Metronidazole is an antimicrobial and anthelmintic agent that can be used to treat a variety of diseases. In medical practice, doctors often use Metronidazole in a dropper to eliminate bacteria, as well as various types of helminths, from the human body. It is worth noting that the drug is administered not only in the form of a solution, but also in tablets, suppositories and as an ointment.
Metronidazole is a medicinal solution that is used to kill helminths and bacteria of various kinds. It is worth noting that the drug is very effective in fighting different types of helminths, which is why this particular solution is used to treat patients in a hospital. In the process of introducing Metronidazole in a dropper into a person’s blood, the main component penetrates cells and tissues, and then begins to gradually destroy helminths. It is worth considering that each type of disease requires a certain dosage; the result of treatment will depend on the correctly selected dose.
How does the medicine work?
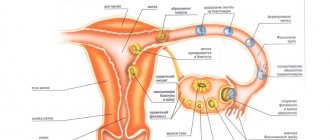
When the active component penetrates the human blood, it begins to spread throughout the body, and then infects helminths and affects protozoan cells. This causes the parasites' DNA to gradually break down, and then the worms die. It is very important to use the drug in the correct dosage; only the attending physician can prescribe the appropriate dose, and the result of therapy will depend on this.
For what diseases is Metronidazole used:
- for viral diseases;
- used to destroy bacterial infections;
- destroys gram-positive microorganisms.
Important! This drug can be used in conjunction with Amoxicillin, in which case the effectiveness of treatment increases, which makes it possible to eliminate Helicobacter pylori.
pharmachologic effect
Antiprotozoal and antimicrobial drug, a derivative of 5-nitroimidazole.
The mechanism of action is the biochemical reduction of the 5-nitro group by intracellular transport proteins of anaerobic microorganisms and protozoa. The reduced 5-nitro group interacts with the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of the microbial cell, inhibiting the synthesis of their nucleic acids, which leads to the death of bacteria.
Active against Trichomonas vaginalis, Entamoeba histolytica, Gardnerella vaginalis, 2 Giardia intestinalis, Lamblia spp., as well as gram-negative anaerobes Bacteroides spp. (including Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides distasonis, Bacteroides ovatus, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, Bacteroides vulgatus), Fusobacterium spp., Veillonela spp., Prevotella (P.bivia, P.buccae, P.disiens), and some gram-positive anaerobes ( sensitive strains of Eubacterium spp., Clostridium niger, Peptococcus spp., Peptostreptococcus spp.). The minimum inhibitory concentration for these strains is 0.125-6.25 μg/ml.
In combination with amoxicillin, it is active against Helicobacter pylori (amoxicillin suppresses the development of resistance to metronidazole).
Aerobic microorganisms and facultative anaerobes are not sensitive to metronidazole, but in the presence of mixed flora (aerobes and anaerobes), metronidazole acts synergistically with antibiotics effective against common aerobes. Increases the sensitivity of tumors to radiation, causes sensitization to alcohol (disulfiram-like effect).
Indications for use
The instructions for using Metronidazole in solution indicate that this drug can be used not only by adults, but also by young children, which is why the solution is often used in pediatrics. This product is quite affordable and at the same time has a minimal toxicity index. Partial elimination of the drug from the body occurs six hours after the last dose. If treatment is carried out in childhood, the medication can be eliminated from the body from one day to thirty hours.
This medicine contains an antibiotic, as well as other excipients. Thanks to its special composition, the medicine easily penetrates into the cells of human organs, and distribution occurs evenly. Most of Metronidazole is excreted by the kidneys, while the remainder is excreted in the feces.
Diseases for which the solution is prescribed:
- systemic infections that have worsened due to the development of anaerobic microorganisms;
- giardiasis of any stage;
- trichomonas urethritis;
- intestinal and extraintestinal amebiasis;
- trichomonas vaginitis;
- cutaneous form of leishmaniasis.
Metronidazole, 24 pcs., 250 mg, tablets
Gastrointestinal disorders: epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, glossitis, stomatitis, metallic taste in the mouth, decreased appetite, anorexia, dry oral mucosa, constipation, pancreatitis (reversible cases), discoloration tongue / “coated tongue” (due to the growth of fungal microflora). Immune system disorders: angioedema, anaphylactic shock.
Nervous system disorders: peripheral sensory neuropathy, headache, convulsions, dizziness; the development of encephalopathy and subacute cerebellar syndrome (impaired coordination and synergism of movements, ataxia, dysarthria, gait disturbances, nystagmus, tremor), which are reversible after discontinuation of metronidazole, has been reported; aseptic meningitis.
Mental disorders: psychotic disorders, including confusion, hallucinations; depression, insomnia, irritability, increased excitability.
Visual disturbances: transient visual disturbances, such as diplopia, myopia, blurred contours of objects, decreased visual acuity, impaired color perception; neuropathy optic neuritis.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: agranulocytosis, leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract: increased activity of “liver” enzymes (aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase). The development of cholestatic or mixed hepatitis and hepatocellular liver damage, sometimes accompanied by jaundice: cases of liver failure requiring liver transplantation have been observed in patients treated with metronidazole in combination with other antibacterial agents.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: rash, itching, skin flushing, urticaria, pustular skin rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Renal and urinary tract disorders: brownish-reddish coloration of urine due to the presence of a water-soluble metabolite of metronidazole in the urine; dysuria, polyuria, cystitis, urinary incontinence, candidiasis.
General disorders: fever, nasal congestion, arthralgia, weakness.
Laboratory and instrumental data: flattening of the T wave on the electrocardiogram.
Instructions for use by adults
When using such a solution, the doctor must take into account all possible side effects, as well as contraindications to the medicine. This is very important, since the medication can be harmful to health if used incorrectly. If you need to find out what dosage should be used to treat parasitic infestations or diseases caused by infection, it is better to seek help from a doctor. The doctor will be able to more accurately determine the dosage, in addition, the solution is most often used in hospital settings.
If Metronidazole is prescribed to a child twelve years of age or older, then half to one gram of an antibacterial agent can be administered intravenously, and the administration process will last from half an hour to sixty minutes. After this, the patient is prescribed 500 mg of the active substance, which must be administered intravenously every eight hours. It is very important to correctly calculate the rate of administration; it should not be more than five milligrams per minute. Treatment with this method lasts for one week; if after the course the patient feels better, the doctor can transfer the patient to maintenance therapy.
Metronidazole – powder, solution, suspension, tablets
Orally and parenterally.
Orally, during or after meals (or with milk), without chewing.
For trichomoniasis - 250 mg 2 times a day for 10 days or 400 mg 2 times a day for 5-8 days. Women must be additionally prescribed in the form of vaginal suppositories or tablets. If necessary, you can repeat the course of treatment or increase the dose to 0.75-1 g/day. Between courses you should take a break of 3-4 weeks with repeated control laboratory tests. An alternative treatment regimen is to prescribe 2 g once to the patient and his sexual partner.
Children 2-5 years old - 250 mg/day; 5-10 years - 250-375 mg/day, over 10 years - 500 mg/day. The daily dose should be divided into 2 doses. The course of treatment is 10 days.
For giardiasis - 500 mg 2 times a day for 5-7 days.
Children under 1 year old - 125 mg/day, 2-4 years old - 250 mg/day, 5-8 years old - 375 mg/day, over 8 years old - 500 mg/day (in 2 doses). The course of treatment is 5 days.
For giardiasis - 15 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses for 5 days.
Adults: for asymptomatic amebiasis (if a cyst is detected), the daily dose is 1-1.5 g (500 mg 2-3 times a day) for 5-7 days.
For chronic amebiasis, the daily dose is 1.5 g in 3 divided doses for 5-10 days, for acute amoebic dysentery - 2.25 g in 3 divided doses until the symptoms stop.
For liver abscess, the maximum daily dose is 2.5 g in 1 or 2-3 doses, for 3-5 days, in combination with antibiotics (tetracyclines) and other methods of therapy.
Children 1-3 years old - 1/4 adult dose, 3-7 years old - 1/3 adult dose, 7-10 years old - 1/2 adult dose.
For balantidiasis - 750 mg 3 times a day for 5-6 days.
For ulcerative stomatitis, adults are prescribed 500 mg 2 times a day for 3-5 days; In this case, the drug is not indicated for children.
For pseudomembranous colitis - 500 mg 3-4 times a day.
For eradication of Helicobacter pylori - 500 mg 3 times a day for 7 days (as part of combination therapy, for example in combination with amoxicillin 2.25 g/day).
When treating anaerobic infection, the maximum daily dose is 1.5-2 g.
In the treatment of chronic alcoholism, 500 mg/day is prescribed for a period of up to 6 (not more than) months.
To prevent infectious complications - 750-1500 mg/day in 3 doses 3-4 days before surgery or 1 g once on the first day after surgery. 1-2 days after surgery (when oral administration is already allowed) - 750 mg/day for 7 days.
In case of severe renal dysfunction (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min), the daily dose should be reduced by 2 times.
Suspension for oral administration. Anaerobic bacterial infections: children - 7 mg/kg every 8 hours, course of treatment - 7-10 days; Giardiasis: children 2-5 years old - 200 mg/day, 5-10 years old - 300 mg/day, 10-15 years old - 400 mg/day. The duration of treatment for giardiasis is 5 days. The course of treatment can be repeated after 10-15 days
Parenterally. For adults and children over 12 years of age, an initial dose of 0.5-1 g IV drip (infusion duration is 30-40 minutes), and then every 8 hours, 500 mg at a rate of 5 ml/min. If well tolerated, after the first 2-3 infusions they switch to jet administration. The course of treatment is 7 days. If necessary, intravenous administration is continued for a longer time. The maximum daily dose is 4 g. According to indications, switch to maintenance oral administration at a dose of 400 mg 3 times a day. Children under 12 years of age are prescribed according to the same regimen in a single dose of 7.5 mg/kg.
For purulent-septic diseases, 1 course of treatment is usually carried out.
For preventive purposes, adults and children over 12 years of age are prescribed 0.5-1 g intravenously on the eve of surgery, on the day of surgery and the next day - 1.5 g / day (500 mg every 8 hours). After 1-2 days, they switch to maintenance therapy orally. For patients with chronic renal failure and creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min and/or liver failure, the maximum daily dose is no more than 1 g, the frequency of administration is 2 times a day.
As a radiosensitizing drug, it is administered intravenously at a rate of 160 mg/kg or 4-6 g/sq.m of body surface 0.5-1 hour before the start of irradiation. Apply before each irradiation session for 1-2 weeks. During the remaining period, radiation treatment is not used. The maximum single dose should not exceed 10 g, course dose - 60 g. To relieve intoxication caused by radiation, drip administration of a 5% dextrose solution, Hemodez or 0.9% NaCl solution is used.
For cervical and uterine cancer, skin cancer, they are used in the form of local applications (3 g dissolved in a 10% DMSO solution), moisten tampons, which are used topically, 1.5-2 hours before irradiation). In case of poor tumor regression, applications are carried out throughout the entire course of radiation therapy. If there is a positive dynamics of tumor clearance from necrosis - during the first 2 weeks of treatment.
How is the medicine used for children under 12 years of age?
If the patient is under 12 years old, then the treatment regimen will be the same, but the dosage calculation will be slightly different; the attending physician will have to calculate the dosage depending on the exact body weight of the child, as well as his age group. As indicated in the instructions, the doctor should use 7.5 mg of the drug per kilogram of the child’s weight. Metronidazole drips are given for seven or eight days. After this, the doctor may prescribe intramuscular administration of the drug if the treatment has shown good results.
Contraindications for use
It is not permitted to use the medicine in ampoules or solution for intravenous administration in all cases. There is a whole list of contraindications for which the use of the medicine is strictly prohibited.
Main contraindications:
- The medicine cannot be used in the first trimester of pregnancy; in the second and third periods, the doctor may prescribe the use of the medicine, but a dosage adjustment must be used;
- period of feeding the baby with breast milk;
- various lesions of the patient’s central nervous system;
- multiple sclerosis and epileptic seizures;
- child's age up to two years;
- disorders of the kidneys;
- allergic reactions to the main component or auxiliary additives;
- acute liver failure; fatty hepatosis and hepatitis, as well as cirrhosis;
- leukopenia.
Helpful information! This drug may not combine well with certain types of medications. During the treatment period, the doctor should stop taking any anticoagulants, Phenytoin, as well as Cimetidine and Phenobarbital. In addition, reviews from doctors indicate that the medicine does not interact well with alcoholic beverages and alcohol-based sedatives.
Pharmacokinetics
With intravenous administration of 500 mg of metronidazole over 20 minutes to patients with anaerobic infection, the concentration of the drug in the blood serum was 35.2 μg/ml after an hour, 33.9 μg/ml after 4 hours, 25.7 μg/ml after 8 hours .
The drug has high penetrating ability, reaching bactericidal concentrations in most tissues and body fluids, including lungs, kidneys, liver, skin, cerebrospinal fluid, brain, bile, saliva, amniotic fluid, abscess cavities, vaginal secretions, seminal fluid, breast milk. Binding to blood proteins is weak and does not exceed 10-20%. With normal bile formation, the concentration of metronidazole in bile after intravenous administration may significantly exceed the concentration of metronidazole in the blood plasma.
Metronidazole is excreted by the kidneys - 63% of the dose, 20% of the drug is excreted unchanged. The half-life of metronidazole is 6-7 hours. Renal clearance is 10.2 ml/min.
In patients with impaired renal function, after repeated administration of the drug, accumulation of metronidazole in the blood serum may be observed. Therefore, in patients with severe renal failure, the frequency of taking metronidazole should be reduced.
Side effects from treatment with Metronidazole
There is a whole list of symptoms that may appear immediately after using this drug. It should be clarified that most of them manifest themselves when the solution is taken for too long, or when the drug is overdosed.
Side effects:
- neutropenia;
- stool disorders, expressed in diarrhea or constipation;
- leukopenia;
- colic in the intestines;
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- attacks of nausea and heartburn;
- dry mucous membranes;
- stomatitis;
- pancreatitis and glossitis develop;
- disorientation may occur;
- a violation of coordination appears;
- dizziness and confusion may occur;
- migraines and increased excitability often occur;
- weakness and insomnia are often observed;
- ataxia may occur;
- hallucinations occur;
- Allergic reactions are common;
- fever and nasal congestion appear;
- urine turns dark;
- women develop candidiasis;
- Cystitis or polyuria may occur.
Important! The list of side effects is very long, it is for this reason that the dosage of this medicinal solution should not be exceeded. Only the attending physician can prescribe treatment.
Metronidazole
Gastrointestinal disorders
: epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, glossitis, stomatitis, taste disturbances (“metallic” taste in the mouth), decreased appetite, anorexia, dry oral mucosa, constipation, pancreatitis (reversible cases), change in tongue color / “coated tongue” (due to the growth of fungal microflora).
Immune system disorders
: angioedema, anaphylactic shock.
Nervous system disorders
: peripheral sensory neuropathy, headache, convulsions, dizziness, the development of encephalopathy and subacute cerebellar syndrome (impaired coordination and synergism of movements, ataxia, dysarthria, gait disturbances, nystagmus, tremor) has been reported, which are reversible after discontinuation of metronidazole, aseptic meningitis.
Mental disorders
: psychotic disorders, including confusion, hallucinations; depression, insomnia, irritability, increased excitability.
Visual disorders
: transient visual impairments, such as diplopia, myopia, blurred contours of objects, decreased visual acuity, impaired color perception; neuropathy/optic neuritis.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
: agranulocytosis, leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract
: increased activity of “liver” enzymes (aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase), development of cholestatic or mixed hepatitis and hepatocellular liver damage, sometimes accompanied by jaundice; In patients treated with metronidazole in combination with other antibacterial agents, cases of liver failure requiring liver transplantation have been observed.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
: rash, itching, skin flushing, urticaria, pustular skin rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Renal and urinary tract disorders
: staining of urine in a brownish-reddish color, caused by the presence of a water-soluble metabolite of metronidazole in the urine, dysuria, polyuria, cystitis, urinary incontinence, candidiasis.
General and administration site disorders
: fever, nasal congestion, arthralgia, weakness, thrombophlebitis (pain, hyperemia or swelling at the injection site). Laboratory and instrumental data: flattening of the T wave on the electrocardiogram.
Additional recommendations
If the patient has a mixed infection, the doctor may prescribe not only the use of this drug, but also additional antibacterial medications. But it is very important to remember that mixing two medications in one bottle is strictly prohibited. The product can be administered as an injection or as a drip using a dropper. The instructions in the instructions indicate that the solution is not recommended for use under 18 years of age if it is mixed with Amoxicillin.
It is worth noting that injections and droppers with such a substance are not combined with the use of ethanol, as this can be very dangerous. As a result, a disulfiram-like reaction begins to develop, which is expressed by painful sensations in the head, severe attacks of nausea and repeated vomiting. Redness of some areas of the skin may be observed, as blood begins to actively flow to them.
With sufficiently long-term treatment, the doctor must constantly monitor the patient’s blood composition, monitoring should be carried out every week. The thing is that the use of Metronidazole leads to the fact that the volume of leukocytes in the blood is greatly reduced. Termination of treatment is possible only if the infection begins to gradually decrease and the patient’s condition returns to normal. Only the attending physician can complete the course of treatment, and only if all the patient’s indications are normal. When a patient has trichomoniasis, both partners should undergo the treatment process.
Important! If treatment is carried out on only one infected person, infection may occur again.
special instructions
Regionally approved standards for antibiotic use should be followed.
It is not recommended to use metronidazole in combination with amoxicillin in patients under 18 years of age.
With long-term therapy, it is necessary to monitor the blood picture. With leukopenia, the possibility of continuing treatment depends on the risk of developing an infectious process.
The appearance of ataxia, dizziness and any other deterioration in the neurological status of patients requires cessation of treatment. May immobilize treponemes and lead to a false-positive Nelson test.
Colors urine dark.
When treating trichomonas vaginitis in women and trichomonas urethritis in men, 10 it is necessary to abstain from sexual activity. Simultaneous treatment of sexual partners is mandatory. Treatment does not stop during menstruation.
After treatment for trichomoniasis, control tests should be carried out during three consecutive cycles before and after menstruation.
After treatment of giardiasis, if symptoms persist, after 3-4 weeks, carry out 3 stool tests at intervals of several days (in some successfully treated patients, lactose intolerance caused by infestation may persist for several weeks or months, resembling the symptoms of giardiasis).
How does Metronidazole interact with other medications?
If the solution is used for treatment together with Disulfiram, it may worsen side effects that are associated with the patient’s nervous system. In order not to harm your health, these two drugs should be used separately, and you must wait at least two weeks between their doses.
Cimetidine, together with Metronidazole, can lead to the development of a large number of side effects, which will have a very negative impact on the patient’s health. If we talk about drugs from the sulfonamide group, then this combination will help enhance the effect on microbes, thereby helping to speed up the healing process. The use of Phenobarbital leads to the fact that Metronidazole, entering the liver, is quickly broken down, because of this the concentration of the drug in the blood decreases. This significantly reduces the effect of the drug. Also, the effectiveness of the solution will be greatly reduced if the medication is used in conjunction with Prednisolone.
Interaction with other drugs
Metronidazole for intravenous infusion is not recommended to be mixed with other medications!
When using metronidazole for injection, there is little interaction with other drugs, but caution should be exercised when used simultaneously with certain drugs.
Warfarin and other indirect anticoagulants.
Metronidazole enhances the effect of indirect anticoagulants, which leads to an increase in the time of prothrombin formation.
Disulfiram.
Concomitant use may lead to the development of various neurological symptoms, so metronidazole should not be prescribed to patients who have taken disulfiram within the last two weeks.
Cimetidine
inhibits the metabolism of metronidazole, which may lead to an increase in its concentration in the blood serum and an increased risk of side effects.
Simultaneous use of drugs that stimulate microsomal oxidation enzymes in the liver ( phenobarbital, phenytoin
) may accelerate the elimination of metronidazole, resulting in a decrease in its plasma concentration.
In patients receiving long-term treatment with lithium
in high doses, when using metronidazole, it is possible to increase the concentration of lithium in the blood plasma and develop symptoms of intoxication.
The antimicrobial effect of metronidazole is enhanced in combination with sulfonamides and antibiotics.
With the combined use of metronidazole and cyclosporine
An increase in the concentration of cyclosporine in the blood plasma may be observed.
Metronidazole reduces the clearance of fluorouracil,
which may cause an increase in the toxicity of the latter.
When used concomitantly, metronidazole may increase plasma concentrations of busulfan.
It is not recommended to combine with non-depolarizing muscle relaxants (vecuronium bromide).
Metronidazole is incompatible with ethanol (disulfira-like reactions develop when used together).
Reviews about the use of Metronidazole
Karina, 26 years old
“The doctor prescribed this antimicrobial drug to me in the form of tablets, since I was diagnosed with candidiasis. I took it in the dosage that was prescribed by the doctor. As a result, I not only got rid of an unpleasant gynecological disease, but also improved the appearance of my skin. The drug is an antimicrobial agent, so it quickly restored the beauty of the skin, eliminating very serious pimples. I do not recommend using the solution for treatment at home yourself, as the medicine has a lot of side effects. It is best to seek help from a doctor, even if there are indications for the use of this medication.”
Victor, 45 years old
“After I had gastric surgery, the doctor prescribed Metronidazole intravenously. The first dose of 100 ml had no effect on my well-being, but then I encountered a lot of side effects. At first there was severe nausea, then problems with stool arose. All this was dangerous for my health, since the surgical intervention took place not so long ago. The attending physician replaced the drug with a similar one, after which all the unpleasant symptoms disappeared.”
Maria, 22 years old
“During an examination at the clinic, the doctor found Giardia in my stool, since the stage of infection was not serious, the doctor prescribed me to take this drug. I used Metronidazole in the form of a solution for intramuscular administration. After a few days of treatment, she underwent repeated tests, which showed a negative result. I didn’t notice any side effects, just a little headache. In general, the drug completely coped with the task, in addition, the skin on the face became clearer.”