- October 22, 2018
- Other drugs
- Inna Makagon
Glucose 40% ensures replenishment of energy costs. When a solution is infused into a vein, intravascular excess hydrostatic pressure increases, the flow of fluid from tissues into the blood improves, metabolism accelerates, toxic substances that form in the intestines are neutralized, absorbed into the blood and enter the liver.
In addition, the drug enhances the contractile function of the myocardium, and the volume of urine increases. When using a hypertonic glucose solution, glycogen deposition in the liver is activated. Glucose also acts as a source of micronutrients and energy that are necessary for the functioning of the body.
Composition of 40% glucose
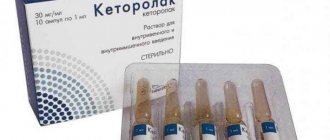
The product is available to patients in the form of a clear, sweet solution without sediment, packaged in clear glass ampoules of 10 and 20 ml. The concentration of the active substance in the composition can be not only 40%, but also 10 or 5%. The first option is used quite often.
The product contains glucose monohydrate in the amount of 0.4 g per 1 ml of solution. Due to it, the main therapeutic effect is achieved. The solution also contains auxiliary ingredients in the form of sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid, and water for injection.
Additional substances do not have therapeutic properties; they are present to maintain a balanced chemical formula. The solution is not always transparent; sometimes it may have a slightly yellowish color. The ampoules are packaged in cardboard boxes.
In most cases, this package contains 10 ampoules. The product with a lower concentration of the active substance is available in bottles of 100 or 200 ml. Typically this solution has a glucose concentration of 5%.
The product is produced by different pharmaceutical companies, so the appearance of ampoules, bottles and packaging differs.
Calcium gluconate: dose, indications, scheme of action
Calcium gluconate is a honey pharmaceutical product aimed primarily at restoring adequate calcium levels in humans. It is actively used in medicine to normalize the physiological reactions of the human body, in which calcium ions play a role.
Calcium gluconate solution for injection is available ready-made and is a clear liquid without color or aroma. The working component of the solution is calcium gluconate. In 10 ml of solution it is 10% (1g). The excipients in the solution for injections are calcium saccharate and distilled water.
In pharmacies you can most often find a 10% solution, in which 1 mg of gluconate per 10 ml of water.
The liquid is contained in a clear glass ampoule.
The package contains 10 ampoules of 10 ml each.
Calcium ions, to the deficiency of which the body reacts so acutely, and which it extremely needs, play a role in the conduction of nerve impulses. They make sure that the organs and systems in the body can work correctly and harmoniously. After entering the body, calcium spreads throughout all its tissues and its role in metabolic processes immediately begins.
Strength of bones, normal blood clotting, increased production of adrenaline by the adrenal glands, decreased vascular permeability - all these processes are impossible without the usual calcium balance in the human body.
Important!
The ions of this substance help teeth and bones remain strong and strong.
The drug is prescribed for such conditions of the body when the level of calcium ions in a person’s blood decreases to a critical level.
Indications for use of calcium gluconate in the form of injections:
- treatment of allergic manifestations with the use of antihistamines.
- in the treatment of inflammatory conditions of any type and different localization.
- problems with kidney function, since the body loses calcium extremely quickly - it is excreted together with urine.
- hepatitis, which occurs with inflammation of the liver parenchyma, as well as in cases where the liver is exposed to any toxic effects.
- disruption of the thyroid gland (hypoparathyroidism) - due to this disease, the concentration of calcium in the blood decreases sharply. The product is not able to restore the lost functions of the glands; it only makes up for the lack of this element.
- the medicine is actively used as an auxiliary hemostatic agent for various bleedings - uterine, digestive, nasal, pulmonary.
- excessive permeability of cell walls.
- bearing a baby, lactation, menopause, intensive growth in children and adolescents - all those periods when the body feels a higher need for calcium.
- rickets and other disorders of vitamin D metabolism.
- bone fractures of any severity and increased fragility of bones.
- appearance of teeth in children.
- poisoning with certain types of salts and acids.
- frequent rhinitis, colds, bronchitis.
- osteoporosis.
- diet low in calcium.
- conditions when calcium is intensively washed out of the body - prolonged diarrhea, treatment with anti-epilepsy products, bed rest for a long time, and others.
Injections should not be used if the following signs are detected:
- individual intolerance to the main component.
- an increase in the concentration of calcium in a person’s blood to 6 meq/l - this also applies to those cases where the increase was already due to calcium injections taken.
- children's age is less than 15 years.
- various kidney diseases.
- excessively high blood clotting, in particular, a tendency to thrombus formation.
- pregnancy and lactation - calcium injections cannot be used specifically.
- excessive excretion of calcium in the urine.
- atherosclerosis.
Intramuscular injections can be carried out at home; intravenous calcium gluconate must be administered only in the treatment room.
The administration of the medicine is carried out extremely slowly - minutes. Preparing the product for the procedure involves heating it to +37 degrees.
Children under 14 years of age are prescribed 7 ml of the product, depending on the disease, once a day or one injection once a day.
For patients under 14 years of age: ml once a day, but administration in this case must only be intravenous. Intramuscular calcium injections should not be given to children - there may be necrotic tissue necrosis at the site of drug administration.
On a personal basis, the doctor must develop a scheme for administering injections, select a dose and determine the duration of the course of treatment.
This is influenced by the patient’s personal data: weight and height, gender, age group, disease and its severity.
Important! Self-administration of a calcium product in the form of injections is unacceptable. Only a doctor can assess the possible benefits and dangers.
Calcium gluconate is injected intramuscularly only into the gluteal muscle - the pain from the injection will not be so noticeable there. This will also avoid the formation of bumps and bruises, and the product will more quickly enter the bloodstream.
It is necessary to carefully disinfect the injection surface. Since necrosis or inflammation at the injection site may develop during implantation, it is necessary to take all safety measures - this will help to avoid complications.
Calcium gluconate injections are given with constant monitoring of electrolytes in the patient’s blood.
When receiving intramuscular injections, you should not take calcium pills right away.
Before starting treatment, it is imperative to ensure that there are no contraindications.
For pregnant women, calcium gluconate is prescribed in injections only in the latest versions - as a rule, during this period, pills with a similar effect are indicated.
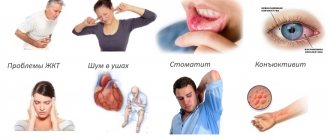
There are not very many side effects and unnecessary consequences from using the product in injections, but it is imperative to take into account the possibility of their occurrence.
The instructions for use describe the following side effects:
- as mentioned above, tissue necrosis at the injection site is a more common unnecessary consequence. It occurs mainly due to a violation of the technique of administering the medicine. To prevent this, each subsequent injection should be given to a different area. You can dilute the regimen of introducing the product with days of rest (with a regimen of every other day). In this case, the method of temporarily canceling injections is extremely effective.
- nausea, sometimes accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea or, on the contrary, constipation.
- decrease or increase in heart rate. This effect can occur if the drug is introduced too quickly.
- redness of the skin at the injection site, swelling and pain.
- there is a possibility of the formation of stones in the intestinal tract - in the case of long-term use of this pharmaceutical and (or) the use of large doses of the drug.
- kidney dysfunction, expressed in swelling of the legs, copious and frequent urination.
- the most serious consequences of taking it can be the development of anaphylactic shock and collapse (up to a fatal ending - very rarely). Then emergency help may be required.
Important! If, however, any of the side effects show themselves, then any administration of calcium must be stopped.
Cases of product overdose are usually associated with its long implementation period or excessively high dosage.
In cases of overdose, symptoms and conditions appear such as:
- nausea, vomiting, constipation.
- fatigue and excessive irritability.
- painful feelings in the peritoneum.
- muscle weakness.
- increased urine production.
- severe thirst and dry mouth.
- increased blood pressure.
- formation of kidney stones.
If an overdose is established, the upcoming use of the product is immediately canceled.
In particularly difficult situations, the patient is prescribed intravenous injections of calcitonin. There may be use of droppers with an antidote.
- The drug slows down the absorption process of drugs of the tetracycline class, pharmaceutical forms of iron and fluorine.
- Increases the toxicity of drugs used to combat heart failure.
- Food products such as spinach, various grains, bran, and rhubarb reduce the absorption of calcium from the digestive system.
Pharmacological properties
Glucose 40% in ampoules has pronounced restorative and hyperglycemic properties. It helps restore the balance of glucose in the blood and prevents its relapse. A similar condition is observed in many diseases, so the use of a safe solution significantly shortens the recovery period.
The substance also has stimulating properties. Helps increase physical strength and endurance, prevents weakness due to lack of sufficient glucose in the blood. The drug takes part in the metabolic process.
Characteristics of the compound, beneficial and harmful properties
Glucose is not a chemical substance in the periodic table of chemical elements (mendeleev’s table), however, any schoolchild must have at least a general understanding of this compound, because the human body extremely needs it. From the course of organic chemistry it is known that a substance consists of six carbon atoms connected to each other using covalent bonds. In addition to carbon, it contains hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The formula of the compound is C 6 H 12 O 6.
Glucose in the body is present in all tissues and organs with rare exceptions. Why is glucose needed if it is present in biological media? Firstly, this hexahydric alcohol is the most energy-intensive substrate in the human body. When broken down, glucose with the participation of enzymatic systems releases a huge amount of energy - 10 molecules of adenosine triphosphate (the main source of energy storage) from 1 molecule of carbohydrate. That is, this compound forms the main energy reserves in our body. But that's not all that glucose is good for.
C 6 H 12 O 6 is used to build many cellular structures. Thus, glucose in the body forms the receptor apparatus (glycoproteins). In addition, glucose, when in excess, accumulates in the form of glycogen in the liver and is consumed as needed. This compound is well used for poisoning. It binds toxic drugs, dilutes their concentration in the blood and other liquids, promoting their rapid elimination (removal) from the body, being essentially a powerful detoxifier.
But this carbohydrate contains not only benefits, but also harm, which gives reason to be wary of its content in biological media - in blood, urine. After all, glucose in the body, if its concentration is excessive, leads to glucotoxicity. The next stage is diabetes. Glucotoxicity occurs when proteins in our human tissues react chemically with a compound. In this case, their function is lost. A striking example of this is hemoglobin. In diabetes mellitus, some of it becomes glycated; accordingly, this portion of hemoglobin does not perform its important function properly. The same thing for the eyes - glycosylation of the protein structures of the eye leads to cataracts and retinal dystrophy. Ultimately, these processes can lead to blindness.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
After the product penetrates the blood, the active substance is distributed and penetrates into cells and tissues. The drug is able to accumulate in the body in small quantities, which explains its speed of action.
Glucose enters cells and is included in the metabolic process. As a result of its processing, the energy necessary for the full implementation of many biological processes in the body is released. Against the background of these changes, there is a significant improvement in brain function, since a fairly large amount of the substance is concentrated in the nerve tissues.
When glucose is processed, a large amount of energy is produced in the form of ATP. This ingredient takes part in almost all vital processes of the patient’s body, helps replenish energy deficits, and prevents loss of strength due to poor diet.
The product also has other effects:
- The composition ingredient stimulates blood filtration, which increases daily diuresis and helps prevent the development of urolithiasis against the background of stagnant urine.
- Glucose has a beneficial effect on the condition of the myocardium, increases its contractility and prevents the spread of ischemia if it is already present.
- The substance helps accelerate tissue regeneration and increase cell metabolism.
- Prevents the rapid destruction of new cells.
- Activates the liver, leading to the deposition of glycogen in it, which takes part in metabolic processes.
- Stimulates redox processes, which help to significantly improve the condition of various disorders.
As a result of this effect, patients feel relief. But the medicine can significantly improve the condition only in combination with other medications. Self-use of the medicine sometimes brings relief if the symptoms are associated with a critical and sudden decrease in blood glucose levels.
Glucose tablets
The carbohydrate is a colorless, odorless crystalline powder, highly soluble in water, with a sweet taste. Glucose is sold in pharmacies in the form of tablets and powder for oral administration. For parenteral use, solutions are intended with a concentration of the active component of 5, 10, 20, 40% in glass or plastic containers of 200, 250, 400, 500, 1000 ml, which are used for infusion (using droppers), or in ampoules of 5, 10, 20 ml – for intravenous administration.
Composition and release form
The tablets have a sweet taste, white color, round shape, flat surface with beveled edges and a dividing strip. The active ingredient is dextrose monohydrate. The composition of glucose and other components in one tablet is presented in the table:
| Component name | Active substance content |
| Active element: | |
| dextrose monohydrate | 1 (0.5) gram |
| Excipients: | |
| potato starch | |
| talc | |
| calcium stearate | |
| stearic acid |
pharmachologic effect
Glucose (dextrose) is a monosaccharide. It is found in the juice of grapes and other berries, so it received an additional name - grape sugar. Glucose units consist of disaccharides (maltose, lactose, sucrose) and oligosaccharides (cellulose, starch, glycogen). In the digestive tract, complex saccharides are broken down into glucose and fructose. As a monosaccharide, the substance is present in the blood, lymph, brain, skeletal muscles and myocardium.
Glycogen deposited in the body also serves as a source of energy - it is broken down into dextrose if necessary. Regulation of the balance of monosaccharide and oligosaccharide is carried out using enzymes. Insulin reduces the level of glucose in the blood, and its antagonists increase the concentration of sugar: glucagon, adrenaline, thyroxine, triiodothyronine. If the activity of the endocrine or central nervous system is disrupted, an excessive increase in sugar levels can occur and hyperglycemia or a sharp drop in its concentration - hypoglycemia.
Dextrose is involved in carbohydrate metabolism and affects metabolic processes:
- Glucose in the body is necessary for the complete breakdown of fats; if there is a deficiency of the substance, fatty acids accumulate (acidosis, ketosis is observed).
- In the process of glucose metabolism, adenosine triphosphoric acid is formed, which is the body's source of energy.
- A hypertonic dextrose solution is capable of: “squeezing” liquid into the bloodstream from organs and tissues, and with it, toxins and removing them from the body; increase the amount of urine; enhance the activity of the heart muscle; dilate blood vessels.
- An isotonic solution can replace fluid loss.
- The substance is used for carbohydrate nutrition of the brain and muscles - glucose absorption occurs quickly, mental and physical performance increases.
Why is Glucose useful?
The properties of the substance to have a positive effect on metabolic processes are used in the treatment of ailments. Pregnant women are prescribed dextrose if they suspect a small fetus, as well as to reduce the risk of miscarriage and premature birth. During this period, it helps to overcome fatigue and improve well-being when sugar levels drop and hands tremble. During pregnancy and lactation, while using the drug, it is necessary to constantly monitor sugar levels. According to the instructions, the drug is prescribed:
- with carbohydrate deficiency, with hypoglycemia;
- in case of intoxication due to liver disease (hepatitis);
- for the treatment of poisoning;
- with decompensation of cardiac activity;
- to replenish fluid after surgery, with diarrhea or vomiting;
- with shock, collapse (sharp drop in pressure).
Indications for use of the solution in ampoules
Glucose is prescribed to patients of different ages and for various disorders. It is the 40% concentration of the solution in ampoules that is considered in demand in critical conditions.
Main indications for use:
- A sudden decrease in blood glucose levels in the absence of somatic pathologies. Patients report severe weakness, headache, dizziness. Many people notice darkening in the eyes or flashing spots during physical activity.
- Carbohydrate deficiency in patients who, as a result of various factors, are unable to consume food orally. In this case, parenteral administration of the solution helps to compensate for the deficiency of important components. The inability to eat food can occur with injuries to the larynx and pharynx, after undergoing surgical interventions on the organs of the digestive tract, and with malignant neoplasms.
- Reducing blood glucose levels in patients suffering from type 1 diabetes. With such disorders, the development of hypoglycemic coma, which is life-threatening, is possible, but the administration of the solution helps to normalize the indicators.
- Loss of fluid from the patient's body as a result of prolonged diarrhea or repeated vomiting. This is often observed with rotavirus infection, poisoning, and withdrawal syndrome.
- Shock, collapse, conditions accompanied by a critical decrease in blood pressure. The product helps increase the volume of circulating blood, which significantly improves the condition. Often the use of the solution helps to avoid death.
The drug is often part of complex therapy for various diseases.
How to drink glucose
Glucose tablets should be taken orally sublingually - by resorption under the tongue. The drug should be taken an hour or an hour and a half before eating, because the use of dextrose reduces appetite. The dosage depends on the age, weight and condition of the patient. You cannot prescribe the drug yourself, as there are a number of contraindications for use.
In case of poisoning
The drug is used as a detoxifying agent. During the treatment of poisoning with hydrocyanic acid, arsenic, carbon monoxide, aniline, paracetamol, along with other drugs, glucose tablets are prescribed to improve the patient's condition. The drug is effective against intoxication of the body due to liver dysfunction. Patients are recommended to take 2-3 tablets at intervals of 2 hours until the condition improves.
For diabetes
Due to severe emotional stress or taking a large dose of insulin, if the required intervals between meals are not observed in diabetes mellitus, a sharp decrease in sugar levels can occur. To normalize it, you need to take chewable tablets. In case of severe hypoglycemia, you should take 1-2 pieces every 5 minutes until weakness, sweating, and trembling disappear.
For milder conditions, take 3-4 tablets every 30 minutes. Stop taking dextrose after the disappearance of characteristic signs
It is important not to confuse the symptoms of hypoglycemia with signs characteristic of hyperglycemia and monitor the sugar concentration using devices. Otherwise, there will be a sharp increase in its level, the patient’s condition will worsen and shock may occur.
Glucose for athletes
Athletes are prescribed tablets during increased physical activity - during intense training. Dextrose is necessary for the muscles of athletes to quickly replenish the body's energy reserves. You should not take the drug before training, because there will be an increase in insulin levels, and then a sharp drop in sugar concentration. It is better to use the drug 1-2 hours before physical activity. To take, dissolve 7 tablets of 1 gram each in a liter of water and drink 4 glasses of liquid at one-minute intervals.
Contraindications
The safe composition and positive effects of the product on the body do not allow its use without prior examination. An allergic reaction to the components of the composition or a tendency to such manifestations is considered an absolute contraindication.
There are other barriers to use:
- Elevated blood glucose levels or hyperglycemia. This condition can also occur in type 1 diabetes. In this case, the patient develops hyperglycemic coma, which is no less life-threatening.
- A severe form of acute or chronic renal failure, in which there is a significant decrease in daily diuresis and associated abnormalities.
- Cirrhosis of the liver, accompanied by the development of ascites, that is, the accumulation of a large amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity. At the same time, the volume of the patient’s abdomen increases, which leads to other disorders as a result of compression of the internal organs.
- Decompensated heart failure, in which there is frequent deterioration of the condition and exacerbation of symptoms.
- Decompensated form of diabetes mellitus. In this case, the specialist makes a decision on prescribing the solution in each case individually, if such a need arises.
- Pathologies of the pancreas, which may worsen when using the solution.
- Hepatitis of viral origin.
- Acute infectious pathologies at an advanced stage.
- Swelling of the brain due to injury and other factors.
- Pulmonary edema due to heart pathologies.
- Diagnosis of hyperosmolar coma.
- Identification of symptoms of acute left ventricular failure in the patient.
Relative contraindications include the advanced age of the patient, when the use of the drug is not always permitted and can provoke complications.
Who is the drug indicated for?
A 5% solution administered intravenously promotes:
- rapid replenishment of lost fluid (with general, extracellular and cellular dehydration);
- elimination of shock conditions and collapse (as one of the components of anti-shock and blood replacement fluids).
The 10% solution has the following indications for use and intravenous administration:
- with dehydration (vomiting, indigestion, in the postoperative period);
- in case of poisoning with all kinds of poisons or drugs (arsenic, narcotic drugs, carbon monoxide, phosgene, cyanide, aniline);
- for hypoglycemia, hepatitis, dystrophy, liver atrophy, edema of the brain and lungs, hemorrhagic diathesis, septic heart problems, infectious diseases, toxic infections;
- during the preparation of drug solutions for intravenous administration (concentration 5% and 10%).
Instructions for use, dosage
Depending on the condition and the presence of associated complications, the drug can be used according to different schemes. It can be infused intravenously using a syringe or administered by drip over a long period of time. Experts prescribe a solution for a single injection or use over several days.
Glucose 40 percent in ampoules
| Violation | Scheme of application and dosage of the product |
| Acute conditions that develop against the background of a decrease in blood glucose levels | For such disorders, the solution is administered very slowly intravenously to an adult in an amount of 20-50 ml. Usually this is enough to eliminate the manifestations. The specific dosage is determined depending on the disorder. If necessary, the administration is repeated 2 times a day at intervals of 10 hours, the course lasts up to 3 days. If there is no therapeutic effect, other solutions are prescribed. |
| Shock or collapse | When such disorders develop, a concentrated solution is used for intravenous injection in an amount of 30-40 ml. After eliminating acute manifestations, the patient is prescribed drip administration of the drug at a rate of 30 drops per 1 minute. The maximum daily dosage of the product is 300 ml. This treatment lasts no more than 3 days. |
| Reduced blood pressure, poisoning and other conditions requiring long-term use | For such disorders, the patient is prescribed a solution in combination with other drugs. The daily dose is 100-200 ml, the product is administered using a dropper. The duration of therapy is 3-5 days depending on the severity of the manifestations. It is prohibited to exceed the dosage or extend the course. Usually this is enough to obtain a therapeutic result. |
It is imperative to administer the product slowly when using the drip and string methods. This will prevent negative reactions. The dosage and duration of use are adjusted depending on the individual patient and his condition, but this is done by the doctor based on examination data.
Foods containing this energy source in large quantities
Food products contain varying amounts of it. It's no secret that the sweeter the nutrient, the more glucose is found there. Therefore, sweets (any kind), sugar (especially white), honey of any kind, pasta made from soft wheat varieties, most confectionery products with a lot of cream and sugar are glucose-rich products, where glucose is contained in very considerable quantities.
As for fruits and berries, there is a misconception that these products are rich in the compound we are describing. This is understandable; almost all fruits taste very sweet. Therefore, it seems that the glucose content there is also high. But the sweetness of these fruits is determined by another carbohydrate - fructose, which reduces the percentage of glucose. Therefore, consumption of large quantities of fruit is not dangerous for patients with diabetes.
Foods containing glucose should be of particular caution to diabetics. There is no need to be afraid and avoid using them.
After all, even a patient suffering from diabetes needs to consume a certain amount of this nutrient (the daily glucose requirement is individual for everyone and depends on body weight, on average - 182 g per day)
It is enough to pay attention to the glycemic index and glycemic load
Rice cereals (especially white short-grain rice), corn, pearl barley, products based on wheat flour (from soft wheat varieties) are products containing glucose in moderate quantities. They have a glycemic index between medium and high (55 to 100). Their use in food for diabetics should be limited.
Side effects
Glucose 40 percent in ampoules can cause complications if not used according to instructions or by the patient. Only in some cases, using all the rules can lead to negative reactions.
The most common complications during therapy:
- Severe pain and development of phlebitis may occur in the injection area. The latter is considered a dangerous complication, since it is characterized by inflammation of the internal walls of the veins into which the solution is injected. The condition is accompanied by pain, a local increase in temperature, the appearance of compaction and redness at the site of the affected vessel. If symptoms persist for a long period of time, the condition worsens and thrombophlebitis develops.
- Complications from the nervous system do not occur so often, but are accompanied by severe disturbances in the form of headaches, sleep disturbances and decreased performance against the background of deteriorating memory and concentration. After stopping the use of the drug, the condition normalizes, but symptoms may persist for a long period, sometimes requiring special treatment.
- From the digestive tract, nausea and bouts of vomiting are observed, aggravating the condition. Patients note worsening digestion and stool disorder, manifested by frequent diarrhea. Against the background of these disorders, appetite worsens and severe thirst is observed.
- From the urinary system, increased frequency of urination and pain in the kidney area are possible. The condition worsens in the presence of chronic pathologies of the paired organ.
- Often, adverse reactions manifest themselves in the form of a significant increase in blood glucose levels and a decrease in the amount of potassium and magnesium. Such disorders lead to deterioration of heart function.
- An allergic reaction manifests itself in the form of a skin rash, burning and itching. Such reactions are not considered common, but can significantly worsen the condition and threaten the patient’s life.
The severity of negative manifestations depends on the duration of use of the drug, the specific dosage and the characteristics of the body of each patient. If negative reactions occur, it is important to stop use immediately. In most cases, this is enough to normalize the condition. In some cases, special treatment is required.
How to use the drug
There are many options for administering the drug.
The most common of them are intravenous injection or infusion. But it is possible to administer glucose subcutaneously or by enema. Glucose injections intramuscularly are prescribed extremely rarely and are used with extreme caution, since this method can cause suppuration. You should not take the drug yourself; after reading the instructions for use, it should be prescribed by a doctor
He will determine the required dosage and will not allow negative reactions to occur.
Is it possible to drink glucose
Glucose can be consumed orally, since its usual solution (without other components) does not contain substances that may have a negative effect. This is a pleasant-tasting liquid, reminiscent of regular sweetened water. The question is whether there will be any benefit from taking the drug in this way.
You can take glucose if your sugar level drops sharply, for example if a person with diabetes overdoses on insulin, or if your blood pressure drops sharply. However, such deterioration in well-being can be successfully combated using simpler and more common methods. For example, drinking strong sweet tea.
If we are talking about poisoning, for which the use of a glucose solution is also indicated, then taking the medicine orally by simply drinking it is not always possible, since intoxication is often accompanied by vomiting.
Overdose data
Glucose is dangerous if its concentration is four times higher than normal. Symptoms of overdose include bloating, diarrhea and vomiting. If you have diabetes, the patient may be in serious condition due to a sharp increase in blood sugar levels. The symptoms are so pronounced that diabetics immediately detect the onset of an overdose, which has the following signs:
- constant thirst and persistent dry mouth;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- apathy and loss of strength, feeling tired;
- the appearance of itching on the skin;
- clouding of consciousness, unfocused, foggy eyes;
- irregular heart function.
Symptoms appear almost instantly. For people with diabetes, elevated sugar levels have dangerous consequences, including death.
Overdose
The drug can provoke an overdose, the most pronounced symptom of which is an increase in osmotic pressure in the blood. This significantly increases the risk of developing hyperglycemic coma. The condition is accompanied by nausea, vomiting and severe headache.
Possible impairment of consciousness and movement disorders. When examining urine, specialists find an increased glucose content in it, urination becomes frequent, and the amount of urine increases. This is due to increased thirst. The patient takes a lot of fluid, which leads to an increase in circulating blood volume and an increase in daily diuresis.
An overdose may be accompanied by tachycardia, increased blood pressure and increased sweating. If such signs are detected, treatment with the solution should be stopped immediately.
After this, symptomatic therapy is prescribed to eliminate the manifestations. The most important stage of treatment is the administration of insulin, which helps normalize blood glucose levels. The patient receives assistance in the event of an overdose in a hospital setting, since constant monitoring of blood glucose levels is required.
Calcium gluconate (injections): what is it prescribed for?
The key indication for the use of the drug is a critically low calcium content in the body, diseases accompanied by increased permeability of cell membranes (especially in blood vessels), and disruption of the passage of nerve impulses in the muscles. Therefore, the drug is used primarily as a mineral supplement that eliminates hypocalcemia.
Microelement deficiency can occur due to prolonged bed rest, chronic diarrhea, long-term use of a number of medications - diuretics, anticonvulsants, glucocorticosteroids.
It is prescribed for:
- insufficiency of the parathyroid glands (hidden tetany, osteoporosis due to hypoparathyroidism);
- violation of vitamin D metabolism (rickets, accompanied by tonic and clonic-tonic convulsions, softening of bones);
- skin diseases (itching, psoriasis, eczema);
- acute parenchymal hepatitis;
- Hamstorp's disease (accompanied by attacks of severe muscle weakness);
- severe intoxications, including those provoked by poisoning with magnesium salts, fluoric and oxalic acids.
There are many more specific reasons for which calcium injections are prescribed.
When a person experiences an allergic reaction to any allergen or complications develop (especially those associated with taking medications), the doctor often prescribes calcium gluconate as part of a broader range of medications. As you know, the appearance of allergies indicates a disruption in the functioning of the human immune system.
- permeability of vessel walls. When a person’s calcium is within normal limits, the walls of blood vessels become denser and do not allow the allergen to enter the body;
- in the complex treatment of allergies together with other medications, the drug has a positive effect on connective tissue cells, accelerating a person’s healing from allergies.
Of course, calcium gluconate, like any antihistamine, does not give immediate results, but it reduces the manifestation of symptoms of the disease, and also, in combination with other antiallergic medications, significantly shortens the treatment period and reduces the risk of complications. Therefore, to relieve allergies, doctors prescribe calcium gluconate intravenously.
Calcium takes part in the body's absorption of vitamin D. For this reason, experts often prescribe calcium-containing preparations to children and women during pregnancy, breastfeeding and menopause. It is during these periods that a rapid loss of microelements, a lack of calcium, and a violation of its metabolism are observed.
In addition, calcium gluconate, which normalizes the content of microelements in human blood, is used for severe diarrhea. In this case, injections of the drug are used in conjunction with dehydrating drugs to restore water and electrolyte balance.
With viral infections, there is a rapid decline in calcium levels in the blood, which, of course, affects the systems and functions of the body, and also causes general weakness. The use of calcium gluconate for infections is due to the following effects of the drug:
- strengthens the musculoskeletal system;
- increases bone strength;
- improves the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- stimulates overall activity and performance;
- ensures the implementation of all metabolic processes.
Calcium gluconate significantly increases the calcium content in the blood, which, in turn, takes part in cleansing the body of toxins and wastes that accumulate during illness and adversely affect the general condition of the patient.
In case of food poisoning and other diseases, intoxication of the liver occurs, as a result of which the level of calcium in the human blood decreases. This condition is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain in the right side;
- heat;
- convulsions;
- increased sweating;
- general weakness of the body;
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
Calcium gluconate prescribed for such symptoms for use in injections increases the content of this microelement in the body, which, in turn, contributes to accelerated human recovery by improving the immune system’s ability to resist the disease.
In addition, the drug is prescribed for the treatment of various kidney diseases, including nephritis and chronic pathologies with high levels of phosphate in the blood serum. In case of renal failure and various nephritis, the introduction of calcium gluconate into a vein normalizes the level of electrolytes in the human blood, which also helps to weaken the inflammatory process and speed up recovery.
Calcium promotes blood clotting. Therefore, if a patient experiences bleeding that does not stop for a long time, then this is a direct signal about its deficiency in the body. In this case, an injection of calcium into a vein will restore the normal content of the microelement and balance the blood clotting process.
Calcium gluconate stimulates the contraction of the smooth muscle cell layer of blood vessels. As a result of this effect, the gap between cells is reduced, and this prevents the penetration of allergens and other pathological agents into the blood.
For children, calcium ampoules are prescribed during active growth to strengthen bones and proper development. The drug can be prescribed for many diseases of varying severity. Calcium gluconate has long proven its effectiveness in the treatment of pathologies such as food poisoning, ARVI, serum sickness, urticaria and for reducing vascular permeability.
As you know, women during pregnancy experience a lack of many vitamins and microelements in their bodies. This phenomenon is associated with the fact that the expectant mother, while carrying a child, gives most of the useful elements to him. Symptoms of calcium deficiency include:
- a sharp deterioration in the condition of the teeth. They begin to crumble, the enamel is destroyed;
- deterioration of hair and nails;
- frequent “goosebumps” all over the body;
- convulsions;
- fatigue.
To return the calcium balance to normal, experts prescribe injections of a drug containing this trace element for use by adult women during pregnancy. Often, medicine is prescribed without waiting for the first symptoms, for prevention. However, pregnant women are only allowed to take it in tablet form.
Contraindications
Like any medicine, calcium gluconate has contraindications, which were identified during clinical trials. The instructions for use indicate that the medicine is prohibited for people:
- with identified symptoms of individual intolerance to the components of the composition;
- with increased calcium levels in the blood;
- under the age of 15;
- with severe kidney disease;
- with an increased level of blood clotting, a tendency to form blood clots;
- during pregnancy and lactation, if we are talking about injections;
- suffering from atherosclerosis;
- when rapid removal of calcium from the body along with urine is detected.
special instructions
Glucose 40% in ampoules is prescribed only if indicated. Otherwise, it is almost impossible to avoid complications. If it is necessary to infuse patients with blood products or pure red blood cells, you should stop using the solution.
To date, there is no data on the effect of the drug on concentration when used as directed. But when used in high doses, you should stop driving vehicles.
The solution is never administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously, as it can cause complications. Accelerated jet or drip intravenous administration can provoke phlebitis and vein thrombosis, especially in patients with a history of predisposition to such complications.
If negative reactions develop after the initial use of the medicine, you should not re-administer the solution. In this case, other drugs with similar properties are used. Use during pregnancy and lactation is not prohibited. But the specialist must strictly control the dosage, which is associated with the risk of developing hyperglycemia in the fetus when administered in high doses.
Pregnant and lactating women receive the drug in a hospital setting, which allows them to monitor their condition and the effectiveness of use. A preliminary consultation with a doctor is required.
Droppers
The isotonic solution is administered subcutaneously from 300 to 500 ml. Administration through enemas or drips (intravenously) is also possible. In this case, the patient should receive about 2 liters per day. solution. A five percent isotonic dextrose solution is injected using a dropper into a vein or under the skin or rectum in case of severe blood loss, dehydration or shock. In this case, you need to administer from 300-400 ml to a liter or two in 24 hours. If the solution is five percent, an instillation rate of up to 7 ml is suitable. per minute, if ten percent, the speed should be three milliliters per minute.
Drug interactions
The solution should not be prescribed simultaneously with products containing the same active ingredient in the composition. Mixing the solution in the same syringe with analgesics, sleeping pills and alkaline drugs is not allowed. This can lead to unforeseen complications.
The patient's tolerance to glucose is significantly reduced when used simultaneously with loop and thiazide diuretics. This should be taken into account when prescribing. A glucose solution can significantly reduce the toxic effects of many medications on the liver.
There is no development of negative reactions when combining the drug with antibiotics, hepatoprotectors and vascular agents. In each case, a preliminary consultation with a doctor is required in order to prevent complications arising from drug incompatibility.
Some introduction nuances
When using the drug intravenously, you should always keep your blood sugar levels under control. The administration of large volumes of glucose can be fraught for those diabetics who have significant electrolyte loss. A 10% solution cannot be used after acute attacks of ischemia due to the negative impact of hyperglycemia on the treatment process.
If there are indications, the drug can be used in pediatrics, pregnancy and lactation.
The description of the substance suggests that glucose is not able to influence the ability to control mechanisms and transport.