Oral leukoplakia is a pathological condition in which changes occur in the epithelium of the oral mucosa. The main symptom of oral leukoplakia is keratinization of the epithelium (normally it is non-keratinized). The changes affect not only the epithelium of the mucous membrane, but also the red border of the lips, the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity, genitals and rectum.
Leukoplakia of the oral cavity is a precancerous condition, and compared to other pathological precancerous conditions it is more common, recorded in 18 percent of patients with diseases of the oral mucosa.
Causes of leukoplakia
The causes of leukoplakia usually lie in damage to the mucous membrane. This may occur as a result of the following factors:
- Violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes. Scratches and wounds resulting from an incorrect bite, biting the cheeks, sharp edges of the teeth due to chipped enamel or incorrectly installed dentures.
- Irritation of the mucous membrane by food - sour, spicy, too salty foods, dishes of extreme temperatures can also provoke microdamage to tissues. Alcohol, tobacco smoke and chewing tobacco also irritate tissues.
- Irritation by galvanic currents - metal crowns increase the risk of developing leukoplakia.
- Occupational hazard. Work in chemical production, work with paints and varnishes, resins, etc. can have a negative effect on mucosal cells.
- Exposure to stomach acid. Gastroesophageal reflux, bulimia and other diseases can reduce the resistance of the mucous membranes and irritate them, increasing the likelihood of developing the disease.
- Decrease in general defenses. Vitamin deficiency, the use of antibiotics, previous operations and severe infections, hypothermia, hormonal diseases, menopause and many other factors that contribute to decreased immunity can be the main or aggravating factors in the development of the disease.
Heredity also matters - researchers have found that the disease more often affects people whose close relatives have leukoplakia of the oral mucosa.
This disease is precancerous, so at the slightest suspicion it is important to consult a dentist.
Ask a Question
Etiology
Leukoplakia is not an independent pathology. It occurs as a pathological condition against the background of other disorders. The triggering factor may be:
- Smoking. The constant chemical and thermal effects of tobacco smoke on the mucous membrane lead to dysregulation of epithelial cell proliferation and mucus secretion, which ultimately causes hyperkeratosis.
- Systematic consumption of cold, hot and spicy foods. Irritating substances (pepper, herbs), as well as inadequate food temperature, cause irritation of the mucous membrane.
- Injuries to the oral cavity. Incorrectly selected dentures, malocclusion, and consumption of hard foods lead to multiple cracks and cuts. When exposed to the same areas of the oral cavity, the disease develops repeatedly.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages. High-proof alcohol (from 25%) not only injures the mucous membrane, but also creates a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria. Against the background of chronic inflammation, the epithelium begins to keratinize.
- Galvanic currents. Dental crowns, which are made of metal materials, require constant exposure to currents. Saliva helps to carry them throughout the oral cavity, which provokes the degeneration of the epithelium.
- Unfavorable environmental factors. Harmful production and poor environmental conditions with increased levels of chemicals, heavy metal salts, and dust particles in the air have a negative effect on the activity of epithelial cells.
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Pathologies such as gastritis, gastroduodenitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers reduce the natural defense mechanisms and resistance of the oral mucosa to harmful factors.
- Genetic predisposition. It has been scientifically proven that the disease is more common in people whose parents are sick.
Leukoplakia is a precancerous disease, therefore, at the slightest suspicion, you should consult a doctor
In addition to the main reasons, there are factors that lead to a weakening of protective and barrier mechanisms. These include: anemia, various hypovitamin deficiency conditions, diabetes mellitus, hormonal imbalance (especially during menopause), infection with the human papillomavirus, HIV infection, prolonged stay in solariums.
Symptoms and manifestations
At the initial stage of development, there may be no characteristic symptoms of leukoplakia. Gradually, small white or gray lesions appear in the mouth - up to several millimeters. The surface of the altered areas is rough and hard. The mucous membranes around the lesion may appear unchanged and healthy.
The disease can spread to almost any part of the oral cavity. When lesions appear on the gums, discomfort and slight pain when chewing and brushing teeth may be added to the external symptom.
Typically, a visit to a doctor occurs when the lesion develops up to 2-4 cm and other manifestations of the disease occur: impaired taste perception, difficulty chewing, pain, repeated inflammation of areas of the mucous membrane.
In children
Leukoplakia can also occur in children; the disease is localized in the mouth during puberty. Children complain of tingling in the throat, painful lesions interfere with their eating. They often bite off the plaques themselves, which leads to a worsening of the clinical picture, resulting in ulcerative processes in young patients. The disease in children often occurs in a mild form. The erosive type or simple leukoplakia may appear after 5 years, since at this age children often injure the oral cavity. In girls, vulvar lesions may occur.
Types of leukoplakia
The type of disease determines treatment tactics, as well as specific symptoms. There are several forms of the disease.
Flat
Flat leukoplakia is the most common variant. In most cases, the disease is discovered accidentally, as part of a routine dental examination or during treatment for other oral diseases. For a long time, this form of the disease does not make itself felt. Only a few weeks or months after the onset of the disease, a slight burning sensation, a feeling of pressure and retraction of the affected area appear. If the tongue is affected, the disease is detected earlier. This is due to loss of taste sensitivity.
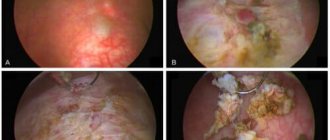
In a flat form, the focus of changes is a dry, rough surface of any shape and size. When the inner surface of the cheeks is affected, the pathology often forms around the excretory ducts of the salivary glands. When it appears on the palate, tongue or under it, the lesion often looks like white stripes with alternating dark areas. In half of patients with leukoplakia, the formation rises above the surface of healthy mucous membranes by 1-3 mm. The color of the plaques can be milky, white or grayish. As a rule, the disease is not accompanied by inflammatory complications.
Verrucous
Verrucous leukoplakia can be a consequence of flat leukoplakia if the provoking factor has not been eliminated. Hyperkeratosis becomes more pronounced, the lesion rises above the surface of the mucous membranes by 3-5 mm. When palpated, it has a hard surface and can be mobile. Usually this form is not accompanied by pain.
The color of the affected area gradually changes to yellowish. Other characteristic symptoms include severe burning during eating and when exposed to water, a feeling of tightness, and discomfort in the oral cavity. This form has a high risk of malignancy.
Erosive
This type of leukoplakia develops from verrucous in 1/3 of all cases. Multiple small ulcers and cracks form in the pathological area of the mucosa. This leads to severe pain. The size of the damage increases, and eating and even talking become difficult.
Violations of tissue integrity become entry points for infection. Therefore, the erosive form is often accompanied by inflammatory complications depending on the location of the pathological focus - gingivitis, glossitis, stomatitis, etc.
Tappeiner's leukoplakia
This form of the disease is characteristic of smokers. Smoking 10 cigarettes a day increases the likelihood of developing the disease by 50 times. Usually areas of the soft and hard palate are affected, and less often - the gums. If you give up a bad habit, the disease may go away on its own.
The mucous membranes of the palate become bluish or gray and acquire a folded structure. The narrowing of the ducts of the salivary glands leads to the accumulation of secretions in the tissues, stagnation and the development of inflammation. The disease has the appearance of multiple red nodules, accompanied by inflammatory processes.
Soft
This type is a benign formation. The lesion is characterized by severe peeling until large areas of keratinized epithelium fall off. Ulcerations and cracks appear on the formation, bleeding is observed. The size of the tumor can reach five centimeters in diameter and rise above healthy tissue by more than a centimeter. Such oral leukoplakia can develop as a result of sudden hormonal changes, depression, and stress.
What it is
Leukoplakia is a disease that can affect all mucous membranes (epithelium of the rectum, bladder, cervix, etc.), but involvement of the oral mucosa is most common. Typical localizations are the surface of the tongue, the buccal mucosa and the corners of the mouth. In areas of the epithelium, hyperkeratosis (increased keratinization) develops, manifested by a white coating and pain when touched or in contact with food. Middle-aged and elderly people are at risk. The disease occurs 2.5 times more often in men than in women.
Leukoplakia occurs on the lining of the lips, the corner of the mouth, or under the tongue, and the inside of the cheeks.
Diagnostic features
Diagnosis of the disease begins with a visual examination by a dentist. The doctor will ask questions about the general state of health, clarify how long ago the complaints appeared, and identify risk factors for the development of the disease. A specialist can confirm this assumption using several methods:
- Biopsy. One of the most accurate diagnostic methods, in which a section of altered tissue is taken and further studied in the laboratory.
- Smear for oncocytology. It is a scraping of the surface cells of the mucosa.
- Schiller's test. An iodine solution is applied to the mucous membrane; the changed areas are not stained.
- Laboratory tests - general blood test, tumor marker testing, etc.
Other diagnostic methods may be required depending on the clinical picture.
Answers to popular questions
- Is it possible to completely get rid of leukoplakia and what is the prognosis?
It is possible to achieve a complete cure in 99% of cases. The prognosis is most favorable if the pathology was detected in the early stages of the disease. If risk factors are not eliminated, there is a risk of relapse. Malignancy of the process is observed in 15% of women.
- Is it necessary to register with a dispensary for this diagnosis?
? After treatment, all women are registered. Every 6 months she will need to visit a gynecologist and have a smear for cytology. Colposcopy and HPV testing are required. If after 2 years there is no relapse of the disease, then the woman is removed from the register.
- Is it possible to get pregnant with cervical leukoplakia?
Leukoplakia is not an obstacle to conception. Pregnancy may not occur for other reasons, for example, due to hormonal imbalance or sexually transmitted infection. You can plan a pregnancy only after getting rid of the pathology.
- Is it possible to get vaccinated against cervical leukoplakia?
Yes, you can get the Gardasil or Cervarix vaccine. They help avoid infection with HPV, which causes the development of both leukoplakia and cervical cancer.
- Is intimacy possible with leukoplakia?
Yes, it's possible. However, experts recommend not to delay the treatment of this pathology.
Author of the article:
Lapikova Valentina Vladimirovna |
Gynecologist, reproductive specialist Education: Diploma in Obstetrics and Gynecology received from the Russian State Medical University of the Federal Agency for Health and Social Development (2010). In 2013, she completed her postgraduate studies at NIMU named after. N.I. Pirogova. Our authors
Treatment methods
Treatment of leukoplakia may require a collegial approach: the participation of the oncologist in developing an action plan. The basis of therapy is the elimination of provoking factors: quitting smoking, changing jobs due to occupational hazards, following a soft diet with no spices, etc. According to indications, correction of dentures, replacement of fillings, treatment of caries, removal of teeth that cannot be restored and other measures are carried out .
As part of complex treatment, the doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Preparations for restoring the normal structure of the oral epithelium. It is usually used in the form of applications to the affected areas.
- Antiseptics. Used for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory complications of the disease.
- Painkillers and symptomatic therapy. Systemic medications or applications of local anesthetics used in dentistry may be used.
Self-medication for leukoplakia in the mouth is strictly not recommended. Many drugs, including some anti-inflammatory drugs, are irritating and increase the risk of developing malignant tumors.
If the disease is severe, hospitalization may be required. The presence of ulcers and erosions is an indication for the use of hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs, proteolytic enzymes, etc. Surgery is indicated when conservative treatment is ineffective. Cryodestruction and excision with a scalpel are usually used.