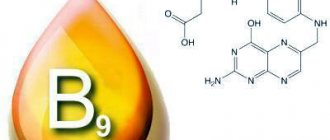
Pantothenic acid, or vitamin B5, is one of the water-soluble vitamins. Its intake comes from food, mainly from foods such as liver, kidneys, eggs, whole grain bread, and it is also produced by intestinal microflora. The daily requirement for an adult is 5–10 mg.
Vitamin B5 is absorbed by the intestinal walls, where it is converted into pantethine, a component of coenzyme A, necessary for metabolism in the body. Without it, the oxidation of fatty acids, the synthesis of hormones, the breakdown of organic acids and many other important processes are impossible. With a lack of vitamin B5, all organ systems are affected, primarily the central nervous system, musculoskeletal system, gastrointestinal tract, skin and excretory system. Symptoms of pantothenic acid deficiency are, first of all, a burning sensation in the toes, lethargy, apathy, and fatigue. With severe vitamin B5 deficiency, the so-called “burning feet” symptom occurs - burning, excruciating pain in the legs and their redness, especially at night, which leads to sleep disturbance and exhaustion of the body.
A deficiency of vitamin B5 can occur when absorption in the intestine is impaired (malabsorption syndrome), with certain diseases of the stomach and intestines, with long-term treatment with antibiotics and sulfonamides, more often in children. Excess pantothenic acid is a very rare phenomenon, usually occurs during treatment with vitamin B5 and is manifested by diarrhea and other digestive disorders.
In order to check the level of pantothenic acid in the body, it is recommended to take a blood test for vitamin B5.
Dietary supplement to strengthen the immune system
Pantothenic Acid is a dietary supplement from the American company NOW Foods that helps replenish vitamin B5 deficiency. Although it is found in many foods and is partly produced by the body, deficiency is common. With an incorrect diet and excessive consumption of flour products and fatty foods, an acute deficiency of the substance occurs. The dietary supplement “Pantothenic acid” will help normalize the functioning of the body and strengthen strength. The product is made exclusively from natural ingredients, without artificial additives or stimulants.
A, B, C, D, E and other letters of the alphabet: a complete guide to vitamins
A lack of vitamin D in children leads to rickets, so vitamin D in the form of drops must be prescribed to infants. In adults, vitamin D deficiency reduces calcium levels, which in rare cases can lead to hyperstimulation of the parathyroid glands, which in turn can eventually provoke their hyperplasia or even the formation of adenoma. At the same time, parathyroid hormone produced by the glands will take calcium from the bones, which will reduce their density.
However, even if vitamin D deficiency does not cause hyperparathyroidism, it is still recommended to compensate for its deficiency. This vitamin is involved in phosphorus-calcium metabolism. At normal vitamin D levels, bone density does not decline as much with age.
It is not necessary to take a test that is popular today to determine your vitamin D level. “If there is such an opportunity, then taking calciferol will be more effective: if there is a noticeable deficiency, we will give a saturating dose for two months, with a normal deficiency - for a month, then a maintenance dose. If this is not possible, it’s okay. It is enough to make sure that there are no contraindications and take a daily preventive dose (2000 international units) - over time, the level of vitamin D will still return to normal,” says Poteshkin.
A contraindication to taking vitamin D is an elevated level of calcium in the blood.
Vitamin K, or naphthoquinones
Another name is antihemorrhagic vitamin. It was discovered by scientists Eduard Doisy and Henrik Dam, for which the latter were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology for 1943 (awarded and awarded in 1944).
Naphthoquinone deficiency is manifested by increased bleeding, primarily in injuries, however, primary hypovitaminosis is rarely observed, except in infants, but secondary deficiency can develop against the background of pancreatitis and some other gastrointestinal diseases. There is also a hypothesis about the effect of vitamin K deficiency on the development of osteoporosis.
A large amount of vitamin K is found in coriander (cilantro), cabbage, spinach, green tea, rowan, green tomatoes, and liver.
Water-soluble vitamins
Vitamin B1, also known as thiamine
The first of the discovered vitamins, it is also called antineuritis.
In the early stages, its deficiency can manifest itself in the form of nausea, loss of appetite, neuralgia, tachycardia even with minor exertion. A specific manifestation is a regular sensation of “crawling goosebumps”. In the later stages, with significant deficiency up to complete vitamin deficiency, beriberi disease develops. It is characterized by heaviness in the legs, a stiff gait (beriberi means “sheep”, the disease received its name due to the similarity of the patient’s gait with the gait of a sheep, another name for the disease is “shackle disease”), persistent constipation, numbness of the fingers and limbs, paralysis , muscle atrophy.
The disease occurs in one of two forms - dry (nerve) or wet (cardiac). However, both the nervous and cardiovascular systems are affected in both cases, just to varying degrees. Today, people with chronic alcoholism suffer from thiamine deficiency.
Thiamine is found in rye bread and wholemeal wheat bread, soybeans, beans, peas, yeast, potatoes, carrots and cabbage, as well as organ meats and egg yolks.
Vitamin B2, also known as riboflavin
It was first isolated from whey and was therefore named lactoflavin. However, in 1935, Richard Kuhn synthesized it artificially, after which the name riboflavin (translated from Latin as yellow alcohol) was assigned to it, and is also used as a dye.
Riboflavin deficiency results in weakness, fatigue, and susceptibility to frequent colds. A specific manifestation is inflammation of the mucous membranes, dry mouth and cracks in its corners, bright red tongue, dry and flaky skin, red eyes.
The main sources of B2 in the diet are liver and kidneys, cottage cheese, egg yolk, sour milk; among plant foods, only almonds are rich in riboflavin.
Vitamin B3, also known as pantothenic acid
It was discovered in 1933 by Roger Williams, and got its name from the Latin word panthos, which means “everywhere”, as it is found in many products of both plant and animal origin. Most B3 is found in royal jelly and brewer's yeast, quite a lot - in liver, egg yolk, buckwheat, oats, and legumes.
Primary hypovitaminosis B3 practically does not occur. Secondary failure can develop against the background of long-term chronic diseases, exhaustion and alcoholism and manifest itself as fainting, psycho-emotional instability, parasthesia and a burning sensation in the feet.
Composition and beneficial properties
Each capsule contains 45 mg of calcium and 500 mg of vitamin B5. The additional component improves the absorption of the first one. There are 100 capsules in total. The quantity is calculated for a course of use of about 3 months.
Among the beneficial properties of the dietary supplement “Pantothenic acid” it is worth noting:
- normalization of hormone production by the adrenal glands - these substances have immunostimulating and anti-inflammatory effects;
- strengthening the body’s defenses, including when affected by viruses and pathogens;
- normalization of intercellular processes and improvement of the transmission of nerve impulses - vitamin B5 promotes the production of neurotransmitters;
- improvement of fat metabolism and oxidation processes;
- lowering blood cholesterol levels;
- improving the condition of the skin, hair and mucous membranes;
- normalization of the digestive system, including improvement of metabolism;
- positive effect on liver function;
- Providing a powerful anabolic effect, thanks to which the patient can easily accumulate muscle mass.
The dietary supplement “Pantothenic acid” helps to get rid of excess weight. This effect is due to the normalization of metabolism. Suitable for a course of rejuvenation and cleansing of the body. Pantothenic acid also has a slight calming effect.
Indications for use
Dietary supplement “Pantothenic acid” is recommended for:
- weakening of the body's defenses;
- frequent colds and viral diseases;
- dermatitis and other skin problems;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- disorders of the nervous system;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- carrying out rejuvenation procedures;
- liver diseases;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- poisoning with food or toxic substances;
- alcoholism.
The Pantothenic Acid supplement is also suitable for those people who lead an active lifestyle and professionally engage in sports. Regular use will help keep the body in good shape and ensure the conversion of nutrients into energy.
Vitamin B1
Cellular energy booster that promotes growth and development. Vitamin B1 increases mental and physical performance, improves detoxification function and metabolism in the nervous system. It also improves mood, has a mild analgesic and wound-healing effect.
Vitamin B1 deficiency causes various disorders in the nervous, cardiovascular and digestive systems. To compensate for its deficiency, include buckwheat, corn, cashews, and lentils in your diet.
The main symptoms of vitamin B1 deficiency:
- loss of appetite;
- violation of movement coordination;
- depression, nervousness;
- weakening of cognitive functions (memory loss);
- muscle weakness.
An extreme form of vitamin deficiency is Beriberi disease, which damages the peripheral nerves or the cardiovascular system. As a result, muscles, especially the legs, become exhausted, severe pain appears in the calves, weakness develops, and gait worsens.
Causes of vitamin B1 deficiency:
- constant consumption of refined products (high-grade flour and products made from it, polished rice);
- increased need for vitamin (pregnancy, breastfeeding, stress, physical activity, infections);
- chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis, antibiotic poisoning, alcoholism);
- smoking;
- Excessive consumption of tea and coffee, as caffeine destroys vitamin B1.
If you notice that your mood has worsened, cramps have appeared in the calf muscles, and your appetite has disappeared against the background of constant stress, perform the study 95-10-201 - Vitamin B1 (thiamine) in CITILAB. The analysis helps to identify vitamin B1 deficiency, prescribe medications in a timely manner and adjust the diet.
Contraindications
The dietary supplement “Pantothenic acid” is not recommended for people with individual intolerance to the components. Women should be careful during pregnancy and breastfeeding. If you have serious cardiovascular diseases, you should consult your doctor before starting the course. The dietary supplement "Pantothenic acid" is not a medicine and can be used exclusively for preventive purposes. The jar of capsules should be stored at room temperature, but not higher than +25 degrees, out of the reach of children. If the integrity of the packaging is damaged, refrain from using the drug.
Vitamin B6
Essentially, vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is a metabolism “activator.” It is necessary for regulating the absorption of proteins, the exchange of amino acids involved in the synthesis of basic neurotransmitters and hemoglobin. With the participation of pyridoxine, glucose is delivered to cells, including brain cells. Vitamin B6 affects cognitive functions: improves memory, thinking, and also improves mood and helps resist stress.
Contained in many plant foods - bananas, nuts (pistachios, hazelnuts), avocados, beans, soybeans, beef liver. It is important to remember that with prolonged or improper heat treatment of foods, this vitamin is destroyed.
The main symptoms of vitamin B6 deficiency:
- fatigue, depression;
- hair loss;
- “jams” in the corners of the lips.
A clear lack of vitamin B6 reduces the synthesis of dopamine, serotonin, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and melatonin. This can lead to psychological and physiological disorders, insomnia, decreased intellectual abilities, irritability, apathy, or, conversely, aggressive behavior.
Causes of vitamin B6 deficiency:
- weakened condition, including after surgery, serious illness;
- atherosclerosis;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- pregnancy;
- long-term excess consumption of protein foods;
- increased physical activity;
- liver diseases, gastritis;
- anemia.
If you notice that your hairstyle has become less voluminous, severe dry skin has appeared in the area of the nasolabial fold, above the eyebrows, in general the skin has become drier and rougher, cuts and scratches are slowly healing - do not put off visiting a doctor. The first thing you need to do is donate blood to CITILAB for research 95-10-203 Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), which will help determine whether there is a deficiency of vitamin B6 in the body or whether there is enough of it.
Mode of application
“Pantothenic acid” is perfectly absorbed by the body, so you can take the dietary supplement with food. The optimal dosage is 1 capsule per day. This amount is enough to replenish the body's resources.
Our online store presents original dietary supplements and vitamin complexes from world manufacturers. We guarantee high quality products and affordable prices. To buy a product, fill out an application on the website and provide the required information. For residents of Moscow we offer delivery by courier; to other cities we will send by mail or through carrier companies. For more information please contact us.
The role of B vitamins for the body
Vitamins are special substances that catalyze a number of chemical reactions occurring in the body and control the production of macroelements. And ultimately they support the functioning of the entire organism.
Each group of vitamins is assigned a letter of the Latin alphabet. But, oddly enough, it was not vitamin A that was first isolated in 1912, but a complex of B vitamins. It was a water-soluble crystalline substance. The author of the discovery, Casimir Funk, called this substance a “vitamin,” that is, a vital substance [1].
In 1913, biochemists McCollum and Davis discovered another “vital substance.” It was called "fat-soluble factor A." The vitamin that Funk isolated a year earlier was assigned the second letter of the Latin alphabet - B. All vitamins discovered later also received the corresponding letter - C, D, etc.
Over time, it became clear that the same crystalline substance isolated by Funk was a whole complex of biologically active compounds. They began to be given serial numbers - B1, B2, etc.
Currently, group B includes 8 essential vitamins[2]. They are coenzymes, that is, substances with the help of which biochemical reactions occur inside cells.
A lack of vitamins makes the processing of proteins, fats or carbohydrates ineffective. Because of this, the nervous system, heart cells, and muscles suffer, hemoglobin synthesis is disrupted, and immunity decreases.
It is not possible to create a depot of B vitamins in the body - they practically do not accumulate in tissues. There is an advantage to this - an “overdose” of these compounds is practically impossible [3]. But, of course, you should not take doses tens of times higher than permissible.