ml eye drops:
- active substance: chloramphenicol – 0.025 g;
- auxiliary components: prepared water, boric acid.
Active substance in 1 capsule: chloramphenicol – 0.25 g.
Active substance in the powder (per 1 bottle): sodium salt of chloramphenicol - 0.5 or 1 g.
Composition of 1 g of liniment:
- active substance: chloramphenicol – 0.05 or 0.1 g;
- auxiliary components: prepared water, sorbic acid, sodium carmellose, castor oil, emulsifier.
Composition of 1 suppository:
- active substance: chloramphenicol – 0.25 g;
- auxiliary component: vitepsol.
Indications for use
Tablets, capsules, powder, suppositories
- chlamydia;
- abscess of cerebral tissue;
- salmonellosis;
- paratyphoid, dysentery infection;
- wound infection with purulent discharge;
- ehrlichiosis;
- typhoid fever;
- lymphogranuloma in the groin area;
- tularemia;
- Yersinia/meningococcus-associated diseases;
- brucellosis;
- urinary tract infection;
- trachoma;
- infectious damage to the biliary organs;
- purulent peritonitis;
- Rickettsia-associated infectious diseases.
Liniment, alcohol solution
Skin lesions associated with bacterial agents:
- pressure ulcers;
- boils;
- trophic ulcers;
- burns complicated by infections;
- cracks in the nipple area during lactation.
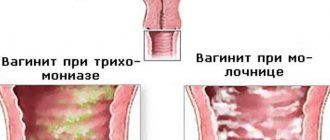
Eye drops
Used in ophthalmology to treat infections.
Contraindications
- kidney diseases with severe impairment of their function;
- skin diseases associated with fungal infection;
- eczema;
- acute form of intermittent porphyria;
- severe liver disease;
- psoriasis;
- diseases of the hematopoietic organs;
- deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase;
- early childhood;
- neonatal period;
- breastfeeding (parenteral and oral forms of the drug);
- individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
Diseases and conditions for which Chloramphenicol is used with caution:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- tendency to develop allergic reactions;
- pregnancy.
Recommended analogues
The drugs of choice are modern drugs - Tobramycin, Gentamicin, Norfloxacin.
Tobramycin
Eye drops are available under the names:
- Tobropt (120-140 rub.);
- Tobriss (125-155 rubles);
- Tobrex (180-210 rub.).
This is a new generation remedy prescribed to adults and children of any age. Undesirable manifestations when using it occur infrequently, including allergic reactions and effects on hearing (ototoxicity).
Gentamicin
The drug is available in the form of eye ointment and drops and has a low price (60-120 rubles).
After its use, allergic manifestations, photophobia, and pain are possible.
Norfloxacin
The drops are known as Normax, their cost ranges from 150 to 170 rubles.
The range of action of the product is also wide: various types of conjunctivitis, when a foreign body gets into the eye, various injuries and burns. It is not recommended to use the medicine for pregnant and lactating women and children under 18 years of age. When instilled, itching and redness of the conjunctiva are possible.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Directions for use and dosage
Capsules, tablets
Tablets and capsules are taken orally 30 minutes before meals. Patients with nausea or vomiting should take the drug 1 hour after eating. Daily dose – 2–4 g, divided into 4 doses.
The daily (single) dose for children under 3 years of age is determined based on the calculation of 0.01–0.015 g per 1 kg of body weight; at the age of 3–8 years – 0.15–0.2 g per dose; children aged 8 years and older – 0.6–1.2 g per day.
The duration of treatment is 7–10 days; with normal tolerability of the drug, it can be increased to 14 days.
Liniment, alcohol solution
Liniment and alcohol solution are used externally to treat skin surfaces. Frequency of application – 2–3 times a day. When using an occlusive dressing, liniment is used once every 1–4 days.
Therapy is continued until the wound surface is completely cleansed.
Eye drops
Drops are used conjunctivally. Frequency of application – several times a day for 7 days.
Vaginal suppositories
Suppositories are administered intravaginally, in the supine position. The daily dose is 2–3 suppositories per day. Duration of treatment is 8–10 days.
The drug can be used in girls during puberty, 1–2 suppositories per day.
Parenteral forms
The dosage regimen is determined individually depending on the severity and type of disease.
Instructions:
Clinical and pharmacological groups
29.009 (Drug with keratolytic and antimicrobial effects for external use) 24.010 (Drug with antibacterial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory and local anesthetic effects for local use in ENT practice) 06.025 (Antibiotic of the chloramphenicol group) 23.007 (Antibiotic for local use in gynecology) 29.0 06 (Drug with antibacterial, local anesthetic and tissue regeneration improving effect for external use) 26.022 (Combined antibacterial drug for local use in ophthalmology) 29.005 (Drug with antibacterial and tissue regeneration improving effect for external use) 29.002 (Antibiotic for external use) 29.026 (Drug with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect for external use) 26.021 (Antibiotic for topical use in ophthalmology)
pharmachologic effect
Broad-spectrum antibiotic. The mechanism of antimicrobial action is associated with a violation of the synthesis of microbial proteins. Has a bacteriostatic effect. Active against gram-positive bacteria: Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp.; gram-negative bacteria: Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Klebsiella spp., Serratia spp., Yersinia spp., Proteus spp., Rickettsia spp.; also active against Spirochaetaceae and some large viruses.
Chloramphenicol is active against strains resistant to penicillin, streptomycin, and sulfonamides.
Resistance of microorganisms to chloramphenicol develops relatively slowly.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, it is quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Bioavailability is 80%. Quickly distributed in the body. Plasma protein binding is 50-60%. Metabolized in the liver. T1/2 is 1.5-3.5 hours. It is excreted in the urine, small amounts in feces and bile.
Dosage
Individual. When taken orally, the dose for adults is 500 mg 3-4 times a day. Single doses for children under 3 years of age - 15 mg/kg, 3-8 years - 150-200 mg; over 8 years old - 200-400 mg; frequency of use - 3-4 times/day. The course of treatment is 7-10 days.
For external use, apply to gauze pads or directly to the affected area. Apply a regular bandage on top, possibly with parchment or compress paper. Dressings are performed depending on the indications after 1-3 days, sometimes after 4-5 days.
Used locally in ophthalmology as part of combination drugs in accordance with indications.
Drug interactions
With the simultaneous use of chloramphenicol with oral hypoglycemic drugs, an increase in the hypoglycemic effect is observed due to the suppression of the metabolism of these drugs in the liver and an increase in their concentration in the blood plasma.
When used simultaneously with drugs that inhibit bone marrow hematopoiesis, there is an increased inhibitory effect on the bone marrow.
When used simultaneously with erythromycin, clindamycin, lincomycin, a mutual weakening of the effect is observed due to the fact that chloramphenicol can displace these drugs from the bound state or prevent their binding to the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes.
When used simultaneously with penicillins, chloramphenicol counteracts the bactericidal effect of penicillin.
Chloramphenicol suppresses the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, therefore, when used simultaneously with phenobarbital, phenytoin, warfarin, a weakening of the metabolism of these drugs, a slower elimination and an increase in their concentration in the blood plasma are observed.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Chloramphenicol is contraindicated for use during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding).
Side effects
From the hematopoietic system: thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia.
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence.
From the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: peripheral neuritis, optic neuritis, headache, depression, confusion, delirium, visual and auditory hallucinations.
Allergic reactions: skin rash, urticaria, angioedema.
Local reactions: irritant (for external or local use).
Indications
For oral administration: infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to chloramphenicol, including: typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever, dysentery, brucellosis, tularemia, whooping cough, typhus and other rickettsioses; trachoma, pneumonia, meningitis, sepsis, osteomyelitis.
For external use: purulent skin lesions, boils, long-term non-healing trophic ulcers, second and third degree burns, cracked nipples in nursing women.
For local use in ophthalmology: inflammatory eye diseases.
Contraindications
Blood diseases, severe liver dysfunction, deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, skin diseases (psoriasis, eczema, fungal diseases); pregnancy, lactation, children up to 4 weeks of age (newborns), hypersensitivity to chloramphenicol, thiamphenicol, azidamphenicol.
special instructions
Chloramphenicol is not used in newborns, because the development of “gray syndrome” is possible (flatulence, nausea, hypothermia, gray-blue skin color, progressive cyanosis, dyspnea, cardiovascular failure).
Use with caution in patients who have previously received treatment with cytotoxic drugs or radiation therapy.
With simultaneous intake of alcohol, a disulfiram-like reaction may develop (skin hyperemia, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, reflex cough, convulsions).
During treatment, systematic monitoring of peripheral blood patterns is necessary.
Preparations containing CHLORAMPHENICOL
• LEVOMYCETIN tab. 500 mg: 10, 20 or 50 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 500 mg: 20 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN-FEREIN eye drops 0.25%: fl. 5 ml or 10 ml • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 250 mg: 10 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN SUCCINATE SOLUBLE powder for preparation. injection solution 1 g: fl. 5 or 10 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 500 mg: 10 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 1%: fl. 25 ml • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 0.25%: fl. 25 ml or 40 ml • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 1%: fl. 25 ml • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 500 mg: 10 or 20 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN-KMP tab. 500 mg: 40 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 3%: fl. 25 ml • OLASOL ◊ aerosol for external use. note: 60 g balloon • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 500 mg: 10 or 20 pcs. • SYNTHOMYCIN vaginal suppositories 250 mg: 10 pcs. • SYNTHOMYCIN vaginal suppositories 250 mg: 10 pcs. • COLBIOCIN eye ointment 10 mg + 180 thousand IU + 5 mg/1 g: tube 5 g • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 0.25%: fl. 25 ml or 40 ml • LEVOMYCETIN-KMP powder for preparation. solution for intramuscular injection 500 mg: vial. 10 pieces. • SYNTHOMYCIN ◊ liniment 10%: tube 25 g • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 250 mg: 10 or 20 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 5%: fl. 25 ml • LEVOMYCETIN-UBF tab. 500 mg: 10, 20, 30 or 50 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 250 mg: 10 or 20 pcs. • CORTOMYCETIN ointment for external use. approx. 5 mg+2 mg/1 g: tube 15 g • LEVOMYCETIN SUCCINATE SODIUM powder for preparation. solution for intramuscular injection 500 mg: vial. 1 PC. included with solvent • SYNTHOMYCIN ◊ liniment 10%: jars 25 g, 800 g, 1000 g or 1800 g, tubes 25 g • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external. approx. alcohol 3%: fl. 25 ml • LEVOMYCETIN SUCCINATE SOLUBLE powder for preparation. injection solution 500 mg: fl. 5 or 10 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 1%: fl. 25 ml • LEVOMETIL ◊ ointment for external use. note: tube 30 g • SYNTHOMYCIN vaginal suppositories 250 mg: 10 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN SODIUM SUCCINATE powder for preparation. solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration of 1 g: fl. 5 or 10 pcs. • NETRAN ◊ ointment for external use. note: tube 40 g, jar 1 kg • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 500 mg: 10, 20, 30, 40 or 50 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 250 mg: 10, 20 or 50 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 5%: fl. 25 ml • LEVOMYCETIN-AKOS eye drops 0.25%: dropper bottle. 5 ml • LEVOMYCETIN eye drops 0.25%: flask. 5 ml or 10 ml • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 0.25%: fl. 25 ml • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 250 mg: 10, 20, 30, 40, 1000, 2000 or 3000 pcs. • SYNTHOMYCIN ◊ liniment 10%: tube 25 g • CANDIBIOTIC ear drops: fl. 5 ml per set with pipette • LEVOSIN® (LEVOSIN) ◊ ointment for external use. note: tube 40 g, cans 50 g or 100 g • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 500 mg: 10 or 20 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 250 mg: 10, 20, 30, 40 or 50 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 500 mg: 10, 20, 30, 40, 1000, 2000 or 3000 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 500 mg: 20 pcs. • SYNTHOMYCIN vaginal suppositories 250 mg: 10 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN tab., coated. coated, 500 mg: 20 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN-FEREIN caps. 250 mg: 10 pcs. • SYNTHOMYCIN ◊ liniment 10%: tube 25 g • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 500 mg: 10 or 20 pcs. • KOLBIOCIN (COLBIOCIN) powder for preparation. eye drops 4 mg + 180 thousand IU + 5 mg/1 ml of ready-made solution: vial. 1 PC. with a reservoir lid and a dropper lid • LEVOMYCETIN-KMP tab. 250 mg: 40 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN caps. 250 mg: 10 or 20 pcs. • LEVOMECOL ◊ ointment for external use. note: tube 40 g, jar 1 kg • LEVOMYCETIN caps. 250 mg: 10 or 20 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 250 mg: 10 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 1%: fl. 25 ml or 40 ml • SALEDEZ solution for local use. approx. alcohol: fl. 25, 40, 100 ml, 100 ml cans. • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 3%: fl. 25 ml • LEVOMYCETIN eye drops 0.25%: flask. 5 ml or 10 ml • LEVOMYCETIN-KMP powder for preparation. solution for intramuscular administration of 1 g: vial. 10 pieces. • LEVOMYCETIN eye drops 0.25%: fl. 5 ml with drip. • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 250 mg: 20 pcs. • SYNTHOMYCIN ◊ liniment 10%: tube 25 g • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 1%: fl. 25 ml • LEVOMYCETIN caps. 250 mg: 16 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 500 mg: 20 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 250 mg: 10 or 20 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN eye drops 0.25%: flask. 5 ml or 10 ml • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 3%: fl. 25 ml • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 5%: fl. 25 ml • CORTOMYCETIN ointment for external use. approx. 5 mg+2 mg/1 g: tube 15 g • LEVOMYCETIN-DIA eye drops 0.25%: flask. 5 ml or 10 ml • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 5%: fl. 25 ml or 40 ml • LEVOMYCETIN SODIUM SUCCINATE powder for preparation. solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration of 500 mg: vial. 5 or 10 pcs. • LEVOMECOL® ◊ ointment for external use. note: tube 40 g, cans 100 g or 1000 g • LEVOMYCETIN tab. 500 mg: 10 or 20 pcs. • LEVOMYCETIN ◊ solution for external use. approx. alcohol 3%: fl. 25 ml or 40 ml • LEVOMYCETIN SUCCINATE SODIUM powder for preparation. solution for intramuscular administration of 1 g: vial. 1 PC. included with solvent
Side effects
- agranulocytosis;
- hypohemoglobinemia;
- leukopenia;
- thrombocytopenia;
- aplastic anemia;
- cardiovascular collapse (in children under 1 year of age);
- diarrhea;
- dyspeptic symptoms;
- attacks of nausea, urge to vomit;
- dysbacteriosis;
- psychomotor disorders;
- delirium;
- changes in consciousness, visual or auditory hallucinations;
- depressive states;
- headache;
- hearing impairment;
- visual impairment;
- optic neuritis;
- dermatitis;
- addition of a fungal infection;
- itching of the skin, urticaria, skin rash;
- hyperemia of the skin;
- angioedema
- irritation of the oral mucosa;
- change in taste perception.
special instructions
During long-term therapy with parenteral and oral forms of the drug, tests are necessary to monitor the state of the blood.
The use of liniment for the treatment of cracks in the nipple area in nursing mothers does not require cessation of breastfeeding.
In cases of infectious diseases, Chloramphenicol is used only in cases where the patient has resistance to other antibacterial drugs, since severe toxic reactions may develop while taking the drug.
Since the active substance of the drug easily passes into breast milk, breastfed infants may develop serious side effects. It is recommended to consult with your doctor regarding temporary suspension of lactation during the period of therapy.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Chloramphenicol
A synthetic antibiotic identical to the natural waste product of Streptomyces venezuelae . It has a wide spectrum of bacteriostatic action, the mechanism of which is caused by disruption of the process of protein synthesis in the microbial cell at the stage of transfer of t-RNA amino acids to ribosomes. Effective against many gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, pathogens of purulent infections, typhoid fever, dysentery, meningococcal infection, active against hemophilus bacteria, Brucella, rickettsia, chlamydia, spirochetes. Weakly active against acid-fast bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, clostridia and protozoa. Penetrates the cells of microorganisms and acts on microbes located intracellularly (rickettsia, chlamydia). Resistance to chloramphenicol develops relatively slowly and generally does not result in cross-resistance to other chemotherapeutic agents. Rapidly absorbed after oral administration, as well as after rectal administration; The maximum concentration in the blood plasma after oral administration develops after 2–3 hours, the therapeutic concentration in the blood remains for 4–5 hours after administration. Bioavailability after oral administration is 80%, with intramuscular administration - 70%. Penetrates well into organs, tissues and biological fluids of the body, penetrates through the BBB and into the CSF (up to 50% of the content in blood plasma). Penetrates the placenta (the concentration in the fetal blood serum can be 30–80% of the concentration in the mother's blood), and is detected in breast milk. 50–60% of chloramphenicol is bound to blood plasma proteins, 32% in premature newborns. Volume of distribution - 0.6–1 l/kg. When administered orally or topically, the therapeutic concentration is created in the vitreous body, cornea, iris, and aqueous humor of the eye (does not penetrate into the lens). It is excreted mainly in the urine (mainly in the form of inactive metabolites), partially in bile (up to 30% of the administered dose). In the intestine, under the influence of intestinal microflora, it is hydrolyzed to form inactive metabolites.
Drug interactions
Effect of chloramphenicol on drugs/substances when used in combination:
- cycloserine: enhances its neurotoxic effect;
- ristomycin: its negative effect is not enhanced by hematopoiesis;
- oxycoumarin derivatives: enhances their anticoagulation properties;
- tolbutamide: disrupts its metabolism;
- chlorpropamide: disrupts its biotransformation.
Effect of drugs/substances on chloramphenicol in combination treatment:
- phenobarbital: reduces its plasma concentration;
- erythromycin, nystatin, levorin: potentiate its antibacterial effect;
- oleandomycin: enhances its antibacterial effect.
Pharmacological incompatibility has been established between chloramphenicol and cytostatics, sulfonamides, glucose, pyrazolone derivatives, and alcohol.
When used simultaneously with oxycoumarin derivatives, hypoglycemia may develop.
The combination of chloramphenicol with diphenine is not recommended due to unpredictable changes in their pharmacodynamics.
Cheap analogues
The drugs Sulfacyl Sodium and Ciprofloxacin have a similar effect.
Sulfacyl Sodium
This over-the-counter medicine is also known as Albucid. It is used for various types of conjunctivitis, blepharitis, purulent diseases of the cornea.
Sulfacyl sodium is non-toxic and is therefore prescribed for the prevention of blenorrhea or purulent conjunctivitis in newborns.
When using drops, unwanted allergic reactions such as swelling, itching and redness are possible.
The cost of the drug is from 18 to 55 rubles.
Ciprofloxacin
This is a prescription antibacterial product. Unlike analogues, it is additionally used for the prevention and treatment of preoperative and postoperative complications. Other indications for its use are eye injuries, foreign body penetration and welding burns.
The price of the medicine varies depending on the manufacturer:
- Ciprofloxacin from a domestic manufacturer – from 15 to 45 rubles;
- Tsiprolet (India) – 45-60 rubles;
- Tsipromed (India) – 125-155 rubles.
The drug is not recommended for use by pregnant and lactating women. In children's practice, drops are allowed from the age of one year.
When used together with other solutions, it is necessary to adhere to a 5-10-minute interval during instillation. When wearing lenses during treatment, it is advisable to discard them or install them after using the product after 15 minutes.