Vitamin F is an anti-cholesterol, fat-soluble vitamin consisting of unsaturated fatty acids obtained from food.
In fact, vitamin F should be understood as a combination of several fatty acids: linoleic, linolenic, arachidonic , therefore, in early sources, there is no mention of vitamin F, and only now this name began to be used after the systematization of the above 3 acids.
In scientific and patent literature, advertising brochures and technical documentation, vitamin F refers to lipid preparations containing essential fatty acids, in particular gamma-linolenic acid.
When both families of polyunsaturated fatty acids were first discovered in 1923, they were classified as vitamins and called "vitamin F." In 1930 it was shown that both families belong to fats and not to vitamins at all
But, nevertheless, leaving the traditional name “vitamin” for polyunsaturated fatty acids, they should, from a biochemical as well as pharmacological point of view, be classified as a special group of biologically active compounds that have both paravitamin and parahormonal effects. The first is supported by their ability to eliminate vitamin deficiency-like phenomena when introduced into the body. The parahormonal action of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the presence of the enzyme prostaglandin synthetase is supported by the ability to convert into prostaglandins, leukotrienes, thromboxanes and other powerful intracellular mediators of hormonal effects.
Linoleic, linolenic, and arachidonic acids are very sensitive to sunlight, elevated temperatures, and are also quickly destroyed upon contact with air, but with proper storage and use of products containing vitamin F, the body is fully provided with it.
Functions of Vitamin F
The main property of vitamin F is its participation in the absorption of fats, normalization of fat metabolism in the skin and the removal of excess cholesterol from the body. This vitamin is especially relevant for fast food lovers, where some food is simply loaded with cholesterol. And in general, in the era of GMOs, it is always worth keeping an eye on what you and I, dear readers, eat.
Vitamin F is also important for the cardiovascular system, because... In addition to removing excess cholesterol, it also prevents its excess deposits in the arteries, strengthens the walls of blood vessels, improves blood circulation, normalizes blood pressure and pulse.
Due to the improvement in fat metabolism, weight normalization occurs, which has a positive effect on the health of people suffering from excess body weight. By the way, if excess weight is a pressing issue for you, I suggest you read this article, which explains quite well how to lose extra pounds.
Vitamin F is a fat-soluble vitamin, so it requires fat to be absorbed.
Vitamin F effectively fights inflammatory processes in the body, improves tissue nutrition, affects the processes of reproduction and lactation, has an anti-sclerotic effect, and ensures muscle function. In addition, it deeply moisturizes the skin, keeping it healthy. Vitamin E (tocopherol) also boasts a similar function.
Read also Table for testing vision (Sivtsev table)
Together with vitamin D, vitamin F promotes the absorption of calcium (Ca) and phosphorus (P), which is essential for bone tissue. Regular use of this vitamin also helps improve the absorption and increase the activity of other vitamins: , , and all representatives of group B.
Vitamin F is used for the prevention and treatment of skin diseases, atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes, bronchial asthma, immunodeficiency and cancer.
Vitamin F has an antiallergic effect. Gamma-linolenic acid can be transformed through dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid into prostaglandins E1. It is known that E1 prostaglandins inhibit the first phase of histamine release, for example from mast cell granules, and relieve allergic bronchospasm caused by histamine, and also have a sensitization-preventing effect, like histamine inhibitors.
Vitamin F plays an important role for the musculoskeletal system. By ensuring normal nutrition of joint tissues, fatty acids have a preventive effect on the development of osteochondrosis and rheumatoid diseases.
Gamma-linolenic acid, like other polyunsaturated fatty acids, is an energy substrate in the process of intracellular respiration and is part of the phospholipids of animal cell membranes. With a lack of it in food, the functioning of biological membranes and fat metabolism in tissues is disrupted, which leads to the development of pathological processes, in particular dermatoses, liver damage, and vascular atherosclerosis develops.
In addition, vitamin F has many other functions:
- treats a number of skin diseases: eczema, dermatitis and allergies; - protect the skin from aging; - maintains a healthy condition: hair, nails, mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract); - has anti-inflammatory and antihistamine effects; — improve the process of sperm maturation, which has a beneficial effect on reproductive function; — stimulates the body’s immune system (defense); - prevents the formation of blood clots; - protects cells from damage by harmful substances; - affects the formation of prostaglandins and much more.
Clinical researches
The conducted clinical study proves the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of the product for daily skin care of children with mild and moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
All products of the Atoderm line were developed with the participation of Denis Vladimirovich Zaslavsky, professor of the Department of Dermatovenerology of the St. Petersburg State Pediatric Medical University, chief specialist in dermatovenerology and cosmetology of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation in the Northwestern Federal District of the Russian Federation.
The brand's products are recommended by the Union of Pediatricians of Russia.
Metabolism of Vitamin F
Essential fatty acids are absorbed in the small intestine, like other fatty acids, and are transported as part of chylomicrons to the organs. In tissues they are used to form the most important lipids that are part of biological membranes and have regulatory activity. During metabolism, some of their double bonds are restored.
If there is enough linoleic acid in the body, then the other two fatty acids can be synthesized. Excessive carbohydrate consumption increases the need for vitamin F.
Read also Hypovitaminosis - causes, symptoms and treatment of hypovitaminosis
The body accumulates this vitamin in the heart, liver, kidneys, brain, blood, and muscles.
Diagnostics
At the first suspicion of hypovitaminosis (this applies not only to vitamin C, but also to other groups of vitamins), you should consult a doctor. The signs described above may be cause for concern. Any doctor, regardless of whether he is a general practitioner or works in a narrow field, must remain vigilant, study medical histories in detail, carry out an external examination, and take into account not only those complaints that have appeared recently.
A more accurate diagnosis is carried out using urine and blood tests in the laboratory. Depending on the situation, a consultation with other doctors may be scheduled and, if necessary, an examination may be carried out with them.
Symptoms of deficiency (hypovitaminosis) of vitamin F
Most often, vitamin F deficiency manifests itself in early childhood (in children under 1 year of age), which may be due to insufficient intake from food, malabsorption, and infectious diseases.
The clinical picture of hypovitaminosis in children is manifested by stunted growth, weight loss, peeling of the skin, thickening of the epidermis, increased water consumption with decreased diuresis, and loose stools. In adults, suppression of reproductive functions and the development of cardiovascular and infectious diseases are also observed.
In addition, vitamin F deficiency can lead to the development of diseases that are difficult to treat, as well as premature aging.
With a lack of vitamin F, the functioning of the liver, immune and cardiovascular systems suffers.
With a long-term lack of vitamin F in adults, the risk of developing arterial hypertension (AH), atherosclerosis, and their complications - heart attack and cerebral stroke increases.
Additional symptoms of vitamin F deficiency:
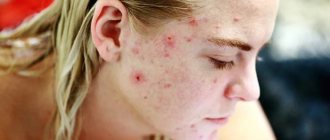
— skin diseases (in particular eczema), even in infants, may occur; - allergic diseases; - dullness, brittleness and hair loss; - brittle nails; - acne; - excess cholesterol; — cracks, incl. anal; - decreased firmness and elasticity of the skin; - appearance of dandruff (seborrhea).
Face masks
Vitamin F for the face is an indispensable element in cosmetic products for maintaining beauty. There are many recipes based on polyunsaturated fatty acids to maintain youthful skin.
Here are some:
- Mask with olive oil and yolk . To prepare the mixture, break one egg, separate the white from the yolk. Mix the yolk with honey and olive oil in equal proportions. Apply the mask to your face and leave for 20 minutes. After time, rinse with warm water. This recipe enriches the skin with beneficial substances, regenerates tissue and promotes the healing of microcracks.
- To eliminate small wrinkles, you can use the following recipe. Mix grated lettuce leaves with one drop of lemon juice, add vegetable oil. Regular masks will protect your skin from negative environmental influences.
- To eliminate age spots, it is useful to use a mixture with homemade cottage cheese and sunflower oil. The whitening properties of fermented milk products even out skin tone, and vegetable oil nourishes tissues and prevents them from drying out.
Vitamin F for the skin stimulates the natural production of collagen, preserves the youth of the face for a long time, and also has an antioxidant effect and removes toxic substances. Be attentive to your health and provide your body with timely assistance in the fight against time.
Indications for taking vitamin F
— various types of dermatoses (eczema, seborrhea, acne, fissures, including anal fissures); - eczema in infants; - allergies; - excess cholesterol; - diabetes; - prevention of phlebitis; — autoimmune inflammatory diseases; - dullness, brittleness and hair loss; - flabby dry skin; - for atherosclerosis; - for rapid healing of wounds, as well as in the postoperative period; — for the prevention of cardiovascular and infectious diseases; - to support the immune system in good shape; — lipid metabolism disorders; - as a comprehensive remedy for restoring reproductive function.
Daily requirement of vitamin F
As you and I already know, unsaturated fatty acids (vitamin F) are essential, but they themselves are not formed in the body, so they must come from food.
The daily requirement of vitamin F is measured in mg.
There is no clear data on the required amount of vitamin F for the body, so there are approximate data - about 1000 mg.
To get this amount of fatty acids to the body, you need to swallow 25-35 g (two tablespoons) of vegetable oil.
For people with high blood cholesterol, overweight, and vascular atherosclerosis, it is recommended to consume 10 times more vitamin F, which is due to its ability to accelerate slow fat metabolism.
Read also Symptoms and signs of hyperactivity in a child
The dosage also increases when playing sports. If the type of exercise is speed-strength, then during training the need is 5-6 g per day, during competitions 7-8 g per day. If classes are aimed at developing endurance, then the entire training period, the dosage of vitamin F is 7-9 g per day, during competitions it increases to 10-12 g per day.
In addition to athletes, the daily dose of vitamin F should be increased for pregnant and nursing mothers. However, during pregnancy and breastfeeding, doses should only be prescribed by a doctor
The absorption of fatty acids in the intestines is influenced by the composition of the food consumed. The more carbohydrates, the less fat-soluble vitamins are absorbed, including vitamin F. Carbohydrates act as a kind of sponge that “absorbs” linoleic and linolenic acids.
Additional amounts of vitamin F are also required for people undergoing treatment for skin and autoimmune diseases, prostatitis, diabetes, and during organ transplant operations.
Consumer Reviews
Alya Nikolaeva about the cream for dry skin “La-Cri” (irecommend.ru)
“The first time I bought this cream for a child (he had very dry skin on his arms and legs), but then the need for the cream disappeared and it just collected dust on the shelf. But then my night cream ran out (suddenly, as always), I delayed buying a new one and as a result I had to rummage through old supplies, hoping to at least find something... then I came across a forgotten tube of La Cree. It was winter (we have windy weather, but no frost), I read it and decided that it would be just right. I have combination skin that needs moisturizing. There are already wrinkles and small creases around the eyes.
In general, without thinking twice, I smeared it on my face.
The cream is in a tube, which is good, it doesn’t come into contact with air and you don’t have to take it out of the jar.
The color is white, the consistency is thick. It smells like baby cream from a distant childhood, but it doesn’t bother me. Economical consumption, lasts a long time.
Despite the fact that the cream is thick, it applies quite well and spreads easily. It took a long time to be absorbed, but since I used it as a night product, this was not critical.
In the morning I was pleasantly surprised, my face was moisturized, no creases had formed on the skin overnight, and later those that already existed became smaller. The face is fresh, not swollen. Photo some time after using the cream (the crease has smoothed out a little).
Being delighted with this effect, I tried to use it during the day, but it turned out to be not very convenient, the cream is still a bit heavy.
I’m already using my second tube, I’m very pleased, this is the most successful of my recent purchases.
Sold in pharmacies and inexpensive.
The cream is recommended from birth. Although in general it is not positioned as natural. The first 3 lines in the composition are occupied by water, liquid paraffin (mineral oil), and emulsifier. All natural components come later, so their concentration is no more than 3%, which is what is written there. So, if you are exclusively for natural cosmetics, this is not your option. But the cream really works."
Tanost about foam shampoo “La Cree” (otzovik.com)
“When my eldest son was born, his entire head under the hairs was covered with a crust. At the maternity hospital they assured me that I didn’t need to do anything special, just wash my hair periodically, and the crust would go away on its own over time. My son is now 2.5 years old, but this problem has practically not gone away. I bought a special softening gel and smeared it with olive oil, but to no avail. And then about four months ago, a pharmacist friend advised me to take La Cree foam shampoo from birth.
We use shampoo about every other day. I really liked its composition: licorice extract, glycerin, olive oil, castor oil, violet extract, salicylic acid, jojoba oil, wheat proteins, rosewood oil.
A bottle with a dispenser, which is very economical and convenient.
The foam is very soft and gentle with a “tear-free” formula.
After four months, there was no trace left of the unfortunate crust; after my head had dried, I simply combed out the flakes that remained on my hair with a comb. We still use La Cree shampoo.”
Sources:
- Dermatology: an illustrated guide to clinical diagnostics according to Professor A.N. Rodionov. / Rodionov A.N., Zaslavsky D.V., Sydikov A.A. Edited by Professor A.N. Rodionova.M.: Border. 2021.- 944 p.
- Skin diseases of newborns and infants. Guide for doctors / Gorlanov I. A., Leina L. M., Milyavskaya I. R., Zaslavsky D. V. St. Petersburg: Folio. 2021.-208 p.
- Clinical reader on pediatric dermatology: Textbook / Kochergin N. G., Gorlanov I. A., Zaslavsky D. V., Olisova O. Yu., Leina L. M., Milyavskaya I. R. M.: Practical medicine 2021 .-127 p.
Photos of vitamin deficiency
You can see photos of vitamin deficiency on our website.
Sources of Vitamin F
Natural
Plants . Vegetable oils from wheat ovary, flaxseed, sunflower, safflower, soybeans, peanuts; almonds, avocado, walnuts, sunflower seeds, black currants, dried fruits, oatmeal, corn, brown rice. All vegetable oils must be first cold pressed, unfiltered, undeodorized (i.e., retain their odor).
Animals. Fatty and semi-fat fish (salmon, mackerel, herring, sardines, trout, tuna), fish oil.
Synthesis in the body. Vitamin F is not synthesized in the body.
Chemical
Information awaited.
Vitamin F is very unstable to elevated temperatures, i.e. it is only found in cold-pressed oils, which should be taken into account when choosing this product. Additionally, sunlight also reduces the vitamin F content of the oil, so it should be stored in a cool, dark place.
What products contain
Most vitamin F is found in vegetable oils.
Unsaturated fatty acids are also found in animal fats, nuts, beans, and seafood. Table of vitamin F content in food
| The product's name | Amount of vitamin F (in g) |
| Fish fat | 99,9 |
| Cod liver | 15 |
| Olive oil | 9 |
| Linseed oil | 18,1 |
| Rapeseed oil | 10,3 |
| Grape seed oil | 70 |
| Sesame oil | 41 |
| Sunflower oil | 66 |
| Mustard oil | 16 |
| Corn oil | 54 |
| Cottonseed oil | 52 |
| Walnut oil | 53 |
| Soybean oil | 50 |
| Peanut butter | 32 |
| Hemp seed | 8,1 |
| Pumpkin seeds | 5 |
| Dry soybeans | 1,6 |
| Walnuts | 6,8 |
| Oat germ | 1,4 |
| Halibut | 1,8 |
| Mackerel | 5,3 |
| Herring | 3,1 |
| Salmon | 2,3 |
| Trout | 2,6 |
| Tuna | 3,2 |
Interaction of vitamin F with other substances
Features of vitamin F - fat soluble, very sensitive to light, heat and contact with air, which gives rise to the formation of toxic oxides and free radicals, so to protect vitamin F it should be taken simultaneously with antioxidants (vitamin E, beta-carotene and selenium).
In order for vitamin F to remain in the body longer, it is necessary to consume it together with vitamin B6, vitamin E or vitamin C.
Among microelements, zinc ions have a beneficial effect on the stability of fatty acids.
Vitamin F has a good effect on the absorption of vitamins.
Helps vitamin D perform its function of strengthening bones.
Promotes more effective deposition of calcium and phosphorus salts in bone tissue.
The effect of vitamin F is enhanced together with zinc and vitamins B6 and C.
Video “Benefits of vegetable and animal fats for the body” ↑
Since our body is not able to produce such substances, a proper diet with a rich assortment of foods containing vitamin F is the best protector against excess fat deposits and an ideal means for preventing the phenomena caused by a constant lack of this element.
A sufficient amount will have a beneficial effect on the well-being and functioning of the entire body as a whole. Take care of yourself and your loved ones. With warmth and care, Ravila.
Similar posts
If your hair splits and grows poorly: beauty recipes Why do we need vitamin B - B3 (niacin) Vitamin D - signs of deficiency or excess and its dosage Radiant facial skin: types of procedures and decorative cosmetics Coconut oil for body skin: benefits, application, reviews Masks for elastic facial skin: recipes and implementation