Write a review
Reviews: 0
Manufacturers: Berlin-Chemie AG
Active ingredients
- Potassium iodide
Disease class
- Thyroid diseases associated with iodine deficiency and similar conditions
- diffuse (endemic) goiter associated with iodine deficiency
- Multinodular (endemic) goiter associated with iodine deficiency
- Thyrotoxicosis (hyperthyroidism)
- Thyroid crisis or coma
- Conjunctival hemorrhage
- Scarring and clouding of the cornea
- Senile cataract
- Other cataracts
- Hemorrhage and rupture of the choroid
- Other disorders of the eye and its adnexa in diseases classified elsewhere
- Sialadenitis
- Disorders of the secretion of the salivary glands
- Sputum
- Impact of radiation pollution
Clinical and pharmacological group
- Not indicated. See instructions
Pharmacological action
- Mucolytic
- Expectorant
- Antithyroid
- Antifungal
- Replenishing iodine deficiency
- Absorbable
Pharmacological group
- Thyroid hormones, their analogs and antagonists (including antithyroid drugs)
- Macro- and microelements
Release form and composition
The drug is produced in the form of tablets: round, flat-cylindrical, with a chamfer, white, on one side with or without the marking “R” (14 pcs. in a blister pack made of aluminum foil and polyvinyl chloride film, in a cardboard pack of 4 or 8 packs and instructions for use of Potassium iodide Renewal).
1 tablet contains:
- active ingredient: potassium iodide – 131 or 262 mcg, which is equivalent to iodine in the amount of 100 and 200 mcg, respectively;
- additional components: microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium hydroxycarbonate (basic magnesium carbonate), colloidal silicon dioxide (Aerosil), lactose monohydrate (milk sugar), magnesium stearate, croscarmellose sodium.
Similar drugs:
- Canned medical bile (Chole conservata medicata) Emulsion for external use
- Potassium iodide (Potassium iodide) Substance
- Cattle bile dry (Ox bile powder dry) Powder substance
- Linin Ointment for external use
- Naphthalan petroleum refined Substance-liquid
- Iodine Vitrum Oral tablets
- Dry extracted bovine bile (Ox bile powder dry) Substance
- Iodine Vitrum Kids Chewable tablets
** The Drug Directory is intended for informational purposes only. For more complete information, please refer to the manufacturer's instructions. Do not self-medicate; Before starting to use the drug Potassium iodide 200 Berlin-Chemie, you should consult a doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal. Any information on the site does not replace medical advice and cannot serve as a guarantee of the positive effect of the drug.
Are you interested in the drug Potassium iodide 200 Berlin-Chemie? Do you want to know more detailed information or do you need a doctor's examination? Or do you need an inspection? You can make an appointment with a doctor - the Euro lab is always at your service! The best doctors will examine you, advise you, provide the necessary assistance and make a diagnosis. You can also call a doctor at home . Euro lab clinic is open for you around the clock.
** Attention! The information presented in this medication guide is intended for medical professionals and should not be used as a basis for self-medication. The description of the drug Potassium iodide 200 Berlin-Chemie is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended for prescribing treatment without the participation of a doctor. Patients need to consult a specialist!
If you are interested in any other drugs and medications, their descriptions and instructions for use, information about the composition and form of release, indications for use and side effects, methods of use, prices and reviews of drugs, or you have any other questions and suggestions - write to us, we will definitely try to help you.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Iodine, the active substance of Renewal's Potassium Iodide, is one of the vital trace elements necessary for the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. After iodides (chemical compounds of iodine) enter the epithelial cells of the thyroid follicle under the action of the enzyme iodide peroxidase, iodine ions are oxidized, forming elemental iodine, which is included in the alpha-amino acid tyrosine molecule. During this process, one part of the tyrosine radicals in the protein thyroglobulin (TG) is iodinated, resulting in the formation of thyronines, the most important of which are triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Thyronines create a complex with TG, which accumulates in the colloid secreted by the secretory cells of the thyroid follicles.
Iodine entering the body in physiological quantities prevents the development of endemic goiter caused by iodine deficiency in food, helps normalize the size of the thyroid gland in children (including newborns) and adolescents, and also affects the T3/T4 ratio and the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Pharmacokinetics
When taken orally, Potassium iodide Renewal is quickly and completely absorbed in the small intestine and distributed in the intracellular space within two hours. The active substance accumulates mainly in the thyroid gland (iodide content above 0.5 mg/g tissue), to a lesser extent in the gastric mucosa, salivary and mammary glands; iodine also passes well through the placenta.
The drug is excreted mostly by the kidneys (trace amounts are detected in the urine 10 minutes after administration), 80% of the dose is eliminated within 48 hours, the rest within 10–20 days. Also, the drug is partially excreted with the secretions of the bronchial, salivary, sweat and other glands.
Indications for use
The decision on the application is made by the National Signaling Center and announced by radio. Without the federal government, the drug should not be taken in large doses. There is currently no reason to take it in Russia. In small doses, due to its pharmacological action (pharmacodynamics), the drug is prescribed for several indications - prevention of endemic and euthyroid goiter.
For the group over 45 years of age, potassium iodide tablets are not usually considered as the risk of hyperthyroidism is largely rated higher than the beneficial effects of radiation exposure. The reason is increased sensitivity to iodine in this age group. For other age groups this increased sensitivity does not exist.
The radioisotope 131I is an important byproduct of nuclear fission and is dangerous because it accumulates in the thyroid gland, which can lead to cancer. The use of non-radioactive iodide saturates the thyroid gland with iodine, as a result of which the radioactive element cannot accumulate.
Potassium iodide tablets are not universally effective for radiation protection. When consumed in a timely manner, they protect only the thyroid gland from radioactive iodine, which enters the body through breathing or food. They do not protect against other radioactive substances. In addition, the required protective measures (for example, temporary stay in enclosed spaces, food control, disinfection) are by no means unnecessary.
A saturated solution of potassium iodide is used as an expectorant in the treatment of pulmonary congestion and as a fungicide in the treatment of sporotrichosis. Sometimes given along with diiodine to relieve sore throat.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- latent thyrotoxicosis (when using daily doses exceeding 150 mcg);
- severe thyrotoxicosis;
- dermatitis herpetiformis;
- toxic adenoma, nodular goiter in case of prescription of daily doses exceeding 300 mcg (except for preoperative therapy for blocking the thyroid gland);
- hereditary diseases caused by lactase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption or galactose intolerance (since the drug contains lactose monohydrate);
- hypothyroidism, except in cases where its development was provoked by severe iodine deficiency;
- hypersensitivity to iodine or any other component of Renewal potassium iodide tablets.
It is necessary to avoid using the drug during treatment with radioactive iodine, as well as in the presence of a malignant tumor of the thyroid gland or if the development of the latter is suspected.
Potassium iodide Renewal should be used with caution in patients with impaired renal function.
How is Yodomarin useful for pregnant women?
It is not uncommon for iodine-containing drugs to be prescribed during pregnancy planning. This is due to the fact that the child’s health depends on the hormones produced by the mother’s thyroid gland – thyroid hormones. The required amount of iodine in the body maintains normal thyroid health and helps to avoid diseases associated with deficiency of the element. Therefore, this microelement is prescribed for prevention and if iodine deficiency is suspected during pregnancy. The consequences of iodine deficiency during intrauterine development can be:
- impaired mental development of a child (cretinism);
- pathologies of brain activity;
- miscarriages, stillbirths;
- dwarfism, other congenital anomalies.
A woman during pregnancy and breastfeeding should receive a double dose of iodine daily, because her thyroid gland produces a double portion of hormones: for the normal functioning of her body and the development of the baby. At least 100 mcg is the daily dose for an adult, and it is difficult to create a daily menu for a pregnant woman consisting of products that contain the required amount of the microelement. Therefore, iodine-containing drugs during this period are more the norm than a rarity.
Potassium iodide Renewal, instructions for use: method and dosage
Potassium iodide Renewal tablets should be taken orally once a day after meals, with enough water.
When prescribing the drug to newborns and children under 3 years of age, the tablet can be dissolved in 1 tablespoon of boiled water at room temperature before taking it.
Recommended daily doses of Potassium iodide Renewal depending on the indications and age of the patient (in terms of iodine content):
- prevention of endemic goiter: children (including newborns) – 100 mcg; adolescents and adults – 100–200 mcg; pregnant and breastfeeding women – 150–200 mcg;
- prevention of goiter recurrence after its surgical removal or after completion of a course of treatment of the disease with thyroid hormone preparations: for all patients, regardless of age, 100–200 mcg;
- therapy for euthyroid (associated with iodine deficiency) goiter: children (including newborns) and adolescents – 100–200 mcg; young adult patients – 300–500 mcg.
For preventive purposes, taking Potassium iodide Renewal is usually recommended for several months or years, and in some cases, if indicated, throughout life.
In newborns, goiter therapy usually lasts 2–4 weeks; in children from one month of age, adolescents and adults – 6–12 months, but if necessary, longer use is possible. The course of treatment is determined by the attending physician on an individual basis.
Why is iodine deficiency dangerous during pregnancy?
In addition to the fact that a lack of iodine in the diet causes unpleasant conditions (weakness, tachycardia, fatigue, nervousness, etc.) in the expectant mother, it can cause serious and irreparable harm to the fetus.
Severe iodine deficiency often causes spontaneous abortions and the birth of children with congenital developmental disorders (including deaf-muteness, strabismus, mental retardation and endemic neurological cretinism).
Even with a slight iodine deficiency, the level of thyroxine in the blood of a physically healthy pregnant woman decreases sharply (while when iodine is consumed in sufficient quantities, thyroxine remains within normal limits, decreasing by 12-15% by the time of birth), which can cause a number of complications during pregnancy and delivery - from spontaneous miscarriages and incoordination of labor to gestosis, premature birth and fetal asphyxia. To prevent the development of complications, a pregnant woman should consume at least 200 mcg of iodine during the day with food or in the form of various supplements.
Potassium iodide: use during pregnancy
Potassium iodide is an inorganic iodine preparation, produced under various trade names (Iodbalance, Microiodide, Iodomarin, etc.) and is often prescribed to children and adults to prevent the development of endemic goiter. Release form: tablets containing 100 or 200 mcg of iodine.
The dosage and method of using potassium iodide during pregnancy are determined by the doctor observing the woman. Be that as it may, you should be prepared for long-term use of the drug: the optimal solution is to start taking iodine supplements several months before the planned pregnancy, which allows you to avoid problems in the first months when the fetal nervous system is formed.
The fourth week of pregnancy is the period when the thyroid gland of the embryo is formed, but it will be able to fully function only by the 16th week of intrauterine development. Until this moment, the process of formation of nerve cells of the unborn child is completely dependent on the hormones produced by the mother’s thyroid gland, and if she does not consume enough iodine, the child’s chances of avoiding health problems are rapidly decreasing: according to WHO experts, iodine deficiency is the most common on the planet cause of mental retardation in children.
Typically, the dosage of potassium iodide during pregnancy is calculated so that the total amount of the active substance consumed during the day reaches 200-250 mcg. For example, if a woman takes a multivitamin that contains iodine, its amount is included in the calculation.
When receiving a standard dose (150 mcg per day) by taking multivitamins, the missing amount of the microelement is compensated by taking 1 tablet of potassium iodide containing 100 mcg of iodine. As a result, the daily requirement (250 mcg) is completely covered. When calculating the daily intake of a microelement, the intake of iodized salt is not taken into account.
It is also not recommended to exceed the daily norm established by doctors, therefore it is better to avoid taking dietary supplements with an increased iodine content (1.5-2 daily norms or more) during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Taking Iodomarin, or potassium iodide, during pregnancy in women who need not just replenishment of iodine deficiency, but complete treatment of an existing goiter, is supplemented with preparations of individual thyroid hormones - Eutirox, L-thyroxine and analogues.
Many women wonder: how safe is it to take potassium iodide during pregnancy? Isn’t it better to replace the drug prescribed by the doctor with folk remedies that are so popular these days? Unfortunately, any medical drug has a certain list of contraindications: in the case of potassium iodide, these are iodine intolerance, diffuse toxic goiter, hemorrhagic diathesis, and pulmonary tuberculosis.
For urticaria, pyoderma and chronic kidney disease, the drug is prescribed with caution, strictly observing the dosage and closely monitoring the body's response to therapy. Simultaneous use of the drug with lithium preparations and potassium-sparing diuretics is not recommended.
But the presence of all the above contraindications and restrictions does not mean that to replenish iodine deficiency you can use means from the arsenal of grandmothers: this approach, as a rule, does nothing but harm the body of the expectant mother and her child.
A particularly dangerous method is considered to be widespread even today, which consists of applying a drop of alcoholic iodine tincture to a piece of sugar, which is then eaten.
This “medicine” contains a gigantic concentration of iodine - much more than a couple of packages of Iodomarin - and significantly exceeds the maximum conditionally safe dose (1000 mcg per day). As a result of the use of such drugs, rapid overgrowth of the thyroid gland may begin, which will require surgery to stop.
Since such drugs in the vast majority of cases are taken for more than one month, with increased sensitivity to them, side effects sometimes appear - a sharp metallic taste in the mouth, salivation, acne, swelling.
To avoid the unpleasant symptoms of iodism, all dietary supplements and medications that contain iodine in any form are prescribed to pregnant women only after medical consultation.
A woman in the early and late stages of pregnancy may be prescribed Iodomarin. How is this drug useful and why is it important not to ignore the doctor’s prescription when it comes to the health of the expectant mother and child? You need to know whether taking this medicine can cause harm.
Overdose
When using Potassium iodide Renewal in daily doses above 150 mcg, there is a risk of latent hyperthyroidism becoming manifest. During long-term treatment with the drug in doses exceeding 300 mcg per day, the occurrence of iodine-induced hyperthyroidism may occur (especially in elderly patients with nodular goiter or toxic adenoma).
Symptoms of acute overdose may include the following effects: brown discoloration of the mucous membranes, abdominal pain and diarrhea (including melena), reflex vomiting, and in particularly severe cases, dehydration and shock. In case of acute overdose, gastric lavage is prescribed, sodium thiosulfate is administered, symptomatic treatment of water-electrolyte imbalances is carried out, and, if necessary, anti-shock therapy.
In case of chronic overdose, iodism may develop, manifested by the following symptoms: dermatitis, acne, metallic taste in the mouth, inflammation and swelling of the mucous membranes (conjunctivitis, rhinitis, bronchitis, gastroenteritis), irritability, fever. In this condition, it is necessary to stop taking Potassium iodide Renewal.
When Iodomarin is contraindicated for pregnant women
Like any drug, Iodomarin is prescribed only after examination by a doctor, in this case an endocrinologist. Self-medication, even with the help of vitamins and minerals, can be dangerous not only for the expectant mother, but also for her fetus. The same situation can occur with self-medication of iodine deficiency - an overdose of potassium iodide can cause:
- angioedema, urticaria;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland, changes in the amount of hormones (thyroxine, triiodothyronine);
- iodine toxicity (unusual weakness, confusion, numbness of the extremities);
- gastritis, rhinitis, brown staining of mucous membranes, anuria, collapse, swelling of the vocal cords.
Despite the universally stated need to take Iodomarin in the early stages of pregnancy, you need to remember that such drugs are prescribed only by a doctor after a blood test that reveals the concentration of thyroid hormones. With hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, exceeding the daily dose of iodine can lead not only to allergies, but also to more serious consequences, such as miscarriage, uterine bleeding.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
In pregnant and breastfeeding women, the need for iodine increases. Potassium iodide is recommended for use according to indications in cases where the iodine intake from food per day is less than 150–300 mcg. However, it should be borne in mind that the drug overcomes the placental barrier quite well and can provoke the development of hypothyroidism and goiter in the fetus. It has also been established that iodine is excreted in breast milk. Due to the above, during pregnancy and lactation, Potassium iodide Renewal can be used only in recommended doses.
Excess
Women who are pregnant and lactating need to reduce the amount of iodine in their diet. for a child. You should not consume more than 300 mg of this substance per day.
If there is an excess of iodine, the baby may experience a lack of thyroid hormones. If a mother consumes more than 12 mg of this substance during pregnancy or breastfeeding, the child may develop congenital hypothyroidism.
Excess iodine is rare, but it is dangerous. For a child, this is fraught with developmental pathologies and miscarriage. Therefore, it is important to monitor pregnancy and consult a doctor, reducing the level of this substance in the mother’s body. It is important to address this issue several months before the planned conception or begin treatment as soon as an excess of this element is detected.
Drug interactions
- angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), including enalapril, captopril, lisinopril: the threat of hyperkalemia increases;
- antithyroid drugs: the effectiveness of these drugs and potassium iodide decreases;
- thyroid-stimulating hormone: the absorption of iodine by the thyroid gland improves and the production of its hormones is activated;
- lithium preparations: the risk of goiter and hypothyroidism increases when these drugs are used simultaneously with iodine received in high doses;
- potassium perchlorate and thiocyanate: the process of iodine uptake by the thyroid gland is blocked;
- potassium-sparing diuretics: hyperkalemia may occur when these drugs are combined with iodine in high doses;
- radioactive isotopes of iodine 131I and 123I: the absorption of these isotopes by the thyroid gland is weakened under the influence of potassium iodide.
How to take, daily dosage
Before conception and during pregnancy, iodine injections should be given. If the dose of the drug is calculated correctly, there will be no side effects or negative results. If the functioning of the thyroid gland is impaired, then iodine accumulates and is not consumed.
Therefore, a number of serious diseases can arise that occur with an excess of this mineral.
Iodine is a metabolic catalyst. It should be taken in combination with calcium, selenium, vitamins C, D, group B.
IMPORTANT:
Not all women know how much iodine pregnant women need per day, so they often harm themselves and the fetus by consuming more of it than necessary. A pregnant woman needs 220 mcg per day, and a nursing mother needs to receive 270-290 mcg per day.
More detailed information about the daily iodine requirement can be found
Reviews of Potassium iodide Renewal
Reviews about Potassium iodide Renewal found on medical websites are in most cases positive. Patients characterize the drug as an effective drug that replenishes iodine deficiency. When used for the treatment of diffuse euthyroid goiter, the drug reduces the severity of symptoms of the disease, prevents the occurrence of complications such as the development of nodular/toxic goiter; when taken for preventive purposes, it provides an improvement in overall well-being, helps reduce irritability and increase concentration. Also, many women were satisfied with the results of the preventive use of Potassium iodide Renewal during pregnancy, since the drug helped prevent the occurrence of iodine deficiency by ensuring the necessary intake of iodine in the body, which is especially important for the normal development of the fetus. The advantages of the drug include its availability and relatively low cost. However, before a course of using potassium iodide, patients are recommended to consult with a specialist.
There are no complaints about adverse reactions.
Video
It is especially important to maintain normal iodine levels
in the body of a pregnant woman: it is
extremely necessary for the health of mother and child
.
A diet low in iodine during pregnancy can cause disturbances in the intellectual development of the child. Adding a little iodine to salt is simple and not at all expensive. Children who received a sufficient amount of it while in the womb develop much better, successfully master the school curriculum and adapt well to life.
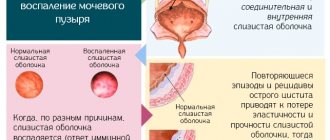
The thyroid gland influences many processes that occur in the body. Iodine deficiency manifests itself in a variety of symptoms that mimic various diseases.
Signs of a lack of an important microelement are:
- drowsiness;
- increased fatigue;
- apathy, lethargy;
- chronic fatigue;
- hair loss, dry skin, brittle nails;
- low level of stress resistance, memory loss, inhibited reactions;
- excess weight, swelling;
- feeling of chills, decreased immunity;
- imbalance of reproductive functions (infertility, disruption of the menstrual cycle);
- cholelithiasis;
- disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract, constipation.
Sometimes iodine deficiency occurs when smoking, begins in early pregnancy and lasts throughout the entire lactation period, in the case of taking oral contraceptives. The first deviation from the norm is the growth of the thyroid gland in a pathological form. Increasing its size allows you to stock up on iodine during pregnancy, which is needed for the production of hormones. These changes can be diagnosed during examination by a doctor, after an ultrasound.
To treat iodine deficiency, the doctor selects a drug.
It is not easy to identify iodine deficiency at the beginning of its development. Need a test. Using a cotton swab dipped in iodine solution, draw lines on the forearm (length - 5 cm):
- thin, translucent;
- medium thickness;
- bright, thick.
The study should be carried out in the evening, a few minutes before bedtime. The result will be available in the morning.
- If there is no first line and the other two are barely noticeable, then there is no iodine deficiency.
- When the oiliest line remains on the skin, preventive measures are needed.
- If all three lines are missing, severe iodine deficiency is observed. This may indicate violations.
IMPORTANT:
Iodine levels can be determined using a reliable method: analysis of the hormones T3 and T4 (ratio 1:4). With a reduced level of T3 and an increased level of T4, we can talk about iodine deficiency. After 3-4 days, you should take the tests again (to obtain average values, collect more accurate data and compare them with previous ones). The test results should be shown to an endocrinologist and gynecologist. The doctor will select treatment and correction methods.
You can get iodine from food, dietary supplements and pharmaceutical preparations.
It is useful to include iodized salt and seafood in your diet. You should not use Lugol's solution and iodine (to treat the skin) to get rid of iodine deficiency. If you lack this microelement, you need to take medications in tablets (this issue should be discussed with your doctor).
special instructions
In patients with renal failure, hyperkalemia may develop during the use of potassium iodide.
Iodine crosses the placenta and is excreted in breast milk; exceeding recommended doses can lead to the development of hypothyroidism and goiter in the fetus or infant.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and complex mechanisms
According to the instructions, Potassium iodide does not have a negative effect on human cognitive and psychomotor functions.