Diseases of the cardiovascular system rank first in terms of morbidity and mortality worldwide. This is due to many reasons, including poor lifestyle, bad habits, poor nutrition, stress, heredity and much more. Every year the age of heart pathologies is getting younger, and the number of patients who become disabled after suffering heart attacks, strokes and other complications is growing. That is why doctors strongly recommend that you pay close attention to your body and immediately go to the hospital if alarming symptoms appear.
List of heart diseases and their symptoms
Cardiovascular diseases are classified into the following categories:
- Arrhythmia - changes in the rhythmic and sequential contraction of the atria and ventricles;
- Coronary heart disease – blood supply disturbances and scar tissue formation;
- Myocarditis, pericarditis, endocarditis – inflammatory diseases of the heart muscle;
- Heart disease - congenital and acquired dysfunction of the ventricular valve apparatus;
- Cardiovascular failure is a group of diseases that are based on the failure of cardiac activity to ensure normal blood circulation;
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a violation of vascular tone;
- Hypertension is a systematic increase in blood pressure.
All these diseases of the heart and blood vessels have different causes of their development, symptoms, treatment methods and prognosis for recovery.
Need to quit smoking
Smoking is dangerous not only for the bronchi and lungs: it negatively affects the entire body. Quit this habit as soon as possible if you are living with heart disease. Smoking is associated with an increased risk of heart attack, stroke and high blood pressure. It increases inflammation and causes the formation of blood clots, and also provokes cancer of various localizations. It's never too late to give up a bad habit and partially eliminate its negative impact on the body. If you can't quit smoking yourself, numerous treatments can help you quit, including everything from nicotine patches and medications to acupuncture and hypnosis.
Arrhythmia
Normally, the heart rhythmically and sequentially contracts its atria and ventricles. This activity is closely related to the functioning of the conduction system, which directs impulses to the heart muscle.
Causes of arrhythmia:
- Structural changes in the conduction system;
- Electrolyte imbalance;
- Autonomic changes in the central nervous system;
- Endocrine diseases;
- Side effects of medications;
- Complications caused by ischemic disease.
Diagnosis of arrhythmia is carried out using a cardiogram; treatment of this pathology is quite complex and is carried out taking into account the individual characteristics of the body.
Types of arrhythmias:
- Ventricular asystole - manifested by fibrillation and flutter of the ventricles, occurs as a complication of heart disease, due to electric shock, overdose of glycosides, adrenaline, quinine (in the treatment of malaria). Prognosis – sudden clinical death is possible due to cessation or a sharp drop in cardiac output. To stop an attack of ventricular asystole, you must immediately begin resuscitation using external cardiac massage and artificial respiration. It is necessary to call a cardiology ambulance team;
- Atrial fibrillation - manifested by atrial fibrillation and flutter (250-300 times per minute), chaotic and irregular contraction of the ventricles. Occurs as a symptom of mitral valve disease, thyrotoxicosis, atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, due to an overdose of glycosides, alcohol poisoning. The patient may not feel the arrhythmia, mistaking it for a rapid heartbeat. Prognosis – the occurrence of thromboembolism;
- Paroxysmal tachycardia - manifests itself as a sudden onset and suddenly ending attack of rapid heartbeat, heart rate - 160-220 beats per minute. Additionally, profuse sweating, increased intestinal motility, and slight hyperthermia are felt. If the attack lasts several days, these symptoms are accompanied by angina pectoris, weakness, fainting, and worsening heart failure. Help with paroxysmal tachycardia - massage the area of the carotid artery, activation of the vagus nerve by pressing on the eyes and the solar plexus area, as well as holding the breath, strong turning of the head. If these techniques are ineffective, it means that ventricular tachycardia or myocardial infarction is occurring - immediate medical attention is required;
- Sinus tachycardia - manifested by a sinus rhythm frequency of more than 90 beats per minute, occurs with a sharp decrease in blood pressure, a significant increase in temperature, anemia, myocarditis. The patient experiences increased heart rate. Help - holding your breath, massage of the solar plexus and carotid artery area, pressing on the eyeballs;
- Sinus bradycardia is manifested by a decrease in heart rate with a sinus rhythm of less than 60 beats per minute. Occurs during myocardial infarction, as a consequence of certain infectious diseases and side effects of medications. The patient feels a slowdown in the heartbeat, his limbs become cold, he may faint or have an attack of angina pectoris;
- Extrasystole is manifested by premature contractions of the ventricles, which the patient feels as a fading heart or an increased beat. After this, the desire to take a deep breath arises reflexively. Frequently occurring systoles require treatment, as they lead to atrial and ventricular fibrillation;
- Heart blocks are manifested by a slowdown or complete cessation of the transmission of electrical impulses through the conduction system of the heart. The patient's heart rate slows down, he faints due to the fact that the brain is not sufficiently supplied with blood, convulsions occur, and heart failure is diagnosed. Prognosis - with intraventricular (complete transverse) blockade, sudden death is possible.
Find out more: What is arrhythmia? Causes and types
Cardiac ischemia
With this serious heart disease, which is based on impaired blood supply to the heart muscle, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris and cardiosclerosis occur.
- Myocardial infarction is an acute disruption of the blood supply to the heart muscle, which results in focal necrosis of its areas. Due to the necrosis of part of the myocardium, the contractility of the heart is impaired. A heart attack occurs due to thrombosis of the arteries that supply the heart with blood, blockage of blood vessels with atherosclerotic plaques. The acute period of a heart attack is characterized by very severe chest pain, the intensity of which is not relieved by Nitroglycerin. Additionally, pain in the pit of the stomach, an attack of suffocation, hyperthermia, increased blood pressure, and rapid pulse are felt. Prognosis – the patient may die from cardiogenic shock or heart failure. Emergency assistance before the ambulance arrives - taking painkillers, Aspirin and large doses of Nitroglycerin.
- Angina pectoris (“angina pectoris”) - manifests itself as sudden pain behind the sternum due to insufficient blood supply to the myocardium. The main cause of angina is atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries. Pain during angina pectoris is paroxysmal, has clear boundaries of onset and subsidence, and is almost immediately relieved by Nitroglycerin. The triggering factor for an attack is stress or physical strain. Compressive and pressing pain occurs behind the sternum, radiates to the neck, lower jaw, left arm or shoulder blade, and may be similar to heartburn. Additionally, there is an increase in blood pressure, perspiration appears, and the skin becomes pale. If angina at rest is diagnosed, these symptoms are accompanied by suffocation and a feeling of acute lack of air. An attack of angina lasting longer than 30 minutes is a suspicion of myocardial infarction. First aid - Nitroglycerin under the tongue twice with a break of 2-3 minutes, accompanied by taking Corvalol or Validol to suppress the headache, then call a cardiac ambulance.
- Cardiosclerosis is damage to the myocardium and heart valves by scar tissue formed as a result of atherosclerosis, rheumatism, and myocarditis. Symptoms are arrhythmia and conduction disturbances. The prognosis is the formation of an aneurysm, the formation of chronic heart failure and heart defects.
Find out more: Causes, symptoms and treatment of cardiac ischemia
Take prescribed medications
Non-adherence to medication is a big problem among people living with heart disease. If you look at some studies, as many as 50% of people are noncompliant with their medications. Missing doses of medications can have serious consequences. For example, if you have a stent (a tube that opens an artery), you must take antiplatelet medications, which thin the blood, otherwise the stent may become blocked by a blood clot. It is also important to strictly follow the regimen for taking blood pressure medications, antiarrhythmics, and cholesterol-lowering medications.
Myocarditis, pericarditis, endocarditis
This group of diseases is characterized by inflammatory processes in myocardial tissues caused by pathogenic microorganisms. Their negative effects are complemented by allergic reactions and autoimmune processes of the formation of antibodies to the tissues of one’s own body.
Types of inflammatory heart diseases:
- Infectious-allergic form of myocarditis - occurs after an infectious disease or during it. Symptoms: general malaise, heart rhythm disturbances, pain in the heart, shortness of breath, joint pain, slight increase in temperature. After a few days, the symptoms of myocarditis increase and worsen. Heart failure develops: bluish skin, swelling of the legs and abdomen, severe shortness of breath, enlarged liver;
- Rheumatic, autoimmune, radiation myocarditis - there are acute and chronic forms, manifested by the following symptoms of intoxication: fatigue, hyperthermia, skin rash, nausea and vomiting. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, deformation of the fingers in the form of drumsticks appears, as well as deformation of the nails in the form of convex watch glasses.
- Endocarditis is inflammation of the endocardium, that is, the inner lining of the heart covering the valve apparatus.
- Pericarditis is inflammation of the membrane that covers the outside of the heart (the pericardial sac).
Such manifestations require immediate medical attention and bed rest. The cardiologist will prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Indomethacin), glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone), diuretics and antiarrhythmic drugs. The prognosis for the development of carditis is complete cure with timely initiation of therapy.
Find out more: Myocarditis - symptoms and treatment
Heart disease
These diseases include dysfunctions and abnormalities in the structure of the valve apparatus: stenosis (inability to fully open the valves), insufficiency (inability to fully close the valves), a combination of stenosis and insufficiency (combined heart disease). If the defect is not congenital, it occurs due to rheumatism, atherosclerosis, syphilis, septic endocarditis, or organ trauma.
Types of heart defects:
- Mitral valve defect (stenosis and insufficiency) - determined by listening to the heart by a cardiologist, is characterized by the appearance in patients of a bright blush and a scarlet tint to the lips. Additionally, shortness of breath, palpitations, swelling of the extremities, and enlarged liver are diagnosed;
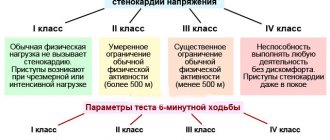
- Aortic valve defect (stenosis and insufficiency) - at the 1st and 2nd stages of the disease there are no complaints, at the 3rd stage angina pectoris, dizziness and decreased clarity of vision are diagnosed. At the 4th stage, even the slightest load leads to disturbances in cerebral and cardiac circulation: arrhythmia, shortness of breath, cardiac asthma;
- Aortic valve insufficiency - at the 1st and 2nd stages there are no complaints; at the 3rd stage of the defect, angina pectoris is diagnosed, pulsation of the arteries of the head, carotid artery, abdominal aorta, which is visible to the naked eye. At the 4th stage, pronounced heart failure and arrhythmia appear. At stage 5, the symptoms of the disease become even more intense;
- Tricuspid valve defect - can be diagnosed by pulsation of the neck veins, enlarged liver, swelling of the arms and legs. There is a direct relationship - the stronger the pulsation of the veins, the more pronounced the valvular insufficiency. Valve stenosis does not produce pronounced pulsation.
Find out more: Causes and symptoms of heart disease, treatment and prevention
Complications of CVD
According to WHO, cardiovascular pathologies are the main cause of death and often lead to disability. Death is not uncommon with large heart attacks and strokes, massive pulmonary embolism, heart failure complicated by pulmonary edema, and cardiogenic shock. A stroke can lead to a wide range of neurological disorders, and chronic cerebrovascular accident can lead to progressive cognitive impairment. Peripheral arterial pathologies are dangerous due to the development of gangrene with subsequent amputation of the limb (often at a young age). CVDs have a detrimental effect on the state of the reproductive sphere: impotence is often registered in men, and infertility and childlessness in women.
Cardiovascular failure
This general term refers to diseases that cause the heart to be unable to pump blood normally. Cardiovascular failure can be acute or chronic.
Types of acute heart failure:
- Cardiac asthma is a consequence of cardiosclerosis, hypertension, myocardial infarction, and aortic heart disease. The basis of the pathology is stagnation of blood in the lungs, since the left ventricle cannot provide normal blood flow in the pulmonary circulation. In the vessels of the lungs, blood accumulates, stagnates, and its liquid fraction sweats into the lung tissue. As a result, the walls of the bronchioles thicken, their vessels narrow, and air penetrates less and less. Significant symptoms of cardiac asthma: a cough called “cardiac”, wheezing, shortness of breath, fear of death, blue lips and skin. Rapid heartbeat and elevated blood pressure complete the overall picture. First aid is to give the patient a semi-sitting position, put Nitroglycerin under the tongue, give Corvalol, and provide hot foot baths. Before the ambulance arrives, to facilitate the work of the heart, you can apply rubber tourniquets to the thighs for 15-20 minutes, trying to press them not on the arteries, but on the veins. Prognosis – if there is no effect from resuscitation procedures, pulmonary edema occurs;
- Pulmonary edema - failure to provide timely necessary assistance for cardiac asthma leads to the fact that the liquid fraction of blood sweats not only into the bronchi, but also into the alveoli and accumulates in them. The air, which nevertheless penetrates in small quantities into the lungs overflowing with liquid, whips this liquid in the pulmonary vesicles into foam. Symptoms of pulmonary edema: painful suffocation, pink foam protruding from the mouth and nose, bubbling breathing, rapid heartbeat. An excited patient develops a fear of death and becomes covered in cold, sticky sweat. High blood pressure decreases sharply as the situation progresses. First aid should be provided quickly - the patient is placed reclining, a hot foot bath is given to him, tourniquets are applied to his legs, 1-2 tablets of Nitroglycerin are placed under the tongue. 2-4 ml of Lasix or Furosemide are administered intravenously or orally. The patient needs fresh air, tight clothing is lightened to the maximum, and windows are opened. Until the attack of pulmonary edema is relieved, transportation to the hospital of such a patient is impossible;
- Right ventricular failure - develops as a result of incorrect transfusion of blood and its substitutes, lung diseases (asthma, pneumonia, pneumothorax), as well as against the background of pulmonary embolism. There is an overload of the right parts of the heart, a spasm of the pulmonary circulation occurs. The resulting stagnation of blood weakens the functioning of the right ventricle. Symptoms: shortness of breath, drop in blood pressure, blueness of the lips and facial skin, severe swelling of the veins in the neck;
- Thromboembolism - the above symptoms are accompanied by severe pain in the chest, expectoration of blood during coughing. The pathology occurs due to the entry of a blood clot into the vessels of the pulmonary artery. Prognosis: blockage is fatal. In this condition, urgent thrombus-absorbing therapy and administration of thrombolytics (Eufillin, Lasix, Strophanthin) are needed before the ambulance arrives. The patient should be in a semi-recumbent position at this time;
- Collapse - a condition that occurs with a sharp dilation of blood vessels and a decrease in the volume of circulating blood. Causes of collapse: overdose of Nitroglycerin or drugs that lower blood pressure, poisoning, consequences of certain infections, vegetative-vascular dystonia. Symptoms are sudden weakness and dizziness, shortness of breath, a sharp decrease in blood pressure, emptying of veins, thirst and chills. The patient's skin becomes pale and cold to the touch, and loss of consciousness may occur. Help before the “emergency” arrives - raise your legs above your head to provide blood to the brain, cover the body, give you hot, strong coffee to drink to raise blood pressure as quickly as possible.
Find out more: Heart failure - causes and symptoms
Hypertension
The true cause of the development of hypertension is not fully understood. Its appearance is provoked by mental trauma, obesity, a penchant for salty foods, and hereditary predisposition.
Stages of hypertension:
- At the first stage, the pressure rises to 160-180 mmHg. Art. at 95-105 mm Hg. Art. An increase in blood pressure is typical for climate change, physical or emotional stress, weather changes, and the inclusion of spicy foods in the diet. Additional symptoms: headaches, tinnitus, insomnia, dizziness. At this stage, there are no changes in heart function or kidney dysfunction;
- At the second stage, pressure indicators increase to 200 to 115 mm Hg. Art. During rest, it does not drop to normal, remaining slightly elevated. Changes in the left ventricle (hypertrophy), decreased renal blood flow, and spasms of cerebral vessels appear;
- At the third stage, the pressure rises to 280-300 mmHg. Art. at 120-130 mm Hg. Art. During this period, strokes, angina attacks, hypertensive crisis, myocardial infarction, pulmonary edema, and retinal damage are not excluded.
If in the first stage of hypertension it is enough to reconsider your lifestyle and diet so that blood pressure levels return to normal, then the second and third stages need to be treated with pharmaceuticals as prescribed by a doctor.
Find out more: Hypertension - causes, symptoms, stages and diagnosis
Diagnosis of heart disease
According to medical statistics, about 60% of premature deaths occur due to cardiovascular diseases. A diagnostic study of the condition of the heart muscle and its functioning will help to make a correct diagnosis in time and begin treatment.
Common diagnostic methods:
- An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a recording of electrical impulses emanating from the body of the subject. It is carried out using an electrocardiograph. Only a specialist can evaluate the ECG results. It will be able to detect arrhythmia, absence or decreased conductivity, ischemic disease, myocardial infarction;
- Cardiac ultrasound or echocardiography is a highly informative study that allows you to evaluate the cardiovascular system as a whole, identify signs of atherosclerosis, see blood clots, and monitor blood flow. Patients who have had a heart attack undergo echocardiography regularly. The procedure helps to detect heart defects, aortic and ventricular aneurysms, and oncological processes in time. Using cardiac ultrasound, you can measure the thickness of the walls of the heart muscle and pericardium, and monitor the activity of the heart valves;
- Magnetic resonance imaging - helps to determine the source of the murmur in the heart, find the area of myocardial necrosis, and identify vascular dysfunction;
- Scintigraphy of the heart muscle is carried out using a contrast agent, which, after entering the blood, helps to evaluate the characteristics of blood flow;
- Holter cardiac monitoring is monitoring daily changes in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels using a mobile device attached to the subject’s belt. It helps determine the cause of heart rhythm disturbances and chest pain.
You can undergo such studies on your own initiative, but only a qualified cardiologist can correctly interpret their results.
Prevention of heart disease
The main factors provoking the occurrence of cardiac pathologies:
- Increased blood cholesterol levels;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Smoking and alcohol abuse;
- Increased blood sugar levels;
- Excess of refractory animal fats and salt in the diet;
- Prolonged psycho-emotional stress;
- High blood pressure;
- Obesity.
To eliminate the risk of heart and vascular diseases, cardiologists suggest following simple rules in everyday life:
- Follow the principles of a healthy diet, reduce the amount of fat in the diet and increase the amount of fiber;
- Quit smoking, do not abuse alcohol;
- Limit the time spent without movement, exercise more often in the fresh air;
- Get enough sleep, avoid stress, treat difficult situations with humor;
- Use a minimum of salt during cooking;
- Replenish potassium and magnesium reserves in the body by taking a complex of microelements;
- Know the gender and age norms for blood sugar, blood pressure, body mass index and strive for such indicators.
If there are prerequisites for the development of pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, risk factors should be immediately eliminated to prevent the occurrence of serious diseases.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a disease characterized by the accumulation of cholesterol in the arteries. This causes blockage of blood vessels and poor circulation. In countries where people eat fast food, this problem occupies one of the leading positions among all heart diseases.
Atherosclerosis causes blockage of blood vessels
Signs
For a long time, atherosclerosis does not manifest itself in any way; the first symptoms are noticeable with significant deformation of blood vessels, due to bulging of veins and arteries, the appearance of blood clots and cracks in them. The blood vessels narrow, which causes circulatory problems.
Against the background of atherosclerosis, the following pathologies develop:
- IHD;
- ischemic stroke;
- atherosclerosis of the arteries of the legs, which causes lameness, gangrene of the limbs;
- atherosclerosis of the arteries of the kidneys and others.
Important! After suffering an ischemic stroke, a patient's risk of developing a heart attack increases threefold.
Causes
Atherosclerosis is caused by many causes. Men are more susceptible to pathology than women. It is assumed that this is due to lipid metabolism processes. Another risk factor is the patient's age. Atherosclerosis affects people mainly after 45–55 years of age. The genetic factor plays an important role in the development of the disease. People with a hereditary predisposition need to prevent cardiovascular diseases - watch their diet, move more, give up bad habits. The risk group includes women during pregnancy, since at this time the metabolism in the body is disrupted, women move little. It is believed that atherosclerosis is a disease of unhealthy lifestyle. Its appearance is influenced by excess body weight, bad habits, poor nutrition, and poor environment.
Treatment
To prevent complications of the disease and normalize the functioning of blood vessels, patients are prescribed treatment with medications. Statins, LC sequestrants, nicotinic acid medications, fibrates, and anticoagulants are used here. In addition, exercise therapy and a special diet are prescribed, which involves avoiding foods that increase cholesterol levels in the blood.
Which doctor treats heart disease?
If you experience shortness of breath, chest pain, swelling, increased or decreased heart rate, or a significant and systematic increase in blood pressure, you should check the condition of your heart and blood vessels. For examination and possible treatment, you need to contact a cardiologist. This doctor treats diseases of the cardiovascular system and carries out subsequent rehabilitation.
If catheterization or angioplasty of the heart vessels is necessary, the assistance of a vascular surgeon may be required. Treatment of arrhythmias is carried out under the guidance of an electrophysiologist. He will be able to comprehensively investigate the causes of heart rhythm disturbances, install a defibrillator, and perform arrhythmia ablation. Open heart operations are performed by a highly specialized doctor – a cardiac surgeon.
Treatment
Depending on the type of pathology, treatment is carried out under the guidance of a cardiologist, neurologist, vascular surgeon, neurosurgeon, cardiac surgeon, phlebologist, rheumatologist. Emergency conditions require the help of a resuscitator. There are conservative and surgical methods for treating CVD.
Conservative methods include:
- drug therapy – medications are prescribed depending on the diagnosis;
- plasmapheresis, autohemotransfusion - in the treatment of rheumatic carditis;
- thrombolysis – dissolution of a blood clot during arterial embolism;
- physiotherapy – in the treatment of chronic cerebrovascular accidents, thromboangiitis obliterans.
Surgical methods for treating CVD:
- thromboembolectomy – surgical removal of a blood clot in case of ineffectiveness or contraindications to thrombolysis;
- thrombectomy – for deep vein thrombosis;
- stenting of peripheral vessels and coronary arteries – for atherosclerosis,
- heart valve replacement – for endocarditis;
- stereotactic aspiration of hematoma – for hemorrhagic stroke.
Today, open surgical interventions are rarely performed; preference is given to vascular surgery - this contributes to the speedy recovery of the patient and minimization of postoperative complications. However, after treatment of severe CVD, patients most often require long-term rehabilitation.
Answers to popular questions
What heart diseases cause disability?
The approach to assigning a disability group in the case of cardiac pathology has recently changed.
Now it is given in the presence of a complex of symptoms:
- Significant persistent disruption of the functioning of organs and systems due to heart disease and its consequences;
- Violation of the ability to work, carry out self-care and non-professional activities (meaning the ability to communicate, study, move, navigate in space);
- The need for social protection measures.
To assign disability, a combination of these signs and a significant limitation in working capacity are required. Once every 1-2 years, a re-examination is carried out, since the health status of heart patients may change for the better.
Basically, patients with the following diseases can apply for disability:
- Condition after myocardial infarction;
- 3 degree arterial hypertension with organ damage;
- Heart defects;
- Severe heart failure.
Can an ECG fail to show heart disease?
Such a common method for diagnosing cardiovascular pathologies as electrocardiography is able to show the activity of heart tissue and make it possible to study its rhythm.
However, an ECG cannot informatively determine:
- Heart defects;
- The speed and direction of blood flow in its valves;
- Excessive or insufficient activity of the heart muscle (a sign of myocardial infarction);
- Is there an accumulation of fluid in the pericardium (heart sac);
- Are there signs of atherosclerosis in the aorta?
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a disorder of the functioning of the heart muscle of unknown or controversial etiology. The insidiousness of the disease is that it often occurs without visible symptoms and causes death in 15% of patients with this pathology. The mortality rate among patients with symptoms characteristic of the disease is about 50%.
Cardiomyopathy is often the cause of sudden death
Signs
Patients with cardiomyopathy experience the following symptoms:
- fast fatiguability;
- loss of ability to work;
- dizziness, sometimes fainting;
- pallor of the dermis;
- tendency to edema;
- dry cough;
- dyspnea;
- increased heart rate.
It is cardiomyopathy that often causes sudden death in people leading an active lifestyle.
Causes
The causes of cardiovascular disease, such as cardiomyopathy, are as follows:
- poisoning;
- IHD;
- alcoholism;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- arterial hypertension;
- myocardial damage of an infectious nature;
- neuromuscular disorders.
Often it is not possible to determine the cause of the disease.