How does a person feel during an angina attack?
Symptoms that a person experiences during an angina attack:
- Pain. It is concentrated behind the chest, on the left side. Sometimes the pain radiates to the neck, teeth, and lower jaw. Less commonly, pain occurs in the space between the shoulder blades, elbow and wrist joints, and mastoid processes.
- The pain can be dull, pressing, squeezing. Sometimes a person experiences heaviness in the chest and lacks air.
- The attack lasts no more than 5 minutes. It often has a relationship with emotional and physical stress.
- Increased blood pressure. Its jump provokes headaches, dizziness and weakness. This symptom does not always develop with angina pectoris.
- Shortness of breath, which indicates oxygen starvation of the myocardium. A person's sweating increases for no apparent reason.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the heart, which a person feels well.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Feeling of fear, increased motor activity.
Hyperhidrosis
Increased sweating. It is a consequence of excessive stimulation of the hypothalamus. As a result of malnutrition of the myocardium, the contractility of the heart decreases.
There may be an increase in heart rate, but the productivity of systoles (contractions) is minimal. Therefore, blood output decreases, which means that the brain does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients.
The hypothalamus, under conditions of ischemia (oxygen starvation), begins to send chaotic signals to the entire body.
Since it is in this structure that the center of heat production and release is located, angina pectoris subjectively manifests itself as a feeling of cold, while the peripheral vessels dilate. The body is actively cooling. Then the reverse process is possible and so on in a circle until blood circulation is restored.
Do angina attacks mean an impending heart attack?
With angina, the pain is sharp and not as long-lasting as with a heart attack. In addition, during a heart attack, nausea and weakness of the body are observed. Also, pain during a heart attack does not go away after taking pills or resting.
However, if pain due to angina occurs quite often and does not go away for a long time, then this may well lead to a heart attack.
You should not think that any pain in the heart area is a sign of the development of angina pectoris. For example, if the pain subsides in less than thirty seconds after drinking water or taking a deep breath, then it is not angina.
Description of the disease
Angina pectoris, or angina pectoris, a chronic disease of the cardiovascular system, is characterized by chest pain during physical or gastronomic stress, in stressful conditions, and sudden hypothermia. This differs from another form - angina at rest. Pressing, squeezing or burning pain occurs due to the fact that the heart muscle cells are in a state of severe oxygen deficiency (ischemia).
Pain in angina pectoris quickly decreases and disappears almost immediately after a person puts a Nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue or stops doing any physical work. This is the main difference between “angina” pain and others.
Angina pectoris is considered the most common type of coronary heart disease and is classified under ICD code I20.8.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 300,000,000 people worldwide suffer from angina. The average age of onset of the disease is 45-50 years. The male to female ratio is 2.5:1. However, this only applies to premenopausal women. After menopause, this figure is compared with men. There is a very specific explanation for this fact.
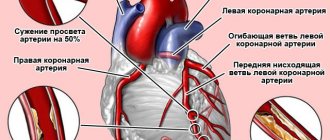
The main cause of angina pectoris is the deterioration of blood flow through the vessels that supply the heart muscle (coronary arteries) due to atherosclerosis. It occurs due to the fact that cholesterol, namely the so-called “bad” variety (low and very low density lipoproteins), is deposited in the walls of blood vessels. Female sex hormones (estrogens) have the ability to reduce the level of this fraction, which reduces the degree of formation of atherosclerotic plaque. And with the onset of menopause, the content of protective hormones in a woman’s blood sharply decreases, which increases cholesterol levels and, accordingly, the rate of development of pathology.
If angina pectoris is not recognized and treated in time, it can lead to myocardial infarction, the number one killer of all diseases.
Classification of angina
Modern medicine distinguishes 3 types of transient myocardial ischemia: stable angina, variant angina, silent myocardial ischemia.
Stable angina
Stable angina is angina pectoris. It usually appears after severe stress or intense physical activity.
Stable angina pectoris is divided into four functional classes, which depend on the severity of the disease:
- First functional class.
Performing normal activities does not cause an attack of angina. We are talking about walking or climbing stairs. An attack can occur during severe physical exertion. It can be either too intense or too long.
- Second functional class.
A person may experience an angina attack when walking quickly, while quickly climbing stairs, after eating, or while spending time in the cold or wind. A stressful situation can trigger angina. Sometimes attacks recur in the first few hours after a night's rest. It is dangerous for the patient to walk more than 200 meters.
- Third functional class.
The patient is forced to limit physical activity, since angina attacks occur after walking a distance of 100 meters or a little more, while climbing one stairwell, on the street, regardless of weather conditions.
- Fourth class of functional activity.
A person loses the ability to perform many activities, since an attack can occur at any time, even when the patient is at rest.
Unstable angina
Unstable angina – angina at rest. Occurs under any load and regardless of stressful situations. It is long lasting and occurs frequently. Symptoms of the disorder develop due to the fact that the myocardium does not receive enough oxygen due to narrowing of the arteries, and not due to increased physical activity.
Some features of the diagnosis, course and treatment of variant angina:
- On the ECG, anginal attacks are accompanied by a transient increase in the ST segment.
- Sometimes severe heart pain can occur after physical activity that a person received in the morning. In the evening and during the day, similar physical activity does not cause pain.
- You can cope with anginal attacks by taking AK and nitrates. The effect of beta blockers is not as strong. In some patients suffering from angiospastic angina, beta blockers can have an anti-ischemic effect.
Silent myocardial ischemia
Very often, myocardial ischemia develops without any obvious symptoms. The person does not feel any symptoms of angina. In this case, the intensity of attacks can be quite high, up to the development of myocardial infarction.
It is possible to detect silent ischemia during exercise tests and during a 24-hour ECG.
There are 3 types of silent myocardial ischemia:
- First type.
Changes in the myocardium of the ischemic type occur without any symptoms. They appear during physical activity and can also be detected during a 24-hour ECG.
- Second type.
Ischemia is recorded in patients with angina attacks.
- Third type.
Ischemia develops in patients without angina, but after a myocardial infarction.
The third and fourth types of angina require emergency medical care. If you ignore this recommendation, the likelihood of developing myocardial infarction or tachycardia increases.
Risk factors
No matter how much you would like to avoid angina, it is important to understand that not all risk factors can be corrected. Unfortunately, the chances of getting sick are inherited. Angina attacks almost inevitably occur in older people.
However, there are many risk factors that can and should be combated. From the life of a person prone to heart disease, it is enough to eliminate just a few dangerous habits - and a number of provoking factors will stop their destructive effect. For example, if a person changes his eating habits, giving preference to light, nutritious, properly prepared food, his weight will return to normal. Cholesterol and blood pressure will decrease. This means there will be fewer risk factors that make it harder for the heart to cope with its tasks.
Risk factors that can be addressed include:
- increased levels of cholesterol and other lipid fractions in the blood. This provokes the deposition of cholesterol in the arteries and further narrowing of the coronary lumen, the formation of blood clots;
- excess body weight;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- smoking. Nicotine causes oxygen starvation and artificial narrowing of the arteries. Smokers have increased blood pressure and angina pectoris occurs earlier than those who do not have bad habits.
- high psycho-emotional stress and stress. In this case, vasospasm and a sharp increase in pressure occur. The consequence can be not only an attack of angina, but also a heart attack.
- women taking hormonal contraceptives.
It is much more difficult to cope with the disease if you have the following pathologies:
- high blood pressure. It causes tension in the myocardial muscle;
- general weakness, intoxication. A weakened body does not cope well with the supply of oxygen to the heart muscle, so anemia often leads to attacks of rapid heartbeat;
- diabetes;
- increased blood viscosity. This leads to the formation of blood clots, further narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels and myocardial weakness;
- endothelial dysfunction;
- early menopause.
Metabolic syndrome is especially dangerous when the patient has several risk factors at once: excess weight, high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol.
Diagnosis of angina pectoris
A person with symptoms of angina should consult a physician or cardiologist. The doctor will listen to the patient’s complaints and collect anamnesis. It is important to clarify what factors become the basis for the development of a pain attack, how long it lasts, and how intense the pain symptom is. You should find out from the patient which medications allow him to cope with the disorder.
After examining the patient, the doctor will give him a referral for laboratory tests. First of all, the patient's blood is studied. It is mandatory to determine the level of cholesterol, LDL and HDL, triglycerides, ALT, AST. Blood is taken for sugar and electrolytes. It is important to take into account blood clotting indicators.
Another important marker of myocardial damage is troponins. If their level is elevated, this indicates a heart attack.
The next stage of the examination is instrumental diagnostics.
It includes procedures such as:
- Electrocardiogram.
In this case, a decrease in the ST segment and a negative T wave in some leads will be noted. The doctor can also diagnose myocardial conduction disorders.
- ECHO-KG.
This study will determine disturbances in myocardial contractility, as well as its local ischemia.
- Daily ECG.
In this case, the cardiogram is taken during the day. A person must write down all his actions that he performs. Physical activity during this period should be moderate. This will allow us to assess how the heart reacts to them, whether the patient experiences ischemic changes in the myocardium, or whether the heart rhythm is disturbed. If a rapid pulse was observed before an attack of heart pain, then this is highly likely to indicate stable angina. If there is no increase in heart rate, then most likely the patient has spontaneous angina.
- Coronary angiography of the arteries.
This diagnostic technique allows you to assess the degree of damage to the coronary arteries, as well as select the optimal treatment method. This study is prescribed to patients with angina pectoris of functional classes 3 and 4, as well as patients with symptoms of myocardial ischemia and people who have a history of episodes of sudden death from cardiac arrest. Most of these patients require surgery, since conservative therapy does not achieve positive results.
Fainting, disturbances of consciousness
It is considered an extremely unfavorable sign. It occurs as a result of a decrease in the intensity of blood circulation in cerebral structures. This is the body’s response to decreased brain nutrition.
In this strange way, the body tries to transfer itself into a “preserved” state, reduce energy consumption, and therefore the need for it, and survive an unfavorable period. Until things get better.
Often observed against the background of a developing stroke. As a result of prolonged deviation of trophism, irreversible changes occur in the brain.
The neurological deficit is never corrected and remains with the patient for life. Among the possible options are disorders of speech, smell, vision, sensory organs, persistent paralysis and paresis.
Disability at a minimum, at a maximum - a quick relapse and death from a recurrence of the emergency condition.
Treatment of angina
Treatment of angina involves taking medications. There are drugs that people with this diagnosis are prescribed without fail, as they improve the prognosis of the disease.
These include:
- Antiplatelet agents:
Thrombo ass, Cardiomagnyl, Clopidogrel. Taking them allows you to prevent the formation of blood clots in the vessels and reduce the likelihood of developing myocardial infarction by 30%.
- Beta blockers:
Bisoprolol, Metoprolol, Nebivolol. They reduce the myocardium’s need for oxygen, allow the lumen of the coronary arteries to expand, and reduce the number of heart contractions. Taking them allows you to normalize the process of oxygen supply through narrow vessels.
- Statins:
Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin. These drugs make it possible to stabilize atherosclerotic plaques and reduce cholesterol levels in the blood, which reduces the likelihood of developing myocardial infarction.
- ACE inhibitors:
Lisinopril, Perindopril, Enalapril. Taking these medications reduces the likelihood of developing heart failure, and therefore reduces the risk of death of the patient.
Angina pectoris requires an integrated approach to therapy. Patients are prescribed several medications that complement each other's therapeutic effect.
Nitrates
Drugs from the nitrate group relax the heart muscle, reduce its need for oxygen, and reduce heart pain caused by muscle spasm. Their intake helps to expand the vessels located on the periphery, so the outflow of blood increases.
- Nitroglycerin (15-51 rubles).
Nitroglycerin is one of the most effective drugs that reduces heart pain that occurs during an attack of angina. The main advantage of the drug comes down to its rapid absorption by mucous tissues.
Nitroglycerin is placed under the tongue. The effect can be felt after a few minutes: a person’s pain in the heart decreases, as the outflow of blood from it is stabilized, and vascular dilatation is normalized.
Nitroglycerin is prescribed for both therapeutic and prophylactic purposes. The doctor selects the dose individually. It largely depends on the patient’s blood pressure, since the drug helps reduce it. It is also necessary to consider what other diseases the person suffers from. Anemia, renal and liver failure, and hyperthyroidism are important.
Nitroglycerin can be addictive, so its regular use to relieve angina attacks helps to weaken the therapeutic effect. If the patient is forced to take the drug on an ongoing basis, breaks must be taken from time to time. In this case, Nitroglycerin is replaced with agents with a similar effect.
Nitroglycerin allows you to reduce the intensity of heart pain after the first dose. If this does not happen, you can take another tablet. When repeated resorption of the drug does not stop the attack, it is necessary to call an ambulance, since there is a high probability that the patient will develop a myocardial infarction.
- Nitrosorbide (28 rubles).
The drug helps reduce pressure in the pulmonary circulation, thereby unloading the myocardium. A person taking Nitrosorbide increases their tolerance to physical activity. However, the drug takes longer to absorb than Nitroglycerin, so it will take longer to stop an attack of angina. Nitrosorbide expands the venous wall, but it does not have a pronounced effect on the arteries and aorta. It can be taken orally, placed behind the cheek or under the tongue at a dose of 10 mg. The drug accumulates in the body over time, so long-term use leads to a decrease in the therapeutic effect. You should not increase the dose; it is better to stop taking Nitrosorbide for a while, replacing it with another drug from the nitrate group.
- Transdermal stickers (1550 rubles).
If a person is forced to take nitrates on a regular basis for preventive purposes, then you can use a patch. It slowly supplies the body with nitrates in the right dosage. The patch is glued to the skin. This treatment can reduce the likelihood of developing an angina attack. The dosage of the drug depends on the size of the sticker.
Adrenergic blockers
Drugs in this group reduce the need for oxygen in the heart muscle by reducing the heart rate. The drugs themselves do not affect the functioning of the myocardium if the person is at rest. The therapeutic effect develops only with physical activity.
- Anaprilin (17-79 rubles).
In the first days, Anaprilin is prescribed in a dosage of 20 mg (the drug is taken 3 times a day). Then the dose is gradually increased and brought to 240 mg per day. The drug can be prescribed to patients with kidney pathologies. If a person suffers from liver disease, then the dose is selected individually. Anaprilin has a number of side effects. These include disorders of the digestive system, allergies, migraines, and insomnia. If the patient complains of deterioration in health, then therapy should be reconsidered.
- Betaxolol (235 rubles).
The drug has a prolonged effect, so it is enough to take it once a day in a dosage of 10 ml. After 2 weeks of treatment, the dose is increased to 20 ml per day. This is done if the therapeutic effect is too weak. The drug is prescribed with caution to patients with severe renal impairment, patients with diabetes mellitus, and people with blood pathologies. An overdose of Betaxolol is dangerous, which can lead to bronchospasm, convulsions and dizziness.
- Atenolol (48 rubles).
The drug is prescribed to a patient with angina pectoris once a day. Take it in the morning after meals. The starting dosage is equal to 50 mg. After 14 days it is increased to 100 mg. Provided that there is no therapeutic effect, the use of Atenolol is abandoned. The drug has contraindications, including: heart failure, hypertension, bradycardia, pregnancy.
Adrenergic receptor blockers should be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account all possible contraindications.
Calcium channel antagonists
These drugs block the production of proteins that lead to spasm of arteries and veins, which has a positive effect on the functioning of the heart. The number of its contractions decreases, and blood outflows to the peripheral circulation. As a result, the person begins to feel better.
- Diltiazem 107 rubles).
Diltiazem is a 3rd generation drug. Despite this, the drug has many side effects. It is recommended for use by patients with angina pectoris and vasospasm. The maximum daily dose is 360 mg, but treatment begins with minimal dosages (180 mg). If the patient develops side effects, then the drug is stopped, as the likelihood of pulmonary edema and collapse increases.
- Gallopamil (250 rubles).
This medicine belongs to the second generation drugs. It is prescribed to people with angina pectoris, as well as to patients who have had a myocardial infarction. The drug unloads the heart muscle and helps relieve spasm from blood vessels. The dose is calculated individually; it can vary between 50-100 mg. Take the drug 2-4 times a day. It is prohibited to prescribe the drug to patients with low blood pressure, pregnant women and children, as well as patients with kidney problems.
- Verapamil (40-155 rubles).
Verapamil is a first generation calcium channel antagonist. It has a positive effect on the functioning of the heart, stabilizes its rhythm, and dilates blood vessels. To prevent the development of angina pectoris, patients are prescribed 320 mg of the drug per day. This dose is divided into four times. It is preventative. If an attack has already occurred, then the dosage is increased to 500 mg. The drug should be prescribed with caution to patients with kidney and liver diseases, as well as people with hypertension.
Diuretics
Diuretics increase urination and help get rid of edema, relieve spasm from blood vessels. They are prescribed in a complex treatment regimen with blockers and antagonists.
- Chlorthalidone (200 rubles).
This is a low-toxic drug that helps reduce blood pressure. It is taken once every 24 hours. It does not flush sodium and potassium from the body, which is its main advantage. If angina is severe, the dose can be increased by 2 times.
- Lasix (55 rubles).
It is a strong diuretic that is used to quickly lower blood pressure. In parallel, the patient should receive magnesium, sodium and calcium supplements. Daily dose – 1 tablet. Diuretics quickly lower blood pressure, so if a person is taking antihypertensive drugs, their dose must be strictly controlled.
Diet
Angina pectoris is a strain that is a variant of the course of coronary artery disease. An attack may occur due to poor nutrition. The first sign that indicates that you are not eating properly if you have angina is the appearance of a burning sensation in the chest area.
The main goal of nutrition is to prevent attacks. With the help of certain products, it is possible to normalize metabolism and also improve blood clotting.
List of prohibited and permitted products
Dietary nutrition must be correct and balanced. The diet includes only those foods that are rich in vitamins and microelements. To normalize metabolism, as well as to restore not only muscles, but also blood vessels, doctors prescribe diet No. 10 to the patient.
List of permitted products:
- Eat fresh vegetables.
- Lenten soups made from vegetables.
- Fruits (unsweetened).
- Egg yolk. It is allowed to use no more than 2 times a week.
- Bread: rye or wheat.
- Porridge. The exception is rice and semolina.
- Meat: rabbit, lean turkey.
- Sea fish.
- Drinks: weak tea, vegetable or fruit juices.
- Nuts.
You can cook dishes using low-fat butter.
Exclude from the diet:
- Do not consume rich broths made from fish or meat products.
- Exclude liver.
- Sweet and rich products.
- If you have angina, you should not eat smoked, spicy, or salty foods.
Sausages and various foods with high fat content are strictly prohibited.
It should be noted that angina pectoris can occur in conjunction with arterial hypertension or diabetes mellitus. In this case, the patient needs to reduce salt intake. The daily dosage of salt should be 2-3 g.
For angina that threatens the development of a heart attack (unstable), including for chronic heart patients, it is necessary to comply with calorie standards. For normal weight, consume 2900 kcal:
- Proteins no more than 100g.
- Fats 90 g per day.
- The largest dose is carbohydrates, no more than 350 g per day.
If you are overweight, the calorie content is reduced, so it ranges from 2000-2100 kcal per day.
- Fat 70 g.
- Carbohydrates 300 g.
Include in your diet foods rich in:
- iodine;
- zinc;
- potassium;
- vitamins from group B;
- methionine;
- manganese.
Foods consumed by a person with cardiac ischemia should be rich in vitamin C.
Retinol helps prevent vasoconstriction. Vitamin C can quickly lower blood pressure. In addition, it has a good relaxing effect directly on the arteries. Additional positive qualities include the ability to reduce vascular permeability.
Surgery
Balloon angioplasty.
This is an operation during which a catheter equipped with a balloon is inserted into the human body through the femoral artery. It is brought to the coronary arteries and installed in the place where there is a narrowing. The vessel expands and the atherosclerotic plaque is destroyed.
The volumes of the cylinder are calculated in advance. For this purpose, the patient is indicated for coronary angiography. After the operation, the study is carried out again, which allows you to monitor the effect of the procedure.
Angioplasty can reduce the number of angina attacks. However, there is a possibility of re-narrowing of the vessel, or the formation of stenosis in other areas. The operation is prescribed for patients with unstable angina, severe vascular stenosis, and also in case of ineffectiveness of drug therapy.
Coronary artery bypass surgery.
During the operation, a shunt is installed between the artery and the aorta. This allows normal blood flow to the heart. This intervention is performed in patients whose angina is severe, for example, with angina at rest.
A shunt can only be installed on large arteries or on the trunk of coronary vessels. If necessary, several shunts can be inserted into the patient at once. This procedure allows you to restore blood flow in all parts of the myocardium.
Menstrual and fertility disorders
Nonspecific and non-obvious signs in women under 50 years of age. Patients come to see a gynecologist with complaints about deviations in duration, delays and other phenomena in the reproductive system.
After a thorough hormonal examination, visual assessment of the uterus, reproductive tract, and ultrasound of the ovaries, nothing is revealed. According to the signs, everything should be fine.
The doctor is at a dead end; in the medical record there is a diagnosis of “unspecified menstrual cycle disorder,” that is, an idiopathic process. In fact, it turns out that we are talking about cardiovascular diseases.
The connection is really not obvious. For normal ovulation, maturation of the egg, and its release, sufficient trophism of the tissues of the pelvic area is required.
Ischemia prevents the normal development of the natural process. Even if the menstrual cycle is intact, the likelihood of infertility is high. The egg is fertilized, and in the early stages spontaneous termination of pregnancy or miscarriage occurs.
Correction of the condition takes place under the supervision of doctors from two specialties. A gynecologist is also needed, but his role is secondary, monitoring effectiveness, dynamics, minor amendments to the treatment regimen.
Emergency care for angina pectoris
Sometimes situations arise in which you need to call a medical team.
These include:
- An attack of angina develops for the first time.
- The attack lasts longer than 10 minutes, the patient becomes increasingly weak and vomits.
- The attack could not be stopped by taking Nitroglycerin. Normally, the effect should develop within 5 minutes.
Until the medical team arrives, the patient needs to provide the following assistance:
- Sit the patient so that his legs are down.
- Don't let the person get up
- Give him an Aspirin tablet.
- Give the patient a Nitroglycerin tablet, which is held under the tongue.
- After 3 minutes, give the patient another Nitroglycerin tablet.
- The drug should not be taken more than 3 times, as this will lead to a sharp decrease in blood pressure.
Anxiety, panic attack
Arises as a response to a traumatic situation.
Interesting:
Studies show that mental reactions to an attack of angina are observed in 95% of patients. Moreover, gender does not matter.
Subjectively, a person feels fear, panic, psychomotor agitation occurs, and the speed of thinking decreases. At such moments, a woman can be dangerous to herself, and injuries are possible.
The condition is treated with tranquilizers or sedatives. Depending on the severity of the manifestation.
Asthenic signs, other mental disorders
Occurs in the late phase of the attack. They manifest themselves as weakness, drowsiness, and inability to concentrate on one specific subject. The speed and productivity of thinking decreases.
Cognitive and mnestic deviations recede as the condition is compensated; they do not lead to persistent neurological deficits. This is a symptomatic manifestation, not a complication.
In addition, there is apathy, reluctance to do anything, lack of pronounced reactions to external stimuli, incentives. A decline in emotional background similar to depression. Fatigue, decreased performance as additional signs.
No special disinhibiting effect is required, but when the patient’s activity drops, the diagnosis becomes significantly more complicated due to the lack of interest in the conversation with the doctor and the patient’s indifference.
Such severe variants of mental disorders are rare, but possible. In some cases, even with a strong desire, the patient will not be able to answer questions due to a semi-conscious state or a full-fledged coma.
Vitamins
In the treatment of angina and coronary artery disease, vitamins and microelements play an important role, ensuring the normal functioning of the heart and vascular system.
Key vitamins needed for cardiovascular diseases:
- Vitamin A - prevents the development of atherosclerosis (fish oil, milk);
- Vitamins C and B6 - helps dissolve cholesterol (citrus fruits, bell peppers, rose hips, legumes, milk, meat);
- Vitamin P - strengthens the walls of blood vessels (citrus fruits, apples);
- Vitamin F - prevents the formation of cholesterol plaques (seafood, fish, vegetable oils).
A course of vitamins is developed by the attending physician based on the specifics of the manifested pathology, if there is an urgent need for it. Taking vitamins on your own may not be effective.
During the treatment of angina pectoris, much attention is paid to the patient’s balanced diet, which is based on the vitamins and microelements necessary for the body. Adhering to a prescribed diet, taking individual vitamins becomes impractical.
You can learn more about the forms of angina from the video:
Diet for angina pectoris
Angina is treated not only by taking medications. A properly selected and balanced diet plays an important role both in the prevention of the disease and during rehabilitation after surgery.
The main goal of the diet is to reduce the amount of saturated fat consumed. They increase cholesterol levels. The amount of such fats should not exceed 40% of the total calorie content of food consumed.
First of all, chocolate, energy and carbonated drinks, and strong black tea are excluded from the diet. Alternative sources of sugar include honey, dried fruits, marshmallows and marshmallows.
It is recommended to consume a minimum amount of salt, as it tends to retain water in the body, which creates additional difficulties for the functioning of the heart. It is strictly forbidden to eat fast food.
For angina pectoris, it is recommended to include the following foods in your diet:
- buckwheat porridge, rice with dried fruits;
- fresh vegetables and fruits, especially bananas;
- dairy products;
- sea fish and seafood of plant origin.
Sea fish contains a large amount of unsaturated fats, which prevent blood clots, the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and improve blood pressure.
Proper nutrition is the best prevention against most diseases, so after reaching 35-40 years of age, it is recommended to consult a qualified nutritionist.