A common cause of bladder diseases is the entry of infectious pathogens into its cavity (Escherichia coli, chlamydia, staphylococci, trichomonas).
Infection can occur directly through the genitals and from other infected organs through the bloodstream. A weakened body cannot cope with the infection and an inflammatory process develops.
Many factors, including non-infectious ones, can contribute to the occurrence of inflammation of the genitourinary system:
- entry of infections or bacteria through the genitals or rectum;
- prolonged overflow of the bladder or its incomplete release;
- tumors in the genitourinary system;
- disturbances of hormonal levels and metabolic processes in the body;
- hypothermia of the lower half of the body;
- circulatory disorders of the pelvic organs;
- pregnancy period;
- poor nutrition;
- inflammatory processes in nearby internal parts of the body.
Pathologies can be provoked by promiscuous sex life without the use of protective equipment, as well as damage to the inner lining of the organ by chemicals. Taking certain medications can damage the integrity of the epithelial layer.
Causes
The causes of pain can be both physiological and pathological. It is important to pay attention to accompanying symptoms, general physical and psycho-emotional state. Most often, pain occurs under the influence of:
- cystitis
- formation of stones in the bladder
- traumatic injuries
- overactive bladder
- cystocele
- polyps
- leukoplakia
- atony
To identify the exact cause of the disorder, you must consult a doctor and undergo laboratory and instrumental examination.
Cystitis
Cystitis is an inflammatory process that affects the bladder. Most often it occurs under the influence of such predisposing factors:
- age: during menopause, the quantitative content of estrogen decreases
- diabetes mellitus
- pregnancy
- abnormal location of the urethra
- use of spermicides as contraception
- sedentary lifestyle
- urolithiasis
- previously suffered diseases of the genitourinary system
- difficulty urinating under the influence of a pathological process
The causative agents of bacterial cystitis are gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms, viruses, and fungi. The clinical picture manifests itself depending on the form of the pathological process.
Acute cystitis is accompanied by:
- pain in the bladder that gets worse with urination
- increased frequency of bladder emptying
- cloudy urine
- increased body temperature
- a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder
The pain intensifies at the end of urination. There are complaints of sleep disturbances and deterioration of the psycho-emotional state.
Choose a specialist, read reviews and make an appointment with a urologist online
Bladder stones
Bladder stones are one of the types of urolithiasis. It occurs as a result of a violation of the physicochemical properties of urine, as well as under the influence of physiological factors: metabolic disorders, the use of certain groups of drugs, inflammatory reactions. The disease often develops due to a violation of the free outflow of urine, stenosis of the bladder neck.
Even with large stones, clinical signs may be absent for a long time. Symptoms occur if the stones come into contact with the walls of the bladder for a long time. Women complain of pain in the bladder and lower abdomen, which intensifies with:
- motor activity
- change in body position
- during sexual intercourse
- during urination
Pain may radiate to the perineum and lower extremities (hips). If the stone is large, the woman can only empty her bladder while lying down. Small stones in most cases come out on their own. To speed up the process, it is recommended to follow a diet and take medications to adjust the alkaline balance of urine. Large stones require surgical intervention. The type and volume of surgery is selected individually for each woman.
Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder is a clinical syndrome in which there are complaints of frequent urination - up to 10 times during the day or at night. This condition negatively affects the psychological state of a woman. Occurs mainly in people of older age groups over 70 years of age. In patients with an overactive bladder, the urge to urinate is so strong that the woman cannot restrain herself.
Consequently, an overactive bladder exhibits a triad of symptoms:
- frequent urination
- strong urges that are uncontrollable
- urinary incontinence
The main goal of treatment is to restore the storage capacity of the bladder and improve the patient’s quality of life. During therapy, conservative methods and medications are used. If they are ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated.
Cystocele
Cystocele is a pathological process that is accompanied by prolapse of the bladder. Occurs due to the following reasons:
- labor activity
- overweight, obesity
- chronic cough, bronchitis
- lifting weights
- hysterectomy - removal of the uterus
Women who have given birth 2-3 times or more are at risk. The risk of cystocele increases during menopause, when the production of the female sex hormone estrogen decreases, leading to weakening of muscle tissue.
Cystocele is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain and discomfort in the bladder, pelvic organs
- feeling of squeezing in the vaginal area
- a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder
- urinary incontinence when coughing, during sexual intercourse
- addition of secondary genitourinary infections
For mild cystocele, specific therapy is not required. It is recommended to perform special Kegel exercises that strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. As the pathological process progresses, estrogen-based drugs may be recommended, as well as the use of pessaries.
Traumatic lesions
The integrity of the bladder can be compromised by blunt trauma or penetrating wounds. Blunt injuries are more common and can result from:
- sudden braking of a car
- falling from a great height
- external strong blow to the lower abdomen
Bladder injuries are often accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the pelvic bone tissue. The greatest danger is a ruptured bladder.
Important! For bruises, drainage is sufficient and there is no need for urgent surgery.
The bladder is more often than other organs subject to traumatic lesions during surgery in the pelvic region:
- transurethral operations
- gynecological procedures
- C-section
- removal of tumor tumors
- colon resection
Predisposing factors include scar tissue after previous surgical interventions, radiation therapy, and tumor processes. The main symptoms of damage: dull pain over the pubic bone and frequent urge to empty the bladder. To confirm the diagnosis, retrograde cytoscopy is used in combination with computed tomography. During therapy, the use of drainage, as well as surgical intervention, is indicated.
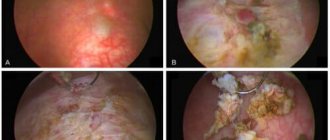
Polyps in the bladder
Polyps are benign neoplasms that are formed due to abnormal proliferation of epithelial cells of the mucous membrane. They can be small (up to several millimeters) and large - 1 centimeter or more, single or multiple. They account for up to 8-12% of all urological diseases and are rare in females.
Important! Symptoms of polyps may be absent for a long time; most often, the disorder is detected by chance, during the next scheduled examination.
Clinical manifestations begin to bother a woman when the tumor grows (the polyp disrupts the process of urination) or mechanical damage. In this case, complaints arise about:
- blood in the urine
- urinary retention
- pain in the bladder
- deterioration in general health: weakness, fatigue, increased fatigue
- the addition of the inflammatory process causes an increase in body temperature
Despite their benign origin, polyps require observation and, if they grow and increase in size, removal. This is due to the risk of transformation of a benign process into a malignant one.
Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia of the bladder is a clinical diagnosis made on the basis of pathological examination. This is a pathological change in the mucous membrane, a non-tumor change in the epithelium. This is the body’s reaction to unfavorable environmental conditions, as well as changes in blood flow in the bladder. Laboratory diagnostics most often do not confirm the inflammatory process; the urine culture tank is sterile. The management of patients with leukoplakia is often carried out by a tandem of specialists: a urologist and a gynecologist.
Leukoplakia is accompanied by complaints of:
- pain in the bladder
- increased urge to urinate
- feeling of pain when emptying the bladder and during sexual intercourse
Treatment is aimed at reducing the inflammatory response and irritation of the organ. The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs, hyaluronic acid, and means for correcting blood circulation. It is important to follow the diet, drinking regimen, and all recommendations of the urologist and gynecologist.
Bladder atony
Atony of the bladder is a pathological process that is accompanied by weakening of the walls of the organ. The patient cannot control the process of urination, there are complaints of pain and urinary incontinence. Atony occurs under the influence of such predisposing factors:
- traumatic lesions of the sacral spine
- disorders of the spinal cord roots
- advanced course of syphilis
- anesthesia
- surgical intervention
- use of psychotropic substances
- muscle weakness
A characteristic symptom of the disorder is urinary incontinence and is aggravated by tension in the abdominal muscle tissue: coughing, sneezing, fast walking, excessive physical activity. At first, urine leaks and is released in small quantities. Subsequently, the urge is accompanied by discomfort, a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen and in the bladder area.
During therapy, a set of measures is used: Kegel exercises, diet, emptying the bladder according to a schedule drawn up in advance. Drug therapy involves the use of antidepressants, calcium antagonists, and anticholinergic drugs. To reduce unpleasant symptoms, a pessary is used - a device inserted into the vagina to provide additional pressure. Physiotherapy is used to stimulate the bladder. If conservative measures are ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated.
Bladder cancer
Bladder cancer is a pathological process that is accompanied by the formation of malignant tumors in the walls of the bladder. The risk group includes women who have a history of chronic cystitis, as well as those who are exposed to bad habits: smoking. Most often, oncologists encounter anterior cell carcinoma, less often - squamous cell carcinoma and adnocarcinoma.
Important! The disease can be asymptomatic for a long time, which makes timely diagnosis and treatment difficult.
The progression of the pathological process leads to hematuria, frequent, painful urination, pain in the bladder and above the pubis. Compression of the ureteric orifices leads to pyelonephritis and chronic renal failure.
Painful Bladder Syndrome
Painful bladder syndrome is a chronic pathological process that is accompanied by pain, discomfort in the pelvic organs, and the urge to urinate frequently. Women are at risk; the disorder significantly reduces the quality of life.
The clinical picture is individual for each woman. Depends on age, hormonal status, lifestyle. General signs are manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain in the area between the vagina and anus
- frequent night urination
- pain during intercourse
- chronic pelvic pain
- constant urge to empty the bladder
- increased pain when the bladder is filled, temporary relief is observed after emptying
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor conducts an oral interview and asks to keep a urination diary. An examination is carried out on a gynecological chair, as well as a cytoscopy and biopsy. During therapy, preference is given to physiotherapy and medications. In some cases, hydrobouging is performed: liquid is injected into the bladder under pressure, which leads to its stretching and increase in volume.
Classic signs of acute and chronic cystitis
An acute process occurs for the first time after contact with an infectious agent, chemical irritant or allergen. Symptoms appear clearly and manifestly: sharp pain when urinating, uncomfortable emptying of the bladder, pain in the lower abdomen, itching and burning at the exit of the urethra. There may be a short-term rise in temperature, nausea or weakness, loss of appetite, and there may be an association with worsening symptoms after ingesting irritating foods or drinks.
Chronic pathology is characterized by the erasure of symptoms, the presence of constant discomfort in the suprapubic region, and nagging pain. In the remission stage, the patient feels quite healthy. Exacerbation occurs after hypothermia, consumption of irritating food or drinks, or repeated contact with an allergen.
Possible complications
Lack of timely treatment is fraught with complications. Stretching the bladder leads to increased pain and urinary incontinence. Due to constant pain and urination problems, the woman’s physical and psychological condition worsens. Sleep disorders arise and the quality of life deteriorates. Secondary bacterial infections are possible; trauma and inflammation of the bladder often causes hematuria and pyuria. The earlier treatment begins, the better the prognosis.
Types of cystitis in women
Bladder inflammation is classified according to various criteria.
The main types of cystitis include the following:
- by the nature of the process: acute or chronic;
- due to the occurrence: bacterial, chemical or allergic;
- by associated factors: postpartum, secondary, postoperative.
Postoperative cystitis occurs after abortion, delivery by cesarean section, and urine is released through a catheter. It is this medical instrument that can become a source of infection.
Which doctor should I contact?
At the first symptoms of a disorder, it is recommended to consult a urologist. The doctor will conduct an oral examination, examination, and prescribe additional instrumental and laboratory tests. Depending on the results obtained, consultation with doctors of related specialties may be required: gynecologist, psychotherapist, therapist. If there are concomitant disorders of the innervation of the bladder, consultation with a neurologist is indicated. It is important to refrain from self-medication and seek medical help in a timely manner.
Choose a specialist, read reviews and make an appointment with a urologist online
Diagnostics
Bladder pain is a nonspecific symptom that can occur with various disorders and pathological conditions. To confirm the diagnosis, you need to consult a doctor and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis:
- general blood analysis
- urine tests: general, according to Nechiporenko, bacteriological examination
- biochemical blood test: urea, creatinine
- examination of vaginal microflora
- examination on a gynecological chair
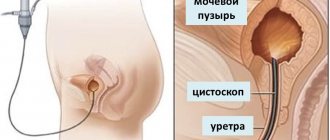
- cytoscopy - examination of the bladder using an optical device that is inserted through the urethra with the preliminary use of anesthetics
- examination of a woman and her sexual partner for sexually transmitted diseases
- sensitivity test with a potassium solution - plain water and a potassium solution are injected into the bladder, after which the woman is asked to describe what sensations arise, how strong the urge to urinate is
- if necessary, an additional biopsy is prescribed
Additionally, ultrasound examination, radiography, and cytoscopy are prescribed - an endoscopic procedure during which the walls of the bladder are examined.
Structure and functions of the bladder
The urethra is a collection of urine that comes from the kidneys through the ureters and then exits through the urethra. It consists of the following parts: wall, neck, bottom and lumen. The capacity of the bladder in an adult can vary, depending on the volume of fluid present, ranging from 250 ml to 700 ml. When full it has the shape of a pear, and when empty it has the shape of a saucer.
The bladder consists of several sections passing from one to another. The main ones are the detrusor (capacity) and two sphincters (obturator apparatus). Sphincters are the most important part of the bladder, consisting of two muscles that prevent fluid from leaving until the bladder is full. The internal sphincter is located at the beginning of the urethra (urethra), it relaxes when the muscles begin to contract and the bladder fills and stretches, the walls become thin. The external sphincter is located in the middle of the urethra and can be compressed spontaneously.
The bladder consists of a front wall, two side walls and a back wall. They, in turn, consist of one mucous and two muscle layers. The inside of the bladder is covered with a mucous layer with small lymphatic follicles and mucus glands. In women and men, the histology and anatomy of the bladder is the same. The bladder of a newborn child is higher than that of a mature person. Thanks to this location, it does not come into contact with the vagina in girls and the intestines in boys.
During pregnancy, a woman feels a more frequent urge to urinate. This phenomenon is associated with an increase in the size of the uterus, which is located behind the bladder and puts pressure on it, which can cause the organ to bend or bend.
The absence of the bladder (agenesis) is a very rare anomaly, which, as a rule, is combined with malformations of other important systems and organs, and is incompatible with life.
Treatment
The treatment regimen is selected individually for each patient, taking into account age, concomitant chronic disorders, the overall clinical picture, and the results of a comprehensive examination. They use an integrated approach:
- drug treatment
- physiotherapy
- lifestyle correction
- change in diet: exclude fatty, spicy foods that irritate the walls of the bladder, as well as alcohol
During the process, the doctor can adjust the prescription, add other medications and dietary supplements.
Important! Physiotherapy can help relieve pain if it is caused by pelvic floor muscle spasms.
During drug therapy, the following groups of drugs are used:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce soreness
- sedatives/antidepressants to relax the bladder and reduce pain
- antispasmodics
- anti-allergy medications to reduce symptoms of frequent urination and reduce urgency (strong urge)
- diuretics
Specific therapy depends on the underlying cause that is causing bladder pain. During treatment, the patient should be under the dynamic supervision of specialists. Deterioration in health, addition of additional symptoms, lack of the expected effect from recommended medications is an indication for re-visiting a doctor and adjusting the prescription.
Nerve stimulation procedures are also indicated for patients. To conduct transcutaneous nerve stimulation, cutaneous electrodes are used. Thanks to electrical impulses, blood flow to the bladder increases and muscle tissue is strengthened. This helps control the urge to empty your bladder and reduce pain. If conservative methods are ineffective and there is a significant deterioration in health, surgical intervention is indicated.
Folk recipes
Alternative medicine has gained extensive experience in the treatment of urological infections. The recipes have many positive reviews, which confirms the effectiveness of the methods. But they can only be used in combination with drug treatment.
Good results are obtained by ingesting decoctions of parsley root, chamomile, and tincture of lingonberry leaves. Drinking lingonberry juice has an excellent sanitizing effect. The healing qualities of “bear ears” and cranberries have long been known. You can prepare the following composition and take it three times a day after meals:
- take dry herbs of rosemary, lovage, centaury, and rose hips in equal proportions;
- pour boiling water for 30 minutes;
- boil in a water bath for 20 minutes;
- leave for 30 minutes;
- strain and drink as above.
It is contraindicated to drink alcohol, strong drinks, or smoke during treatment.
Prevention
To prevent pain in the bladder, adhere to the following recommendations:
- promptly treat emerging chronic diseases and gynecological disorders
- Once a year they undergo a routine examination by a gynecologist
- observe the regime of work, rest, sleep: go to bed no later than 23:00 in a completely dark, cool room
- adjust the diet: reduce carbohydrates, spicy, fatty foods, alcoholic drinks;
- refrain from bad habits
- maintain a drinking regime to prevent congestion, growth and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms in the bladder
- prefer moderate physical activity
At the first symptoms of pain in the bladder, it is recommended to seek medical help as soon as possible and undergo a comprehensive examination. The earlier treatment begins, the better the prognosis.
Features of clinical manifestations
Women have a shortened and wide urethra, which facilitates the penetration of infections into the upper urinary tract.
Women are more likely to experience bladder diseases such as cystitis, pyelonephritis and urethritis, and the onset of the disease usually goes unnoticed and treatment begins already in the chronic stage.
In men, due to the longer canal, the lower parts of the urinary system suffer from inflammation, and the prostate gland and urethra are affected. As a result of the penetration of pathogens of sexually transmitted infections and the development of urological pathologies (neoplastic tumors, adenomas), bladder diseases occur in men. The symptoms are pronounced, which makes it possible to stop the disease in the acute period of development.
Inflammation of the genitourinary system most often manifests itself in the form of characteristic symptoms:
- short intervals between urination;
- a small amount of fluid released and a feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied;
- urination is accompanied by pain, cutting and burning;
- cloudy urine mixed with blood and pus is released;
- frequent cases of involuntary urination.
At the beginning of the development of inflammation, a high temperature may appear, the patient feels general malaise and nagging pain in the abdomen. Advanced disease has less pronounced symptoms.