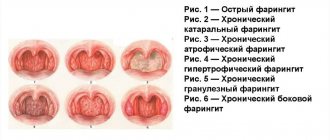
What is this?
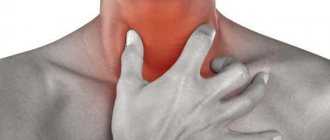
Sore throat is classified as an acute infectious condition that has a viral nature of spread. It mainly affects the tonsils on the palate, and in some cases it affects some tissues of the nasopharynx, such as the laryngeal and tongue tissues.
The pathology is characterized by the presence of many varieties of its course. To determine the exact pathology that occurs in each individual case, a visit to a local primary care physician is necessary for examination.
After performing an analysis of the mucous membrane of the throat area, the pharyngoscopic picture of this disease is determined.
After relying on the specific data obtained as a result of the study, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis.
In this way, herpetic, catarrhal, as well as lacunar and other forms of tonsillitis can be diagnosed. Completeness of the picture is given by taking photographs of the disease in each individual case.
Diagnostics and laboratory tests
The diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical manifestations and is confirmed by laboratory data in both children and adults.
A general blood test is performed, which shows an increase in the number of leukocytes, an increase in rod nuclear neutrophils and an acceleration of ESR. In a general urine test, due to intoxication in the acute period, a small amount of protein, single leukocytes and red blood cells are detected. In a throat smear, culture reveals the growth of streptococcus or staphylococcus.
For any sore throat, it is necessary to take a swab from the nose and throat for diphtheria.
Causes
The reasons for the occurrence and development of the problem vary depending on its type and generally come down to the following:
- hypothermia due to prolonged stay in a poorly heated room;
- entry into the patient’s body of viruses that are infectious in nature;
- rapid development of pathogenic microorganisms in the patient’s body when they enter a favorable environment;
- the patient’s stay in prolonged, direct contact with the carrier of this disease;
- decreased immunity after an acute respiratory viral infection;
- the consequences of improper treatment of a previously occurring disease, which is also infectious in nature;
- intoxication of the entire body through direct contact with a possible allergen, which as a result becomes the causative agent of the disease;
- other reasons that may be associated with a violation of the level of local immune defense of the patient.
Depending on the causes of angina, the attending physician prescribes methods of treatment for this condition.
In any case, a preliminary examination of the patient is necessary in order to determine the exact cause of sore throat.
Etiology
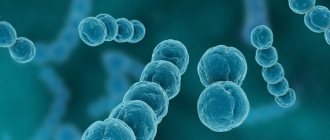
Streptococcus is the most likely causative agent of sore throat.
Sore throat is a disease of streptococcal etiology. In approximately 85% of all cases, streptococcus is detected in pharyngeal swabs of patients. This is a spherical bacterium, located in pairs or in a chain. Most of these microorganisms, of which there are quite a few, are non-pathogenic or opportunistic bacteria that make up the normal flora of the human body. However, several species are dangerous to the warm-blooded inhabitants of the globe and cause diseases.
These are group A streptococci, which, when multiplied in the body, release exotoxins and produce pathogenic enzymes.
Properties of streptococci:
- die when boiled and exposed to disinfectant solutions;
- preserved at low temperatures and drying;
- in pus and sputum remain pathogenic for months.
Other pathogens
Staphylococci cause damage to the pharynx in approximately 12-13% of cases. These are round, single microbes that produce exo and endotoxins and specific enzymes that disrupt cell activity. Approximately 2-3% of inflammatory changes in the pharynx are caused by the symbiosis of Vincent's bacillus and spirochete (ulcerative membranous sore throat of Simanovsky-Vincent). The development of tonsillitis , as a complication of other ailments, is caused by the addition of streptococcus or staphylococcus to the main pathogen.
Syndrome of another disease
In some infectious pathologies, acute tonsillitis is one of the symptoms or a specific form of the disease (herpetic sore throat with enterovirus infection, anginal form of syphilis or listeriosis, anthrax). In such cases, the pathogen affecting the tonsils is the causative agent of the main lesion.
What does a sore throat look like?
A sore throat in the throat area can be identified by a number of external signs.
The most common ones include:
- redness of the throat and nasopharynx where the virus enters, which causes this condition;
- some swelling in the throat where the disease-causing virus is located;
- irritation gradually spreading to nearby areas;
- white dots that quickly spread over all surfaces of the mucous membrane of the throat.
In some cases, all symptoms without exception are observed simultaneously.
Then we can talk about the development of a complex form of the disease, which requires urgent placement of the patient in a hospital hospital.
Forms
The clinical picture is due to the direct impact of the microbe on the cells of the mucous membrane, the entry into the blood of waste products of bacteria and substances formed during their death, destroyed cells, and the influence of toxins produced by the bacterium.
The following forms are distinguished:
Catarrhal
The pathological process and intoxication are moderately expressed, there are practically no changes in the throat, hyperthermia is short-lived, does not rise above 38 degrees.
Follicular
Purulent deposits in the form of islands are visible on the tonsils, the temperature can rise to febrile levels, poor health, and enlarged submandibular lymph nodes.
Lacunarnaya
Pronounced purulent deposits in the lacunae, severe sore throat, fever up to 40 degrees, weakness, lack of appetite.
Ulcerative-necrotic
The tonsils are covered with a dirty gray, sometimes green coating, mucosal defects, fever, unbearable sore throat.
Not complicated
Ends with recovery, without residual manifestations and consequences within 10 days.
Complicated
- Local spread of the inflammatory process. Paratonsillitis, peritonsillitis, and epiglottitis develop.
- Complicated by the appearance of long-term consequences. Possible involvement of damage to the joints (arthritis), heart (endocarditis, myocarditis), kidneys (glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis).
Atypical form
. It occurs with normal temperature and not intense pain.
Common
Sore throat of the palatine tonsils, lingual tonsil, lateral ridges, widespread with damage to the entire lymphoid ring of the pharynx (forms of the disease according to the extent and localization of local changes)
First signs and symptoms
The initial signs and symptoms of such a disease can be considered the following manifestations:
- a sharp increase in temperature occurring against the background of chills;
- general malaise observed due to the development of intoxication of the whole body;
- increased fatigue after physical activity;
- sharp pain in joints that does not go away over time;
- difficulty swallowing, which is a consequence of the development of an inflammatory process in the tonsils; in such cases, the opening in the nasopharynx becomes smaller and food becomes more difficult to pass through it;
- When the disease is severe, necrotic areas form, which become clearly visible by their dark gray background.
Epidemiology
Distribution routes:
- Airborne, when infection occurs from a sick person, or a carrier when droplets of infected saliva enter the mucous membrane of a healthy person.
- Contact, when saliva gets into contact with germs through direct contact, for example through kissing, or when using insufficiently treated utensils or personal hygiene products, medical instruments.
- Hematogenous, when the pathogen enters the pharynx from other foci of inflammation in the body (otitis media, caries, sinusitis, boils) When opportunistic human flora is activated against the background of immunodeficiency conditions caused by diseases of the immune system, severe pathology of internal organs, and neuropsychic stress.
Immunity does not develop after a sore throat
How to diagnose?
Diagnosis of this disease is carried out after a direct examination of the patient and identification of all signs of his condition.
The full picture of the disease becomes completely clear after a preventive examination of the patient, identifying all external signs of his condition.
Depending on the symptoms of the disease, the principles of its treatment are prescribed, including the use of methods of both traditional and traditional medicine.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention for streptococcal infection.
It is recommended to avoid hypothermia, contact with patients with streptococcal infections and the presence of pustular rashes. If you have symptoms of chronic tonsillitis, have your tonsils washed by an otolaryngologist at least twice a year. In order to improve local immunity, use lysobacter.
In conclusion, I would like to say that bilateral purulent tonsillitis is an infectious disease that requires adequate complex therapy. With appropriate treatment, it completely regresses with complete recovery. However, if the therapy regimen is not followed, severe complications arise, sometimes leading to permanent decrease in working capacity. Treat a sore throat correctly; at the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor!
Do not be ill! See you!
Purulent sore throat
The purulent variety of this condition implies the presence of purulent discharge in the mouth from the location of the disease.
Accompanied by abscesses in places where the disease spreads, which are infectious in nature. The discharge of purulent masses can occur either periodically or be observed constantly.
The patient begins to complain of severe chills, his body temperature rises sharply, sometimes up to 39 degrees Celsius and above.
Preventive actions
There is no 100% effective prophylactic remedy, however, there are a number of recommendations to reduce the likelihood of developing purulent tonsillitis.
Attention! Strengthen your immune system through hardening procedures and including foods rich in vitamins and minerals in your diet.
The child must observe the rules of personal hygiene, since most infectious agents enter the body through household means. Also, to strengthen the immune system, follow a work and rest schedule.
It is necessary to exclude hypothermia of the body and promptly treat diseases of the oral cavity and nasopharynx.
Purulent tonsillitis is a common pathological condition that requires mandatory treatment. The disease is dangerous due to early and late complications.
Catarrhal
This type of condition in question is characterized by damage to the mucous membranes of the tonsils, after which severe pain occurs when swallowing.
Are you looking for an answer to the question: how to correct malocclusion in an adult? Then you just need to follow the link and read our article. If you are interested in the question of how long you can keep arsenic in your tooth during pregnancy, then our article will be very useful to you!
The patient's body temperature rises sharply, up to 38 degrees Celsius and above.
The lymph nodes increase in volume, the patient feels some discomfort, the palatine tonsils increase in size and noticeably redden.
After a sore throat (Criteria for recovery)
During the treatment, general well-being improves, sore throat disappears, and temperature normalizes. In the pharynx, the inflammatory process regresses. The tonsils are reduced in size and cleared of plaque. The submandibular lymph nodes become small and painless.
Patients need to take a course of antibacterial agents for 10 days.
After completing the course of treatment, a control study of a general blood test, a general urinalysis, and an ECG are performed.
The patient is considered healthy after a sore throat if there are no clinical manifestations of the disease and normal test results.
Viral
The viral type of sore throat manifests itself in severe pain in the neck area, this is the main symptom.
In addition, the patient has a strong fever, he has a feeling of chills, and his body temperature rises.
The neck often swells, severe pain occurs in the throat, his voice changes and a sharp, rather unpleasant odor appears in the mouth.
Traditional recipes for sore throat.
When treated at home, the following simple recipes will help you quickly overcome a sore throat; they will relieve pain and inflammation:
- Milk and honey . An alternative drink to raspberry tea. Milk has a calming effect and relieves pain. For greater effect, it is recommended to serve slightly hot with the addition of butter. Not recommended for people with allergies and individual intolerance to bee products. Contraindicated for children under one year of age.
- Solution with honey for rinsing: in a glass of boiled water, pre-cooled to a temperature of about 40 degrees, dissolve a spoonful of honey that is in the house. Add a spoonful of apple cider vinegar 6% to it.
Compresses
When applying compresses, the inflammatory processes that have begun are stopped, pain in the throat is reduced and blood circulation improves.
Important. Compresses can only be used at normal temperatures. When the disease has entered its late phase, and when abscesses have formed, they cannot be done.
For children, the best time to apply compresses is before bed. Your feet should be warm under a blanket or in socks. Apply 1-2 times during the day.
An adult compress is applied for 3-4 hours with breaks of 2 hours between them.
Alcohol compress: 70% medical alcohol is diluted with boiled water in a 1:1 ratio. An alcoholic herbal tincture will give the maximum effect. If you don’t have it in your house, you can add a small amount (3-5 drops) of essential oil to the existing alcohol.
Lavender, sage, mint, eucalyptus are suitable.
Not recommended for people with sensitive skin, there is a high risk of burns.
Potato compress
Preparation: wash and boil the potatoes with the skins. Mash and add a couple of drops of alcohol-based iodine and a spoonful of vegetable oil. Wrap everything in a gauze bag. Wait until the compress has cooled down a bit so that it can be applied to the skin painlessly. Place the bag on your throat and wrap your neck well. The compress can be kept throughout the night.
Lacunarnaya
Lacunar tonsillitis can occur in a patient at any age, without exception.
As a rule, this form of the disease is characterized by the presence of high body temperature, the development of fever, the occurrence of persistent changes in the timbre of the patient’s voice, as well as the spread of pus over the surface of the palatine tonsils.
Carrying out special measures reduces the likelihood of sore throat spreading in the future.
The duration of this form of the disease takes one week.
Follicular
The follicular form of the disease manifests itself in accumulations in the lacunae of a peculiar fibrous type exudant.
White plaques form, gradually spreading over the entire surface of the patient's throat.
Treatment is comprehensive and includes a set of measures to eliminate all symptoms of this condition. This form of the disease usually lasts from six to eight days.
How to treat?
Treatment of angina is carried out using folk and traditional medicine. In case of high temperature, the patient is advised to undergo intensive bed rest in the first days of the disease. It is necessary to provide him with complete peace and quiet.
The doctor prescribes medications that are indicated by the principles of traditional medicine in each specific case of the disease.
Physical activity is sharply limited, the sick person is offered only soft food, mainly vegetable and dairy based. It is also important to drink plenty of warm drinks.
Treatment is often carried out with medications. Fusafuccin is used for inhalation; among its negative reactions is the ability to cause irritation of the mucous membrane of the throat.
Ambazon and Gramicidin tablets are used; if it is necessary to reduce the temperature, analgesics and fever-reducing agents are used.
The danger of sore throat and its treatment
Follicular and lacunar tonsillitis are very contagious diseases that often occur in the form of “family epidemics.” Therefore, if one of the family members gets sick, he must be placed in a separate room and not share dishes, towels and other household items with him.
Treatment of purulent sore throat includes taking antibiotics in the form of tablets (only as prescribed by a doctor). Rinsing also promotes faster recovery as it helps remove pus from the mouth. For the first 1-2 days (or more if the fever persists), you must adhere to strict bed rest. To reduce the temperature, you can take antipyretic medications. During the entire period of illness, you need to drink warm drinks often and a lot. Do not take food that irritates the throat (hot, cold, spicy, hard). Vitamins also have a positive effect.
Diet
Dietary instructions require the use of foods that do not irritate the oral mucosa.
Avoid the use of anything hot, spicy, or anything that can cause allergic reactions to the oral mucosa.
It is also recommended to follow some simple dietary guidelines:
- porridge with milk is consumed, its consistency reminiscent of jelly;
- pureed fruits and purees;
- only white bread;
- Small pasta is best eaten;
- It is also important to consume dietary fish varieties, in particular pollock, cod and bream.
It is best to coordinate your diet with your doctor.
Do you want to know how to properly do speech therapy massage for children at home? Detailed information on this issue is presented in the article. At what age is the frenulum under the tongue cut in children, you can read this link.
You can learn more about the reasons for increased salivation in women during menopause from the article.
Diagnosis of the disease
After the development of characteristic symptoms, you need to call a doctor at home or go to the clinic yourself.
The following doctors can make a diagnosis: therapist, ENT specialist, infectious disease specialist, general practitioner.
Since acute tonsillitis has characteristic complaints and clinical manifestations, diagnosing a sore throat is not difficult.
Important to know: Treatment of herpes sore throat in children
It is more difficult to establish the cause (bacterium) that caused the development of the disease. To clarify the pathogen, swabs are performed from the mucous membranes of the tonsils and pharynx. They take smears to exclude the causative agent of diphtheria (Lefler's bacillus).
The examination reveals not only the pathogen itself, but also determines which antibiotics it is sensitive to.
This is necessary for high-quality, effective treatment.
Complications and consequences
The following factors should be noted as possible complications of the described condition:
- transition of the disease from acute to chronic;
- the occurrence of serious hearing problems;
- complications affecting brain function;
- significant vision problems;
- complications consisting in disruption of the vestibular apparatus;
- deterioration in the functioning of brain cells.
In some cases, a combination of some consequences of the disease at the same time is possible.