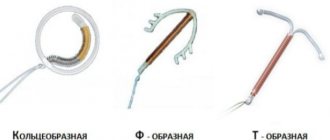
- Types of intrauterine devices
- Mechanism of action
- How to place an intrauterine device
- Removing a contraceptive
- Complications
- Indications for use
- Contraindications
Prevention from unwanted pregnancy, or contraception, helps a woman maintain her health:
- reduces the frequency of abortions;
- helps plan pregnancy and prepare for it;
- in many cases it has an additional therapeutic effect.
One type of contraception is intrauterine. It is used most often in China, the Russian Federation and Scandinavia. In everyday speech, the term “intrauterine device” is often used.
Advantages of intrauterine contraception:
- relatively low cost;
- long period of use;
- rapid restoration of fertility after removal of the IUD;
- Possibility of use during breastfeeding and with concomitant diseases;
- therapeutic effect on the endometrium (using a hormonal intrauterine system);
- preservation of the physiology of sexual intercourse, lack of preparation, fullness of sensations during intimacy.
The principle of operation of the intrauterine device
An intrauterine device (IUD) is a contraceptive that is inserted into the uterine cavity and inhibits the movement of sperm, damaging them. It also prevents the attachment of a fertilized egg to the walls of the uterus. Externally, it is a small object made of plastic and copper. Some modern models add gold, silver or hormones.
The IUD is inserted into the uterine cavity and damages sperm
Once the IUD is installed, the probability of pregnancy approaches zero. The IUD deprives sperm of the ability to fertilize and also prevents the appearance of an embryo in the uterus. The contraceptive effect is achieved through:
- deterioration of conditions for egg attachment due to injury to the walls of the cervix by a foreign object;
- decrease in sperm activity and viability;
- increased contraction of the muscles of the uterus, which is why the egg enters its cavity ahead of time and is not yet able to implant.
On what day of menstruation is Mirena placed?
A highly effective means of protecting against pregnancy is the Mirena internal spiral, which is preferred by many girls. In addition to protecting against unwanted pregnancy, Mirena also has a therapeutic effect and protects against diseases. Only a doctor installs Mirena. This is a plastic intrauterine contraceptive with progestogens.
On what day of the cycle is the Mirena intrauterine device placed for pregnancy? It is administered in the first 7 days of menstruation or immediately after an abortion. You can replace it regardless of the cycle. This IUD has some features that are manifested in its effect on the body. With Mirena, the menstrual cycle and periods improve - the discharge becomes less abundant, the critical days are reduced, and the pain decreases.
Negative aspects are breakthrough bleeding, menstruation after installation of Mirena becomes painful due to pregnancy. There is also a risk that the device will come out on its own or become dislodged, which can lead to pregnancy.
Pros and cons of installing an IUD
It is important for women who want to install an IUD to understand the advantages and disadvantages of this type of contraception. Main advantages:
- Ease of use: once you install the coil, you no longer have to think about methods of protection for the entire life of its service. There is no danger of forgetting to take (use) the drug in a timely manner, as happens, for example, with oral or local contraceptives.
- The IUD does not dull sensations during intimacy.
The intrauterine device does not interfere with sexual activity, and there should not be any unpleasant sensations. Pain during sex or outside of intimacy may indicate the development of complications (partial prolapse of the IUD, damage to the uterus). You should see a doctor to find out the cause of this condition.
obstetrician-gynecologist Ekaterina Osennyaya
https://summerinside.ru/seks-posle-ustanovki-vnutrimatochnoy-spirali-10-intimnyih-voprosov-vrachu/
- This method of contraception is relatively inexpensive, because the duration of use of the IUD ranges from 3 to 10 years.
- Non-hormonal IUDs have no contraindications such as smoking and breastfeeding.
- If the IUD contains hormones, then it not only prevents fertilization, but also controls the volume and regularity of menstruation, and prevents ectopic pregnancy.
The disadvantages include:
- inability to install an IUD on your own;
- it is unacceptable to install it in nulliparous women;
- Being a contraceptive, the intrauterine device is not a barrier to sexually transmitted infections.
Side effects
Despite the many advantages and disadvantages of using an IUD, there are a number of possible unpleasant consequences:
- displacement of the spiral, which can provoke mechanical damage to the uterus;
- infection during installation;
- heavy periods in the first six months of using the device;
- spotting in the middle of the cycle, between menstruation;
- itching and burning in the vagina;
- pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- increased body temperature, chills;
- puncture of the uterus during insertion of the IUD.
As a rule, such troubles occur from the unprofessional actions of the doctor installing the IUD.
Restoration of the menstrual cycle
After removal of the contraceptive, scanty bleeding is often observed due to prolonged suppression of ovarian function and the development of the endometrium. The normal period should be restored within 3 cycles. If, after this period, menstruation resembles spotting, an examination by a gynecologist is necessary.
In the absence of complications and side effects, periods should return to their previous levels. Sometimes the long-term effect of a contraceptive on the reproductive system changes the nature of menstruation.
Types of intrauterine devices
Depending on the material from which the spiral is made, the contraceptive effect may be enhanced. There are several types of such funds.
Copper spiral
The copper coil protects against pregnancy mechanically, stimulating the uterus to contract more and preventing the process of egg implantation. Copper ions have a detrimental effect on sperm, suppress their motor activity and prevent penetration into the egg. The copper spiral has a peculiarity: over time it can oxidize in the uterine cavity, so it can be installed for no more than three years.
A copper spiral can be installed for no more than 3 years
Spiral with added silver
Some models also contain silver, which inhibits the oxidation of copper and increases the life of the product. In addition, silver has an anti-inflammatory effect, adversely affecting bacteria and sperm. This spiral can be installed for up to 7 years.
Silver in the coil kills bacteria and sperm
Spiral containing gold
In spirals of this type, gold is contained in a 1:1 ratio with copper, which, like silver, reduces sperm motility. Its service life is 7–10 years.
The service life of a spiral with the addition of gold is 7–10 years
Hormonal IUDs
This spiral looks similar to a regular one. But unlike others, it has a cylinder containing the hormone levonorgestrel. It is released in doses and has a contraceptive effect, the same as when taking hormonal birth control pills. This achieves double protection: on the one hand, the spiral works according to the principle of mechanical action described above. On the other hand, it eliminates the possibility of conception at the hormonal level, interfering with the maturation of the egg.
The advantage of this type of IUD is that levonorgestrel does not enter the bloodstream, which means there are no side effects such as weight gain or chest pain. Depending on the manufacturer, the service life is on average 5 years.
The hormone from the IUD does not enter the blood and does not cause side effects
Who is the IUD suitable for?
In the absence of pathologies and contraindications, the intrauterine device can be installed on the second day after birth. The presence of an IUD does not in any way affect the process of uterine restoration, but in each case the doctor individually decides on the possibility of its use.
If the IUD was not installed in the maternity hospital before discharge, then it can subsequently be installed only during the first menstruation. In case of cesarean section, it is recommended to insert an IUD after six months from the moment of injury to the uterus. And after an abortion or miscarriage, gynecologists allow it to be administered immediately.
As a method of contraception, the spiral is most suitable for:
- women who have given birth;
- patients who do not have gynecological diseases;
- in cases where, for various reasons, oral contraceptives are contraindicated.
Doctors do not recommend installing a spiral in the following cases:
- the patient has not yet given birth;
- the cervix is injured;
- there are chronic diseases of the pelvic organs;
- a woman often changes sexual partners;
- vaginal infection is not cured;
- there is an inflammatory process in the reproductive organs;
- there are features of the anatomical structure of the uterus that can contribute to the prolapse of the spiral;
- tumors are present (both benign and malignant);
- sexually transmitted diseases have not been cured.
Video: more about intrauterine devices
Contraindications
Installation of intrauterine devices has certain contraindications. Before using this method of contraception, you should study the existing contraindications, which are divided into absolute and relative.
Absolute:
- Pregnancy;
- Oncology of the genitals;
- Exacerbation of inflammatory diseases of the genitals;
- If you have an active sexual life, there is a risk of contracting infections transmitted through sex;
- Bleeding.
Relative:
- Chronic forms of inflammatory diseases of the uterus;
- Menstruation that occurs with painful sensations;
- Too much discharge during menstruation;
- Underdevelopment of the uterus;
- Previously there was an ectopic pregnancy;
- Cervical distortion;
- Anemia and other blood diseases;
- Decreased cervical tone;
- No history of labor.
IUD installation
Before installing the IUD, a woman is prescribed a number of examinations and tests in order to exclude the presence of contraindications:
- vaginal smear;
- blood test for sexually transmitted diseases and infections;
- general urine analysis;
- ultrasound examination of the uterus.
Gynecologists recommend abstaining from sexual intercourse for several days before the procedure. The IUD is placed on the third to fifth day of the menstrual cycle. This period is considered optimal for several reasons:
- during menstruation, the endometrium (the mucous membrane of the uterus) is renewed, which ensures reliable fixation of the spiral;
- at this time, the cervix is as open as possible, which facilitates the process of inserting the IUD;
- in medical theory, this period excludes the presence of pregnancy (and yet such cases do occur).
The IUD should only be administered by a gynecologist in a hospital setting. The whole process takes about 10 minutes. It happens like this:
- The patient lies down in the gynecological chair.
- The doctor examines the uterus to determine its position (in which part of the pelvis it is located, whether it has a bend), in order to avoid punctures during the insertion of the spiral.
- The doctor treats the uterine cavity and external genitalia with a special antiseptic solution.
- A speculum is inserted into the vagina.
- The upper part of the uterus is pulled out using a special clamp.
- Then a probe is inserted to measure the length of the uterine cavity.
- Immediately before installation, the spiral is removed from the sterile packaging.
- The IUD is inserted into a special tube through which it is inserted into the uterus. Once attached, the tube is removed.
- The gynecologist shortens the threads (tendrils) of the spiral, which will later be needed to remove it.
The IUD must be inserted by a gynecologist in a hospital setting.
Women who have had an IUD installed say that the pain is nagging in nature and in severity resembles menstrual pain. After ten days, you will need to visit a gynecologist to make sure that the procedure was performed correctly, the spiral is secured, not displaced, and there are no other deviations. Within two weeks after installation of the IUD, a woman is recommended to:
- do not have sexual intercourse;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- refrain from taking a hot bath;
- do not use gynecological tampons.
Removing the spiral
You can remove the spiral at any time during its service life. Typically, its removal, as well as its introduction, occurs during menstruation. In this case, the most favorable will be the first and last days, when bleeding is least abundant. However, these are general guidelines to make IUD removal easier. If necessary, you can remove the spiral on any other day. If its removal is due to the end of its service life, then the next one can be introduced immediately. In addition to the expiration of the spiral’s shelf life, there are other indications for removal:
- a woman's desire to become pregnant;
- displacement or prolapse of the IUD;
- the onset of pregnancy (both uterine and ectopic);
- menopause;
- pain, bleeding, inflammation and swelling caused by the insertion of the IUD.
How the extraction process works:
- The genitals are treated with an antiseptic.
- A gynecological speculum is inserted.
- The tendrils of the IUD are grabbed with tweezers and pulled out of the uterus.
The procedure for removing the coil is absolutely painless and takes a few minutes.
The procedure lasts several minutes and is absolutely painless. During the extraction process, the spiral tendrils may be torn off. In such a situation, the doctor removes it with a medical hook. It often happens that the IUD grows into the wall of the uterus (as a rule, this happens when the IUD has been used longer than expected). In such cases, curettage is performed using anesthesia. Sometimes the spiral grows into the uterus in such a way that its removal becomes possible only through the abdominal cavity under general anesthesia. To avoid this, it is necessary to monitor the service life of the IUD and not miss its end.
Does the procedure cause pain?
Many people worry whether it is painful to insert an IUD without menstruation. Judging by the reviews and comments from the website of girls who use an IUD, or who have had one, the installation process is painless. The most unpleasant sensations are experienced when the doctor tightens the cervix before inserting a probe as it passes into the cervical canal. If the patient is especially sensitive, it is necessary to inform the specialist about this, and before the procedure he will treat the opening of the cervical canal with lidocaine or use another type of anesthesia.
Pregnancy with an IUD installed
The use of an intrauterine device provides an almost 100% guarantee against pregnancy during its service life. However, the risk is still present and is most likely in cases of expiration, incorrectly installed coil or its displacement.
In gynecological practice, although it is rare, pregnancy is diagnosed when an IUD is installed without signs of displacement, incorrect installation and when its service life has not yet expired. Gynecologists find it difficult to explain why fertilization occurs in such cases. Pregnancy that has occurred while using the IUD can be recognized by the usual signs:
- delay of the next menstruation;
- nausea and (or) vomiting;
- chest pain and increase in size;
- increased level of hCG in the blood.
It is important to understand that the signs of intrauterine and ectopic pregnancy are the same. When an IUD is installed, the latter occurs more often. Treatment occurs by removing the fallopian tube in which the embryo was attached. In the future, this reduces the likelihood of getting pregnant by half. In any case, if there is a suspicion of pregnancy, the woman should immediately consult a doctor to confirm or exclude this fact. Even if the embryo is attached to the wall of the uterus, it may be mechanically damaged by the spiral. Therefore, the gynecologist should monitor the course of pregnancy, taking into account the presence of the IUD, and often prescribe ultrasound examinations.
There are often cases when the IUD, injuring the walls of the uterus, provokes its contraction, which leads to miscarriage. There are also situations when the spiral prevents the growth of the embryo. Depending on the clinical picture, the doctor decides whether it is necessary or impossible to remove the coil. Each case is individual. Many women who became pregnant with an IUD went through their entire pregnancy with it and gave birth to healthy children.