Watery eyes are a common symptom that every person experiences at least once in their life. But if in one case excessive tearing is a consequence of exposure to unfavorable external factors, then in another case it indicates the presence of serious health problems. Therefore, it is very important to detect and fix the problem in time. This can be done in the ophthalmologist’s office, after undergoing a detailed diagnosis.
Tearing as a symptom
Increased lacrimation is manifested by excessive secretion of tears and an imbalance between the production of this secretion and its removal through physiological channels. From the outside it seems that the person is constantly crying.
There are retention and hypersecretory types of lacrimation. In the first case, tears are produced in normal quantities, but due to impaired outflow, they do not go through the lacrimal ducts into the nasal cavity, but remain in the eyes. In the second option, the lacrimal glands produce an excessive amount of secretion.
Tearfulness occurs for various reasons: it can be caused by injuries, foreign bodies, and infectious diseases. Depending on the reason for the watery eyes, this symptom may be accompanied by other clinical signs. Assessing their compatibility allows the ophthalmologist to establish the cause of the pathology, make the correct diagnosis and select the optimal treatment.
Watery eyes are the main symptom
If a person has no symptoms other than increased watery eyes, this may indicate one of the following causes.
Possible diseases
Watery eyes may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the eyes, which can be caused by conjunctivitis, keratitis, or blepharitis. In some cases, watery eyes indicate problems with the lacrimal gland.
Allergies are also accompanied by copious amounts of tears. Moreover, the allergen can affect not only the mucous membrane of the eyes.
Lacrimation also occurs with dacryocystitis. Dacryocystitis is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac, which is caused by narrowing or blockage of the nasolacrimal duct.
The disease can occur as a result of inflammation of the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, and skull bones located next to the lacrimal sac.
How to treat eye keratitis at home, see here.
Dacryocystitis is very dangerous because it can lead to meningitis and brain abscess.
Dry eye syndrome
The pathology occurs due to overwork of the visual organs and infrequent blinking. When a person works a lot at the computer, watches TV for a long time or stays in a room with dry air, his cornea dries out because the tear film does not renew itself in a timely manner. An early sign of the syndrome is tearing, as the visual organs try to compensate for the lack of moisture and produce an excess amount of tears. Active secretion production in this case does not save the situation, since the watery part of the tear film predominates over the fatty and mucinous part.
The appearance of tears on the street
When going outside, a person may notice that tears involuntarily flow from his eyes. The reason for this is unfavorable environmental conditions. It's too bright sun, wind, frost. So hypothermia leads to spasm of the tear ducts.
Some people have sensitive corneas from birth. Therefore, any irritants cause profuse secretion of tears. They have to constantly put drops in their eyes or wear sunglasses to cope with the symptom.
Watery eyes outdoors in older people is associated with weakening of the lacrimal sac and eyelid muscles. In this case, eye exercises can help.
Ectropion, or inversion of the eyelid
This disease can occur for several reasons: due to improper hygienic eye care, surgical treatment, or tumor growth in the eyelid area. Any of these reasons leads to the fact that there is free space in the area between the conjunctiva and the lower eyelid. Because of this, the lacrimal punctum shifts, and the patient constantly feels tears. At the first stage of the development of the disease, its only symptom is excessive lacrimation. But in the absence of proper therapy, ectropion can become complicated by conjunctivitis and blepharitis, which will cause additional symptoms in the form of redness and foreign body sensation.
The main functions that a tear performs
The main function of a tear is protective.
One of the most important functions that a tear performs is protective. It should be noted that tears are necessary for constant hydration of the so-called conjunctiva. They also moisturize and protect the outer surface of the cornea, resulting in a significant improvement in its optical characteristics.
In addition, tears also have a so-called trophic function. After all, they consist not only of salts that are in dissolved form, but also of various protein compounds that nourish the cornea.
Tear also consists of special antibacterial components, due to which it also has pronounced bactericidal properties. In addition, the protective functions of tears are additionally expressed in the ability to mechanically remove various types of foreign bodies (dust, dirt particles) from the surface of the mucous membrane and cornea of the eye.
The daily rate of tear secretion by the lacrimal glands of the accessory type of the eye is no more than 1 milligram. This amount is absolutely enough to moisturize and protect the surface of the eyes from drying out.
However, when a foreign substance enters the surface of the eye, is exposed to strong wind, or when excessive light irritation occurs, the so-called large gland, which is responsible for the increased secretion of tears, is activated and begins to perform its functions.
Blocked tear ducts
A common cause of watery eyes is blockage of the tear ducts as a result of infection, injury, surgery, tumor, age-related narrowing, cyst formation and other pathological processes occurring in the nasolacrimal duct. Sometimes tear ducts become blocked due to medications (for example, glaucoma drops or chemotherapy drugs can cause this condition).
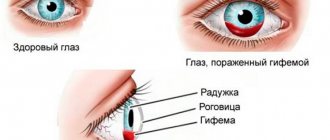
With this disease, the eyes constantly water and vision becomes blurred. If the blockage provokes an exacerbation of dacryocystitis or conjunctivitis, bloody or purulent discharge appears.
How to find the reason?
To find out the cause of excessive tearing, a specialist must find out all the symptoms from the patient, examine the eyes and examine the patency of the tear ducts. The biomicroscopy method (using a slit lamp) allows you to assess the condition of the eyelids, the correct growth of eyelashes, the condition of the eye slit, conjunctiva and cornea. Using biomicroscopy, a presumptive diagnosis can be made.
In addition, the following methods are used to establish causes:
- Color samples. They are needed to determine the active patency of the lacrimal canals.
- Rinse the tear ducts. This is done to establish passive cross-country ability.
Lagophthalmos
Another name for this pathology is “hare’s eye.” When it occurs, the lower eyelid droops and moves away from the eyeball, as a result of which the lacrimal opening is displaced. Lagophthalmos often develops with strokes, encephalitis and other diseases of the nervous system that affect the nucleus of the facial nerve. The disease progresses with lesions of the lateral part of the facial nerve, cicatricial changes in the eyelids, exophthalmos, enlarged tumor behind the eyeball, and fusion of the eyelids.
The first and only sign of hare's eye at an early stage is unilateral lacrimation. At this stage, the organ of vision has a normal color, is not prone to swelling and does not feel pain. Subsequently, against the background of lagophthalmos and constant drying of the cornea, corneal dystrophy or ulcer, keratitis may develop, resulting in other clinical signs - hyperemia, pain, foreign body sensation.
How are tears produced?
The organs that supply the eye with tears are divided into two types.
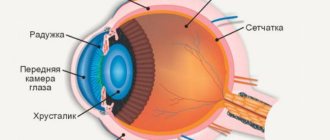
The organs responsible for the secretion of tears in the human body are a whole system that plays one of the most important roles. It ensures normal and stable functioning of the eye. Tears are a special, transparent, salty substance.
This substance is necessary for constant washing, as well as moisturizing the entire surface of the eyeball. It protects the eyes from excessive drying and has a weak alkaline reaction. The organs responsible for the secretion of tears are divided into 2 groups:
- Tear secretory organs.
- Organs of the lacrimal type.
In the organs of the tear secretory type, the process of secretion and release of tears occurs. These organs consist of the lacrimal gland, as well as accessory small glands. The lacrimal organs are responsible for the uninterrupted process of removing tears from the body. They are a complex system that consists of many anatomical structures.
Conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis is a seasonal disease that manifests itself in the spring as a reaction to pollen from flowering plants. In addition to excessive production of tear secretion, it is characterized by unbearable itching, burning in the eyes, swelling and hyperemia of the eyelids, and photophobia. Shortness of breath, sore throat, and nasal congestion are often associated.
The infectious type of conjunctivitis is characterized by the appearance of purulent discharge and excessive production of tears.
Neuritis
Inflammation of the facial nerve causes weakening or paralysis of the facial muscles. With neuritis, the lower eyelid goes down, the person cannot completely close the eye, and there is an excess of tear fluid. Other symptoms often appear: the face becomes asymmetrical, taste sensitivity decreases, while auditory sensitivity, on the contrary, increases greatly.
Tearing when wearing lenses
Sometimes lacrimation does not appear as a sign of a disease, but as a reaction to wearing contact lenses. Excessive secretion of tear fluid can be caused by:
- incorrect selection of contact vision correction means;
- using lenses longer than prescribed;
- poor hygiene during the care of optical products, as a result of which fungus, protein deposits, and dirt form on the surface of the lens, which injure the conjunctiva and provoke an inflammatory process;
- personal intolerance to contact optics;
- prolonged exposure to the sun or wind;
- dust getting between the lens and the conjunctiva.
To ensure that wearing lenses provides comfort and does not cause ophthalmological symptoms, you need to follow the recommendations of doctors:
- select correction products with a qualified ophthalmologist;
- follow the rules of lens care and adhere to wearing periods;
- regularly use artificial tears to clean the cornea from dust;
- On a sunny day, wear sunglasses.
Watery eyes during a cold
The cause of lacrimation during a cold lies in swelling that spreads to the nasal mucosa and nasolacrimal duct. The symptom disappears along with the disease that led to the appearance of edema.
The main task of the doctor when making a diagnosis is to identify the cause of lacrimation. To exclude the possibility of diseases of the visual organs, he examines the fundus of the eye, measures intraocular pressure, and prescribes an ultrasound or x-ray of the visual organs. Laboratory tests of tear fluid and a test for the patency of the tear ducts are also performed.
To cure lacrimation as a symptom, the effect is made directly on the disease that caused it. Conservative therapy is usually carried out, based on the use of antiallergic, anti-inflammatory, antihistamines and antibiotics. Surgical intervention is indicated only in cases of narrowing or obstruction of the lacrimal canals, ptosis, and eversion of the eyelid. How the operation is performed and what its results can be seen in the commentary:
Common causes of tearing in children
Excessive tear production in children may be a symptom of the following conditions:
- spasm that occurs when there is a sudden change in air temperature; in parallel with lacrimation, swelling of the mucous membrane develops and pus is released;
- rhinitis - a disease in which the nasolacrimal duct narrows, which increases the production of tears;
- eruption of “eye” teeth - fangs located on the upper jaw;
- eczema, which is accompanied by dryness and peeling of the eyelids;
- eye injury: increased production of tears is caused by both minor injuries (the child scratched himself in his sleep) and serious penetrating wounds, which are accompanied by severe pain, bleeding, and sometimes the inability to open the eye; the latter require an immediate visit to an ophthalmologist.
Why do my eyes water?
The reasons are different - in some cases, the problem of excessive outflow of eye fluid is solved by replenishing vitamins B12 and A. These microelements ensure the proper functioning of the organ of vision. With vitamin deficiency due to poor nutrition or restrictive diets, a person develops a dangerous illness - xerophthalmia. The disease leads to transparency and the development of an inflammatory process in the cornea. Subsequently, the patient completely loses vision due to the death of the cornea. Other reasons why your eyes become watery are:
- allergic reaction;
- seasonal exacerbation;
- stress;
- nervous exhaustion;
- penetration of foreign particles;
- migraine;
- corneal injury;
- incorrectly selected contact lenses;
- viral infection;
- eversion of eyelids;
- huge pressure;
- narrowing of lacrimal openings;
- disruption of tear production;
- age-related disorders;
- sinus diseases;
- sinusitis;
- pathology of the lacrimal sac.
On the street
The visual organ is sensitive to the influence of the environment and its changes. The situation when the eyes water on the street is a natural defensive reaction if the visual organ is simply slightly moistened. When the flow of tears cannot be stopped, this is a reason to consult an ophthalmologist. There are the following reasons for watery eyes on the street:
- windy weather (the mucous membrane tries to protect itself from drying out);
- strain of vision in the sun, looking into the distance, concentrating on one object;
- overwork;
- incorrectly selected glasses increase stress when walking;
- ingress of street dust and debris;
- allergy (to pollen);
- low-quality cosmetics;
- conjunctivitis;
- lack of nutrients;
- spasm of the tubules;
- rhinitis.
The child has
The eye fluid has antiseptic and bactericidal properties, washes and nourishes the cornea, protecting it from damage and drying out. The reasons why a child’s eyes water are the same as those of adults: when exposed to stress, influenza, acute respiratory viral infections, or a foreign body, the fluid that accumulates in the tear duct begins to be released. Mothers should know that a child’s increased tearfulness may be due to other conditions:
- allergies (more often occurs in children older than one year);
- infection;
- avitaminosis (lack of vitamins);
- obstruction of the lacrimal canaliculi (can be observed in a newborn baby at 2-3 months).
One eye is watering
When the tear duct becomes clogged, one eye begins to water. When this symptom appears, professional help from a doctor is necessary, since ignoring it will lead to narrowing of the lacrimal canal. This will be followed by a secondary infection, which subsequently develops into a purulent form of dacryocystitis or acute peridacryocystitis (phlegmon of the lacrimal sac). If there is increased secretion of eye fluid, you should visit not only an ophthalmologist, but also:
- allergist;
- neurologist;
- ENT doctor.
Why do tears flow from my eyes for no reason?
Normally, tears drain through the nasolacrimal duct in the nose. If there is an obstruction in the tear ducts, then the fluid has nowhere to go. If a situation arises when tears flow from the eyes for no reason, you should go to an ophthalmology clinic to diagnose the condition of the ducts. Having discovered unfavorable results of tests and studies, the specialist will rinse the lacrimal ducts for the patient.
Increased lacrimation with a cold
Infection of a person with colds is characterized not only by redness of the eyes and tearing, but also by general weakness, malaise, cough, runny nose, and fever. Why do your eyes water when you have a cold? An organism vulnerable to illness undergoes pathological changes that affect all organs, including the visual ones.
Not only the eyeballs are involved in the inflammatory process. The surrounding tissues begin to ache: the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and sinuses. Swelling of the nasal septum and swelling occurs. The passages to the sinuses close, making it difficult for mucus to drain, putting pressure on the eye sockets. The tissues of the nasolacrimal canal swell, it becomes blocked, and the only way to remove fluid is the lacrimal canal.
- Who suits caramel hair color and how to achieve this shade
- Garlic paste for the winter
- Shrub roses - description and name of varieties with photos. Growing and planting homemade bush roses in the garden and pot
Eyes itchy and watery
Two unpleasant symptoms indicate an adverse effect on the body: increased lacrimation and itching. The reasons that cause this phenomenon can be simple (it’s easy to get rid of them by eliminating the irritants), and more serious, requiring treatment. List of diseases that cause itchy and watery eyes:
- hypovitaminosis;
- blepharitis, conjunctivitis;
- trichiasis;
- cataract;
- demodicosis;
- keratoconus;
- glaucoma.
Diagnostics
To determine what caused the tearing, the ophthalmologist carries out a number of diagnostic measures. He carefully collects anamnesis, finds out the nature and duration of clinical signs, and the presence of diseases in the patient that can provoke such symptoms.
A physical examination of the visual organs and adjacent areas is carried out: the ophthalmologist examines the cornea and conjunctiva for damage, palpates the lacrimal sac area to determine swelling and pain, assesses the symmetry of the facial muscles, and, if necessary, conducts a biomicroscopic examination.
In some cases, the doctor takes a so-called Schirmer test, which allows you to determine the level of secretion production. If this value exceeds 25 mm, they speak of dry eyes due to increased evaporation. If fluid production is below 5.5 mm, this indicates insufficient secretion production.
As an auxiliary diagnostic method, probing and flushing of the lacrimal drainage system with a special saline solution with or without staining is used. Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor selects a comprehensive treatment.
Our advantages
"Moscow Eye Clinic" offers comprehensive diagnostics and effective treatment of all types of lacrimation. The use of the most modern equipment and the high professional level of specialists working in the clinic eliminate the possibility of diagnostic errors.
Based on the results of the examination, each visitor will be given recommendations on choosing the most effective methods of treating the eye pathologies identified in them. By contacting the Moscow Eye Clinic, you can be sure of a quick and accurate diagnosis of lacrimation and its effective treatment.
All questions you are interested in can be asked to specialists by calling 8 (800) 777-38-81 and 8 (499) 322-36-36 or online using the appropriate form on the website.
Fomenko Natalia Ivanovna
Treatment Options
Watery eyes are a symptom, so you can get rid of it only by treating the underlying pathology. Depending on the cause of excess tears, your doctor may prescribe antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal, antihistamine, or anti-inflammatory medications.
Complex therapy includes folk remedies that have an anti-inflammatory effect (decoctions of chamomile, calendula). Most often they are used in the form of compresses and rinses. Such products must be used strictly as prescribed by a doctor.
For dry eye syndrome, effective treatment is the use of drops with the function of artificial tears and the reduction of intense visual loads.
If tearing is caused by wearing contact lenses, following recommendations for their use and hygiene will help.
Therapy with folk remedies
How to treat lacrimation? You can often cope with excessive lacrimation and pain in the eyes using various folk remedies:
- Compress or wash the eyes with fresh, warm, strong brewed black or green tea.
- Infusion of dill seeds. Pour a tablespoon of seeds into a glass of boiling water and let it brew for a couple of hours. Strain the infusion and use it to wash your eyes several times a day.
- Coconut oil. Lubricate the area around the eyes with oil, repeat the procedure several times a day.
- Aloe infusion. Pour crushed aloe leaves with warm boiled water in a ratio of 1 to 10, let it brew for several hours. Strain and rinse your eyes with the infusion morning and evening.
There are many other folk recipes for watery eyes. Before using any of them, you should first consult your doctor.