Causes of development and infection of scabies
The causative agent of scabies is the scabies mite, a representative of the arachnid class. It is very small, it is almost impossible to examine it without a microscope. The female grows up to 0.5 mm, which is almost 2 times larger than the males. The scabies mite has a protruding oral organ, two pairs of front legs and two pairs of back legs with suckers.
Scabies mites mate on the surface of human skin, after which the males die, and the females make holes in the skin, bite deeper with their jaws and create scabies burrows. In them, females lay eggs, from which larvae develop, then adults, and after 2 weeks the process is repeated. The female tick lives for 1 month, but during this time she makes a large number of passages under the epidermis and lays up to 4 eggs per day. The scabies mite multiplies so quickly that if left untreated, after 3 months it multiplies to 150 million individuals.
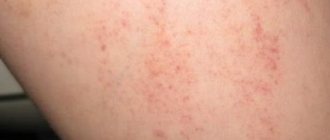
In the scabies canals under the skin there are not only mite eggs, but also their waste products. All this is toxic to the human body, so after some time an allergic reaction appears along with inflammation, which is manifested by severe itching of the skin. Since the scabies mite is most active at night, the itching intensifies in the evening, and at night it becomes unbearable. A person scratching itchy areas transfers the infection to healthy skin, and the foci of infection increase.
The most convenient places for scabies mites to settle are the palms and areas between the fingers, wrists, elbows, and male genitals. These places have little hair, they are covered with a thick epidermis, contain many sweat glands, which serves as a favorable environment for the development and life of scabies mites.
Pathogen
The causative agent of scabies is itch. The parasite is small in size - males reach 0.2 mm, females are larger - up to 0.45 mm. The body is yellowish-white in the shape of a wide oval with four pairs of legs. The mouthparts are gnawing and sucking, there are no eyes.
On the back of the scabies mite there are pointed bristles and scales directed backwards, which prevent backward movement in narrow passages made in the host's skin. Mites form scabies in the skin, secreting saliva, which contains special enzymes that dissolve tissue. The parasites feed on the resulting substance.
Mechanism of scabies infection
Scabies is most often transmitted through prolonged or direct contact (contact sports, children's games, handshakes). It takes about 30 minutes for infection to occur. Children, for example, become infected if they sleep in the same bed with infected parents. This is facilitated by tick activity in the evening and at night. But there is a chance of becoming infected through the use of other people's linen, towels, washcloths, and sleeping bags. A moderately moist environment promotes tick survival for up to 5 days. The spread of scabies is characterized by localization in groups such as a boarding school, dormitory, barracks, hospital, prison or in an asocial environment.
When an adult scabies mite comes into contact with the skin, scabies infection occurs. Within 2-3 hours a characteristic rash may appear. Sometimes hidden infection occurs; the incubation period in this case lasts up to 14 days.
Symptoms of scabies
Scabies is characterized by three main symptoms: itching, worsening at night, nodular-vesicular rashes in certain places and scabies. These are the main clinical symptoms of scabies. First, the patient discovers in the interdigital folds, abdomen, groin, elbow bends, and thighs the first signs of scabies - blisters that appear in pairs. They can also appear on the buttocks, genitals in men, and mammary glands in women. The scabies mite chooses the most vulnerable places to invade. In young children, the soles of the feet, face, scalp, and then the entire body of the child may be affected.
Upon closer examination, you can see uneven, thin lines barely rising above the surface of the skin, laid straight or in zigzags. These are scabies. Sometimes the passage ends at the end with a transparent bubble, through which you can see a white dot - the body of the tick. If no burrows are found, it may be scabies without burrows.
A nodule appears at the site of the tick bite; when scratched, it becomes covered with a bloody crust. Constant injury to the skin as a result of scratching is complicated by the appearance of various types of purulent infection and the occurrence of an eczema process.
The primary rash manifests itself in the form of small erythematous papules, single or fused. The amount of rash does not prove the number of parasites, but indicates a pronounced allergic reaction to the secretions of the female tick. In infants, in addition to the presence of papules and scabies, a vesiculourtic rash appears, areas of oozing, paronychia and onychia occur. Scabies in children under one year of age looks like urticaria, in complicated cases it resembles eczema, sometimes the nails can be affected - they become loose, thickened, and crack. Intense itching disturbs the child, sleep is disturbed, complications such as allergic dermatitis, pyoderma such as impetigo, lymphadenitis, leukocytosis, albuminuria can develop, and in infants this can provoke the development of sepsis.
Folk remedies
Photo: parazitoved.ru
There is a popular belief that kerosene is a good remedy for skin diseases, in particular scabies. Under no circumstances should such a remedy be used, because in addition to the toxic effects for the entire body caused by the absorption of kerosene, a local allergic reaction may develop on the skin, which will only worsen the condition.
To treat scabies use:
- Bread kvass. Salt generously, heat to 60-70 degrees and put your hands in it. Keep for up to ten minutes, but only if the temperature feels comfortable. Otherwise, this remedy should be abandoned.
- The bay leaf is crushed and mixed in equal parts with butter. The resulting mixture is rubbed into the affected areas.
- Apply pure birch tar to the affected areas for several hours, then wash off with heated water and bran.
- An ointment made from lard, sulfur and table salt. The ingredients are taken in a ratio of 4:2:1, respectively. Grind thoroughly and mix until a homogeneous mass is obtained. The ointment is rubbed into the affected areas of the skin for 5-7 days.
- Another folk recipe for ointment made from sulfur and tar. Take a tablespoon of lard and laundry soap, and a teaspoon of sulfur and birch tar. The soap should be grated. Mix until a homogeneous ointment is obtained. After thoroughly washing in a hot shower with soap and a washcloth, apply ointment to the skin and do not wash off until the next day. The procedure should be repeated three days in a row.
- Mix a teaspoon of turpentine with two tablespoons of butter and lubricate the affected areas of the skin.
- Mix one part celandine juice and four parts vaseline oil and apply to the skin twice a day.
- A tincture is prepared from the herb fumaria officinalis. Three tablespoons are infused in 100 grams of vodka in a dark place for a week. The tincture should be used to treat the skin. Since the recipe takes a full week to prepare, it might make sense to keep one on hand just in case.
- A couple of hours before using a hot bath, rub lavender essence into the affected areas of the skin and repeat this procedure for at least five days in a row. Use this method with caution, allergic reactions are possible!
- Hot baths with decoctions of ragwort, burial ground, and verbena. Both a mixture of herbs and each individually are used. One bath requires 30 grams of dry herb, boiled in a liter of water. Before use, strain the broth. The bath should be used before bedtime.
Horse sorrel decoction and compresses with it. Lubricate the skin with the decoction, grind the fresh leaves into a paste, apply to the affected skin and wrap in plastic overnight.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
Typical form of scabies
The typical form of scabies is characterized by all the symptoms: blistering paired rashes, itching, especially disturbing in the evening and at night, and scabies ducts. It is the most common. If the infection occurs through the hands, then itchy red spots and thin winding lines of scabies appear between the fingers and on the wrists. In men, scabies moves to the penis, scrotum, and the entire body becomes infected, except for the face and scalp. The patient himself spreads the disease throughout his body by touching and scratching the foci of infection. Clothing also serves as a carrier of scabies mites throughout the body. That is why it is so important to disinfect clothes, bedding, and treat the room during treatment. It is necessary to examine the patient's family and people in close contact with him to avoid re-infection after the course of treatment. Scabies should be treated under the supervision of a dermatologist.
Scabies without burrows develops after the patient is infected not by adults, but by larvae, which take some time to develop. There are no scabies, but there are blisters.
Nodular scabies
Nodular (nodular) scabies or scabious lymphoplasia is characterized by the presence of a few round itchy nodules or indurations. Their diameter is from 2 to 20 mm, color - from pink-red to brown. Scabies are located on the surface. Nodular scabies is characterized by localization in the area of the scrotum, penis, inguinal and axillary folds, near the anus, on the inner surface of the thighs and buttocks, and on the areola.
Sometimes these few nodules are the only sign of scabies. They will be a strong reaction of the immune system to the presence of ticks in the body and to the results of their vital activity. Seals are caused by the proliferation of lymph tissue in the skin. Even several weeks or even months after effective treatment, nodes and itching can be bothersome. The reason for this is unfertilized living female ticks, which do not have the opportunity to mate or reproduce. They do not make holes in the roof of the passages, thereby limiting the access of medicine from the surface of the skin. Females live up to 4-6 weeks, excrete waste products, so treated patients experience an allergic reaction in the form of itching for a long time.
Brief description of the disease
Scabies in humans is an infectious parasitic skin disease. It has been known to mankind since ancient times, but for a long time doctors could not identify the parasite and therefore denied the pathogenic nature of the disease, and the appearance of skin defects was associated with the emotional state of patients. Nowadays, it is known that scabies in children and adults is caused by the activity of Sarcoptes scabiei mites. They are widespread in everyday life, easily pass from person to person and cause various allergic reactions. Despite the prevalence of pathogens, timely laboratory diagnosis of scabies is difficult due to the insufficient level of training of personnel in many dermatovenerological institutions and the lack of necessary equipment.
Crusted scabies
Crusted (Norwegian or crustose) scabies was first described by Norwegian dermatologists Beck and Danie Lssen in 1848. Most often, this type of scabies develops in patients with immune system disorders or impaired skin sensitivity. Patients do not feel itching or cannot scratch the infection. This condition is typical for immunodeficiency, leprosy, syringomyelia, paralysis, senile dementia, as a result of regular use of psychotropic drugs. Cortical scabies is characterized by pronounced hyperkeratosis; in the foci of inflammatory infiltrate there are up to several million mites. If we compare that with a typical form of scabies, the number of mites on the patient’s body is approximately 15 individuals, then one can imagine that a patient with crusted scabies, literally swarming with parasites, is especially infectious.
When a person is infected with scabies mites from other mammals, pseudosarcoptosis occurs - a disease that has a short incubation period; there are no scabies burrows. Ticks do not reproduce on hosts that are unusual for them, and the disease is not transmitted to other people.
Diagnosis of scabies
Domestic dermatology identifies characteristic eponymous symptoms that facilitate diagnosis: Ardi's symptom: indicates the appearance of pustules and purulent crusts in the elbow area; Gorchakov's symptom - bloody crusts on the elbows. The Michaelis symptom signals the appearance of bloody crusts and impetiginous rashes in the fold between the buttocks with transition to the sacrum; Sezari's symptom reveals scabies, which on palpation feel like some kind of elevation.
The final diagnosis is made after analysis of clinical manifestations, laboratory and epidemiological data obtained after the examination. For this, the following diagnostic methods are used: traditional - removing the tick and examining it under a microscope; a thin section of the epidermis of the scabies tract will reveal both the mite and its eggs; layer-by-layer scraping of scabies; alkaline skin preparation.
Scabies will be better visible if you apply iodine tincture or ink to the skin. In some cases, a videodermatoscope is used, which allows you to magnify the object being examined up to 600 times.
Treatment of scabies
Scabies never goes away on its own and can last, sometimes worsening, for a long time. To cure, nothing special is required other than the use of local remedies. It is only necessary to destroy the pathogen and its eggs. The drugs used for treatment can be divided into 4 groups. Synthetic derivatives of balsamic products include benzyl benzoate.
Sulfur derivatives include sulfur ointments of varying concentrations, Wilkilson's ointment. Insecticidal preparations for killing parasites include pyretra ointments, K soap, flicid, Lysol, creolin. Traditional methods of fighting parasites use gasoline, kerosene, autol, fuel oil, oil, and ash lye. Before treatment, the patient must wash off the mites from the surface of the skin, then rub the prescribed drugs into the affected areas. The drugs should be used according to their intended purpose.
Today, medicine recommends the use of more gentle and effective drugs for the treatment of scabies. For example, Lindane, permethrin, crotamiton, spregal, produced in the form of a solution or aerosol.
To get rid of scabies, it is necessary to undergo a preventive course of treatment for everyone in contact with the patient. During treatment, it is not recommended to wash or change bed linen, only at the end of treatment. The patient's bed and clothes must be boiled and ironed with a hot iron. The remedy should be applied before bedtime.
Ointments for scabies in the photo, 7 pieces with descriptions
Benzyl benzoate ointment for scabies
Zinc ointment for scabies
Spregal for scabies
Crotadem ointment for scabies
Permethrin ointment for scabies
Permethrin for scabies
Medifox for scabies
Together with medications, folk remedies are often used to reduce the symptoms. But using only home medicine recipes is unacceptable; in any case, the help of a specialist is necessary. If the disease is not cured on time, it becomes chronic.
Find out more