Instructions for use
Concor Cor belongs to highly selective β1-blockers that do not have an internal sympathomimetic effect, clinically significant membrane-stabilizing qualities and are indicated for long-term use in patients with symptoms of CHF (chronic heart failure).
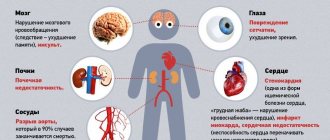
A failing heart is unable to provide blood to tissues that meet their metabolic needs at rest or during exercise. The condition is a serious and sometimes life-threatening complication of many cardiac diseases:
- coronary heart disease (CHD) 50-70%;
- hypertension 12-17%;
- dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) 7-14%;
- valvular heart defects 6-12%;
- other pathologies of the cardiovascular system 5-10%.
Activation of the sympathoadrenal system (SAS) plays an important role in the development of CHF. In most patients, the pumping function of the heart decreases and there is chronic hyperactivation of neurohormones (adrenaline and norepinephrine).
Effects of excessive activation of the SAS in CHF:
- Dysfunction and reduction in the number of cardiomyocytes (through necrosis and apoptosis);
- Deterioration of cardiohemodynamics (blood supply to the myocardium);
- Reduced density and strength of binding of the receptor to the biologically active substance;
- Persistent tachycardia;
- Myocardial hypertrophy;
- Induction of myocardial ischemia due to tachycardia, hypertrophy and vasoconstriction (vasoconstriction);
SAS regulates the functions of internal organs through catecholamines. Norepinephrine has the most aggressive properties. An increase in the level of this hormone from 600 to 900 pg/ml leads to an increase in mortality by 35-40%. Also, its high concentration increases the likelihood of fatal arrhythmias.
β1-adrenergic receptors are localized in the myocardium, adipose tissue, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys and are stimulated by hormones of the adrenal medulla.
Effects of β1-AR stimulation:
- increased strength and heart rate;
- stimulation of impulse transmission along nerve fibers;
- increased secretion of renin in the kidneys (development of arterial hypertension);
- activation of lipolysis (breakdown of adipose tissue);
- decreased motility and tone of intestinal smooth muscles.
Indications: what does the drug help with?
The main indication for continuous use of Concor Cor: CHF and left ventricular systolic dysfunction (EF <40%), the main clinical signs of which are:
- decreased tolerance to physical activity;
- dyspnea;
- fluid retention in the body;
- progressive course;
Symptoms of left ventricular failure:
- venous congestion in the lungs - shortness of breath on exertion, cough, hemoptysis, cardiac asthma;
- decrease in minute blood volume - weakness, drowsiness, nocturia (increased nocturnal diuresis), acrocyanosis (bluish tint to the tip of the nose, lips, ears, fingers and toes), arterial hypotension;
- Myocardial dysfunction – tachycardia, heterogeneous pulse, dilatation of the left heart.
The use of Concor Cor in patients with CHF can slow down the progression or initiate reverse development of LV dysfunction and circulatory failure, and also reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death.
Effects of Concor Cora:
- Decrease in heart rate (negative chronotropic effect), which eliminates myocardial ischemia (due to less oxygen demand of heart tissue and prolongation of diastolic coronary blood flow).
- Blocking myocardial remodeling processes (reducing hypertrophy and cardiac cavities).
- Normalization of LV diastolic function.
- Increased cardiac output (EF).
- Hypotensive effect (reduction of afterload on the myocardium). The drug relaxes the smooth muscle fibers of the vascular wall and reduces its total peripheral resistance (TPPR). Inhibition of the secretion of renin, which, when converted to angiotensin II, causes vasoconstriction (arteriolar spasm).
- Slowing of AV conduction. The drug reduces the concentration of Ca2+ in the cells of the sinoatrial and AV nodes, which prevents the occurrence of rhythm disturbances.
- Reduced electrical instability of the myocardium.
- Inhibition of the sympathoadrenal system. Interfering with the interaction of norepinephrine with specific receptors.
- Decreased pressure in the portal vein system.
- Reduced production of intraocular fluid;
Long-term use of Concor Cor helps to increase the number of β-adrenergic receptors, as a result of which the effect of its use gradually increases.
Concor Cor belongs to the β-AB group with dual clearance (partially soluble in lipids and water). It undergoes biotransformation by hepatocytes by 45-65%, the rest is excreted by the kidneys in its primary form. This explains the low possibility of competition of the drug Concor Cor with other medications and its relative safety in the treatment of patients with concomitant hepatic and renal dysfunction.
The drug is almost completely adsorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The half-life is 9-12 hours. Eating does not change the bioavailability of the drug.
Concor Cor is characterized by high cardioselectivity (14-19 times higher affinity for β1-β2-AR). This makes it safe to prescribe the drug to a wide range of patients (side effects occur in 0.1-1%).
The drug in average therapeutic doses does not change bronchial patency and breathing parameters in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Concor Cor is safe for patients with diabetes, as it does not cause an increase in basal blood sugar levels and does not require dosage adjustment of antidiabetic drugs.
Directions for use and doses
Concor Cor is taken once a day, preferably during breakfast, with a glass of water. The tablet must not be chewed.
The clinical protocol for the treatment of CHF with LV systolic dysfunction involves the use of a complex of drugs: ACE inhibitors, β-blockers (Concor Cor), angiotensin II antagonists, diuretics and cardiac glycosides.
Before starting treatment, you need to make sure that the patient does not have data indicating an exacerbation of cardiac pathology.
Treatment with Concor Cor begins with a gradual increase in dose to the average therapeutic dose and taking into account the body's reactions.
Dose titration scheme (transition to the next stage is possible if the previous dose is well tolerated):
- first week – 1.25 mg Concor Cor;
- second – 2.5 mg;
- third - 3.75 mg;
- fourth - eighth weeks - 5 mg;
- ninth – twelfth weeks – 7.5 mg;
- further maintenance dose is 10 mg/day.
You should be aware of possible manifestations of transient exacerbation of circulatory failure, arterial hypotension or a decrease in heart rate during saturation therapy.
Contraindications
Contraindications for prescribing Concor Cor for CHF are:
- decompensated acute cardiovascular failure, requiring resuscitation measures with intravenous administration of inotropic agents (adrenaline, norepinephrine, dopamine, dobutamine);
- cardiogenic shock, alveolar pulmonary edema;
- AV blockade II-III degrees;
- sinus node dysfunction syndrome;
- sinoatrial block;
- symptomatic decrease in heart rate, arterial hypotension;
- uncontrolled bronchial asthma;
- severe obliterating diseases of peripheral vessels;
- untreated pheochromacytoma;
- metabolic acidosis;
- intolerance to the components of the drug.
Side effects
Possible adverse reactions when using Concor Cor:
- bradycardia, transient worsening of CHF, hypotension, impaired intracardiac conduction, orthostatic collapse;
- vertigo, migraine, fainting;
- hearing loss;
- bronchospasm in patients with asthma and COPD, allergic rhinitis;
- nausea, bowel dysfunction;
- itching, hyperemia, swelling, urticaria;
- muscle weakness, cramps;
- decreased potency;
- depressed mood, sleep disturbances, nightmares;
- increased TG, transaminase activity (ALT, AST);
- asthenia, fatigue.
If a double dose is accidentally taken, dizziness, third-degree AV block, decreased heart rate, and hypotension may develop. Therapy for this condition is symptomatic.
Review: Cardiovascular drug "Concor Cor" - By the way, for tachycardia.
Advantages:
Reduces heart rate.
Flaws:
Side effects.
"Concor Cor" is a selective beta-blocker.
It has a heart-shaped, white, biconvex film-coated tablet with a score line on both sides.
From time to time, attacks of heartbeat (tachycardia) appear, and in this case you have to resort to medications if you also have a high pulse.
"Concor Cor" - began to be taken as prescribed by a doctor, and this drug should be strictly followed under the supervision of a doctor - in order to avoid the opposite effect in the form of angina pectoris (side effects).
If the pulse is high with normal pressure, then not only the heartbeat may decrease, but also the blood pressure, so in this case hypotension and bradycardia are possible, so Concor Cor should be taken with caution.
“Concor-cor” itself took several days, in a course regimen for 10 days, after a few days I noticed an improvement, the heartbeat really decreased, but on the other hand, with constant use, side effects appear in the form of low blood pressure and bradycardia.
If “Concor-cor” is taken for a long time, that is, constantly, then you should NEVER quit abruptly in order to avoid withdrawal syndrome and worse results.
To avoid withdrawal symptoms and worse results, the drug should be stopped gradually, reducing the dose of the medication, but not sharply.
Be healthy!
Time of use:
2 courses.
General impression
.
By the way, for tachycardia.
What to take for cardiac arrhythmia
Arrhythmia is a fairly common heart disease in which the heart rate is abnormal. A person suffering from arrhythmia feels a sinking heart or, conversely, an increase in the frequency of its beats. Medicines for cardiac arrhythmia are prescribed only by a doctor. You must first undergo examinations such as ECD, Holter monitoring and others. Which medications you can take depends on the type of arrhythmia.
Medicines for tachycardia
With tachycardia, the heart rate is above 90 beats per minute.
1. In this case, hawthorn, elecampane, and valerian tincture are prescribed. Corvalol for cardiac arrhythmia quite effectively helps reduce the heart rate.
2. In especially severe cases, it is recommended to take drugs such as verapamil, lidocaine, digoxin, etmozin, propranolol, rhythmilene. It is forbidden to take strong drugs on your own. They must certainly be prescribed by the attending physician after the examination.
3. Tea with lemon balm, infusion of hawthorn flowers and motherwort herbs are suitable as folk remedies for the treatment of tachycardia.
Medicines for bradycardia
With this disease, there is a slowing of the heart rate. The heart beats at a frequency of no more than 60 beats per minute.
1. You can speed up the work of the heart with the help of medications such as atropine, atenolol, aminophylline, alupent. They cannot be taken on their own. All of the drugs listed are quite potent and, if taken incorrectly, can cause harm to the body.
2. You can speed up the work of the heart with the help of folk remedies. In this case, decoctions of yarrow and young tops of pine branches are suitable for the treatment of bradycardia. It is also recommended to eat a lot of nuts and a mixture of lemon and garlic.
Medicines for atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is characterized by chaotic contractions of both atria.
1. Allapinin for arrhythmias helps normalize heart function. You can also take amiodarone, disopyramide, sotalol, etacizine, quinidine, propafenone. In addition, Concor is taken for arrhythmia. This drug has a long shelf life, but is expensive. As a cheaper analogue, you can use bis-sagamma.
2. Folk remedies for atrial fibrillation can be taken without fear. The following will help to cope with an attack: hawthorn tincture, valerian rhizomes, trifoliate, peppermint collection, calendula flower tincture, eleutherococcus extract.
Medicines for extrasystole
Extrasystole refers to premature contractions of the heart.
1. You can fight this heart disease by taking the following medications: oxprenolol, pindolol, atenalol, propranolol, metoprolol, sotalol, amiodarone, talinolol. Medications are prescribed only by a doctor.
2. For those who prefer traditional medicine, this disease can be treated with infusions of valerian, calendula flowers, cornflower, lemon balm and horsetail. In addition, you can take hawthorn for arrhythmia and decoctions of adonis, rosehip seeds, and valerian.
Analogs and substitutes for medicines
The active substance in Concor Cor is Bisoprolol. The drug is quite cheap, the price of 30 tablets varies from 160 to 200 rubles.
Analogues presented on the Russian market:
Bisoprolol, Aritel, Biprol (Russia);- Bidop, Bisoprolol Richter (Hungary);
- Bickard, Corbis (India);
- Bisokard (Poland);
- Cordinorm, Bisostad, Bisoprolol Hexal, Sandoz, Ratiopharm, Teva (Germany);
- Bisoprolol KRKA (Slovenia);
- Dorez (Macedonia);
- Coronal (Slovakia).
Substitutes for Concor Cor can be medications containing the active substance Metoprolol. These two β-blockers have similar mechanisms of action and indications for use. The difference between them is that Metoprolol has a short duration of action and must be taken 3-4 times a day.
Drug interactions
The following combinations with Concor Core are not recommended:
- verapamil, diltiazem - can contribute to a decrease in myocardial contractility and disrupt AV conduction;
- quinidine, disopyramide, phenytoin, flecainide, lidocaine, propafenone and other class I antiarrhythmic drugs - can cause a decrease in AV conductivity and cardiac contractility;
- clonidine, methyldopa, rilmenidine, moxonidine and other centrally acting antihypertensive drugs - can lead to a decrease in heart rate and cardiac output, and to vasodilation against the background of a decrease in central sympathetic tone; their abrupt cancellation, especially before bisoprolol is discontinued, increases the risk of developing rebound arterial hypertension.
With simultaneous use of Concor Cora:
- amiodarone and other class III antiarrhythmic drugs may cause increased AV conduction disturbances;
- slow calcium channel blockers, dihydropyridine derivatives (including nifedipine, amlodipine, felodipine) may increase the risk of arterial hypotension; in patients with CHF there is a high probability of subsequent deterioration in cardiac contractile function;
- beta-blockers for local use (including eye drops for the treatment of glaucoma) can enhance the systemic effect of bisoprolol (lowering blood pressure, lowering heart rate);
- hypoglycemic agents for oral administration, insulin can enhance their effect, mask or suppress signs of hypoglycemia, including tachycardia;
- parasympathomimetics may increase the risk of developing bradycardia and worsen AV conduction disturbances;
- agents for general anesthesia increase the likelihood of cardiodepressive effects and arterial hypotension;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can reduce the hypotensive effect of the drug;
- cardiac glycosides can cause an increase in impulse conduction time, increasing the risk of bradycardia;
- beta-agonists, including isoprenaline and dobutamine, may help reduce the effect of each drug;
- antihypertensive drugs, phenothiazines, barbiturates, tricyclic antidepressants may increase the hypotensive effect of bisoprolol;
- norepinephrine, epinephrine (adrenomimetics that affect alpha and beta adrenergic receptors) can enhance their vasoconstrictor effect, causing an increase in blood pressure;
- mefloquine increases the risk of bradycardia;
- MAO monoamine oxidase inhibitors (except type B) increase the hypotensive effect of beta-blockers and increase the risk of developing a hypertensive crisis.
conclusions
The effectiveness of β-AB has been proven by numerous studies, due to which medications in this group are included in clinical protocols.
Long-term therapy in patients with LV dysfunction improves quality of life and reduces mortality by 25-30%.
It is worth remembering that in no case should you suddenly stop taking it due to the high likelihood of developing a transient exacerbation of the disease.
Before using the drug, you should consult your doctor and read the instructions carefully.
Side effects
- from the cardiovascular system: very often – bradycardia; often - a feeling of numbness or coldness in the extremities, a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, worsening the symptoms of CHF; uncommon – orthostatic hypotension, AV conduction disturbance;
- from the central nervous system: often – headache, dizziness; rarely – loss of consciousness;
- mental disorders: infrequently – insomnia, depression; rarely – nightmares, hallucinations;
- from the digestive system: often – nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea; rarely - hepatitis;
- from the organ of hearing: rarely – hearing impairment;
- from the organ of vision: rarely - decreased tear secretion; very rarely - conjunctivitis;
- from the respiratory system: infrequently - bronchospasm (if a history indicates bronchial asthma or airway obstruction); rarely – allergic rhinitis;
- from the musculoskeletal system: infrequently – muscle cramps, muscle weakness;
- from the reproductive system: rarely - impaired potency;
- dermatological reactions: rarely – hypersensitivity reactions (skin itching, rash, hyperemia); very rarely - alopecia; with psoriasis - possible exacerbation of symptoms of the disease, psoriasis-like rash;
- laboratory parameters: rarely - increased concentration of triglycerides, activity of liver enzymes in the blood plasma (alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase);
- general disorders: often - increased fatigue, asthenia.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to bisoprolol or other components of the drug.
- AV block.
- Acute and chronic (decompensation) heart failure .
- Arterial hypotension.
- Sick sinus syndrome.
- Bradycardia.
- Sinoatrial blockade.
- Bronchial asthma or COPD .
- Cardiogenic shock.
- Disorders of the arterial part of the peripheral circulation.
- Pheochromocytoma.
- Age up to 18 years.
- Metabolic acidosis.
Compound
The composition of one Concor Cor tablet includes hemifumarate and bisoprolol fumarate in a quantitative ratio of 2:1. Excipients: colloidal silicon dioxide , corn starch, MCC, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, calcium hydrogen phosphate. Shell composition: macrogol 400, hypromellose, dimethicone 100, titanium oxide.