Many people experience loss of sensation in the lower extremities, or more precisely in the toes. Unpleasant sensations predominantly occur at night, occurring periodically or on an ongoing basis. In most cases, numbness occurs due to being in an uncomfortable position or severe stress, but serious illnesses can also act as a causative factor. Why do my toes go numb and how to deal with it? This will be discussed in more detail in this article.
Numb toes
Causes
Our body is completely riddled with nerves. They are sensitive and motor. The smallest branches of the sensory nerves perceive signals from the environment and transmit them further to the spinal cord and brain. During their normal functioning, we feel touch, pain, heat, cold. We can pull the limb back in time if we touch something hot and feel pain when injured.
Changes in sensitivity occur in cases where one of the links in this chain is broken:
- Damage at the level of peripheral fibers (peripheral poly- or mononeuropathy). Nerve fibers may suffer from impaired blood circulation, metabolic disorders, or direct toxic effects.
- Lesions of the conductive link (spinal cord level).
- Damage to the cerebral cortex (strokes, tumors, hemorrhages).
So to the question: “Why do my toes go numb?” There can be no clear answer. A comprehensive examination and examination by a neurologist is necessary to determine the level of damage to the nervous system.
First aid
You can cope with unpleasant sensations at home. But first aid is truly effective only in cases where the causative factor of numbness is not some disease. Otherwise, a doctor's help is required.
You can cope with numbness at home
How to relieve this symptom at home if it is not possible to see a doctor? To do this you need to perform several steps:
- lie down on the bed and begin to make circular movements with your feet, first clockwise and then counterclockwise . After 20-30 seconds, begin to alternately move your foot left and right and down and up. Performing such exercises will help disperse the blood in the lower extremities;
- Gently massage each foot using moisturizer . Each toe should be thoroughly massaged;
- apply a warm compress for 10 minutes . This should improve blood circulation in your legs.
How to do a foot massage
If the discomfort does not disappear or it appears regularly, then you need to consult a doctor, because numbness in the fingers in this particular case is a sign of serious disorders in the body.
Peripheral neuropathy
This is a condition where our peripheral sensory fibers cannot fully perceive and transmit signals to the brain. There are only about 100 causes of neuropathy. In this case, polyneuropathy (damage to many nerves) and mononeuropathy (damage to one nerve) are distinguished. In addition to numbness, polyneuropathy is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Pain.
- Feeling of a tight sock and glove
- Tingling
- Creepy crawling sensation
- Thinning of the skin.
- Uncertainty, unsteadiness when walking.
Numbness may start in one finger and then spread to others. All fingers and feet may become numb.
The most common causes of neuropathy:
- Diabetes. Symptoms of neuropathy appear sooner or later in most diabetics. Diabetic toes go numb in 60-70% of patients. The reason for this is the metabolic disorders that occur in tissues when blood sugar levels are high. Small nerve fibers simply die off. And this complication begins precisely from the lower extremities.
- Kidney failure – a large amount of toxins accumulate in the blood.
- Hypothyroidism is a decrease in thyroid function.
- Deficiency in food of vitamins B, E, A. Vitamins B1, B6, B12, as well as some fat-soluble vitamins are involved in the structure of nerve sheaths and conduction processes.
- Alcohol. This is perhaps the second most common cause of neuropathy after diabetes. Alcohol has a toxic effect on nerve tissue, causing the death of small nerve fibers.
- Intoxication with various chemicals - solvents, insecticides, glue, mercury, lead and others.
- Infections that cause damage to nerve tissue: HIV, herpes, Epstein-Bar virus.
- Autoimmune diseases – rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus, vasculitis.
- Some medications can cause nerve damage: anticonvulsants, antibiotics, antituberculosis drugs, cytostatics (polyneuropathy is a common complication of chemotherapy).
- Lack of microelements in the body, such as potassium, magnesium, calcium, iron. They are necessary to participate in electrochemical reactions of nerve impulses.
Mononeuropathies
Mononeuropathy is a lesion (incarceration, injury, tumor) of only one nerve or nerve bundle. In this case, the symptoms are asymmetrical, as with polyneuropathy, but correspond to damage to certain fibers. The toes may be numb only on the right or only on the left foot, or only one toe.
Examples of nerve damage in the leg
- Sciatica. Quite a common pathology. This is pinching or inflammation of the sciatic nerve, the largest nerve trunk in our body. It manifests itself mainly as pain, but there may also be weakness and a feeling of numbness in the foot.
- Tarsal tunnel syndrome. Appears when the tibial nerve is pinched in the area of the tarsal canal (it is located behind the inner ankle). It manifests itself as severe pain in the sole and numbness of the inner edge of the foot and heel.
- Injuries. Nerves can be injured due to injuries, dislocations or fractures. The localization of numbness depends on the specific damaged branch. So, for example, if one of the branches of the peroneal nerve is damaged, only the ring toe will become numb; if another branch is damaged, only the space between the first and second toes will go numb.
- Morton's neuroma. This is a thickening of one of the nerves that runs between the long bones of the foot. Symptoms are tingling, pain and numbness in the foot.
- Neuritis of the peroneal nerve. In this case, the dorsum of the foot and the side of the lower leg become numb, but movement disorders come to the fore: the foot “does not obey”, hangs down, and turns under when walking.
- Compression of nerve endings by uncomfortable, tight shoes can also be classified in this group. The little toe is the first to be affected. The sensation persists for some time even after removing shoes. If this is a one-time occurrence, then the symptoms are reversible. If the foot is subjected to constant “execution” by tight shoes, the nerve fibers can be damaged irreversibly.
Symptoms
If the legs go numb infrequently and this condition goes away quickly, then such patients do not need to worry about anything. However, there are people who experience long-term effects of paresthesia symptoms. This causes them great discomfort in everyday life and forces them to seek medical help. Such cases always require a special examination, which will accurately help identify the cause of such a pathological condition. A person should pay close attention to their condition if they have the following symptoms:
- blue skin around the numb finger;
- pain with prolonged loss of sensation;
- spread of numbness to the entire leg;
- feeling of numbness in the leg throughout the day;
- swelling and redness in the damaged area;
- significant changes in the nature of gait.
Spinal causes
Sensory impairment can occur when the main conductor of nerve impulses, the spinal cord, is damaged. The main reasons for this:
- Intervertebral hernia, a consequence of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. It can lead to compression of the spinal root, spinal cord, or cauda equina.
- Spinal cord tumor.
- Congenital anomalies - spina bifida, congenital stenosis.
- Spinal stenosis.
- Multiple sclerosis. This is an autoimmune disease accompanied by the destruction of the myelin sheath of the nerve trunks. The first sign may be a loss of sensitivity in the limbs.
Damage to the spinal cord will be manifested not only by loss of sensitivity, but also by muscle weakness, as well as dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
Associated symptoms
In some cases, numbness of the fingers on the lower extremities may occur in parallel with other symptoms, including:
- general weakness of the body;
- slight tingling in the legs;
- goosebumps;
- decreased temperature in the legs;
- painful sensations;
- complete loss of sensation in the affected area.
Numbness may be accompanied by other symptoms
The patient may also experience signs of the underlying pathology that caused the numbness. Moreover, the severity of the symptoms that appear will depend on the stage of the disease.
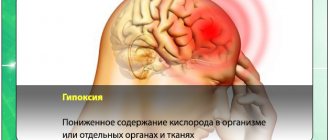
Brain damage
The cerebral cortex contains centers that receive signals from the peripheral nervous system and convert them into sensations. Therefore, when these centers are damaged, our tactile, temperature and pain sensitivity is disrupted.
The reasons for this may be:
- Strokes.
- Transient ischemic attacks.
- Brain injuries.
- Tumors.
Brain lesions that manifest only as sensory impairment are not as common, but are still possible. More often, a combination of hemihypesthesia and hemiplegia is observed (numbness and movement disorders in one half of the body).
Circulatory disorders
Another big reason why toes go numb is poor circulation. In many pathologies, blood microcirculation is disrupted, and this will especially manifest itself in the distal sections (that is, those furthest from the central vessels), namely in the extremities.
If there is not enough oxygen supplied to the tissue, the nutrition of the nerves suffers and sensitivity decreases.
We have all ever felt such numbness due to poor circulation:
- In the cold, when spasm of small blood vessels occurs.
- Being forced to stay in an uncomfortable position for a long time (for example, when you need to stand still for a long time or sit for a long time in an airplane or car).
But these conditions are reversible; just warm up, move around or change your position.
Patients with diseases of the circulatory system may experience symptoms of numbness and “numbness” of the limbs constantly. The most common of them:
- Raynaud's disease. It manifests itself as spasms of blood vessels, while the fingers go numb and freeze.
- Atherosclerosis and endarteritis of the vessels of the lower extremities. It is especially common in experienced smokers. The main symptom is pain when walking, but numbness also often occurs.
- Heart failure.
- Varicose veins of the legs, venous edema.
- Thrombosis of the arteries of the lower extremities.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
Disturbances in the normal structure and functioning of the spinal column have a detrimental effect not only on posture and motor activity, but also on the innervation of the entire body. With spinal osteochondrosis, the pathological process mainly involves intervertebral discs and vertebral bodies ; serious degenerative and trophic changes occur in them. This leads to disruption of the normal position of the intervertebral discs or to the occurrence of hernias, which compress the nervous apparatus of the spine.
The lumbosacral spine is responsible for the sensitivity of the lower extremities. It is with pathologies of this area that numbness of the thumbs on one or both sides may occur.
If there is a loss of sensation in the big toe against the background of frequent, recurrent pain in the lumbar region, one should suspect the presence of osteochondrosis and consult with an orthopedist or neurologist. As a rule, pain radiates to the lower limb; sensitivity disorders, disturbances in nervous regulation and normal blood supply to the legs and feet also appear.
Treatment of the disease must be comprehensive ; in advanced stages, various types of surgical intervention can be used.
Why is there numbness at night?
All of the above reasons lead to paresthesia, which appears at any time of the day. However, it happens that the toes become numb only at night, or worsen at night and in the evening. This may be explained by the fact that during the day we receive many different signals from the environment, which somewhat suppress these painful sensations in the legs. In addition, they are also less pronounced during movements.
At night, a person does not move, does not receive “distracting” signals, and this feeling of numbness, crawling, discomfort comes to the fore, to the point that sleep is significantly disturbed.
Paresthesia in the legs at night can occur with:
- Initial manifestations of any neuropathy.
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region.
- The onset of multiple sclerosis.
- Uncomfortable position while sleeping.
- Restless legs syndrome. It manifests itself as paresthesia in the legs, sometimes in the feet, sometimes inexplicable sensations, and the need to constantly make movements. The reason is not entirely clear.
Numbness of the big toe of the left / right foot: causes and treatment
Numbness of the thumb is manifested by unpleasant sensations of loss of flexibility and sensitivity of the limb. It happens that it is accompanied by burning, tingling, chilliness, and tightening of the skin. Numbness occurs when the passage of nerve impulses to the brain from receptors is disrupted. When changing body position, sensitivity usually returns quickly. However, when, after changing a position, unpleasant sensations do not leave a person, this indicates the presence of a serious illness.
Dr. Ignatiev's clinic specializes in issues of numbness of the big toe. In a short time, doctors get rid of the annoying problem.
Causes of numbness in toes
First of all, the legs become numb due to impaired innervation. This is called paresthesia.
The main cause of numbness in the toes is very likely to be osteochondrosis. If you pay insufficient attention to the treatment of this disease, you can get various complications affecting the musculoskeletal system. Since the spine underlies the entire structure of the body, it requires timely treatment. Osteochondrosis is characterized by narrowed intervertebral spaces and pinched nerves. Scoliosis, radiculitis, and intervertebral hernias can cause numbness of the big toe.
Metabolic disorders can lead to a feeling of muteness in the thumb . A disease such as gout is especially common. It affects the joints of the big toes and causes numbness.
Disorders in the functioning of the arterial vessels located in the legs can contribute to the formation of various unpleasant sensations. Inflammation of the vascular walls leads to the formation of deposits, which disrupts the natural blood circulation of the legs. Carpal tunnel syndrome, along with nerve injuries, can lead to numbness in the big toe.
There are other diseases that can cause numbness:
- oncological diseases;
- diabetes;
- micro-strokes;
- pathological disorders in the functioning of arteries and nerves;
- polyneuropathy.
Symptoms
Numbness of the thumb occurs as a result of impaired blood flow in a specific part of the body or due to nerve damage. Impaired sensitivity can be the result of infection, injury, inflammation, or other inflammatory processes. In a huge number of cases, numbness of the thumb is associated with diseases that are not life-threatening, but sometimes it indicates the presence of a tumor or stroke. Numbness in the thumb is often associated with pain and is accompanied by sensory disturbances, tingling and burning. Depending on the underlying cause, numbness may disappear quickly, for example during sleep, if
put your hand behind your head.
Then the unpleasant sensations disappear after several movements of the limb. Chronic numbness of the thumb over a long period of time indicates damage to a certain nerve due to, for example, multiple sclerosis or diabetes. Also, chronic numbness indicates a pinched nerve, as with carpal tunnel syndrome. In any situation, numbness that lasts several minutes deserves close attention from medical personnel.
Symptoms that accompany numbness:
- burning sensation;
- anxiety;
- itching;
- frequent urination;
- tingling when walking;
- pain in the neck;
- rash;
- needle tingling;
- muscle spasms;
- lower back pain;
- increased sensitivity to touch.
There are a number of symptoms that often accompany numbness and can be signs of serious conditions. These features should be taken into account by doctors, since it is often necessary to provide emergency medical care and perform therapeutic procedures.
These are the symptoms:
- dizziness;
- labored breathing;
- short-term loss of consciousness, lethargy;
- difficulty moving;
- weakness;
- impaired vision;
- paralysis;
- impaired speech;
- numbness in the limb.
Diagnosis and treatment of numbness in the legs
Based on the history of the disease, the collected anamnesis, physical examination, study of symptoms, he prescribes a general examination plan. It necessarily includes instrumental and laboratory techniques. High-precision, modern methods are of great help in making the correct diagnosis in a short time and identifying the causes of numbness of the big toe. Usually an MRI of the spine, ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities, and x-rays are prescribed.
Dr. Ignatiev’s clinic works in the treatment of diseases of the spine and the entire musculoskeletal system. Specialists with many years of experience and high qualifications conduct thorough research. We have modern digital equipment that can detect hidden lesions in the spine. Today, doctors use their own proprietary treatment methods, which allows for recovery much faster.
Which doctor should I contact and how urgently should I do it?
What to do if your toes go numb? You can go straight to a neurologist. But it’s easier to contact a therapist who will conduct an initial examination, prescribe the minimum required amount of research and refer you to the right specialist. You need to be prepared to answer the questions:
- When did the numbness first appear?
- Is it permanent or does it go away?
- Under what circumstances does it intensify (when walking, in the cold, or do the fingers go numb only at night).
- What other symptoms occurred along with the numbness?
- Do you abuse alcohol?
The therapist will assess the condition of the heart, check the pulsation of blood vessels, and outline an examination plan. The neurologist will check reflexes and sensitivity.
In what cases should you contact a doctor immediately?
- If sensory loss appears suddenly and is accompanied by muscle weakness in one leg or in an arm and leg (possible stroke).
- If it starts from the fingers, it quickly spreads to the foot, lower leg, while the leg freezes and turns pale (suspicion of thrombosis).
- If the symptom appears after an injury.
- If urinary or fecal incontinence occurs at the same time (possible compression of the spinal cord).
When you shouldn't put off visiting a doctor
When numbness in your fingers occurs regularly, this means you should consult your therapist. Especially if loss of sensitivity is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Pain syndrome;
- First the big toe goes numb, then the whole foot and lower leg;
- Numbness appears after sleep and persists throughout the day;
- The skin tone on the fingertips changes - they become bluish, white or red;
- Swelling of the limb;
- Gait disturbance;
- The leg stops responding to cold and heat.
What examinations are prescribed for numbness of the toes?
Basic examinations:
- General blood and urine tests. A blood test may show a decrease in hemoglobin, which may indicate a lack of iron in the body. It is also possible that leukocyte counts and ESR may increase, which indicates an inflammatory process.
- A biochemical blood test will show the level of glucose, inflammatory proteins, creatinine (an indicator of kidney function), and basic blood electrolytes (potassium, calcium, sodium).
- X-ray or MRI of the lumbar spine can reveal signs of osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernia.
- Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the legs (determines the condition of both arteries and veins).
- Electroneuromyography. This is a method for studying the conductivity of peripheral nerves. Allows you to determine the level of their damage.
Additional research:
- Determination of thyroid hormone levels.
- Serum iron.
- Determination of the content of essential vitamins in the blood (B1, B6, B12, E).
- Study for markers of infectious diseases (HIV, herpes, Epstein-Bar virus).
- Nerve biopsy.
Diagnostics
A detailed interview with the patient and examination allows the attending physician to find out why the toes are numb. To confirm the preliminary diagnosis, the patient is prescribed additional diagnostic procedures:
- Laboratory research. General urine and blood tests, blood testing for sugar, tumor markers, and biochemical analysis are performed. If necessary, serological or microbiological analysis of the submitted material can be carried out.
- Instrumental diagnostics. Depending on the expected diagnosis, ultrasound of the vessels of the limb, radiography, MRI, CT may be prescribed.
If there is a suspicion that the tip of the finger began to tingle due to bone tuberculosis, then an additional biopsy is performed.
Why is this condition dangerous?
It would seem that paresthesia in the toes only causes discomfort, and if you get used to it, you can continue to live without problems.
In fact, weakening pain sensitivity is dangerous. Why? If a person does not feel pain, he will not be able to notice in time any damage to his skin, chafing, or wounds that need to be treated. Without treatment, they can progress and become inflamed.
This is especially dangerous for patients with diabetes. There is such a thing as “diabetic foot”. Diabetes causes not only neuropathy, but also poor circulation in small vessels, as well as decreased resistance to various infections. As a result, diabetics often develop ulcers on their feet. If they are not noticed and treated promptly, they can lead to gangrene and amputation.
In addition, numbness may be the first symptom of a severe systemic disease, the outcome of which will be better the earlier treatment is started. Therefore, you should not delay a visit to the doctor with this symptom.
Prevention
Preventive measures will help reduce the incidence of unpleasant symptoms:
- Wearing shoes of the right size, incorrectly selected ones leads to compression of blood vessels.
- You should not be on your feet for long; they need to be given rest. If your job requires you to stand all day, you should take a 5-minute break every 2-3 hours to relax your feet.
- Do not overcool your feet in winter.
- Watch your posture while sitting and walking.
- Maintain a normal weight appropriate for age.
- Review your diet, include foods rich in vitamins in your menu, and reduce your salt intake.
- Low levels of magnesium can lead to numbness. This mineral is necessary for the normal functioning of the nervous system and proper blood circulation. Add foods containing magnesium to your diet: soybeans, mangoes, dark chocolate, peanut butter, bananas.
- If numbness is caused by diabetes, you should take care of your feet. Wear compression stockings and massage using lotions and gels containing capsaicin.
- Alcohol consumption should be reduced.
- To prevent dehydration, which creates problems in blood circulation, you should drink enough water throughout the day.
- Stop smoking.
- Self-massage your legs, feet, and arms daily.
Treatment
If your toes are numb, treatment will depend on the diagnosis.
- First of all, factors contributing to neuropathy are eliminated - blood sugar is normalized, alcohol and smoking cessation is recommended, and contact with harmful substances is eliminated.
- Treatment of the underlying disease (surgical treatment for disc herniation, treatment of heart failure, insulin therapy for diabetes, hemodialysis for renal failure, treatment of infections).
- In the treatment of neuropathy, drugs such as thioctic acid, B vitamins (complex Milgamma, Neuromultivit, Combilipen, or separately Thiamine, Benfotiamine, Cyanocobalamin, Pyridoxine), Neuromidin, Proserin, vascular and metabolic agents are used. In some cases, hormones and plasmapheresis are prescribed.
- Moderate intensity massage in long courses.
- Physiotherapeutic methods - transcutaneous electrical neurostimulation, UHF, darsonvalization, magnetic field, paraffin or ozokerite applications, radon or hydrogen sulfide baths.
What to do if your toe is numb
If paresthesia is caused by any disease, then you can get rid of it only by curing it. Therefore, specific treatment is prescribed by a doctor after examination and diagnosis. In addition to special medications, numbness in the toes can be relieved on your own.
- Massage helps a lot in this case. Moreover, you need to rub not only your toes, but also your entire foot. Massage is effective for numbness due to uncomfortable shoes or posture, as well as frostbite. For various diseases, it can only be used as an auxiliary measure.
- Physiotherapeutic treatments help. Most often, mud and mineral baths, paraffin baths, a magnet, and electrophoresis are used.
- If your fingers periodically go numb, and the reason for this has not been found, you can use therapeutic exercises. Walking barefoot on your toes, rotating your feet, lifting a scarf with your toes, or rolling from heel to toe helps a lot.
- Medicines used to treat numbness include anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, as well as drugs that improve blood circulation and relax muscles.
- It is advisable to take some kind of multivitamin preparation containing B vitamins. It will help normalize the passage of nerve impulses.
- Contrasting foot baths help a lot. You need to first dip your feet in cold water, then in hot water. And so several times, holding your feet in each container for half a minute. Such baths can be taken daily, which will not only help normalize blood circulation, but also increase immunity.
- It’s good to rub your finger with camphor ointment or honey at night. After this, put on a sock or bandage your foot.
What you can do at home yourself
So, the diagnosis has been made. Perhaps the stage of inpatient treatment has been completed and the patient has been discharged. Basic recommendations that a patient with neuropathy will have to follow at home:
- Complete cessation of alcohol and smoking.
- If the patient is diabetic, then it is necessary to maintain normal sugar levels. You need to measure blood glucose not only on an empty stomach, but also after meals, several times a day, keep a diary, and independently adjust the insulin dose according to the number of bread units (XE).
- Choose shoes that are the right size, comfortable, with low heels, and made from natural materials.
- Inspect your fingers and feet daily for abrasions and abrasions. You can use a mirror to inspect your soles.
- Foot baths with warm water for 10-15 minutes in the evening.
- Self-massage of feet.
- Contrast dousing of feet (alternately with hot and cold water).
- Walking. For almost all causes of paresthesia in the extremities, walking at a moderate pace for at least 30-40 minutes every day is recommended. This improves blood circulation in the legs.
- Taking medications as prescribed by a doctor.
- Taking vitamin and mineral supplements.
Author:
Akimova Valentina Konstantinova general practitioner