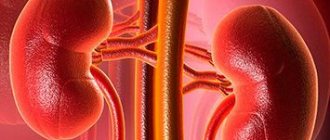
Kidney disease is so common that almost everyone has experienced it.
If there is pain in the lower back, lower back or side, then the person thinks that he has pain in the kidney organ. But this is not always true.
This pain syndrome can also occur with other diseases of the internal organs. This article will discuss exactly what kind of pain arises from kidney pain.
What are kidneys?
Kidneys are an important organ of our body. The proper functioning of all other systems depends on its operation. If the kidney organ fails, the person feels pain and discomfort. Various diseases arise.
The main purpose of the kidneys is to cleanse the blood. They operate continuously and distill about 200 liters of plasma per day. There are two kidneys in the human body. One is located on the right, the other on the left. The internal organ has a complex structure and plays a huge role in the functioning of the body.
Various symptoms, including pain, indicate problems in the functioning of the kidney organ. Based on the tests and what pain is present with kidney pain, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
Diuretics
When one of the kidneys hurts, the cause of the pathological condition may be the accumulation of excess fluid in the paired organ. Swelling is characteristic of chronic renal failure and nephritis. A single dose of a diuretic will allow you to remove excess water. It is best to use one of these tools:
- Hypothiazide,
- Trigrim,
- Furosemide,
- Diuver,
- Diacarb.
You can use medications with diuretic activity only if there is sand or small stones in the kidneys. If a large stone is detected during diagnosis, then at the beginning of therapy it is dissolved or crushed.
Causes of kidney pain
Depending on the pain associated with kidney pain, the causes of the disease are determined.
Pain in the internal organ can occur due to an inflammatory process that affects the glomerular apparatus (glomerulonephritis). Appear if the pyelocaliceal part of the kidneys becomes inflamed (pyelonephritis). The occurrence of a foreign stone indicates urolithiasis, which is accompanied by renal colic.
Pain in the kidneys occurs due to cysts and various formations that have arisen in the cavity of the renal organ. Nephroptosis and disruption of the renal system caused by renal failure cause negative sensations.
Pain in the kidney can be caused by injury, a large volume of fluid taken in a short period of time, heavy physical activity, or pregnancy.
Possible complications
Kidney cancer can lead to metastases in the brain, lungs, and pelvic bones; provoke death. Due to the constant bleeding that accompanies the tumor, hemoglobin levels decrease and iron deficiency anemia develops. Large stones can change their position inside the renal pelvis and block the outflow of urine. Urine is retained inside the bean-shaped organ, causing it to stretch and increase in size.
Glomerulonephritis is the leading cause of renal failure. If inflammation of the glomerular apparatus is eliminated in a timely manner, the chances of a favorable prognosis increase. Kidney injury is dangerous due to loss of the organ; pyelonephritis is often combined with cystitis (inflammation of the bladder).
Common symptoms of kidney disease
What kind of pain in the kidneys indicates a pathology in the body? This is pain in the upper part of the lower back, under the ribs. It is in this area that the paired organ is located. The nature of kidney pain depends on the diagnosis. Painful sensations can be pulling, sharp, aching and stabbing. They differ in the strength of their manifestation. They are permanent and temporary.
The pain is often accompanied by fever, heat and poor health. Patients experience dizziness, nausea and headaches. Lost appetite. The volume of urine excreted decreases. Temperature and pressure rise. Swelling occurs. Frequent and difficult urination. Urine acquires an uncharacteristic color and a pungent odor. It contains blood or pus. The consistency of urine becomes viscous.
Until the patient is examined by a nephrologist, one should not say that the kidneys hurt, because there are other organs next to them, the disruption of which can cause a similar picture.
Symptoms
When the kidneys hurt, there are other symptoms caused by dysfunction of the organs:
Pain syndrome
The nature of the pain can be different, which is primarily determined by pathology. The pain can be paroxysmal, so intense that you literally want to climb the wall. Such pain is typical during an attack of urolithiasis, when a calculus has blocked the exit of the ureter from the renal pelvis.
Also, very pronounced pain appears when the kidney wanders, when it changes its topography in the body, which is accompanied by stretching of the ligaments supporting the kidney and pinching of blood vessels and nerves. Acute pain, accompanied by intoxication, is characteristic of acute pyelonephritis (its purulent-destructive forms), when a cyst ruptures, including a parasitic kidney or abscess.
There is no doubt that acute pain appears at the time of open kidney injury and immediately after it. Dull, aching or nagging pain is characteristic of chronic renal pathology (chronic glomerulonephritis, hydronephrosis, kidney tumor, etc.). Often, pain in the kidney/kidneys radiates to the leg, sacrum, or simply pain in the abdomen.
Localization of pain
It is very difficult to understand for yourself where the kidneys hurt. In urology, the effleurage symptom is used to diagnose kidney diseases. To determine the symptom, the doctor places his hand, palm down, on the projection area of the kidney (just above the lower back), approximately at the level of the lower thoracic ribs, and performs light tapping movements with his fist. The patient is sitting or standing at this time. With a positive symptom, the patient feels pain, which is localized somewhat laterally and spreads from the back to the abdomen.
Until now, many doctors confuse the concepts of “effleurage symptom” and “Pasternatsky symptom.” The latter is carried out in the same way, but after it is performed, red blood cells appear in large quantities in a general urine analysis. Gross hematuria is also possible, when the patient, during urination, notices that the urine has become brown or reddish.
Dysuric phenomena
Urinary disorders are almost always observed with kidney pathology. Pain when urinating, heaviness in the kidneys that appears during urination, frequent urination, or, on the contrary, urination is difficult or impossible (for example, during an attack of renal colic) may be disturbing.
Change in urine
A clear and characteristic sign of renal pathology, which may alert the patient, is that the urine changes its color. Possible darkening and turbidity of the urine, the appearance of flakes or drops of pus in it, which indicates an inflammatory process, or the urine becomes red or brown - kidney injury, urolithiasis.
Signs of intoxication
With the development of the inflammatory process in the kidneys, characteristic symptoms of intoxication appear: weakness, fever alternating with chills, dizziness, appetite disturbances, nausea and vomiting.
Swelling
The appearance of edema is also considered one of the typical signs of renal pathology. Swelling occurs not only on the legs, but also on the face (classic “bags under the eyes”), which are especially pronounced in the morning, immediately after waking up. In overweight people, swelling may spread throughout the body.
Itchy skin
When pain appears in the kidneys, skin itching (often unbearable) may occur. The mechanism of development of this symptom is diverse, itching occurs as a result of metabolic disorders and the accumulation of urea in the blood (gout, amyloidosis), chronic kidney diseases when their filtration function is impaired (glomerulonephritis, hydronephrosis), vascular diseases in which the renal vessels also suffer (blockage them or stenosis), kidney cancer (formation of proteins by malignant cells that clog the renal tubules - impaired filtration), connective tissue diseases (scleroderma, lupus).
Disorders of the cardiovascular system
The appearance of tachycardia, shortness of breath, increased blood pressure, palpitations and chest pain, shortness of breath and cough. All of these signs are characteristic of long-term renal diseases, which leads to the development of chronic heart failure.
During pregnancy
Pregnant women are at high risk for developing kidney disease. Firstly, a woman’s body works in an intense mode during this period, and all organs, including the kidneys, experience a double load. Secondly, in expectant mothers, phosphorus-calcium metabolism changes, as well as the metabolism of oxalic and uric acids. In addition, under the influence of the main pregnancy hormone, progesterone, the renal pelvis and ureters expand, their tone decreases, and the outflow of urine becomes more difficult, which increases its concentration. Thirdly, pregnant women have a weakened immune system and are susceptible to various respiratory infections.
During pregnancy, the kidneys hurt most often as a result of the development of:
- glomerulonephritis (as a complication of tonsillitis);
- pyelonephritis (if it occurs for the first time, during gestation, they speak of gestational pyelonephritis);
- urolithiasis.
The appearance of not only pain, but also any other suspicious signs described above should alert the woman and requires an urgent visit to an obstetrician-gynecologist. Kidney diseases in expectant mothers have a negative impact on the course of pregnancy and can provoke premature birth or miscarriage, and in the later stages the development of preeclampsia.
Symptoms of kidney diseases
And now we will talk about what kind of kidney pain indicates a particular ailment.
Urolithiasis disease
Kidney pain is acute. This is due to kidney stones that damage the lining of the urinary system. During attacks, renal colic is observed with stabbing, severe and constant pain. Localized in the lower back and side.
Pyelonephritis
Infectious lesion of the renal system. Accompanied by a dull and aching pain in the right or left side. The pain is minor, but causes some discomfort to the patient. In addition to pain, the patient experiences fever, nausea, and swelling.
Glomerulonephritis
A disease with an inflammatory process affecting the renal glomeruli and tubules. The pain is sharp and piercing. They occur in the area where the kidneys are located, on both sides. The patient feels lethargic, weak and gets tired quickly. Swelling and blood appear in the urine.
Atherosclerosis of the renal arteries
Develops together with atherosclerosis. Cholesterol plaques form in the renal arteries, preventing blood from circulating fully. The pain is periodic and aching in nature.
Kidney cyst
Its occurrence is accompanied by mild pain in the back and lower back. The cyst interferes with the full flow of urine.
Benign tumors
This is an adenoma, hamartoma or oncocytoma. Their appearance is asymptomatic, but when they reach large sizes, they put pressure on the kidneys and interfere with the full functioning of the organ. Causes aching, pulling pain in the lower back or side.
Kidney cancer
Occurs when a malignant tumor appears. Dull and nagging pain occurs in the area where the organ is located. Quite weak, they are not immediately noticed. As the tumor grows, the pain intensifies.
Hydronephrosis
The disease is associated with stagnation of urine. It occurs due to a narrowing of the passage through which urine passes from the renal pelvis to the ureter. Characterized by severe aching or stabbing pain in the lumbar region.
Vesicoureteral reflux
A disease in which urine from the bladder is thrown back into the ureter. Develops against the background of acute pyelonephritis. It is characterized by aching pain in the kidney area, increased body temperature, swelling, and weakness.
Kidney failure
There is a throbbing severe pain in the kidney area. The urine becomes thick and has an unpleasant odor. The disease is accompanied by increased blood pressure and disruptions in water metabolism in the body.
Kidney tuberculosis
The pain is stabbing in nature. It is constantly present, which causes insomnia. Pus and blood appear in the urine.
Features of the functioning and structure of the kidneys, causes of pain
The structure of the kidneys is a rather complex mechanism that ensures the gradual purification of blood and the removal of fluid and metabolic products from the body. Each of the stages can be carried out fully only if the anatomical structure of the kidney is preserved and intact, as well as coordinated communication with the vessels of the human body.
Doctors distinguish the following stages of urine excretion:
- Primary (ultrafiltration). The pressure inside the blood capillaries is so strong that the smallest molecules (colloidal particles) leak through them into the kidney (glomerulus), while larger molecules remain in the vessel (most proteins, white blood cells, platelets, red blood cells).
- Secondary (reabsorption) . After formation, the ultrafiltrate enters the nephron tubules, which are dotted with capillaries over the entire surface. Substances necessary for the body that enter during the primary phase of urine formation are reversely absorbed into the blood. The remaining substances enter the ureter with the fluid and are excreted from the body.
Note. Of the 160 liters of primary urine produced by the body per day, only 1.5 liters remain for subsequent excretion. The remaining 95% is returned to the bloodstream of the cardiovascular system.
Schematic structure of a healthy organ.
A feature of the structure, in addition to the mechanism of urine excretion described above, is the absence of pain receptors in the tissues of the organ itself. However, as is known, with kidney diseases, patients often indicate pain.
The anatomy of the organ is such that each of the kidneys is covered with a special dense capsule (fibrous structure), which is equipped with nerves that provide its sensitivity. Various kidney pathologies cause pain according to the mechanisms described in the table.
Table No. 1. Description of changes causing discomfort, mechanisms of signal transmission to humans:
| Name of change | Short description |
| Occurs due to a decrease in the filtering capacity of the organ caused largely by renal failure or the ingress of pathogenic microorganisms. The infection is fraught with the development of purulent inflammation throughout the tissue of the organ. Painful sensations due to edema occur when the kidney capsule is stretched. |
| Loss of anatomical structure and shape can occur due to many different pathologies; the most dangerous are inflammatory processes and the proliferation of benign/malignant tumors. The deformation leads to tension in the fibrous tissue of the capsule, causing pain in the area where the organs are located. |
| Narrowing of the lumen of the ureter, its blockage with stones, and a number of other pathologies can lead to stagnation of urine in the kidney. With an increase in the amount of urine inside the pelvis, it increases, the tissues swell, when the size of the kidney reaches a critical level, the fibrous membrane stretches. |
As a result of the changes described above, the organ transmits signals to the brain through its influence on the nerve membrane receptors. The body, receiving signals from the capsule, transforms them into pain, indicating malfunctions in the urinary system.
Due to the absence of pain nerve endings in the organ, many diseases are asymptomatic. Stretching the capsule to a size that causes painful symptoms takes time. The appearance of a pain syndrome, unfortunately, as a rule, indicates the progression of the disease, its achievement of a severe form of development, and the occurrence of complications.
The exception is pain, most often acute in renal colic. The mechanism of discomfort is associated with the mechanical effect of the calculus on the nerve endings of the walls of the ureter.
Characteristics of pain in the kidney area
What kind of kidney pain occurs with diseases of the kidney organ? It can be different:
- Pulling. It speaks of inflammation and is permanent (pyelonephritis).
- Aching and pressing. Indicates an inflammatory process and serious kidney diseases (tuberculosis, cancer). Constantly present.
- Pressing. Occurs during inflammation of a paired organ, development and formation of a tumor. As the disease progresses, the pain intensifies. It becomes sharp and pronounced.
- Sharp. Talks about urolithiasis. Alternates with stabbing, which indicates the movement of stones along the urinary tract. May go to the right leg.
- Spicy. Indicates the presence of kidney stones. It radiates to the leg or groin.
- Stitching and throbbing. Indicates an inflammatory process, the presence of stones or a malignant tumor.
Depending on what kind of kidney pain a person has, the doctor determines the diagnosis. To clarify it, he prescribes a series of tests and additional examination.
Treatment
Pyelonephritis is eliminated through antibiotic therapy and antipyretic medications. Additionally, you must adhere to a diet and stay in bed. The consumption of sour, spicy, salty foods and dishes, coffee and alcohol is contraindicated. It is important to stop pyelonephritis before it becomes chronic in order to prevent exacerbation of renal inflammation.
Glomerulonephritis is eliminated with antibiotics, vitamins, and antispasmodics. Additionally, adherence to bed rest and diet are indicated: it is necessary to avoid salty, sour foods and alcohol. The patient's diuresis and fluid balance are monitored, since it is important to monitor the ratio between fluid intake and urine output. This will prevent the appearance of edema and correct the degree of its severity.
Kidney cancer is eliminated by chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery. The type of intervention depends on the stage of the tumor process at the time of its detection. Chemotherapy may be given before and after surgery to reduce the number of cancer cells. In most cases, treatment involves nephrectomy - removal of a kidney affected by a malignant process.
Drug removal of stones: taking Fitolit, Urolesan, Canephron, intramuscular administration of Furosemide or Lasix to force diuresis. Laser lithotripsy is the targeted destruction of stones with a high-energy beam. The stones are crushed into sand, washed out during the operation, a catheter is installed in the patient, and he is transferred to the ward. After laser stone crushing, there is a short recovery period, which makes intervention the preferred option for stone removal. Regardless of the treatment method, the patient is advised to urinate in a container for the near future. The action allows you to track the release of particles of stones or sand, which is of diagnostic value.
Stones in the kidneys
Urolithiasis is perhaps the most common disease of the kidney organ. What kind of pain does the patient experience with kidney stones? Pain in this case is not constant, but periodic. The pain is strong and sharp. Occurs due to:
- stone damage to the mucous membrane of the organ;
- failure to pass urine;
- increased pressure in the renal pelvis;
- inflammatory process;
- spasm of the ureter at the location of the stone.
Attacks of urolithiasis are manifested by renal colic. This is a strong unbearable stabbing pain in the kidney area. In addition, there is an increased body temperature, poor health, bloody urine appears, and its outflow becomes difficult.
Treatment of this disease is carried out in a hospital. Patients are prescribed antispasmodics and painkillers. If necessary, stones are removed.
Differences in diagnosis
If your back hurts, where your kidneys are, you need to visit a therapist. A specialist will be able to distinguish kidney diseases from lower back problems using tapping. After the examination, he will issue a referral to a nephrologist, orthopedist or neurologist.
If your lower back hurts in the kidney area due to back diseases, you will need the following examination:
- X-ray - allows you to identify injuries, degenerative-dystrophic processes, in particular, osteophytes, hernias;
- CT and MRI are the most reliable methods for studying the spine, allowing you to assess the condition of muscle tissue, nerve endings and the spinal cord. Read more about CT scan of the kidneys →
Kidney diagnosis is completely different. The patient needs to take a blood and urine test, their results will show the inflammatory process and disturbances in the functioning of the urinary system. Additionally, an ultrasound examination of the kidneys is performed. According to its results, an increase in organs and their swelling can be seen; stones and their location can be identified. After the examination, a decision is made on further treatment.
You cannot make a diagnosis or prescribe treatment on your own. You should also not take painkillers regularly. Only a doctor can correctly distinguish whether the kidneys or lower back hurt.
Author: Oksana Belokur, doctor, especially for Nefrologiya.pro
Kidney injuries
What symptoms of pain in the kidneys occur in diseases were written above. But pain in the kidneys also occurs when the organ is injured. Moreover, their strength does not always characterize the severity of the damage.
- Mild kidney injuries occur from a blow to the lower back or from a fall on the back. The pain in this case is mild. The state of human health suffers slightly. In some cases, blood may appear in the urine.
- Moderate injuries include kidney rupture. It occurs inside the organ. May involve the renal calyces and pelvis. The pain associated with this injury is not severe, but acute. The victim feels unwell. His blood pressure drops, weakness and lethargy are observed. Swelling and bruising appear at the site of injury, and there is blood in the urine.
- Severe damage. In this case, not only the insides of the kidney are ruptured, but also the organ itself. With such an injury, the pain is severe and acute. Localized in the lumbar region. Accompanied by internal bleeding, a sharp drop in pressure, and loss of consciousness.
What kind of pain with kidney disease occurs during pregnancy?
Very often, kidney pain occurs in pregnant women. This is due to the fact that the body works in an enhanced mode during this period, and the enlarged uterus puts pressure on the organs surrounding it.
Painful sensations of a pulling nature indicate diseases of the urinary system. Dull and aching pain indicates pyelonephritis. Acute, strong and prickly pain occurs with urolithiasis. Glomerulonephritis is indicated by acute pain in the lower back.
During pregnancy, if you experience pain in the kidney area, it is important to immediately consult a doctor. Establish the correct diagnosis and begin timely treatment.
First aid and treatment: what is important to know
The only question that everyone has when their back hurts in the kidney area is what to do and how to quickly get rid of the discomfort.
Simple remedies for pain in such cases do not help much, so to get rid of the pain symptom, you can try taking a hot bath for 15-20 minutes (the water temperature should be about 39 degrees). A warm heating pad applied to the problem area of the body will also help you hold on until the ambulance arrives. This, although not for long, will ease your condition while waiting for help. But this method should be used very carefully, especially for pregnant women or in the presence of various pathologies, so as not to aggravate the situation or cause harm.
Treatment of pain in the kidney area will be effective only after a complete diagnosis and consultation with a doctor; until this point, you can only reduce the discomfort. Therefore, you need to be careful when using various medications so as not to harm your body.
Traditional approach
Classic treatment includes diet and medications:
- Diet. You should pay attention to the amount of liquid and salt consumed. Their uncontrolled use can lead to swelling and high blood pressure. For people with kidney disease, restrictions on the amount of salt consumed are mandatory. Depending on the severity of the disease, this dose can range from 3 to 7 grams per day. Dietary nutrition is prescribed by a doctor, but you should independently monitor your potassium and phosphorus intake. You can eat apples and pears from fresh fruits, but it is better to exclude dried fruits from your diet.
- Medications. The doctor prescribes all pills and injections depending on the diagnosis. In case of kidney disease, simple painkillers are ineffective, so stronger drugs are used. If an inflammatory process is detected in the body, anti-inflammatory drugs will be used. Antibiotics, diuretics and antispasmodics are required in the prescribed treatment regimen. Depending on the patient’s well-being, antipyretics may be prescribed.
ethnoscience
Now there are many recommendations and recipes of traditional medicine for the treatment of kidney disease. It is worth knowing that you must inform your doctor about taking such drugs so as not to harm the body.
It is also worth noting that when using traditional methods, it may take much longer for a complete recovery. Popular natural foods for treating kidney pain include radish, blue cornflower, horsetail, and corn silk. To remove sand from the kidneys, for example, you need to eat more watermelon; cranberry or lingonberry juice also contributes to this.
Diseases of other organs with pain in the renal area
Pain in the area of the kidney organ can also occur with diseases of other organs. Pain in the lower back is caused by lumbar osteochondrosis. The pain radiates to the leg. Muscle weakness, tingling and numbness of the limbs are observed.
Severe and acute pain occurs when there is a hernia in the spine. Such symptoms occur with injuries to the spine, ribs, spinal cord, liver and spleen. In this case, the symptoms are mixed, and the diagnosis is established after a thorough examination of the patient.
Pain in the kidney area occurs with acute appendicitis and is accompanied by a number of negative symptoms. Pain occurs at the location of the kidneys due to prostate pathology. Here there is a disturbance in the outflow of urine, problems with potency arise, and the pain radiates to the perineum.
How can you tell if your kidneys are hurting?
The main sensation occurs from the back under the lower ribs and above the pelvis. This condition is accompanied by an unpleasant pain syndrome of stabbing, aching, pulling, cutting or acute paroxysmal nature.
It is impossible to unambiguously diagnose the cause of the problem only with the help of a visual examination or a person’s sensations, since in the immediate vicinity of the kidneys there is the liver, intestines, spinal column, ureteric system and spleen, so in any case a comprehensive diagnosis will be required, most likely in a hospital setting.
Diagnostics
Which doctor should I contact for kidney pain? This question is asked by almost everyone who has encountered this problem for the first time. To diagnose the disease, you can contact a therapist, urologist or nephrologist. But only a nephrologist is considered a specialist in kidney diseases.
The patient is examined by palpating the abdomen and pelvis. Pain is felt when pressing on the affected area. To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis, according to Nechiporenko and for the nutrient medium;
- Zimnitsky's test;
- a picture of the urinary system;
- Ultrasound;
- excretory urography;
- CT or MRI.
After the examination, treatment is prescribed, which is influenced by the diagnosis and severity of the disease.
What medications are used for kidney pain?
If pain occurs in the kidney area, complex treatment is prescribed, which includes:
- antispasmodics;
- analgesics;
- antibiotics;
- herbal preparations;
- diuretics.
When pain occurs, painkillers are used first. They are divided into three groups. The first includes antipyretics. They relieve pain and lower body temperature. The second group includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They not only relieve pain, but also relieve fever and have an anti-inflammatory effect. If the pain is severe, narcotic painkillers are prescribed.
What painkiller should you take for kidney pain? Only a doctor can answer this question, based on the severity of the disease and diagnosis.
Functional and anatomical properties of the kidneys
If you have kidney pain, it will be difficult to correctly determine the symptoms and treatment at home. The kidneys have a rather complex structure, so if pain occurs, it is necessary to undergo an examination to rule out other diseases and identify the underlying cause.
The detailed anatomy of the organ is quite complex, so we will only explain the main points. The organ is paired and has a bean-shaped shape and a dense consistency. It is located behind the peritoneum in the lumbar area at the level of the first two lumbar vertebrae. A person’s right kidney is always located slightly lower than the left, and this is normal and is due to the presence of the liver above it. The left organ is slightly larger in size than the right. Kidney tissue has a two-layer structure and is called “parenchyma”. It plays the role of a filtering mechanism. Decay products and harmful substances are removed using the pelvis. The ureter emerges from this part of the organ, connecting it to the bladder. Through the pelvis, all harmful substances from the blood enter the bladder and are then excreted naturally. Beneficial substances are separated through the renal tubules and reabsorbed into the bloodstream.
The organ performs two main functions: it filters blood and other fluids in the body and removes all harmful substances out. This work is carried out daily and around the clock. But in addition to filtration, the organ also performs a number of other functions, for example, ensuring water-salt balance in the body.
Herbs for kidney pain
Sometimes medicinal plants are used to relieve discomfort. What herbs are most effective for kidney pain? There are many plant uroseptics. Among them:
- Dandelion. Has diuretic properties. Improves blood circulation.
- Celery seeds. Cleanse the kidneys. They have antifungal properties.
- Corn silk. Reduce pain when urinating and eliminate inflammation.
- Parsley. Diuretic. Relieves pain and inflammation.
- Plantain. Characterized by antibacterial action. Is a diuretic.
- Cabbage. Removes toxins. Relieves the inflammatory process.
- Blooming Sally. Antiseptic. Removes spasm, inflammation, pain.
- Nettle. It has diuretic and anti-inflammatory properties.
Herbal remedies should be used only in combination with the main treatment and cannot replace drug therapy prescribed by a doctor.