Syphilitic chancre is an ulcerative or erosive formation that appears in the primary stage of syphilis infection and is its main symptom. There are 13 types of chancre due to syphilis: ordinary and atypical. Syphilis is treated with medications and a special regimen.
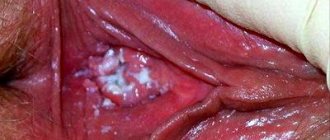
The appearance of syphilistic chancre is the first sign of the disease
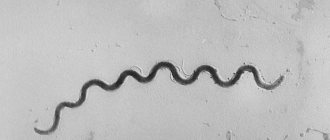
The causative agent of syphilis
Syphilis is caused by a bacterium called Treponema pallidum. When it comes into contact with the skin, after some time a compaction called a chancre is formed - this is considered the primary manifestation of syphilis or primary syphiloma. This bacterium is quite stable and persists in the environment for about three years, but when boiled it dies within fifteen minutes.
There are two types of chancre - soft and hard, they should not be confused, because they have completely different etiologies. Chancroid is also an infectious disease that is sexually transmitted. But it is distinguished by pain on palpation and purulent filling, and also softness. Its more accurate name is chancroid.
Tryponema pallidum is a formidable aggressor for the human body, especially a weakened one, but it dies when the temperature rises above 37 degrees, but it is resistant to cold and requires long-term treatment.
Syphilis is transmitted mainly through sexual contact and direct contact, for example, if a sick person kisses a healthy person in the place where there is a cut or wound. Infection is also possible if you use objects that have been in close contact with a sick person - these can be personal hygiene items, spoons, underwear, in this case, after three to seven weeks, primary syphiloma called chancre occurs.
Causes
Treponema pallidum enters the body during unprotected sexual intercourse, kissing, or using other people's personal hygiene products. Infection can occur through secretions from chancres if they get on mucous membranes or wounds. In rare cases, infection occurs after the use of unsterile instruments during surgery or in beauty salons.
Sometimes infection begins through a blood transfusion. Chancres rarely form on the eyelids, near the eyelashes. They mainly appear in people who prefer to contact their genitals with their tongue. Then, during the process, infection occurs, and treponema pallidum attaches to the mucous membranes.
Several syphilomas at once are often provoked by scabies, injuries, and coal rash. If a person has chronic diseases or severely reduced immunity, then the likelihood of chancre formation is very high.
Primary sign of syphilis
The time that elapses from infection with the tryponema bacterium until chancre appears is called the incubation period; it lasts within a month, less often than two. This point may depend on whether the person was taking antibiotics at the time of infection with primary syphilis, since they slow down the reproduction of their pathogens.
This point is extremely important, firstly, in order to notice a sign of the disease in time, and secondly, in order to accurately calculate and determine who else is infected or could become infected during this period.
From the moment the first chancre appeared and then disappeared, the incubation period ends and primary syphilis begins, and then, almost immediately, the lymph nodes that are closest to it enlarge. Nodular formations are always very hard, mobile, painless and without visible changes on the skin itself.
If you take a test at this time, the serological reaction to syphilis will be positive and it’s time to start treatment; at this time it will be the fastest and most effective.
So, the primary sign that a spiral triponema has settled in the body is a chancre in the form of a dense nodular formation and subsequent lymph nodes.
How long does it take for a syphilitic rash to appear?
No one can answer exactly when a syphilis rash will appear, but in most cases it begins to appear towards the end of the primary period. This period is about 2-3 months after infection or one and a half to two months after the appearance of chancre.
It all starts with small bright spots or compactions that are located symmetrically throughout the body. If a relapse occurs, the rashes appear in smaller numbers, they are located in separate areas and grouped into rings or garlands.
Features of chancre
Chancre most often appears on the genitals, less often on the mucous membranes of the mouth and simply on the skin. At first it looks like a simple red spot, and then the epithelium is damaged, and the spot turns into an erosive formation. The size and type of syphiloma depends on how deeply the tripiloma has penetrated; if it has penetrated into the muscle tissue, it looks like this:
- size within two one to two centimeters;
- firm roundness with smooth edges;
- skin without inflammation;
- sometimes there is a slight purulent coating on the skin;
- the seal does not hurt or itch.
This syphilitic formation is sometimes called a “crying chancre” due to the fact that when pressure is applied to it, a yellowish liquid appears, which contains treponema. This is usually used when taking tests to confirm the diagnosis.
The peculiarity of this inflammation is that it can go unnoticed due to the fact that it is practically asymptomatic, so a person who is inattentive to himself and his hygiene will simply not notice it.
And after three or four weeks it passes without a trace and then the most dangerous period begins. This period is characterized by the fact that syphilis passes into a latent, clinical form, which can last for quite a long time.
In the meantime, a person’s well-being will deteriorate more and more, as the bacterium multiplies very rapidly throughout the body, causing pain and aches in the muscles and joints. And also a strong enlargement of the lymph nodes, sometimes the size of a large hazelnut.
An interesting fact is noted by domestic syphilidologists that infection cannot always occur through contact with an infected patient; it all depends on the state of the immune system of each person individually. Some even consider, albeit theoretically acceptable, possible self-healing from tryponema pallidum.
Treatment methods
To prevent infection and the formation of syphil, you need to use condoms and not give your personal hygiene items to other people. If contact with an infected person does occur, then start taking sulfonamides within the first hours.
With timely treatment, chancre disappears after a week, heals completely in 1-2 months - often before secondary syphilis develops, but then appears again. The cause is an infection, so therapy is primarily aimed at eliminating it and preventing its spread, preventing subsequent complications.
However, for this it is necessary to differentiate syphilis from:
- other sexually transmitted diseases;
- acute tonsillitis;
- fungal infections;
- herpes;
- traumatic ulcers and erosions;
- tuberculosis.
To do this, blood tests are performed using nonspecific tests (for example, PRP, Wasserman reaction). If a positive result is obtained, then specific diagnostics are additionally carried out, with the help of which the presence of antibodies to certain pathogenic microorganisms is detected.
Drug treatment
The therapeutic regimen includes drugs for external and internal use. The causative agents of the disease are highly sensitive to penicillin, tetracycline and macrolide antibiotics.
During treatment, blood is regularly drawn for testing. This is used to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy. Antibiotic treatment is supplemented with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory external agents.
| Drugs | Effect of drugs, treatment regimen |
| Azithromycin, Ceftriaxone, Doxycycline | Prescribed if the patient is allergic to penicillin drugs. |
| "Bicillin" | Contains only one antibiotic. Available in powders, it works for a long time. Causes the death of Treponema pallidum. The drug is administered 2 times a day, 3 million units. with an interval of 5 days, or 5 million units. once at the same interval. |
| "Erythromycin" | One of the safest antibiotics that can be given even to children. Adults are prescribed 3-4 tablets (0.5 mg) per day on an empty stomach, 30 minutes before meals. If after it, then after 1.5 hours. The dosage is calculated based on body weight. |
| "Extencillin" | The main drug for the treatment of primary syphilis. Prescribed to eliminate an infection that causes the formation of chancres. The drug is administered intramuscularly, twice a day. Before this, Extencillin is mixed with novocaine - 2.4 million units/0.5% (at the rate of 100,000 units/ml). If syphilis is primary, then the drug is administered once, into the buttocks. |
| Disinfectants | If there are chancres and ulcers, they are disinfected with benzylpenicillin and dimexide - in the form of lotions and baths. Such compresses help the active substances penetrate deep into the tissues. Applications with mercury or heparin ointment may be prescribed. They are changed daily. To speed up the healing of hard chancre, from which a yellowish substance comes out, the affected areas are lubricated with products containing erythromycin. Mercury-bismuth and syntomycin ointments are highly effective. |
| For washing, rinsing | When syphilitic chancre appears on the mucous membranes of the mouth, it should be rinsed with a solution of furatsilin mixed with boric acid and gramicidin. Their proportions are prescribed by a venereologist. |
| When a fungal infection occurs | If a fungal infection occurs during antibiotic treatment, then Tinidazole (1.5-2 g once a day, for up to 10 days), Metronidazole (250 mg twice a day, for 10 days) are additionally prescribed. . |
| Probiotics | These drugs are given after the end of antibacterial therapy. Antibiotics destroy not only pathogenic, but also beneficial microflora. Therefore, after them it is necessary to take probiotics, which restore the microflora of the digestive system. For example, “Bifiform”, “Linex” (2-3 capsules per day, course from 10 to 21 days). |
| Multivitamins | They are necessary as an additional means to improve the general condition and strengthen the immune system (for example, “Duovit”, “Alphabet”, “Vitrum”). Give one tablet once a day, the course of treatment is a month. |
| Antihistamines | They are prescribed only when allergic reactions occur (Suprastin, Tavegil). They are given 1-2 tablets per day, with meals. |
Azithromycin
All drugs are selected individually, depending on contraindications and concomitant diseases. Treatment is required for anyone who has had sexual contact with someone who is sick, especially if condoms were not used.
During therapy, these people need to temporarily abstain from sexual intercourse. Especially if hard chancre appears on the genitals. When they are localized on the fingers or in the oral cavity, you need to use only individual cutlery and personal hygiene items.
Traditional methods of treatment
Chancres and erosions can be lubricated with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory folk remedies. For example, fresh burdock root oil. It is crushed, filled with vegetable oil and left for 24 hours. Then cook over low heat for 15 minutes, cool and filter. The product is used to lubricate chancre, erosions and ulcers several times a day.
Applications are made with propolis infusion. The tincture (10%) is diluted in boiled water in a ratio of 1:3. You can also tie fresh plantain and burdock leaves to chancre and ulcers (you need to mash them first). Additionally, baths with iodine are given.
Chancres and erosions are smeared with an infusion of yarrow, onion, and resin from coniferous trees. They are taken in equal proportions and mixed with natural wax or pork fat to the consistency of an ointment. Then apply the product to the affected area.
After completion of therapy, the patient should be observed by a venereologist, first every three months for a year. Then - at intervals of 6 months, then - once a year. The duration of control examinations is determined by the venereologist.
Chancre of atypical form
Atypical forms of hard chancre include: chancre-amygdalitis, chancre-felon, indurative edema; they appear when syphilis occurs in combination with other sexually transmitted infections. Then syphilomas appear in the plural and look like herpes and are considered complicated.
Knowing the characteristics of atypical forms will help not to confuse them with other diseases; here are the most common forms:
1. Chancroid-amygdalitis (anginal). The name itself suggests that it affects the tonsils, which during illness become swollen, thickened with pronounced redness. Due to the growing compaction, inflammatory hyperemia may begin, and the voice will become nasal. General malaise and fever are felt for some time.
2. Chancre felon. Panaritium is an acute purulent inflammation of soft tissues. This speaks for itself, and it most often occurs on the leg and has a spherical shape, with suppuration inside. It is difficult for a leg or finger to move due to increasing sharp shooting pains and swelling with severe redness. An ulcer forms at the height of the resulting panaritium, followed by the formation of necrosis of the edges of the wound. This form of syphiloma mainly affects medical workers who, through their negligence, are injured by a contaminated instrument.
3. Indurative edema. In both men and women, it most often forms in the genital area and since it may be similar to other diseases of the genital organs, a mandatory consultation with a doctor is required, who will take the discharge for analysis to confirm the diagnosis.
These are the most unpleasant forms of manifestation of secondary syphilis; they significantly complicate diagnosis and create additional health problems, causing tissue trophic disorders and impairing blood circulation. Atypical types of chancre threaten tissue atrophy, going far beyond syphiloma.
In the mildest course of this process and provided that it can be stopped in time, ugly scars will remain on the skin, and in the worst case, self-amputation of the affected area of the body or genital organ will occur. Such destructive changes are nothing more than gangrene, in which further treatment of this part of the body is useless. But this happens mainly with very weakened patients and alcoholics.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of syphilis is based on the detection of pale treponema in chancroid discharge, the results of a serological blood test and, if necessary, additional research data.
Infection with Treponema pallidum can occur through dental or other medical instruments, bedding, personal hygiene products of a sick person, and dishes.
Differential diagnosis of chancroid is necessary. Hard and soft chancre (chancroid) have a number of similar symptoms, but soft chancre is painful, has soft edges, and also forms purulent-hemorrhagic exudate.
Chancres that are localized on the genitals
Regarding the genital chancre, the French even have an apt expression that the first to be punished is the place where they sinned in a fit of passion.
Due to the fact that syphilis infection most often occurs during sexual intercourse, chancre in most cases occurs on the genitals or in the immediate vicinity of them. In men, the affected areas are the penis, its head and the body itself, and in women, these are the labia majora and minora and the cervix.
There are detailed descriptions of what syphilitic manifestations on the genitals of women and men may look like, but often this may not be the case. The primary manifestations of the disease can be quite vague, painless and not arousing any suspicion, and therefore most often remain unattended, while the disease progresses more and more.
And in women, if the internal organs of the small pelvis are affected, no symptoms are observed at all, the lymph nodes cannot be palpated, and the disease can be found out only by doing a tomography.
General information
Mention of lesions resembling chancroid is found in the works of Avicenna, in Chinese manuscripts dating back to 2600 BC. e. and in a Japanese book on medicine of 808 AD. e.
Descriptions of clinical manifestations that are similar to syphilitic ones are also found in the works of Hippocrates, Galen, Celsus, Dioscorides, Plutarch and Archogen.
The description of the signs of chancre belongs to A. Fournier, who studied syphilis (Fournier’s first work on this topic dates back to 1857).
It was Fournier, who identified 9 signs of chancroid, who described rare cases of its appearance on the chin, heel and cheek as a result of domestic infection.
Chancre of the tonsils was first described in 1861 by Diday, and Legendre studied it in 1884.
Chancre of the eye was first described in 1850 by Ricor, who identified chancre of the eyelid, ciliary margin and conjunctiva.
A rare case of chancre of the ear was described in 1878 by Hulot.
Extragenital localization of chancre
Extragenital localization means extragenital, and most often the localization site is in the mouth on the tongue, lips or cheeks. There are rare exceptions, for example, in some eastern countries, contact of the tongue with the lower eyelid is acceptable, in which case the Triponema pallidum bacterium is located there. The manifestations of chancre in these places are the same as in others - at first they are bumps with slight redness, gradually turning into ulcers, possibly with cracks and a crust.
If chancre is localized on the fingers, then they look club-shaped, the finger will swell and turn red, perhaps with a bluish tint, and a sharp and unpleasant odor will emanate from the surface plaque.
Perhaps the most unpleasant place of localization is the anus, when every act of defecation will be accompanied by pain, and there may be mucus and blood in the discharge.
How to properly treat a syphilitic rash?
Under no circumstances should you prescribe treatment for yourself, even if you read about it on the Internet or were advised by friends. The course of the pathology is different for each person, and the characteristics of the body are different, so the selection of medications is individual. It will be difficult to cure syphilis simply with ointment. A rash on the arm or other part of the body should be treated in a comprehensive manner. An antibiotic should be prescribed first. Most often, a penicillin drug with different durations of action is prescribed. If these antibiotics are not suitable, then they can be replaced with macrolides or Tetracycline.
To prevent allergies when taking antibiotics, the doctor recommends starting to take antihistamines, such as Claritin.
The rash also needs to be treated locally, in this case “Synthomycin emulsion”, “Levomekol” ointment or powder with talcum powder will help. It is not necessary to treat ulcers and rashes with an antiseptic.
If you start therapy in a timely manner and strictly adhere to all the doctor’s recommendations, then in this case you can avoid the serious consequences of this pathology, and in particular the appearance of scars on the skin. It is best, of course, to take all measures to avoid contracting this disease, and for this you need to take a more serious approach to choosing sexual partners and lead a healthy lifestyle.