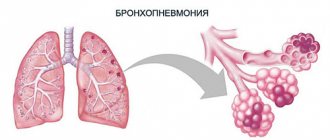
It all starts with a cold. The temperature rises, and then there is a chill. Breathing quickens, and when you inhale, a sharp pain appears in the chest. The cough begins to torment, and the sputum may later turn slightly pink. It is almost impossible to clear your throat; your voice begins to hoarse. After visiting a doctor and undergoing certain procedures, the diagnosis of “pneumonia” is announced. If the form is severe, the doctor will write out a referral to a hospital, but if it is mild or moderate, then, most likely, it will be possible to be treated on an outpatient basis. What kind of disease is this and how to treat pneumonia at home?
Types of disease
Experts classify the disease depending on the severity of its course, the mechanism of development, and the type of pathogen. In addition, there is a classification that divides the disease depending on the area of damage to the lung tissue.
Depending on the degree of damage to lung tissue, there are 3 types of pathology:
| Variety | Peculiarities |
| One-sided | This type is considered the mildest form of inflammation. Only a small area of the right or left lung is affected. Usually the lesion is small and does not cause severe symptoms. |
| Double-sided | In this case, the right and left lungs are involved in the process. They form foci of different sizes, which complicate the course of the pathology. Usually the disease is severe and can cause complications. |
| Total | The most severe form of pneumonia, when the process involves not only the lung tissue, but also the hilar zones of the lungs. In this case, the patient’s condition is critical; in most cases, untimely treatment increases the risk of complications. |
Depending on the severity of the pathological process, mild, moderate and severe pneumonia are distinguished. The latter is considered the most dangerous, the second occurs quite often, and the first often occurs in a hidden form, which can also provoke unpleasant consequences.
If we take into account the nature of the disease and its onset, we can distinguish acute and chronic forms.
Acute occurs primarily and immediately provokes severe symptoms.
Chronic occurs with less pronounced symptoms; the patient experiences a relapse from 2 to 4 times a year. In some cases, relapses are severe.
Depending on the mechanism of development of the pathology, several forms of inflammation are also distinguished.
Primary pneumonia becomes an independent disease, secondary pneumonia is a consequence of another inflammatory process.
Post-traumatic and post-infarction - the result of stagnation of sputum in the lungs during a long stay in a horizontal position and impaired blood outflow in the pulmonary circulation.
In addition, there are postoperative types of inflammation of the lung tissue, the mechanism of development of which is similar to post-traumatic. Depending on the type of pathogen, viral and bacterial pneumonias are distinguished, as well as fungal, protozoal and mixed. The second type is considered the most common and responds well to treatment if started in a timely manner.
Epidemiologists also divide the disease into several types depending on the predisposing factor:
- Community-acquired inflammation is said to occur when the patient is diagnosed with pneumonia immediately after seeing a doctor.
- The in-hospital form develops while the patient is in the hospital. Usually he is undergoing treatment for some other organ, and pneumonia is a complication. In most cases, the nosocomial form is very difficult and lengthy to treat, since it is provoked by microorganisms resistant to antibiotics.
- The immunodeficiency type occurs against a background of weakened immunity.
- Atypical pneumonia is dangerous because it occurs latently or is accompanied by atypical symptoms.
Depending on the type of disease, the clinical picture of the pathology differs. In addition, there are extensive pneumonia, focal and lobar. Each type is accompanied by different manifestations.
Clinical guidelines
For a quick recovery from pneumonia, it is important to follow all medical recommendations and not change the dosage of medications or the rules for taking them without consulting a doctor.
If the patient smokes, you need to give up cigarettes during treatment - the tars and carcinogens that are part of tobacco products worsen the condition of the respiratory system, and can also reduce the effectiveness of some medications.
Alcohol should also be avoided, as ethyl alcohol in combination with certain chemicals can cause unwanted reactions in the body.
Nutrition plays an important role - food should be light, but high in calories, with a high content of vitamins and nutrients. Additionally, you can take vitamin complexes that help the body return to normal faster, but with complex therapy, it is better to consult a doctor before taking them.
Like any other disease, pneumonia can be prevented rather than treated - for this you need to follow simple rules of prevention.
Lead a healthy lifestyle. Smoking, drinking alcohol and other bad habits destroy the body's natural defenses, causing it to become more vulnerable.
Maintain personal hygiene. After each return home, you need to thoroughly wash your hands, and during periods of epidemics, rinse your mouth with disinfectant solutions.
Increase immunity. A weak immune system is one of the main causes of respiratory diseases. You can improve your immune system through hardening, regular walks in the fresh air and proper nutrition. Several times a year you can take immunomodulatory drugs - Arbidol, echinacea tincture, etc.
Get a vaccination. Some types of influenza and pneumonia can be protected by vaccination. The vaccine does not provide 100% protection against infection, but it prevents complications of diseases and makes their course easier.
Avoid contact with sick people. All types of pneumonia, except fungal pneumonia, can be transmitted from person to person. To prevent infection, it is necessary to avoid contact with sick people, especially those who are in an acute period.
Correctly treat infectious diseases. In half of the cases, pneumonia is a complication of influenza and other respiratory diseases, so they cannot be tolerated “on your feet.” At the first signs of infection, you should consult a doctor and stay in bed until complete recovery.
It is especially important to follow the rules of prevention for people who have recently had pneumonia, as the disease can recur. In addition, you need to do fluorography every six months - this diagnostic method allows you to detect not only pneumonia, but also other diseases of the respiratory system, including tuberculosis and malignant neoplasms.
Stages and degrees
Pneumonia (treatment in adults involves the use of drugs from different groups), regardless of the form and variety, proceeds in several stages. The difference is considered to be symptoms, which for different types of disease may be present or absent and manifest with varying degrees of intensity.
The initial or mild stage is accompanied by the absence of symptoms or their mild manifestation. The patient reports weakness and a slight increase in body temperature, but believes that these are manifestations of a cold.
At the middle or advanced stage, more pronounced symptoms appear. Body temperature rises significantly, cough and other severe signs of pneumonia appear. The severe or advanced stage is characterized by acute manifestations, fever, and pain throughout the body. Other symptoms characteristic of inflammation also appear.
It is important to remember that with a severe form of the pathological process, one stage passes into another much faster than with a latent course.
That is why doctors almost cannot distinguish this transition during the acute onset of the disease. However, in each form these stages are present in the clinical picture.
Infection
There are several ways, and the simplest and most common is airborne. The secretions that come from a virus-infected person freely penetrate to a healthy person, and, under certain conditions, begins destructive work.
Bacteria and viruses that cause disease may be present in the body, but are suppressed by the immune system. The state in which it plays a decisive role, whether a person gets sick or not; being a carrier and being sick are not the same thing.
Only with hypothermia, or with a general weakening of the body for various reasons, does the activity of viruses and bacteria increase.
Symptoms
The disease is characterized by many severe symptoms. Externally, the disease manifests itself only at a progressive and advanced stage. The patient's skin becomes pale and cool to the touch, and facial features become slightly sharper. With a long course of the pathology, the patient loses weight, the skin becomes moist or dry.
Other manifestations of pneumonia:
- Weakness and pain in muscles and joints.
- Drowsiness and decreased performance.
- Sleep disturbance, manifested by restlessness, nightmares, and night sweats.
- Fever or slight increase in body temperature. The second is observed during the chronic course of the inflammatory process.
- Shortness of breath during exercise. In advanced cases, the symptom manifests itself even at rest, especially with nervous tension.
- Cough of varying intensity, which depends on the degree of damage to the lung tissue. In this case, a small amount of sputum is released at the initial stage. As the condition progresses, the amount of sputum increases and the intensity of the cough intensifies. The sputum has a yellowish or greenish tint. However, with lobar pneumonia, a characteristic symptom is rusty-colored sputum.
- Deterioration of appetite, up to its complete absence.
- Intense thirst and dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth.
- Chest pain that gets worse with deep inhalation and exhalation.
- Tachycardia, arrhythmia. Similar symptoms appear in mature patients with a history of cardiovascular pathologies.
- Headache and dizziness, aggravated by exercise or anxiety.
Some patients develop signs of respiratory illness such as a runny nose, sore throat, and watery eyes.
Hospitalization for pneumonia
Hospitalization may be required if:
- Patient over 65 years old
- Decreased kidney function (little urine)
- Systolic blood pressure below 90
- Diastolic blood pressure 60 mm or lower
- Rapid breathing (30 or more breaths per minute)
- There are signs of impaired consciousness
- Body temperature is below normal
- resting heart rate below 50 or above 100
Hospitalization is carried out either in therapeutic departments or in intensive care units if correction of vital functions is necessary.
Children may be hospitalized if:
- They are younger than 2 months
- They are lethargic or excessively sleepy
- They have trouble breathing
- They have low blood oxygen levels
- They appear dehydrated
Reasons for appearance
Pneumonia (treatment in adults requires preliminary examination) can be caused by various factors.
Common reasons include the following:
- Frequent respiratory and viral pathologies, which are complicated by pneumonia.
- Negative effects of environmental factors on lung tissue.
- Weakening the body's defenses.
- Regular hypothermia.
- Lack of timely treatment for colds.
- Allergic reaction to pollen, animal dander and other substances.
Primary pneumonia is caused by the penetration of bacteria into a person’s lungs, secondary pneumonia is caused by chronic bronchitis and other pathologies of the respiratory system. The immunodeficiency type is the result of a weakened immune system as a result of the AIDS virus entering the body.
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Hospital-acquired pneumonia develops while the patient is in the hospital. The bacterial form is a consequence of the penetration of microorganisms into the lungs. In 30% of all cases, inflammation is caused by streptococci. In addition, the disease can be provoked by staphylococci, gonococci, and chlamydia. In 40% of cases, the causative agent of the disease cannot be identified.
Post-traumatic and post-infarction pneumonia is the result of stagnation of sputum in the lungs and blood in the pulmonary circulation. This occurs when the patient is in a horizontal position for a long time and is not able to fully cough up sputum.
The atypical form of the disease is considered the most difficult to diagnose, since it is provoked by various bacteria, as well as other factors.
Antibiotics in the treatment of pneumonia
The basis of treatment for pneumonia in adults is pharmacotherapy. Unfortunately, you cannot do without antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal (if necessary) agents. The choice of the right drug directly depends on the results of laboratory tests. A pulmonologist examines blood, urine, and sputum tests. It would not be superfluous to carry out bacteriological culture, which is necessary to determine the resistance of pathogenic microorganisms to drugs.
The most popular tablets and injections are:
- "Sumamed", "Azithromycin" (macrolides);
- "Flemoxin", "Augmentin" (penicillins);
- "Sparfloxacin" (fluoroquinolos);
- "Suprax", "Ceftriaxone" (cephalosporins).
Most often, adults are prescribed intravenous therapy. In the first 2-3 days, you need to suppress the reproduction and spread of bacteria in the body as quickly as possible.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the disease, the patient must undergo an examination, which includes several effective methods.
Clinical and biochemical blood tests are carried out free of charge in public clinics; in private clinics the price is approximately 300-400 rubles. The method is standard and helps to assess the general condition of the patient, as well as detect signs of inflammation at an early stage. For example, eosinophilic pneumonia is detected by a complete clinical blood test.
A general examination and interview of the patient allows us to identify the probable cause of the pathology. The specialist not only listens to the patient’s complaints, but also conducts auscultation, that is, listens to the lungs to identify wheezing or other disorders.
Usually, a person’s breathing is difficult, there may be an absence of wheezing or a pronounced manifestation of it, which depends on the form and stage of the disease. The method is effective, usually does not require payment and is carried out in any institution.
Sputum analysis is one of the most effective methods, which is carried out in public clinics and does not require payment.
The patient collects sputum in a sterile container; the doctor explains the collection rules. After this, the material is sent to the laboratory for diagnostics. The result helps to identify the causative agent of the disease.
X-ray of the lungs is the most effective diagnostic method, the cost of which does not exceed 300 rubles.
It is carried out in any institution and helps to identify the location of the lesion. Thanks to the images, the specialist can assess the extent of tissue damage.
Thanks to a comprehensive diagnosis, the doctor identifies the stage and form of the disease, which helps prescribe the most adequate therapy.
Prevention
To prevent pathology, it is recommended to strengthen the immune system through proper nutrition and adherence to the principles of a healthy lifestyle. It is necessary to exercise, monitor your body weight and give up bad habits, especially cigarettes.
In addition, respiratory diseases, as well as bronchitis, should be treated promptly. This should be paid special attention to patients who suffer from chronic bronchitis. Additionally, it is recommended that if you develop a severe cough that persists for more than 7 days, you should visit a doctor who will perform auscultation of the lungs.
Patients who are forced to remain in a horizontal position for a long time after surgery or injury require special care. It should be regularly and gently lifted, allowing full coughing to clear the phlegm. If you follow the recommendations, the likelihood of developing inflammation is significantly reduced.
Treatment methods
Experts use several methods to treat pneumonia. Medicines, folk remedies and other procedures help quickly eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
Treatment regimen
Regardless of the form of the disease, specialists use 3 antibiotic treatment regimens. The choice depends on the age of the patient. The only difference is the dosage of the drugs and the duration of their use.
The most common schemes:
- Patients aged 20 to 40 years are prescribed Amoxiclav in combination with Doxycycline.
- For patients over 40 years old - Clarithromycin and Ceftriaxone, as well as Sumamed.
- Patients over 60 years of age receive only Ceftriaxone, since other antibiotics are potent.
In addition, each regimen includes antipyretic, mucolytic, and anti-inflammatory medications. Additionally, treatment includes probiotics, as well as medications to cleanse the blood and restore water balance in the body.
Medications
Pneumonia (treatment in adults includes strong antibiotics) is treated using several drugs from different groups. For severe cases, agents for parenteral administration are used, for mild and moderate cases, oral agents are used.
The most commonly prescribed medications are:
- Azitral is an antibiotic from the macrolide group, characterized by high efficiency and relative safety. For mild cases, the patient is prescribed 1 tablet (500 mg) 2 times a day for 5-7 days. In severe cases, 200 ml of saline solution is injected intravenously, to which 1 bottle (1 g) of medication is added. The procedure is carried out 2 times a day for 7-10 days. The drug quickly destroys bacteria of various types and relieves inflammation. The price of the medicine is from 100 to 200 rubles. depending on the form and dosage.
- Ceftriaxone is an effective antibiotic that can quickly destroy bacteria in the lung tissue. It is used in the form of a powder, from which a solution is prepared for intramuscular and intravenous administration. The patient receives from 2 to 4 g of the drug per day, the course duration is 10 days. The cost of 1 bottle is from 20 rubles.
- Lazolvan is a mucolytic agent that stimulates the production and discharge of sputum. It is prescribed in the form of tablets and solution for intravenous administration. Tablets should be taken 2 pieces 3 times a day for 10 days. The solution is administered intravenously once a day from 2 to 4 ml. The duration of the course is 10 days. The product is considered very effective. The price of the medicine is from 60 to 350 rubles.
- Nimesil – powder for preparing a solution for oral administration. For 1 dose, take 1 sachet, which is dissolved in 100 ml of warm water. It is allowed to take 2 to 4 times a day in case of extreme heat, pain and inflammation. The course lasts 5 days. The product is very effective, helps to quickly reduce body temperature, eliminate pain and improve general condition. The price of the product is from 40 rubles. for 1 sachet.
- Reosorbilact is a solution for cleansing the blood of toxins that are present in excess in the patient’s systemic bloodstream. It is effective and has a gentle effect on the body. The patient is administered 200-400 ml of solution intravenously per day using a dropper. The course lasts from 5 to 10 days. The price of the medicine is from 120 rubles. per bottle.
- Ringer's solution is a salt-based solution that replenishes fluids and helps prevent dehydration. The patient is administered intravenously 200-400 ml per day for 5 days. The drug is effective and safe, reduces the manifestations of intoxication in the form of headache, nausea and other symptoms. The price of the medicine is from 80 rubles. per bottle.
- Aloe is a drug in the form of a solution for intramuscular administration, it is highly effective and stimulates the resorption of lesions in the lung tissue. The patient is administered 1 to 2 ml of solution intramuscularly daily, the course lasts 10 days. The price of the medicine is from 100 rubles. per package.
- Linex is a drug for normalizing intestinal microflora. The capsules help prevent dysbiosis caused by antibiotic treatment and are considered very effective and safe. The patient takes 1 capsule per day. Course duration – 7 days. The price of the medicine is 300 rubles. per package.
During the recovery period, the patient is prescribed vitamin complexes, which are selected individually. Typically, therapy lasts no more than 2 weeks, but in advanced cases it will take up to 4 weeks for complete recovery.
Traditional methods
Pneumonia (treatment in adults may include traditional medicine) is sometimes treated using unconventional methods. Home recipes cannot become the only method of therapy, but act as an auxiliary one.
- A decoction of thyme and coltsfoot helps stimulate the production and removal of mucus from the lungs. For 1 liter of water you will need 5 g of each ingredient in dry form. Cook the mixture for 3 minutes, leave for 30 minutes. After this, take the filtered product 200 ml 3 times a day. Course duration is 5-7 days.
- Linden decoction – a natural antipyretic and diaphoretic. You can get it by boiling 5 g of dry herb in 500 ml of water for 2 minutes. The finished and filtered product should be taken before bed, 300 ml. The course lasts 5 days.
- Aloe juice should be taken for 7 days, 10 ml per day. It can be prepared by grinding fresh fleshy leaves. After this, you should squeeze them through cheesecloth, and store the resulting juice in the refrigerator for no more than 3 days.
Other methods
To speed up the recovery period of the lungs, massage, acupuncture and special breathing techniques are used.
The massage must be performed by a specialist. The doctor uses a technique that speeds up the removal of residual mucus from the lungs. The session lasts 20 minutes, the frequency is once every 2 days, the number of procedures is from 10 to 15.
Acupuncture is an effective alternative treatment in which needles are inserted into specific points on the patient's skin and left there for a period of time. The session lasts from 30 to 40 minutes and is carried out once every 3 days for a month.
The patient can use a special breathing technique independently at home. It consists of completely emptying the lungs of air, followed by a sudden filling of them. After this, you need to exhale sharply again and hold your breath for 3-5 seconds. It is better to perform the exercise immediately after waking up, do from 3 to 10 approaches. Course duration is 2-4 weeks.
How many days does it take to treat the disease?
The duration of the therapeutic course depends on the clinical course of pneumonia and the general condition of the body in adults and children. On average, it lasts from 7 to 10 days, and if necessary, can be extended to 14 days or more. For uncomplicated pneumonia, sometimes 3-4 days of antibiotic therapy is sufficient.
As a rule, relief occurs after 3-5 days of treatment, but the absence of symptoms does not mean complete recovery. To completely stop the inflammatory process and destroy all pathogens, it is important to follow the doctor’s instructions and continue to take medications. Complete restoration of the functions of the respiratory system occurs within 1-2 months, and in some cases longer - cough and other residual effects can be observed for several more weeks.
Possible complications
Without treatment, complications almost always develop.
The most common of them:
- Transition of the disease into a chronic form.
- Spread of inflammation to the second lung when one of them is affected.
- Blood poisoning due to the penetration of bacteria.
- Respiratory failure.
- Necrosis of lung tissue.
- Bronchial asthma.
- The formation of a purulent focus in the lung, that is, an abscess.
- Damage to the endocardium due to the spread of bacteria.
- Exudative pleurisy.
- Emphysema.
The most severe complication is death. This is quite often observed with lobar pneumonia.
Pneumonia is a dangerous disease that can cause serious complications. Treatment of this pathology in adults is carried out after a preliminary examination and identification of the form, degree of neglect of the condition, and the probable cause.
Article design: Vladimir the Great