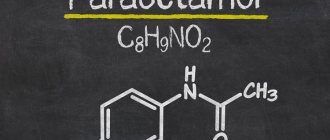
Flucoldex-S is a drug (tablets) that belongs to the analgesics category. The instructions for use highlight the following features of the drug:
How to dissolve vascular plaques, normalize blood circulation, blood pressure and forget the way to the pharmacy
- During pregnancy: contraindicated
- When breastfeeding: contraindicated
- In childhood: contraindicated
- For liver dysfunction: contraindicated
- If renal function is impaired: contraindicated
- In old age: with caution
Pharmacological properties of the drug Flucoldex
Flucoldex is a combination drug. The analgesic effect of paracetamol includes effects on the central and peripheral nervous system. The antipyretic effect is mediated by the effect on the regulatory centers of the hypothalamus. Caffeine has a stimulating effect on the central nervous system, mainly on the cerebral cortex, respiratory and vasomotor centers, increases mental and physical performance, reduces drowsiness, a feeling of fatigue and weakens the effect of central nervous system depressants. Caffeine has a pronounced effect on the cardiovascular system: it increases strength and increases heart rate, blood pressure during hypotension, and has a moderate diuretic effect. Increases the secretion of gastric glands. Phenylpropanolamine hydrochloride, an α-adrenergic active compound without irritating effects on the central nervous system, has a predominantly direct effect on adrenergic receptors. Often included in combination medications to reduce the severity of cold symptoms. Chlorpheniramine maleate is an antiallergic agent, a blocker of histamine H1 receptors. Shows a moderate sedative effect and has antimuscarinic activity. Flucoldex is a multicomponent drug. The effect of the drug is the cumulative effect of its components, so pharmacokinetic observations are impossible; the dynamics of all components cannot be studied using markers or biological methods.
Release form and composition of Flucoldex
Flucoldex is produced in the form of tablets and also in the form of a suspension.
Each Flukoldex tablet contains paracetamol (500 mg), caffeine anhydrous (30 mg), phenylpropanolamine hydrochloride (25 mg), chlorpheniramine maleate (2 mg), as well as additional components: sodium benzoate, starch, gelatin, magnesium stearate, talc, polyvinylpyrrolidone, sorbitol, sodium starch glycolate, sunset yellow dye.
5 ml of Flucoldex suspension contains 125 mg of paracetamol and 2 mg of chlorphenamine maleate.
pharmachologic effect
Combined drug.
Paracetamol
blocks COX only in the central nervous system, affecting the centers of pain and thermoregulation. The lack of influence of paracetamol on the synthesis of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues determines the absence of a negative effect on water-salt metabolism (retention of sodium and water ions) and the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Chlorphenamine
- blocker of histamine H1 receptors. Prevents the development and facilitates the course of allergic reactions. It has antiallergic, antipruritic, antiexudative effects. Reduces capillary permeability, prevents the development of tissue edema, relieves spasm of smooth muscles. Has a suppressive effect on the central nervous system.
Flucoldex 100ml syrup for children nabros pharma
pharmachologic effect
Combined drug.
Paracetamol blocks COX only in the central nervous system, affecting the centers of pain and thermoregulation. The lack of influence of paracetamol on the synthesis of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues determines the absence of a negative effect on water-salt metabolism (retention of sodium and water ions) and the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Chlorphenamine is a histamine H1 receptor blocker. Prevents the development and facilitates the course of allergic reactions. It has antiallergic, antipruritic, antiexudative effects. Reduces capillary permeability, prevents the development of tissue edema, relieves spasm of smooth muscles. Has a suppressive effect on the central nervous system.
Composition and release form Flucoldex 100ml syrup for children nabros pharma
Syrup - 5 ml: paracetamol 125 mg, chlorphenamine maleate 2 mg.
100 ml - polymer bottles (1) complete with a measuring cup - cardboard packs.
Directions for use and doses
Inside.
Indications for use Flucoldex 100ml syrup for children nabros pharma
Feverish syndrome (colds and infectious diseases); pain syndrome (mild and moderate severity): arthralgia, myalgia, neuralgia, migraine, toothache and headache, algodismenorrhea; pain from injuries, burns; sinusitis; rhinorrhea (acute rhinitis, allergic rhinitis).
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity; deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; liver and/or kidney failure. With caution Congenital hyperbilirubinemia (Gilbert, Dubin-Johnson and Rotor syndromes), alcoholism, angle-closure glaucoma, prostatic hyperplasia, pregnancy, lactation; old age, children's age (up to 12 years).
Use of Flucoldex 100ml syrup for children nabros pharma during pregnancy and breastfeeding
With caution: during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding).
Use in children
With caution: children's age (up to 12 years).
special instructions
For hyperthermia lasting more than 3 days and pain lasting more than 5 days, consult a doctor.
Paracetamol distorts laboratory results when quantifying the content of sugar and uric acid in plasma.
During the treatment period, it is necessary to refrain from drinking ethanol (hepatotoxic effects may develop).
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
During the treatment period, it is necessary to refrain from driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Side effects of Flucoldex 100ml syrup for children nabros pharma
Systemic reactions: allergic reactions (skin rash, itching, urticaria, angioedema),
From the digestive system: nausea, epigastric pain, dry mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, throat.
From the organ of vision: mydriasis, paresis of accommodation, increased intraocular pressure.
Laboratory parameters: hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, methemoglobinemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia.
From the urinary system: nephrotoxicity (renal colic, glycosuria, interstitial nephritis, papillary necrosis), urinary retention.
Drug interactions
Inducers of microsomal oxidation in the liver (phenytoin, ethanol, barbiturates, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants), ethanol and hepatotoxic drugs increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites, which makes it possible to develop severe intoxications even with a slight overdose.
Long-term use of barbiturates reduces the effectiveness of paracetamol.
Ethanol contributes to the development of acute pancreatitis.
Microsomal oxidation inhibitors (cimetidine) reduce the risk of hepatotoxicity.
Paracetamol reduces the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs and increases the effect of indirect anticoagulants.
Long-term combined use of paracetamol and other NSAIDs increases the risk of developing “analgesic” nephropathy and renal papillary necrosis, and the onset of end-stage renal failure.
Simultaneous long-term administration of paracetamol in high doses and salicylates increases the risk of developing kidney or bladder cancer.
Diflunisal increases the plasma concentration of paracetamol by 50% - the risk of developing hepatotoxicity.
Myelotoxic drugs increase the manifestations of hematotoxicity of the drug.
special instructions
For hyperthermia lasting more than 3 days and pain lasting more than 5 days, a doctor’s consultation is required. Paracetamol distorts laboratory test results when quantifying the content of sugar and uric acid in plasma. During the treatment period, it is necessary to refrain from drinking ethanol (hepatotoxicity may develop ). Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
During the treatment period, it is necessary to refrain from driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity to any component of Flucoldex;
- children under six years of age;
- deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase;
- renal and/or liver failure;
- lactation period;
- pregnancy;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- heart failure (chronic form);
- diabetes;
- blood diseases;
- arterial hypertension;
- analgesic nephropathy;
- prostatic hyperplasia;
- pheochromocytoma.
Flucoldex should be used with caution in cases of congenital hyperbilirubinemia (Gilbert, Rotor and Dubin-Johnson syndromes), alcoholism, angle-closure glaucoma, prostatic hyperplasia, and in old age.
Instructions for use
According to the instructions, Flucoldex in the form of a suspension should be used in the following standard doses:
- children 3-5 years old - 5 ml twice a day;
- children aged 6-10 years – 5 ml three to four times a day;
- children 10-15 years old – 10 ml three times a day;
- adults and adolescents over 16 years of age - 10 ml of suspension four to six times a day.
The course of treatment is five days.
Flucoldex tablets are recommended for use by adults two to three times a day (one tablet).
Judging by the reviews of Flucoldex, the drug is well tolerated in most cases. However, the following side effects are possible: loss of appetite, dizziness, dry mucous membranes, increased blood pressure, stimulation of the central nervous system, vomiting, gastrointestinal irritation, allergic reactions, epigastric pain, hemolytic disorders, urinary retention.
Some reviews of Flucoldex indicate that with long-term use the medication has a hepatotoxic effect. In addition, long-term use of Flucoldex in large doses can lead to the development of glucosuria, interstitial nephritis, and papillary necrosis.
Drug interactions
- long-term combined use of Flucoldex and barbiturates reduces the effectiveness of paracetamol;
- paracetamol reduces the effect of uricosuric drugs and increases the effectiveness of indirect anticoagulants;
- long-term simultaneous use of paracetamol and other NSAIDs increases the risk of developing renal papillary necrosis and “analgesic” nephropathy;
- Diflunisal increases the concentration of paracetamol in the blood plasma by 50% (risk of hepatotoxicity);
- myelotoxic drugs increase the manifestations of hepatotoxicity of Flucoldex;
- long-term combined use of salicylates and paracetamol in high doses in the treatment increases the risk of developing bladder cancer.
Answer
Flucoldex
Flukoldex is a combined two-component drug for symptomatic (eliminating symptoms, not the cause of the disease) treatment of acute respiratory infections. Paracetamol prevents the formation of the enzyme cyclooxygenase in the central nervous system, thereby affecting pain and thermoregulatory centers. Limitation of action within the central nervous system and the absence of its spread to peripheral tissues determines the absence of a negative effect on water-mineral metabolism and the inner lining of the gastrointestinal tract. Chlorphenamine is an antagonist of histamine H1 receptors. Prevents the development and reduces the severity of allergic reactions. Suppresses itching, prevents the effusion of exudate into the interstitial space. Makes the walls of small blood vessels less permeable, prevents the development of swelling, and eliminates spasms of smooth muscles. Has an inhibitory effect on the central nervous system. It is used for febrile conditions accompanied by an increase in body temperature to febrile values, joint and muscle pain, lesions of peripheral nerves, characterized by attacks of pain in the area of innervation of any nerve, migraine pain, cephalalgia, dentalgia, painful menstruation, pain of traumatic origin, inflammation of the adnexa. sinuses, runny nose (including allergic nature). Possible undesirable side reactions: skin rashes, sensation of painful tickling skin irritation, causing the need to scratch the irritated area, urticaria, Quincke's edema, painful sensation in the epigastric region, chest, oral cavity and pharynx, preceding vomiting, pain in the epigastric region, hyposalivation, dryness mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and throat, dilation of the pupil, weakening of the ability to distinguish small details of visible objects at close range (paresis of the ciliary muscle), increased fluid pressure inside the eye, acute attack of pain in the lumbar region caused by a sharp disruption of the outflow of urine from the kidney and impaired circulation in it. The drug is not used in case of individual intolerance to any active or auxiliary component, insufficiency of liver and/or kidney function.
There is a group of patients in whom the drug is used with extreme caution. These include persons suffering from alcoholism, benign prostate adenoma, closed-angle glaucoma, women during pregnancy and breastfeeding, and elderly patients. In pediatric practice, the drug is used starting from the age of 12. If the elevated body temperature does not decrease within three or more days and/or the pain does not subside within five or more days, you should consult a doctor to adjust treatment. During the course of medication, you should avoid consuming ethanol-containing products due to the possible increase in the negative effect of paracetamol on the liver. During the course of pharmacotherapy, it is recommended to refrain from driving a car and engaging in other activities that are a source of danger and require increased attention and reaction speed. The analgesic effect of the drug develops within half an hour after taking it, reaches its peak after 1-2 hours and lasts for a total of about 4-5 hours. The antipyretic effect becomes clinically significant 1-1.5 hours after administration. Due to the selectivity of action, paracetamol rarely causes allergic reactions and does not affect blood flow in the renal arteries and platelet aggregation abilities. Long-term use of barbituric acid preparations suppresses the pharmacological activity of paracetamol. Taking the drug together with ethanol increases the risk of inflammation of the pancreas. Paracetamol potentiates the effects of indirect anticoagulants. Long-term use of paracetamol and other NSAIDs increases the likelihood of developing chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis and hastens the onset of end-stage renal failure.
Side effect
Systemic reactions:
allergic reactions (skin rash, itching, urticaria, angioedema),
From the digestive system:
nausea, epigastric pain, dry mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, and throat.
From the side of the organ of vision:
mydriasis, accommodation paresis, increased intraocular pressure.
From the laboratory parameters:
hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, methemoglobinemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia.
From the urinary system:
nephrotoxicity (renal colic, glycosuria, interstitial nephritis, papillary necrosis), urinary retention.