How to deal with the appearance of yellow discharge? Do they talk about illness, and do you need to see a doctor urgently? It is worth considering that each representative of the fair sex has its own characteristics of the body. Therefore, sometimes mucous discharge may be normal, in particular, the appearance of leucorrhoea; a change in its color and consistency is allowed before menstruation, in the middle of the cycle.
There are frequent cases of yellow discharge that does not indicate any disease. However, they can be regarded as the norm only if there are no symptoms of the development of the disease.
Types of yellow discharge
Yellow discharge can be divided into natural - considered by gynecologists as an acceptable norm - and pathological. The latter come with or without scent.
Without smell
Yellowish, odorless discharge may indicate the development of diseases of the female reproductive system. The causes of the condition can be:
- Colpitis. Physiological secretion increases, but does not change the color or smell. Typical manifestations are itching, burning in the area of the external genitalia, swelling and hyperemia of the tissues of the vulva, discomfort when urinating.
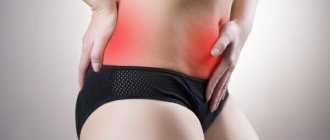
- Adnexitis (combined inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes). Additional signs are pain in the lower abdomen, spreading to the lumbar region, poor health, and increased temperature.
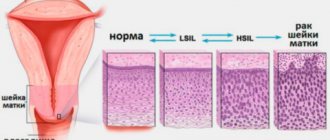
- Cervical erosion. Damage to the vaginal segment of the cervix may also be accompanied by the appearance of yellow leucorrhoea. This sign indicates the appearance of an inflammatory process and the addition of a secondary bacterial infection.
After treating erosion, the presence of yellowish impurities in the mucus is normal.
- Sexually transmitted diseases. The introduction of pathogens (infectious agents) into the mucous membrane causes not only a modification of the physiological secretion, but is also accompanied by such conditions as swelling of the labia majora and minora, severe itching, etc. An example of such pathologies is chlamydia.
With smell
Discharge in women of a yellowish color, accompanied by the appearance of an unpleasant aroma, cannot be a variation of the norm. This symptom indicates the development of some pathological process.
Yellow discharge in women with a specific odor may be a sign of the following diseases:
- Vaginosis (vaginal dysbiosis). Leucorrhoea with this pathology takes on a characteristic fishy amber and becomes more watery in consistency. Pathology is an inflammatory process that forms in the vaginal mucosa against the background of a violation of the natural balance of microflora. The cause may be taking medications from the group of antibiotics, changes in hormonal levels, violation of intimate hygiene rules, etc.
- Endometriosis. A hormonal disease accompanied by pathological proliferation of uterine endometrial cells and its exit beyond the organ. An additional sign of the disease is the appearance of profuse vaginal leucorrhoea of dark yellow or brown color. It has a consistency similar to water and has a very unpleasant, pungent stench.
- Cancerous tumors of the female reproductive system. For such diseases, the development of bleeding is typical, as is the appearance of a red-yellow secretion. A yellow tint indicates the presence of purulent components in the leucorrhoea. The smell of the secretion becomes very unpleasant (contains notes of rot). Additional signs are pain spreading to the lower abdomen and sacral region, general weakness, apathetic mood, weight loss.
Thick yellow discharge in women, which acquires a heavy foul odor, in the presence of cancer pathology, accompanies the formation of a fistula canal connecting the organs of the female reproductive system with the rectum or bladder.
- Thrush (vaginal candidiasis). White-yellow mucus of a cheesy nature with the smell of sour milk indicates the development of thrush. Additionally, symptoms such as swelling and severe itching appear. In the absence of treatment for this gynecological pathology, leucorrhoea transforms into greenish-yellow. Erotic areas appear on the surface of the mucosa.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system. Most often, such secretion, of an unnatural yellow color and with an unpleasant odor, accompanies decompensated diabetes mellitus. In this case, the mucus develops a characteristic odor of acetone and painfully severe itching of the vulva.
- STD. Not all diseases from this group are accompanied by daily odorless leucorrhoea. The vast majority of vaginal mucus begins to emit an uncharacteristic aroma. The following symptoms may indicate an STD - severe discomfort in the external genital area, swelling of the mucous membranes, redness of the tissues. Gonorrhea, gardnerellosis, and trichomoniasis occur with the appearance of an unpleasant odor of leucorrhoea.
Yellowish discharge that appears during the period after an abortion/diagnostic curettage in women indicates infection and the addition of a secondary bacterial infection.
Self-diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections is impossible, since the external symptoms of such diseases are quite similar. Only a specialist can determine the type of pathogen and prescribe adequate treatment after conducting appropriate research.
Diagnostics
If there is vaginal discharge, the first step is a gynecological examination of the tissues of the vagina and cervix. This research method helps to establish the nature of the cervical secretion (infectious or non-infectious), the presence of inflammatory processes, ulcers, and neoplasms.
But a gynecological examination allows only a preliminary diagnosis. To clarify it, you will need to undergo a comprehensive examination.
The cost of a gynecological examination depends on which medical institution the woman went to - budgetary or commercial. In budgetary organizations, services are provided free of charge. In commercial settings, the cost of one appointment can vary from 500 to 1200 rubles, depending on the region of residence.
After a gynecological examination, an ultrasound examination is prescribed. This is an informative method for diagnosing diseases of the reproductive system.
During the ultrasound process, the main attention is paid to the following indicators:
- location of internal organs, their relationship with each other;
- determination of the size of the uterus, contours;
- condition of the internal epithelium of the uterus, myometrium, endometrium;
- sizes of appendages, their structure;
- the presence of adhesions, follicles, cysts;
- dimensions of the cervical canal, structure.
The cost of an ultrasound also depends on the region of residence. On average, the cost of the study is 600-1000 rubles. In government institutions it is free of charge. It is also mandatory to take a microscopic smear from the vagina, which helps to determine the nature of the discharge (infectious or non-infectious).
During its implementation, the following are assessed:
- leukocyte count;
- number of epithelial cells;
- presence of lactobacilli;
- presence of pathogenic microflora.
The price of such a study also varies depending on the clinic. The approximate cost of taking a gynecological smear is 800-1000 rubles.
As a rule, these diagnostic methods are enough to determine the cause of the appearance of orange discharge, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. But if the doctor suspects cancer, an additional Ca125 tumor marker is given (blood test, costs 900 rubles).
Each case is individual. And it is difficult to say exactly what procedures will be performed to make a diagnosis. Diagnostics are prescribed taking into account the patient’s complaints and the results of a gynecological examination.
Possible reasons
Possible reasons for the appearance of yellowish mucus without or with odor are numerous. In particular, both abundant and scanty leucorrhoea without a strong aroma can act as a symptom of disorders in the functioning of the organs of the female reproductive and genitourinary system. They are considered a sign of an inflammatory process.
But a natural cause for their occurrence cannot be ruled out. Vaginal leucorrhoea in women without odor can form physiologically. The fact is that they contain secretion inside the vaginal glands, dead epithelial cells, and dead bacteria. It is their combination with the initially transparent mucus that causes the change in its natural shade to a pronounced white or yellowish color.
Vaginal leucorrhoea in women without odor can appear after artificial and natural termination of pregnancy. Rejection of bloody secretion during this period is normal.
Sometimes yellow vaginal mucus occurs after sexual intercourse. If it appears after unprotected sexual relations, then the cause is the mixing of physiological female secretions and the partner’s ejaculate. The discharge returns to normal after about 8 to 10 hours. If the secretion turns yellow after using a condom, the cause is the active activity of the vaginal glands that produce natural lubrication.
Other reasons for the appearance of yellowish leucorrhoea include:
- unbalanced diet - the presence of a large amount of spicy, fatty, acidic foods in the menu can cause changes in the composition of secretion;
- hormonal imbalance;
- the period before and after the end of menstruation;
- ovulation period - the appearance of a thick and abundant secretion of a yellow-transparent color indicates the release of an egg ready for fertilization;
- taking oral contraceptives, accompanied by rapid changes in hormonal levels, a woman often notices scanty yellowish discharge;
- frequent change of sexual partners - such a modification of mucus is a reaction of adaptation of the vaginal environment to the new microflora of the partner.
Preventive measures
In addition to regularly visiting a doctor and observing all the rules of intimate hygiene, it is necessary to carry out disease prevention.
Main preventive measures:
- A woman needs to visit a gynecologist regularly - at least twice a year;
- Moderate physical activity allows you to maintain strong immunity of the body and normalize hormonal levels;
- The main cause of inflammatory and infectious diseases is sex without contraception. When having sex, you need to use barrier contraceptives. Some hormonal contraceptives can also cause heavy discharge.
- Poor nutrition also affects the health of the genitourinary system. A woman’s diet should be balanced, it should include fresh fruits and vegetables, nuts, meat and fish, and dairy products. You should not oversaturate your body with an abundance of flour sweets, salty and fried foods.
- To maintain hygiene of the genital area, you need to use only proven products. In some situations, you can use folk remedies - decoctions of medicinal herbs and flowers.
- To avoid an allergic reaction to the materials from which underwear is made, it is better to choose clothes made from natural materials. Cotton and linen underwear sets allow you to maintain healthy genitals. The underwear should be comfortable and loose, without putting pressure on the body.
- It is better to maintain sexual relations with a permanent, trusted partner. Constantly changing men can lead to serious sexually transmitted diseases.
- Pregnant women should monitor their health and observe intimate hygiene more carefully.
By adhering to these rules, women can avoid problems with the functioning of the genitourinary system and not be subject to infections and inflammation.
Consequences if left untreated
In the absence of adequate treatment for the condition, the development of negative consequences for women’s health cannot be ruled out. They are determined by the identified pathology.
Any inflammatory process, if left untreated, is prone to chronicity. The consequences of inadequate therapy or its complete absence may include:
- frequent relapses with exacerbation of symptoms typical of the disease;
- infertility;
- habitual miscarriage;
- premature birth;
- ectopic pregnancy and others.
With the advent of menopause, the risk of oncology of the female reproductive system increases.
Possible complications
If pathological vaginal discharge is not treated in time, it can lead to serious complications:
- infertility;
- recurrent miscarriages;
- cancer;
- violation of the MC;
- Reiter's syndrome;
- abscess;
- sepsis.
Even if the appearance of orange discharge in women is not accompanied by additional symptoms, do not put off visiting a doctor. Some diseases can occur in a latent form and their only manifestation is a change in the nature of vaginal mucus.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
When is it necessary to contact a gynecologist?
Yellow, odorless discharge in women can be considered an acceptable physiological norm if it is not accompanied by the development of pathological symptoms. It must be remembered that a slight increase in the usual volume of mucus with a slight change in color is possible before the start of menstruation, as well as before and during the period of ovulation. The acceptable standard is from light yellow to yellowish with creamy nuances.
Physiological secretion has a uniform consistency. There are no lumps in it. A deviation from the norm is indicated by the appearance of:
- Curdled leucorrhoea.
- Copious and thin foamy mucus.
If such changes occur, it is recommended to seek medical help. The gynecologist will take a smear to examine the vaginal microflora. Additionally, bacterial culture is performed. It is necessary to identify the causative agent of the disease and test sensitivity to drugs.
Cause for concern or normal?
Such a symptom is not always a sign of exposure to abnormal factors. Often the yellow tint of leucorrhoea is explained by the course of physiological processes provoked by objective reasons. The color and consistency of female sexual secretion is influenced by many factors: fluctuations in hormone levels, the composition of natural microflora, taking medications and other reasons.
In some cases, the appearance of abnormal leucorrhoea cannot be explained by natural factors. If, in addition to suspicious marks on the underwear, a woman notices an unpleasant odor, the appearance of discomfort and pain in the intimate area, or malaise, then we are talking about a pathological condition that requires the help of a specialist.
Treatment of diseases causing yellowish discharge
If an inflammatory process is detected, accompanied by the appearance of purulent leucorrhoea, the patient needs urgent hospitalization. Inpatient therapy will also be required if the following symptoms are present:
- significant pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- increase in body temperature to high levels.
If purulent mucus is a consequence of an exacerbation of chronic pathology of the female reproductive system, then the patient needs to undergo treatment in a specialized hospital.
But whatever the patient’s well-being, if leucorrhoea is detected that is uncharacteristic in composition and color, she needs to visit a gynecologist as soon as possible. The doctor will determine the type of disease and prescribe treatment appropriate to the diagnosis.
To prevent the development of complications and avoid chronicity of the disease, you need to regularly visit the gynecologist’s office. If uncharacteristic leucorrhoea appears with accompanying pathological symptoms, it is advisable to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Prevention
Prevention is much preferable to drug treatment. To prevent the appearance of pathological secretion, it is important to follow simple rules:
- adequate hygiene;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet with limited sugar;
- a reasonable attitude towards sexual intercourse, the use of barrier methods of contraception;
- maintaining the balance of vaginal flora during antibiotic treatment with the help of special preparations;
- and careful attention to health, expressed in immediate consultation with a doctor (in case of problems) and annual scheduled examination for preventive purposes.
What does yellow secretion mean when taking birth control pills?
Hormonal contraception consists of taking combination drugs. They contain different dosages of sex hormones that suppress the maturation process and the release of the egg.
Each female body is individual, so standard dosages are not suitable for everyone.
An incorrectly selected dose of hormones causes atypical discharge of different colors, including yellow.
Spotting outside of menstruation means that you need to consult a gynecologist, correct or discontinue the drug.