Release form
The pharmaceutical industry produces Gentamicin in the form of a sterile medicinal liquid for administration into the muscle or venous system, which bypasses the gastrointestinal system.
A homogeneous mixture for injection is ampoules with the main active antibacterial substance dissolved in water for injection. The drug has the appearance of a transparent or yellowish liquid, odorless. The hermetically sealed glass vessel with the medicine contains 2 cubic meters. ml of medicine, which contains 0.08 g of the main substance.
How does Gentamicin work?
The drug Gentamicin is sold in pharmacies in various dosage forms. The most popular solution is the drug; Gentomycin ointment and tablets of the same name can also be found on sale. The solution is produced in Belarus. The price for a package of 10 ampoules of 4 mg is 40 rubles.
The drug belongs to the group of aminoglycoside antibiotics and is intended for injection into a muscle or into a vein.
The active substance is gentamicin (no color or slightly greenish) in the form of sulfate, there are a number of additional components - water, sodium disulfite. The main effect of the drug is bactericidal; gentamicin is intended to stop infectious processes of various localizations.
The drug penetrates the walls of the microbial shell, interacts with bacterial proteins and disrupts their production. As a result, the microbial cell dies. A number of infectious agents are highly sensitive to this medicine:
- coli;
- salmonella;
- shigella;
- enterobacteria;
- Klebsiella;
- Proteus;
- serratia;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- Acinetobacter;
- streptococci.
The drug, when used in a course of use, destroys even strains of staphylococci that are resistant to antibiotics from the penicillin group, but some types of streptococci have developed resistance to it. Neisseria, Treponema pallidum, and many anaerobes are also not affected by the drug. The maximum concentration in the body is reached half an hour after administration of the solution. The drug is excreted by the kidneys, a small part - by the liver.
pharmachologic effect
Gentamicin is an antibacterial agent from a group of organic substances that consist of amino sugars linked by a covalent bond to an aminocyclic ring. Being a drug with a wide spectrum of action, it suppresses the microbiological multi-stage process of protein synthesis and maturation in living organisms.
The drug is highly effective against many types of bacteria that do not stain with crystal violet, as well as microorganisms that retain color after washing with a special solvent.
Such domains of living organisms include:
- rod-shaped intestinal bacterium;
- facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped Proteus;
- pseudomonas pseudomonas;
- opportunistic bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae;
- rod-shaped peritrichial asporogenous gram chemoorganotrophic microorganism enterobacter;
- rod-shaped serration marcescens;
- pathogenic bacterium Citrobacter freundi;
- non-sporogenous microorganism of the genus Salmonella;
- highly contagious Proteus shigella;
- microbe of the genus Staphylococcus.
The following microorganisms are resistant to aminoglycoside antibiotics:
- nonmotile lanceolate diplococcus – pneumococcus;
- ovoid asporogenous bacteria of the genus streptococci;
- elongated microorganism enterococcus;
- treponema pallidum;
- organisms that gain viability in an oxygen-free environment;
- rod-shaped bacteroids;
- spore-forming obligate anaerobes Clostridia.
The drug Gentamicin is one of the main drugs that fight complex purulent inflammation in the body. Sometimes the drug should be prescribed if other antibacterial agents do not show sufficient therapeutic effect.
Bacterial resistance to the drug appears very slowly - this makes Gentamicin active against a large number of microorganisms.
When used intramuscularly, the concentration of the drug in the liquid biological part of the blood, which does not contain red blood cells, reaches its maximum after ½ hour. In this case, the therapeutic activity remains for about 1/3 of the day.
The administration of Gentamicin in the form of droppers allows the drug to exceed the concentration of the main substance in the connective fluid tissue, compared with parenteral use.
During pregnancy
The use of the medication is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding, because the active component of the composition penetrates the placenta and is found in breast milk. It is undesirable for the active substance to enter the child's body due to the development of negative symptoms and suppression of the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Indications for use
Gentamicin for injections is prescribed for the following pathological conditions, according to the instructions for use:
- infection of the body by microorganisms streptococcus and staphylococcus;
- invasive infection of newborns;
- rapidly developing inflammation in the gallbladder;
- angiocholitis;
- inflammation of the renal tubular system with damage to the pelvis;
- acute process in the urinary system;
- damage to the alveoli and interstitial tissue of the lungs, as a result of the introduction of bacteria;
- complications in the pleura after pneumonia;
- pleural empyema;
- severe general condition of the body due to an inflammatory process in the peritoneum;
- complex purulent process in the body;
- inflammation in the cerebral ventricle;
- development of a bacterial process in the wound cavity;
- infection caused by high temperatures;
- penetration of microorganisms into the skeletal system;
- inflammation of the prostate gland;
- skin staphylococcal infection;
- purulent inflammation of the follicles;
- staphylococcal necrotic lesion of the sebaceous glands;
- introduction of Staphylococcus aureus into the skin;
- paronychia;
- inflammation of the sebaceous glands;
- acne;
- secondary skin infection;
- suppuration after insect bites;
- ulcerative varicose veins;
- infectious lesions of the upper and lower eyelids;
- inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eyes;
- inflammatory process of the lacrimal sac;
- cloudiness, ulceration of the ocular cornea;
- bacterial process in the glands that are located in the thickness of the eyelids.
Indications - who will Gentamicin help?
WE RECOMMEND THE ARTICLE!
Amosin and Amoxicillin are taken for sore throat, bronchitis and a number of other infectious diseases. Read more >>
The solution can be used not only for injection into a vein or muscle, but also externally. In ophthalmology, indications for the use of Gentomycin injections include various infectious and inflammatory diseases affecting the organs of vision (as a primary or secondary lesion). These include:
- keratitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- keratoconjunctivitis;
- blepharitis;
- meibomite;
- dacryocystitis;
- iritis;
- endophthalmitis;
- stye, boil, abscess.
In case of an eye infection, it is important to pre-test the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics so that the treatment is not unnecessarily prolonged and ineffective! Among the pathologies of internal organs, the solution is indicated:
- infectious cholecystitis, cholangitis;
- inflammatory process in the renal parenchyma - pyelonephritis;
- cystitis, urethritis caused by the above microbes;
- peritonitis.
The drug is often recommended for complicated infections of the respiratory system - pneumonia, bronchitis, acute tracheitis. For sepsis, Gentamicin is most often administered together with other antibacterial agents (penicillins, cephalosporins).
The drug helps well with burns, extensive infections of the skin and subcutaneous soft tissues.
Gentamicin solution is used to wash festering wounds and treat ulcers - boils, canbuncles, gangrene, foci of streptococcal pyoderma, ulcers.
Directions for use and doses
The antibacterial agent Gentamicin must be prescribed for many pathological processes in the body:
- Acute sinusitis (in hospital treatment conditions). For this disease, an otolaryngologist prescribes intramuscular injections of the drug. The dose of the drug should be calculated based on the patient's weight. Typically, the required amount of antibacterial agent is 0.170 g per 1000 g of patient weight, which should be injected into the muscle in the morning and evening. The duration of therapy is no more than 7 days to avoid negative manifestations.
- Inflammation of the tonsils of the palate . For sore throat, antibiotics should be prescribed. Otherwise, complications from the cardiovascular system may develop. Gentamicin for inflammation of the tonsils should be used intramuscularly and only as prescribed by a physician. The course of treatment for different types of the disease is different, but no more than 10 days. The amount must be calculated according to the age and weight of the patient. Children under 12 years of age – 0.003 g per 1000 g of weight. From 12 years of age and older, the dose of the drug must be increased to 5 mg/kg, which should be divided by the number of times prescribed by the general practitioner.
- Prostate infections . The disease should be treated with Gentamicin, both intramuscularly and intravenously. The amount of the drug must be calculated based on the type and complexity of the pathological process. The drug should be administered intramuscularly twice a day. Intravenous use should be limited to once daily IV use. The dose of the drug is 0.100 g-0.170 g for one-time intramuscular use. When administered by drip, the amount of the drug for 24 hours should be administered once. Therapy should be continued for 10 days, unless otherwise recommended by a urologist.
- Contagious diseases of the digestive system . For intestinal infections, depending on the causative agent of the pathological process, Gentamicin should be used. This drug does not allow microorganisms to develop resistance to the antibiotic for a long time, which very often happens with intestinal infections. The duration of therapy for pathologies of the digestive system should not exceed five days. The drug should be administered intramuscularly every 12 hours. The amount of the product must be calculated in accordance with the weight and age of the patient. For adults (patients over 12 years of age), the drug should be prescribed in a daily dosage of up to 5 g. Children's age - the amount of medication corresponds to no more than 3 g per day.
- Reovirus infection . Rotavirus in the body affects not only the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, but also the respiratory system. To prevent a secondary infection from occurring, antibacterial agents should be used to treat this pathology. The drug Gentamicin is a universal antibacterial agent. The medicine should be used for 7 days in the morning and evening. The dose of the drug is calculated based on the patient’s body weight. Patients over 12 years of age should take the drug in an amount of 1.7 mg per 1 kg of weight at a time. Children need to use no more than 3 g of medication per day, which must be divided into several times (in accordance with the recommendations of an infectious disease specialist).
- Ear infection . For otitis, antibacterial intramuscular drugs should be prescribed if local therapy has not brought a positive result. Gentamicin should be considered a priority drug. The drug is universal and fights many microorganisms. For the treatment of otitis media, antibiotics should be used only as prescribed by an otolaryngologist, due to the large number of negative manifestations. Treatment with the drug should not last longer than 7 days.
To make an intramuscular injection you should know certain rules:
- For hypodermic injections, it is necessary to take syringes with a volume of 2.5-3 ml and insert the needle to a depth of no more than 2 cm.
- Antibacterial agents must be injected into the muscle. To do this, you should take a syringe with a volume of 5 ml (the diameter of the needle is designed for the density of the muscle). The injection site for the medication is usually the upper, outer quarter of the gluteal muscle.
- Before using the medicine, the skin should be wiped with ethyl alcohol.
- Select the drug into a pre-prepared syringe.
- Slightly release the medicinal liquid through the needle using a piston so that there is no air.
- It is necessary to insert the needle at an angle of 45-60 degrees into the relaxed gluteal muscle.
Gentomycin for injections must be administered correctly, at an angle of 45 degrees. - After the manipulation, you should remove the needle from the body and press down the injection site with a cotton swab with alcohol to avoid infection and the formation of a hematoma.
Side effects and overdose
When taking the medication, the following undesirable effects may occur:
- dyspepsia (nausea, vomiting, salivation, diarrhea, colitis);
- decreased appetite or complete loss of it;
- cephalgia;
- confusion;
- weight loss;
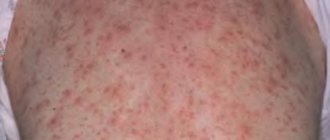
- allergies (itching, rash);
- anaphylactic shock;
- fever;
- dizziness;
- pain at the injection site;
- Quincke's edema;
- blood diseases;
- tinnitus, hearing problems up to deafness;
- muscle cramps and numbness;
- epileptic seizures;
- disturbances in the functioning of the genitourinary system;
- weakness;
- anemia;
- changes in the composition of the blood, an increase in certain cells;
- psychosis (in children).
If any unwanted effects occur, it is recommended to consult your doctor. The specialist will reduce the dose or discontinue the drug, and select its analogue.
Cases of overdose are rare. Manifests itself as an increase in adverse reactions:
- breathing problems (up to respiratory arrest);
- nausea,
- vomit;
- kidney damage;
- dysfunction of the auditory organs.
For recovery, blood cleansing is indicated. Adult patients are given Atropine, followed a couple of minutes later by a combination of Prozerin and calcium supplements. First, a minimum dose of Proserin (3 ml) is administered. If this is not enough to alleviate the patient’s condition, then the same amount of the substance is reintroduced.
In case of overdose, children are given only calcium supplements. For breathing problems, ventilation is indicated.
Use in childhood
The use of the drug for the treatment of children under 3 years of age is necessary only for health reasons.
At the age of up to 5 years, the drug should be used at the rate of 0.015 g - 0.030 g, from 6 years to 12 years - 3 mg/kg. The duration of therapy is determined by a pediatrician.
Price
You can buy the medicine through online platforms or pharmacy kiosks at prices that depend on the form of release of the drug and the trade markup. Approximate cost of drugs in Moscow pharmacies:
| Product type | Internet price, in rubles | Pharmacy cost, in rubles |
| Ampoules 4% 2 ml 10 pcs. | 45 | 50 |
| Ointment 0.1% 15 g 72 | 80 | |
| Powder 10 g | 25 | 30 |
| Eye drops 5 ml | 30 | 35 |
Side effects
Negative manifestations from the use of Gentamicin can occur in many body systems.
Gastrointestinal tract:
- vomiting reflex;
- increase in ASAT and ALT;
- increase in the amount of bilirubin.
Blood:
- decreased red blood cells;
- decreased leukocyte levels;
- granulocyte deficiency;
- low platelet count.
Nervous system:
- migraine;
- weakness;
- decreased hearing due to the effect of the drug on the nerves;
- unsteadiness of gait.
Immunological disorders:
- nettle rash;
- chills;
- anaphylactic shock;
- excessive sensitivity to ultraviolet rays.
Instructions for use of Gentamicin
It is best to use Gentamicin after determining the sensitivity of the microflora that caused the disease to it.
The instructions indicate the average dosages used for treatment:
- for urinary tract infections for adolescents over 14 years of age. and adults, a single dose is 0.4 mg per kilogram of weight, and a daily dose is 0.8-1.2 mg per kilogram of the patient’s weight.
- For sepsis and other severe infections, a single dose is 0.8-1 mg per kilogram, and a daily dose is 2.4-3.2 mg.
The maximum dose is 5 mg per kilogram per day.
For children under 14 years of age, Gentamicin sulfate is prescribed only for special indications.
The daily dose for infants and newborns is 2-5 mg per kilogram of weight. Children from 1-5 years old. Prescribe 1.5-3.0 mg per kilogram, for children 6-14 liters. – 3 mg per kilogram.
The maximum dosage of Gentamicin for children of different age categories is 5 mg/kg/day.
The daily dose is usually divided into two or three doses. The course lasts on average 7-10 days. Gentamicin injections are usually given intravenously for 2-3 days, and then switch to intramuscular injections.
For intramuscular administration, Gentamicin sulfate is used in the form of a ready-made solution or diluted 2 ml. sterile water powder. For intravenous injections of Gentamicin, only a ready-made solution can be used.
Gentamicin cream or ointment is used for purulent skin inflammation, folliculitis, and furunculosis. At the same time, the affected areas are lubricated two to three times a day for one to two weeks.
For conjunctivitis, keratitis, and other infectious eye diseases, Gentamicin drops are used - three to four times a day.
Overdose
If Gentamicin is used incorrectly, symptoms of overdose may occur.
These include:
- strengthening of the gag reflex;
- unsteadiness of gait;
- respiratory failure;
- muscle damage.
To relieve symptoms, neuromidin, calcium gluconate and calcium chloride should be administered (intravenously only).
Drug interactions
When using an antibacterial drug, you should be aware of the necessary interactions:
- The simultaneous use of Gentamicin with aminoglycoside drugs, tricyclic glycopeptides and lactam antibiotics causes a risk of damage to the auditory nerves.
- Use of NSAIDs with drugs reduces the rate of elimination of the antibacterial agent from the body, which can lead to intoxication.
- Using Gentamicin with medications that contain opiates may create a peripheral nerve block.
- Possible intoxication of the body increases with simultaneous use of an antibacterial agent with diuretic drugs.
special instructions
The use of the medication requires caution. Rules of use are described in the special instructions section of the instructions:
- the medication is used with caution in myasthenia gravis, parkinsonism, and renal dysfunction;
- During therapy, monitoring of renal, auditory and vestibular function is necessary;
- external use of the product for a long time on large areas of the skin can cause a resorptive effect, especially in chronic renal failure;
- if the patient suffers from infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract and is treated with Gentamicin, he needs to drink more fluid;
- during treatment with aminoglycosides, it is necessary to monitor creatinine clearance, magnesium, and potassium levels in the blood serum, especially in elderly people;
- the toxicity of the drug depends on the plasma concentration - at 10 mcg/ml, damage to the vestibular apparatus is possible;
- ototoxicity during treatment with the drug is manifested by dizziness, tinnitus, hearing loss, it is recommended to conduct audiometry 1-2 times a week and stop therapy if negative symptoms appear;
- when using Gentamicin, microbial resistance, antibiotic-associated diarrhea, and pseudomembranous colitis may develop;
- for burns with a body area of more than 20%, cystofibrosis, ascites, sepsis, endocarditis, chronic renal failure with hemodialysis, the entire daily dose of the drug solution cannot be administered;
- the active substance in the composition can inhibit spinal neuromuscular transmission, so it should be used with caution in diseases of the nerves and muscles, using muscle relaxants;
- sodium metabisulfite in the solution may cause hypersensitivity reactions;
- one ampoule contains 2.13 mg of sodium, which is important for people on a diet low in this element;
- During treatment with the drug, you should refrain from driving vehicles and machinery, as it reduces concentration, visual acuity and the speed of psychomotor reactions, and can cause drowsiness, convulsions, and epileptic seizures.
- Withdrawal syndrome - how to relieve it at home. Signs of withdrawal in addicted people
- How to password protect a folder on your computer
- How to cast on stitches on knitting needles for beginners
Analogs
The pharmacological industry produces drugs similar to the drug Gentamicin:
| Drug name | Composition of the medicine | Application area | Cost, rub. |
| Amibiotic | Semi-synthetic antibiotic imikacin | Inflammatory pathologies in the body caused by the introduction of gram-negative bacteria | 240 rub. - 300 rub. |
| Braxon | Antibacterial substance of the amyglycoside series tobramycin | Severe infectious diseases whose pathogens are resistant to penicillins | 720 rub. – 810 rub. |
| Kanamycin powder for injection | 1st generation antibiotic kanamycin | Purulent pathological processes in the body | 37 rub. – 50 rub. |