It is not clear why bruises on the legs can bother women at any age. In the absence of a blow or bruise, a woman is embarrassed to hear accusations of clumsiness addressed to her, so she tries to hide the bruises under trousers or a long skirt, but this is not only a matter of aesthetic discomfort. Bruises on the legs of women, especially numerous or appearing with enviable regularity, may indicate health problems.
Bruise: what happens?
A bruise (hematoma) is the external result of damage to blood vessels located close to the surface of the skin. Blood that gets into the subcutaneous layers appears as a purple spot. Quite quickly, red blood cells begin to break down, and the bruise takes on a bluish tint.
Within a week, the hematoma begins to “bloom”: from the periphery, its shade changes to greenish and yellowish. However, if you go for a swim with such a “blooming” bruise, the hematoma will again become purple-bluish. As a rule, the bruise is painless, only with large-scale subcutaneous hemorrhage is a slight thickening under the skin felt.
Usually hematomas go away on their own within a couple of weeks. But this process can be accelerated if you follow certain recommendations.
Mechanism of occurrence
A hematoma on the leg occurs due to mechanical damage to vessels of various sizes. As a result, blood flows into the surrounding tissues and forms accumulations in the resulting voids between damaged muscle fibers.
Depending on where the hematoma is localized, the following types are distinguished:
- subcutaneous;
- internal;
- intra-articular.
The course and prognosis of the condition depends on the size of the formation and its location.
Hemarthrosis - hemorrhage into the joint cavity - has the most complex clinical picture and requires urgent intervention by specialists.
An internal hematoma on the leg occurs with pronounced clinical symptoms (pain, discoloration of the skin, swelling). The accumulation of blood is located between the muscle fibers and can be significant. The larger the caliber of the damaged vessel, the more severe the damage and the higher the risk of complications.
When a bruise is a reason to see a doctor
Not every bruise deserves attention. Worrying about any blemish on your body is dangerous for your mental health. But you shouldn’t let your guard down either. Bruises should be a concern if:
- they are large, painful and appear as a result of minor force (for example, your hand was squeezed loosely)
- there are a lot of bruises and you can’t figure out where they came from
- bruises do not go away for a long time (last for several weeks)
If you have mentally checked at least one box, make an appointment with your doctor. Now let's move on to the most common pathological causes of bruises.
Bloated stomach, confusion. What does cirrhosis of the liver lead to? In recent years, cirrhosis of the liver has increasingly appeared in people who are indifferent to alcohol.
The main differences between a hematoma and a bruise
In medical terminology, the term “bruise” does not exist. This expression is typical for popular speech when it is necessary to indicate the presence of a small subcutaneous hemorrhage. This formation usually has a characteristic bluish color, does not cause any particular inconvenience and goes away on its own.
A hematoma is a significant accumulation of blood between tissues that causes discomfort to the patient. As a result of improper treatment, a complication may develop in the form of infection followed by suppuration.
Recommendations
There are a number of rules that, if followed, will reduce the number of bruises. Basic recommendations:
- Run, swim, walk (any type of physical activity).
- Wear comfortable, flat shoes.
- You should avoid visiting saunas and baths.
- It is not recommended to carry heavy weights.
- You should drink plenty of fluids (plain water).
- Avoid skin exposure to direct sunlight.
Be sure to take vitamins and lead a healthy lifestyle. If the bruise does not go away for a long time, then you should not self-medicate. It is better to consult a doctor for advice. Only with a professional eye will the doctor be able to adequately examine the affected area and prescribe the necessary diagnostics, and subsequently treatment. Take care of yourself.
Causes of hematoma on the leg
The lower extremities are one of the most vulnerable places for injuries of various types. Damage leads to disruption of the mechanical integrity of blood vessels and the formation of blood accumulations.
After the fall
The legs are often injured during a fall. Such injuries can be combined with fractures of the lower leg and femur, knee, ankle and hip joints.
After the bruise
A leg bruise with subsequent development of hemorrhage often develops in domestic conditions when colliding with pieces of furniture.
After the blow
Athletes (especially football players) often suffer severe injuries in the leg area. They have extensive hematomas with a deep location, the treatment of which requires urgent medical intervention.
Symptoms
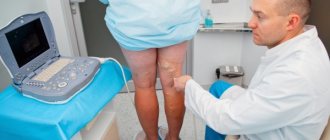
Clinical signs of hematoma are few. As a rule, immediately after an injury, limited/spread swelling appears, which can quickly increase in the absence of inflammatory phenomena. After 24-36 hours, due to rupture/crushing of small blood vessels of the skin and underlying subcutaneous tissue and soft tissue, bruises appear on the skin, which are clearly visible. The severity of pain can vary from its absence in case of minor household injuries to severe in case of severe injury. When pressing on the skin, pain is limited to the site of the bruise. Movement in the limb is preserved, and the victim can step on the leg. The swelling fluctuates.
After 4-5 days, fibrinous crepitus appears, a dense border ridge is determined along the periphery of the hematoma, and palpation reveals a clear fluctuation in the central part of the hematoma. This symptomatology is due to the presence of liquid blood in the hematoma cavity, the formation of blood clots and the deposition of fibrin on the walls of the hematoma. Local temperatures are elevated. Less commonly, enlargement of the nearest regional lymph nodes occurs. On the lower extremities, below the site of the bruise, a doughy, cold-to-the-touch swelling may appear, formed due to the transudation of blood serum into the tissue. Pain from pressure on the skin is usually limited to the site of the injury. Gradually, the color of the bruises becomes yellowish-green, then slightly brown and disappears.
If the internal hematoma is located deep in the large muscles, then infiltration and swelling forms in the deeper layers; accordingly, the clinical signs are somewhat different: local edema is usually absent, and an increase in the volume of the limb is more typical. When a hematoma becomes infected and a phlegmon/abscess forms, the pain syndrome sharply increases, pronounced local hyperthermia and hyperemia , and symptoms of general intoxication are added.
Hematoma without an external cause
If a bruise on the leg has formed without any external influence, you will need to analyze the likelihood of factors that could cause such a condition. The most common causes of hematoma are the following diseases:
- hemophilia;
- decreased permeability of the vascular wall against the background of hemorrhagic vasculitis;
- angiopathy;
- atherosclerotic lesions of the vessels of the extremities;
- phlebeurysm.
The integrity of the vascular wall is compromised after recent surgical interventions and with a lack of vitamins C, P and K.
Vitamin deficiency
There are vitamins that are necessary for normal blood clotting and regeneration of the body after injury. These substances include vitamins E and K. Vitamin K got its name from the first letter of the surname of the American hematologist Quick. It is not difficult to guess which function is the main one for the vitamin - it prevents bleeding and hemorrhages, and, therefore, the appearance of bruises.
The need for vitamin K as a medicine usually occurs when there are problems with the liver, because it produces prothrombin.
Prothrombin is a blood plasma protein that is a precursor to the enzyme thrombin. Thrombin is necessary to convert the blood clotting factor, soluble fibrinogen, into insoluble fibrin. Prothrombin is synthesized in the liver, so determining its concentration helps assess organ function.
Vitamin K stimulates the production of plasma protein and thus restores coagulation. It is found in large quantities in the leaves of nettle, honey, birch, linden, raspberry and rose hips, as well as in soybean oil, liver, casein, walnuts, cabbage (white cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli, kohlrabi) and all vegetables with green leaves.
What other vitamins are important:
- Vitamin E also improves blood clotting. The substance thins thick plasma, prevents the appearance of blood clots in thrombosis, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis
- zinc and iron are needed for rapid healing of all kinds of damage, including capillary
- B12 is involved in hematopoiesis
- Vitamin C plays an important role in the formation of new tissues: without it, blood vessels become fragile
- Vitamin P is needed for collagen production
With a deficiency of all these substances, bruising may occur: the vessels become brittle and fragile, and the body does not have enough strength to quickly block the bleeding.
Choline is a liver vitamin. Where to find it Vitamin B4 protects the liver from damaging factors and prevents the development of fatty liver disease.
First aid for injury
The main task in case of damage is to stop bleeding and promote the rapid formation of a blood clot.
To achieve this goal, it is necessary to create hypothermia of the affected area as quickly as possible. You will need to apply an ice pack wrapped in a cloth or any cold object to your leg. This needs to be done as quickly as possible, since low temperature not only helps stop bleeding, but also increases the resistance of cells to hypoxic conditions.
To quickly form a blood clot in a damaged vessel and stop bleeding, the leg should be placed in an elevated position and ensure complete rest.
Treatment of hematoma
To quickly resolve the spilled blood, it is advisable to use special medications on the damaged area. Their use can prevent infection of the hematoma with its subsequent suppuration. After a few days, compresses should be applied to the site of the bruise to warm it up.
Pain syndrome requires the administration of anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs locally, in the form of tablets or injections. Medicines that have proven themselves to be effective:
- Diclofenac;
- Ibuprofen;
- Indomethacin;
- Arcoxia.
How much drugs should be used is decided individually depending on the course of the pathological process.
Dimexide helps deliver the ointment with the active agent, which must be applied as a compress to the affected area. As a result of this treatment of a hematoma on the leg after a bruise, the local inflammatory reaction and swelling of the surrounding tissues decrease.
External medications
The most important are ointments based on heparin and troxerutin. They:
- reduce tissue swelling;
- stop bleeding when blood vessels rupture;
- reduce the permeability of the vascular wall.
The next day after a leg injury, you can use the following topical medications:
- Thrombocide;
- Heparin ointment;
- Lyoton;
- Troxerutin ointment.
Classification
The classification of hematomas is based on several principles.
- By localization in the soft tissue structure - subcutaneous, subfascial/aponeurotic, intermuscular, subperiosteal.
- According to the nature of the vessel - arterial, venous and mixed.
- Clinical signs are simple, pulsating.
- According to the degree of distribution - limited, diffuse, encysted hematomas.
Soft tissue hematomas are divided into:
- Lungs - appear within 24 hours after the injury. Painless or accompanied by mild pain. No treatment is required, they disappear in 10-15 days.
- Moderate - appear within 5-6 hours after injury, accompanied by severe pain and slight swelling. The motor function of the lower limb suffers slightly. Consultation with a traumatologist is necessary.
- Severe - appear within 2 hours after injury. There is widespread swelling and acute pain, and function suffers. Treatment is needed.
What to do if the hematoma is started?
Quite often, due to the patient’s frivolous attitude towards his condition, the resulting lump remains untreated. An old hematoma under unfavorable conditions can become inflamed and infected, even if time has passed since its occurrence. If complications develop, the accumulation of blood will have to be removed surgically and the wound sanitized with antibacterial and antiseptic drugs.
Subsequently, it is necessary to continue treatment with absorbable agents (chestnut and heparin-based ointments) and thermal procedures.
List of sources
- Urakov A.L. DIAGNOSTICS OF SOFT TISSUE DAMAGE DURING BLEEDING//Advances of modern natural science. – 2015. – No. 1-6. – pp. 951-957.
- Gumanenko E.K. Military field surgery. 2nd ed., rev. and additional 2012. - 768 p.: ill.
- Kornilov N.V. Traumatology and orthopedics: textbook. Ed. N.V. Kornilova. — 3rd ed., add. and p First Aid: Textbook/Under the general editorship of Doctor of Medical Sciences. Professor Vartanyan F.E. – M.: Russian Society of the Red Cross, 1997, – 215 p. reworked - 2011. - 592 p.: ill.
Preventive measures
To avoid injury to blood vessels with unpredictable consequences, you will need to take the following measures:
- include in your diet a sufficient amount of foods with vitamins C and P (black currants are especially rich in this combination);
- for increased fragility of blood vessels, the combination drug Ascorutin is recommended;
- food should contain protein foods of animal and plant origin and collagen.
If injury could not be avoided and a hematoma still forms on the leg, you should consult a specialist. Timely assistance will make it possible to maintain the healthy condition of the lower extremities.
A hematoma that has formed on the leg should not be confused with an ordinary bruise. To do this, it is necessary to carefully assess the damage immediately after the injury. The appearance of alarming symptoms (pain, swelling, fever) is an urgent reason to visit a medical facility.
Oncology
According to the British association Living with Leukaemia, 24% of people with leukemia (blood cancer) develop bruises. They are caused by a deficiency of platelets, which are responsible for blood clotting. In healthy people, the number of platelets varies from 150,000 to 450,000 in every microliter of blood. A smaller amount will cause bleeding. Scientifically, this phenomenon is called thrombocytopenia.
Liver cancer can also cause bruising because the body's synthesis of clotting proteins is impaired. In addition to bruises, hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer) manifests itself through severe pain in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, jaundice, itchy skin, and fever.
There is also a risk of bruising with intestinal cancer - due to impaired absorption of the already mentioned vitamin K. This usually occurs in the later stages of the disease.