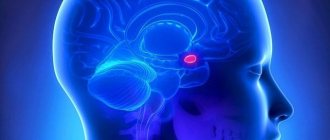
Increased prolactin in women (hyperprolactinemia) is a condition characterized by an increase in the concentration of lactotropic hormone in the blood.
Prolactin (lactotropin, mammotropin, mammotropic hormone, lactotropic hormone LTG) is a peptide hormone that is synthesized by acidophilic cells of the anterior pituitary gland. Almost all known effects of prolactin are related to reproductive function. It ensures the growth and development of the mammary glands, promotes the secretion and maturation of colostrum, as well as the transformation of the latter into mature milk.
In a woman's body, prolactin is responsible for lactation.
In the blood, LTG is found in several forms (monomeric, dimeric, tetrameric). The biologically active form of the hormone is monomeric (consists of one peptide chain).
Elevated prolactin in women is more often detected at 25–40 years of age. In men of the same age category, this condition is registered much less frequently.
Increased LTG often causes increased appetite and, accordingly, body weight, up to obesity, which is recorded in 40–60% of cases of hyperprolactinemia in women.
What is prolactin
The content of the article
Prolactin is a hormone that is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. One of the main roles of prolactin is the secretion of milk in the mammary glands of nursing mothers. It is also responsible for the proper functioning of the reproductive system. Hyperprolactinemia is a disorder of the endocrine system in which prolactin levels are kept high.
The secretion of prolactin exhibits a diurnal rhythm, that is, its concentration depends on the time of day. Higher levels of the hormone are observed at night during sleep, during meals, exercise, or significant anxiety.
The highest level of prolactin in the female body during pregnancy (a hormone produced in the pituitary gland, placenta, pituitary gland of the child). Then we can talk about natural hyperprolactinemia, that is, excess prolactin. In all other cases, an increase in prolactin is a serious pathology.
Causes of hyperprolactinemia
Normally, healthy people do not secrete any fluid from the chest. Women may have discharge during pregnancy and, naturally, during feeding, but five months after the end of lactation there should be no discharge from the breast.
Most often, hyperprolactinemia is caused by hypofunction (decreased activity) of the thyroid gland and adrenal cortex. Prolactin levels are also increased by chest diseases, herpes zoster, pituitary adenomas and other tumors, as well as cirrhosis of the liver, kidney and bronchial tumors.
The main causes of galactorrhea are very unpleasant conditions:
- small (2-3 cm) benign tumors in the pituitary gland;
- disruption of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands;
- ovarian diseases affecting their function (cysts, polycystic disease);
- taking drugs that change hormonal levels;
- renal and liver failure.
It is not without reason that the causes of hyperprolactinemia include stress, both mental and physical. It causes an increase in endorphins, which increase the activity of the brain and hypothalamus and, as a result, leads to an increase in the secretion of prolactin. The cause of the disease may be long-term use of pharmacotherapy, such as antipsychotics.
These are not all the reasons. Discharge in the chest can also be caused by taking lactogenic tinctures, for example, from fennel, regular trauma to the breast (rough sex, use of sex toys - pumps, rough underwear, etc.), trauma and disruption of nerve fibers during injuries and operations on the spinal cord etc. The range of reasons is really wide and varied, so only a good specialist will be able to identify the true problem.
There is only one thing you should not worry about - if galactorrhea begins in a newborn baby. This condition is associated with the mother’s hormonal balance during childbirth, so after a while everything will return to normal.
To identify the causes of increased prolactin, the doctor prescribes additional tests and studies:
- Tests for tumor markers;
- Tests for sex hormones;
- ;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- Ultrasound of the pelvis.
Contraindications for violation
It should be noted that high prolactin does not mean that a tumor has developed in the brain or the presence of any other disease. Despite this, during the treatment period it is necessary to follow all the recommendations listed by the doctor.
ATTENTION! Self-prescribing and taking medications is strictly prohibited, as the risk of aggravating the situation increases.
To successfully complete treatment, a woman will need to adhere to a list of rules:
- complete cessation of alcohol and smoking;
- stop using powerful psychotropic drugs;
- reduce physical activity;
- minimize the consumption of protein foods;
- avoid stress, worry, anxiety.
Nutritional Features
When prolactin is elevated in women, doctors recommend following a special diet that minimizes the consumption of foods high in protein:
- pork meat;
- beef;
- chicken's meat;
- eggs;
- liver;
- cottage cheese;
- cheese products;
- fish;
- lentils;
- beans.
There is no need to completely exclude these products from the menu. Vitamin complexes containing folic acid and foods such as Brussels sprouts, varieties of lettuce, broccoli, spinach, and a variety of vegetables and fruits . To strengthen the body's immune forces and supply microelements, consume sunflower seeds, nuts, and peanuts daily .
Symptoms of hyperprolactinemia in men, women, children
Typically, the disease manifests itself with recurrent headaches, depression, chest pain, obesity, skin problems and hypertrichosis. These symptoms are accompanied by hot flashes and decreased libido.
The patient is concerned about constant discharge from the chest: fluid may be released drop by drop, and perhaps in large volumes. Women's menstrual cycles become disrupted, and sometimes periods stop altogether, leading to infertility. With hyperprolactinemia, the skin deteriorates, oily seborrhea and acne occur, and facial hair grows.
Clinical symptoms are also associated with diseases of bone density (osteoporosis, osteopenia), decreased libido, galactorrhea, impaired fertility (ability to conceive. Among the distinctive symptoms associated with the disease is a decrease in visual acuity. In the fight against increased levels of prolactin in women, the secretion of male hormones increases - androgens. Therefore, acne may appear on the face, and hairs grow in places typical for men - on the face, stomach, chest. In turn, hair begins to fall out.
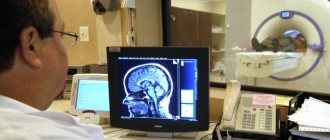
The diagnosis of hyperprolactinemia is made based on medical history, clinical examination and additional studies. If the doctor suspects a tumor of the pituitary gland, an ophthalmological examination and brain studies: computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are also necessary.
How to check prolactin levels: prolactin tests
To find out the level of this substance, you need to take a blood test for hormones. Before testing the level of prolactin in the blood, you should refrain from eating and drinking. It is best to get tested after waking up, between 8 and 10 am. On the day before the examination, you should not be overtired or stressed:
The correct concentration of prolactin in the blood is:
- 4.5–33 ng/ml is normal in the follicular phase;
- 4.9–40 ng/ml normal in the luteal phase
The results obtained can be interpreted according to the following scheme:
- 5–25 ng/ml is normal;
- above 25 ng/ml - disruption of the menstrual cycle and anovulatory cycles;
- above 50 ng/ml - delayed menstrual cycle;
- above 100 ng/ml - risk of pituitary tumor.
The given prolactin standards are used in deciphering hormone tests by a gynecologist or endocrinologist. When analyzing data, specialists take into account many factors that can affect the results. For example, when assessing hormonal factors, age, the presence of concomitant pathologies and hormonal therapy, etc. are important.
It is also important to understand that another hormone, dopamine, is responsible for the appropriate level of prolactin. It inhibits the production of prolactin (the higher the level of dopamine, the less prolactin is released). Another regulator of prolactin secretion is estrogens, which increase its production and secretion. Therefore, the doctor prescribes additional tests for hormones, this helps to identify the true causes of the pathology and prescribe the correct treatment.
Decoding the results
The test results are presented using a special table with 4 columns, the first of which indicates the hormone fractions (prolactin and post-PEG monomeric prolactin), the second - the patient’s current indicators, the third - acceptable reference values, and the fourth - the unit of measurement.
Prolactin content is measured in different units:
- honey/l;
- mIU/l;
- ng/ml.
Each laboratory uses its own unit of measurement, to which the current indicators are adjusted. In order to independently decipher the results of the analysis, you should compare individual indicators with the reference value, taking into account gender and age.
How is hyperprolactinemia treated?
To cure galactorrhea, you need to find out the causes of hyperprolactinemia. Since increased prolactin secretion occurs in many conditions, proper diagnosis is important.
First, blood tests are prescribed (clinical, biochemistry and hormones). The examination reveals hormonal imbalances and problems in the functioning of internal organs (liver, kidneys). Then, depending on the results, the following is carried out:
- ultrasound examination of the internal genital organs to detect cysts;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland to exclude nodes in its tissues that affect hormonal levels;
- x-ray of the “sella turcica” - the area of the skull in which the pituitary gland is located, to exclude a tumor;
- MRI and CT scan of the head. Based on the results of the examinations, it is determined whether there are tumors in other parts of the brain;
Depending on the cause of the disease, two types of treatment can be used - medication or surgery (tumors leading to hyperprolactinemia that do not exceed 1 centimeter can be treated pharmacologically).
Treatment depends on the cause of hyperprolactinemia:
- In case of hormonal imbalance and polycystic ovary syndrome, medications are prescribed to normalize hormonal levels. Taking birth control pills and products containing estrogens helps. Medicines are selected by the doctor individually based on test results;
- If problems with the thyroid gland are detected, iodine preparations are prescribed;
- To suppress milk production, medications that suppress prolactin secretion are indicated;
- Small tumors in the pituitary gland are treated with chemotherapy, and large tumors are removed.
- Good results are obtained by using basic drug therapy in combination with the prescription of dietary supplements and herbal medicines.
The following drugs are often used:
- Bromocriptine (Bromergon, Ergolaktyna, bromocriptine) is an effective drug, but may cause side effects such as nausea and dizziness.
- Norprolac is an effective, rather expensive drug.
- Dostinex is an inexpensive drug (prescribed with caution, as it has contraindications.
Naturally, medications are selected exclusively by an endocrinologist and only after receiving all the test results. Incorrect hormone therapy will lead to even greater hormonal imbalance, which will result in obesity, diabetes, kidney and liver failure and other complications.
Neurosurgical treatment is recommended if drugs do not sufficiently reduce prolactin levels or intolerance (drug resistance) or the doctor finds a tumor.
Forecast
Hyperprolactinemia does not pose a threat to the patient's health, and, if diagnosed early, can be easily treated. In the absence of therapy, the disease is complicated by infertility, pathology of the endocrine glands, and the formation of benign and malignant tumors. Specific measures to prevent hyperprolactinemia have not been developed.
To prevent the disease, the following rules should be followed:
- lead a healthy lifestyle - avoid alcohol, smoking, eat right and pay enough attention to physical activity;
- have a permanent sexual partner;
- avoid excessive psycho-emotional stress;
- undergo preventive medical examinations in a timely manner.
If you experience even minor complaints, you should immediately consult a doctor.