Vitamin B2 is an essential compound that ensures the full functioning of all body structures necessary to maintain life. Riboflavin represents flavins - organic substances of an enzymatic nature that are included in cellular structures. The vitamin is yellow in color, remains intact when exposed to heat, but is destroyed under ultraviolet rays. In pharmacies, riboflavin is sold both in ampoules and tablets. Due to its diverse positive effects on the human body, the vitamin is actively used for medicinal purposes and in cosmetology.
Indications
Vitamin B2 Riboflavin is prescribed to patients with severe B2 deficiency in the body or at risk of developing it. Indications for prescribing tablets are various conditions of the body:
- burns;
- infections;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- chronic stress conditions;
- hyperthyroidism;
- anemia or neuropathy;
- undergone operations.
The drug is also part of treatment courses, the drugs of which increase the body’s need for this vitamin.
Admission rules
The instructions for use of riboflavin tablets indicate that adults should take 2 pieces 3 times a day to relieve signs of deficiency. For children from 4 years of age, the drug is prescribed 1-2 tablets 2-3 times a day, depending on age. It is advisable to take the medicine with food to increase its bioavailability. Take the tablets with a sufficient amount of clean water. Dietary supplements contain higher concentrations of the active component, so they are advised to take 1 capsule 2 times a day.
Different diseases may require different daily dosages, so you should consult your doctor before taking vitamin B2. The course of treatment ranges from 30 to 45 days. For diseases of the visual system, local treatment is prescribed - 2 drops of a special solution in each eye 3 times a day. Injectable drugs are used only as prescribed by doctors and under the strict supervision of medical personnel, therefore the article does not provide recommendations on the schedule of vitamin B2 injections.
Recipe for a mask for hair growth with riboflavin (video):
Benefits of vitamin for the human body
Riboflavin performs many important functions in the human body:
- restores the condition of the nervous system;
- eliminates the effects of stress;
- optimizes hemoglobin levels in the blood;
- increases brain performance;
- makes the body more resistant to infections;
- normalizes the functioning of the thyroid gland;
- maintains visual acuity, improves visual ability in the dark and in bright light;
- strengthens and tones the skin and mucous membranes;
- improves the condition of hair and nail plates.
Side effects and contraindications
Riboflavin preparations rarely have side effects. In some cases the following are noted:
- allergic skin rashes;
- darkening of urine;
- liver dysfunction;
- blurred vision.
In case of overdose the following occurs:
- tingling in different parts of the body;
- numbness of the skin;
- burning pain on the surface of the eyeballs.
If the above symptoms appear, you should stop using the drug.
There are no contraindications for use as such. Do not use riboflavin preparations only if the components are intolerant.
Release form and chemical composition
Vitamin B2 is sold in several dosage forms:
- tableted;
- drip;
- powder;
- injection.
Drugs in tablets from different manufacturers are called Riboflavin or Vitamin B2. And the drug in ampoule form is called Riboflavin mononucleotide.
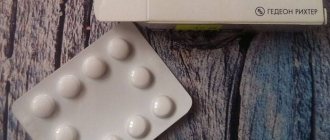
- Tablets are cylindrical, yellow in color. They come in the form of dragees. The composition includes riboflavin in an amount of 3 or 11 mg. The packaging box contains 30, 50 or 90 tablets. Dragees are sold in plastic jars. One jar contains 50 or 90 units.
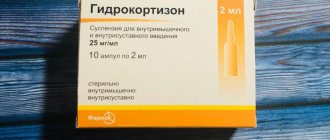
- The injection solution is a clear, deep yellow liquid. The active substance is riboflavin mononucleotide. The drug is sold in cardboard packaging of 10 ampoules.
- Eye drops are available in the form of an aqueous solution containing 0.01% riboflavin.
- Riboflavin powder is yellow in color and has a crystalline structure. Sold in plastic bags of 10, 20, 25 kg. The active substance is 6,7-sulfoxide-9-(D-1-ribetyl)-isoalloxazine.
Symptoms of vitamin deficiency
Hypovitaminosis B2 is usually caused by poor diet or problems with the digestive tract. Vitamin deficiency negatively affects the functioning of the entire body. Symptoms of a deficiency state are:
- nervous disorders;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- impaired concentration;
- anemia;
- seborrheic skin lesions;
- stomatitis;
- pain in the lower extremities;
- redness of the tongue.
Riboflavin deficiency causes especially great harm to children's bodies. A child with vitamin deficiency lags significantly behind his peers in both physical and intellectual development.
Drug interactions
When used simultaneously with alcohol, the absorption of riboflavin slows down.
Chlorpromazine, amitriptyline and imipramine reduce the effectiveness of the drug.
When taken together with m-anticholinergics, the absorption of riboflavin and its bioavailability increase.
The drug reduces the antibacterial activity of doxycycline, oxytetracycline, erythromycin, lincomycin and tetracycline.
Riboflavin prevents and reduces the side effects of chloramphenicol (primary inflammation of the optic nerve and disruption of the hematopoietic process).
Thyroid hormones accelerate the metabolism of riboflavin, probenecid reduces its absorption in the intestine.
The drug is incompatible with streptomycin.
Causes of hypovitaminosis associated with a lack of vitamin B2
At this time, vitamin deficiency associated with a deficiency of this element is a very common phenomenon. This is mainly explained by the fact that people, usually middle-aged, without sufficient information, eat foods low in vitamin B2.
Here are the most typical causes of a deficiency of this vitamin:
Unhealthy nutrition, lack of meat and fish products, vegetable and dairy dishes in the menu, mostly carbohydrates and refined food sets are consumed;
consumption of foodstuffs that have been subjected to chemical processing and contain a considerable number of preservatives, synthetic dyes, and many other elements; decomposition of riboflavin in products due to improper storage and cooking;
- Long-term gastrointestinal diseases,
- Liver diseases,
- Thyroid gland;
- Infectious diseases;
- Mental or physical overload;
- Stressful situations;
- Pregnancy period
- Breast-feeding;
- Old age;
What is riboflavin?
Riboflavin is a substance belonging to the prosthetic group of flavin enzymes and is a water-soluble vitamin. The component takes part in most processes that ensure the normal functioning of internal organs and systems.
The ingredient is indispensable for ensuring metabolic processes, strengthening the immune system and forming blood cells. Today on pharmacy shelves you can see the vitamin in various dosage forms. In dry form, the ingredient is poorly soluble in alkaline liquids and alcohol, has a specific aroma and a bright yellow color.
The substance is resistant to acidic environments, reacts negatively to solar radiation, but is subject to rapid recovery.
Physiological action
The active forms of Riboflavin, Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and Riboflavin-5-phosphoric acid or Flavin mononucleotide (FMN) are coenzymes, parts of enzymes that mediate many redox reactions.
Thus, along with its “brother”, Thiamine (vitamin B1), it participates in the utilization of glucose with the formation of ATP molecules. Also, under its action, high-energy glycogen is formed from glucose, which is deposited in skeletal muscles and the liver.
In addition to carbohydrate vit. B2 regulates many types of protein and fat metabolism. Thus, with its participation, Niacin (vit. PP) is synthesized from the amino acid Tryptophan. In addition, the vitamin is endowed with antioxidant properties, inhibits LPO (lipid peroxidation), prevents damage to cellular structures by free radicals and the formation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels.
These processes have a positive effect on the condition of organs and tissues.
- The cardiovascular system
It has an anti-atherosclerotic effect, “cleans” blood vessels from plaques. It also expands capillaries and prevents the formation of blood clots. The result is blood supply to organs, incl. and myocardium, improves. Accordingly, the risk of coronary heart disease, hypertension, cardiosclerosis and myocardial infarction is reduced.
- Blood
Vit. B2 stimulates the synthesis of red blood cells. Thus, it further enhances the delivery of oxygen to tissues.
- Nervous system
Improves blood circulation and enhances metabolic processes (metabolism) in brain tissue. The result is a reduced risk of cerebral strokes. Mental performance also increases, a good mood and good spirits are formed, and sleep is normalized. Riboflavin increases stress resistance, eliminates negative emotions (depression, anxiety, fear) and prevents the occurrence of mental disorders.
- Gastrointestinal tract
Improves the barrier properties of the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines, increases their resistance to the action of toxic compounds, pathogenic (disease-causing) bacteria and viruses. Under the influence of Riboflavin, the formation of bile in the liver increases and the absorption of dietary fats in the intestine improves.
- Respiratory system
Increases the resistance of the mucous membranes of the bronchial tree to the effects of infection and toxic substances.
- Musculoskeletal system
Thanks to the synthesis of protein and glycogen, muscle growth occurs and muscle strength increases.
- Endocrine system
Riboflavin regulates the function of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands, ensures the synthesis of some biologically active substances, in particular, glucocorticoids (Cortisol) and catecholamines (Adrenaline, Norepinephrine).
- Eyes
Here Riboflavin acts as a synergist, an “ally” of Retinol (vit. A). It increases visual acuity, improves color and light perception, and also prevents clouding of the cornea and lens with the development of cataracts.
- Skin and appendages
Increases skin elasticity, stimulates hair and nail growth, and thereby improves appearance. Under the influence of Vit. B2 skin regenerates after damage (wounds, burns), aging slows down.
- Immunity
Stimulates humoral immunity - promotes the formation of immunoglobulin antibodies, thereby increasing resistance to bacterial and viral infections.
- Reproductive function
Ensures the normal course of pregnancy, growth and differentiation of fetal tissues.
Daily requirement
| Category | Age | Norm, mg |
| Infants | Up to 6 months | 0,5 |
| 6 months - 1 year | 0,6 | |
| Children | 1-3 years | 0,9 |
| 4-6 years | 1,0 | |
| 7-10 years | 1,4 | |
| Men | 11-14 years old | 1,7 |
| 15-18 years old | 1,8 | |
| 18-59 years old | 1,5 | |
| 60-74 years | 1,6 | |
| Over 75 years old | 1,4 | |
| Women | 11-14 years old | 1,5 |
| 15-18 years old | 1,5 | |
| 18-59 years old | 1,3 | |
| 60-74 years | 1,5 | |
| Over 75 years old | 1,3 | |
| Pregnant | 1,8 | |
| Nursing | 2,0 |
According to studies conducted in the USA, if the daily intake of Riboflavin in adults is less than 0.55 mg, then after 3 months. a deficiency of this vitamin occurs.
History of discovery
Vit. B2 was first isolated from milk back in 1879. However, at that time the effect of vitamins had not yet been studied, and the term “vitamins” itself did not yet exist. Simply, it was found that the new substance has healing properties.
This is where all the research ended until the beginning of the twentieth century, when scientists developed the concept of vitamins, vital amines, nitrogen-containing substances, without which life is impossible. The first vitamin discovered was Thiamine, vit. IN 1.
This vitamin was used to prevent and treat beriberi, a dangerous and quite common disease at that time. As a matter of fact, at first Thiamine was called vit. B, without any indexing. This vitamin, among other things, was unstable to heat and was quickly destroyed.
However, it was subsequently found that it was heterogeneous, and a thermostable fraction was isolated from it. The new substance was initially called vit.G after the English scientist Goldberger. However, they soon decided to designate it as vit. B2, thereby marking the beginning of the indexation of B vitamins - soon after vit. B2 will appear vit. B3, B4, B5, etc. In 1933, the molecular structure of the new vitamin was determined, and in 1935 it was obtained synthetically under the name Riboflavin.