Prohibited during pregnancy
Prohibited during breastfeeding
Prohibited for children
Has restrictions for older people
Has limitations for liver problems
Has limitations for kidney problems
Parkinson's disease is a neurological degenerative disease that most often occurs in older people. To date, it cannot be completely cured, but negative symptoms can be relieved with the help of special medications.
Often, for this pathology, medications are prescribed based on the substance levodopa, which, according to the instructions for use, can be used both for Parkinson’s disease and for parkinsonism that has developed as a result of various types of lesions of the central nervous system.
general information
Drugs with levodopa are the most popular drugs in the fight against parkinsonism. They are produced by pharmaceutical companies from different countries in the form of combination products.
Drug group, INN, application
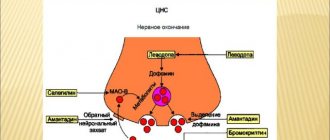
When buying levodopa-based products, it is important to understand what it is. The full name of the substance is dihydroxyphenylalanine. This is a special amino acid that is a product of tyrosine hydroxylation and a precursor to the hormone dopamine.
In Parkinson's disease, the amount of dopamine in the nerve ganglia of the brain is reduced, so it is advisable to restore its content in the central nervous system. Levodopa or L-dopa (dopa) is synthesized artificially. When this substance enters the body, it is processed and converted into dopamine.
Pharmacokinetic features of Levodopa
Drugs containing levodopa belong to a special group of drugs – antiparkinsonian drugs. They are not able to completely cure the disease, but they effectively eliminate negative symptoms. The international nonproprietary name is the name of the drug depending on its active substance, which determines its action in the body, the INN of drugs with dopa is Levodopa.
Such drugs are used in the field of neurology. They are prescribed to relieve unpleasant symptoms and improve the quality of life of patients with Parkinson's disease.
Release form, cost
The substance levodopa is presented in the form of a powdery substance in the form of large packets. It is not sold in its pure form in pharmacies. Most often, it is combined with excipients and released onto pharmacy counters in the form of tablets for internal use. In this case, the manufacturer himself determines the optimal content of active and additional components in 1 tablet.
Drugs that contain levodopa are produced under different trade names, and the retail price depends on the manufacturer. Here is the average cost of different drugs in Russia:
| Drug name | Cost in rubles |
| Levodopa\Benserazide, 200 mg + 50 mg (Teva, Israel), No. 100 | 1070 |
| Nakom (carbidopa + levodopa), Sandoz, No. 100 | 1368 |
| Madopar (levodopa + benserazide), No. 100 | 669 |
| Stalevo (carbidopa, levodopa, entacapone), No. 30 | 2803 |
| Tidomed Forte (carbidopa, levodopa), No. 100 | 586 |
Also, prices may vary depending on the content of active ingredients in 1 tablet. You can purchase the medicine only with a special prescription from a doctor.
Indications for use
The instructions for use indicate that Levodopa is designed for older people who exhibit symptoms such as tremors, muscle rigidity and others.
Levodopa is used for:
- Parkinson's disease;
- parkinsonism syndrome;
- treatment of hereditary extrapyramidal diseases;
- treatment of deforming muscular dystonia;
- treatment of reactive stuporous states (especially in patients with reduced dopamine excretion).
Carbidopa and Levodopa
The drug contains 2 active components. Available in the form of flat round blue tablets. One such tablet contains:
- 250 mg levodopa (l dopa);
- 25 mg carbidopa.
This medicine belongs to the combined antiparkinsonian drugs. Due to the inhibitor of peripheral dopa decarboxylase (carbidopa), the ability of levodopa to penetrate directly into the central nervous system is increased. This also reduces the likelihood of side effects.
Indications for prescribing the drug are Parkinson's disease, as well as the development of its symptoms (secondary parkinsonism) against the background of various lesions of the central nervous system (for example, due to encephalopathy, infections, chemical poisoning). It is not recommended to take the medicine if there are such contraindications:
- individual intolerance to active or auxiliary components;
- presence of glaucoma;
- severe cardiac pathologies (arrhythmia, failure);
- malignant formations on the skin, including melanoma;
- severe mental disorders;
- combination with MAO drugs.
The drug has many side effects, so it should be taken as recommended by your doctor. The drug is not prescribed for children under 18 years of age, pregnant and nursing mothers.
The dosage is determined by the attending physician and depends on the severity of symptoms and the general condition of the patient. The optimal dose is determined by titration. In this case, treatment begins with the smallest dose (half a tablet), which is gradually increased to the most effective one. For most patients, it is enough to take 1 tablet 3 or 4 times a day. It is prohibited to exceed the permissible daily dose, which is 8 tablets.
Contraindications
Among the problems of use and possible complications the following can be identified:
- atherosclerosis;
- hypertension with high blood pressure;
- endocrine;
- renal failure;
- liver diseases;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- problems with the lungs and respiratory tract;
- narrow-angle glaucoma;
- blood diseases;
- melanoma;
- allergic manifestations in the body to the drug.
People suffering from the following diseases or who are in a certain condition should take this kind of medication with caution:
- bronchial asthma;
- stomach ulcer;
- psychosis;
- psychoneurosis;
- emphysema;
- have had myocardial infarction;
- wide-angle glaucoma;
- taking antidepressants;
- women of childbearing age who are sexually active without contraception;
- pregnancy, childbirth and lactation;
- children and youth under 25 years of age.
Levodopa\Benserazid-Teva
The drug is produced by a pharmaceutical company (Israel). It is a combined antiparkinsonian drug. It comes in the form of round pink tablets, each of which contains:
- levodopa (100 or 200 mg);
- benserazide (25 or 50 mg).
Due to the presence of a peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor of aromatic L-acids in the drug, the conversion of levodopa to dopamine in the kidneys, heart, liver, stomach and intestines is reduced. This leads to an increase in the supply of this substance to the brain.
At the same time, there is a decrease in the manifestation of adverse reactions from peripheral organs. Also, the patient requires a smaller dose of levodopa to achieve optimal effect.
The medicine is used for primary and secondary parkinsonism. It is contraindicated for use when:
- intolerance to the components that make up the drug;
- endocrine disorders;
- glaucoma;
- severe dysfunction of the kidneys, liver or cardiovascular system;
- severe psychosis;
- concomitant use with MAO inhibitors;
- pregnancy, as well as in childhood and lactation.
The drug can provoke severe side effects, including inhibition of hematopoiesis, impairment of neurological and mental functions, problems with the heart and digestive organs. Allergic reactions often occur.
It is recommended to take the tablets orally half an hour before meals or an hour after meals. The initial single dose is about 50\12.5 mg of active components, it is taken 2 or 3 times a day. Then the dosage is gradually increased by 2-4 times. A maximum of 800 mg of levodopa\200 mg of benserazide can be taken per day.
Interaction
Pharmacokinetic interactions
With simultaneous use of trihexyphenidyl (m-anticholinergic), the rate, but not the extent, of absorption of levodopa decreases.
Ferrous sulfate reduces the Cmax and AUC of levodopa by 30–50%; these changes are in some cases clinically significant.
When used simultaneously with antacids, the degree of absorption of levodopa/benserazide is reduced by 32%.
Metoclopramide increases the rate of absorption of levodopa.
Pharmacodynamic interactions
Antipsychotics, opioids and antihypertensive drugs containing reserpine inhibit the effect of levodopa/benserazide. If necessary, use the lowest doses of these drugs.
When used concomitantly, pyridoxine may reduce the antiparkinsonian effect of levodopa/benserazide.
Levodopa/benserazide should not be used with non-selective MAO inhibitors. If it is necessary to use levodopa/benserazide in patients receiving irreversible non-selective MAO inhibitors, at least 2 weeks should pass from the moment of stopping the MAO inhibitor before starting the dose. Premature (within 2 weeks after discontinuation) use of levodopa/benserazide after a non-selective MAO inhibitor (eg tranylcypromine) can cause a hypertensive crisis.
Selective MAO type B inhibitors (including selegiline, rasagiline) and selective MAO type A inhibitors (moclobemide) can be used during treatment with levodopa/benserazide. In certain cases, selegiline may increase the effect of levodopa/benserazide without causing a dangerous interaction. It is recommended to adjust the dose of levodopa/benserazide depending on the individual needs of the patient in terms of therapeutic efficacy and tolerability.
The combination of selective MAO inhibitors type B and selective MAO inhibitors type A is equivalent to taking a non-selective MAO inhibitor, therefore this combination should not be used with levodopa/benserazide.
If it is necessary to use antihypertensive drugs during treatment with levodopa/benserazide, the possibility of developing orthostatic hypotension must be taken into account.
Levodopa/benserazide potentiates the effect of sympathomimetics (epinephrine, norepinephrine, isoproterenol, amphetamine), so this combination of drugs should not be used. If simultaneous use is still necessary, then the state of the cardiovascular system should be carefully monitored and, if necessary, reduce the dose of sympathomimetics.
It is possible to use levodopa/benserazide with other antiparkinsonian drugs (anticholinergic drugs, amantadine, dopamine receptor agonists), and not only the desired but also the undesirable effects may be enhanced. It may be necessary to reduce the dose of levodopa/benserazide or other drug. When levodopa/benserazide is used concomitantly with a catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor, a reduction in the dose of levodopa/benserazide may be necessary.
Since a patient receiving levodopa/benserazide may experience fluctuations in blood pressure and arrhythmias during halothane anesthesia, it is necessary to discontinue the drug 12–48 hours before surgery.
Protein-rich foods may reduce the therapeutic effect of levodopa/benserazide.
Levodopa/benserazide may affect laboratory results of catecholamines, creatinine, uric acid, glucose, alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin. An increase in the concentration of urea and creatinine in the blood, a false negative reaction to glucose in the urine when using the glucose oxidase method, and a false positive result from the Coombs test can be detected.
Madopar
This is a modern Swiss antiparkinsonian drug. It is available as fast-acting tablets or modified-release capsules (which release more slowly in the stomach). The drug contains 2 active components:
- levodopa (100 or 200 mg in 1 tablet);
- benserazide (25 or 50 mg, respectively).
The medicine is a combination drug prescribed for parkinsonism and restless legs syndrome. Contraindications include:
intolerance to components;- decompensated dysfunction of the kidneys, liver and endocrine and cardiovascular systems (the exception is patients with “restless legs” disease who are on hemodialysis);
- severe mental abnormalities;
- presence of glaucoma;
- period of pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- simultaneous use with MAO inhibitors;
- age less than 25 years.
Sometimes the use of the drug can provoke adverse reactions, among which mental and neurological disorders, heart problems, and orthostatic hypertension are often observed.
The medicine is used internally. Different forms have their own specific uses. For example, modified-release capsules should not be opened because the effect will be lost. But fast-acting capsules are dissolved in water before use, and then the resulting liquid is immediately drunk. The dosage and duration of treatment are selected individually for each patient.
Side effects
From the hematopoietic system: very rarely - hemolytic anemia, transient leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
From the nervous system: often - headache, dizziness, convulsions, spontaneous movement disorders (such as chorea and athetosis), episodes of freezing, weakening of the effect towards the end of the dose period, on-off phenomenon, increased manifestations of restless legs syndrome; very rarely - severe drowsiness, episodes of sudden drowsiness.
Mental disorders: rarely - agitation, anxiety, depressed mood, insomnia, delirium, aggression, depression, anorexia, moderate enthusiasm, pathological gambling, hypersexuality, increased libido; very rarely - hallucinations, temporary disorientation.
From the cardiovascular system: very rarely - arrhythmias, orthostatic hypotension (weakens after reducing the dose of the drug), increased blood pressure; frequency unknown - hot flashes.
From the digestive system: very rarely - nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, isolated cases of loss or change in taste, dryness of the oral mucosa; frequency unknown - gastrointestinal bleeding.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: rarely - skin itching, rash.
From laboratory parameters: infrequently - transient increase in the activity of liver transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, increase in bilirubin concentration, increase in urea and creatinine in the blood, change in urine color to red, darkening when standing.
Other: frequency unknown - febrile fever, excessive sweating.
Stalevo
This drug belongs to the combined dopaminergic drugs. It is available in the form of reddish-brown round film-coated tablets. One tablet contains:
- levodopa (100, 150 or 200 mg);
- carbidopa (25, 37.5 or 50 mg);
- entacapone (200 mg).
Transfer of patients to Stalevo
The effect of the drug is ensured by the activity of levodopa. Carbidopa increases its bioavailability, entacapone enhances the body's clinical response and helps prolong the action of levodopa.
Medicine is prescribed for Parkinson's syndrome when other drugs with levodopa do not give a positive result. Contraindications include:
- individual intolerance to the active and auxiliary components of the drug;
- liver failure;
- glaucoma;
- pheochromocytoma;
- combination with MAO inhibitors;
- neuroleptic syndrome;
- rhabdomyolysis;
- skin pathologies (for example, melanoma);
- psychoses;
- cardiac arrhythmias, heart failure.
The drug is also not recommended for use by children, pregnant women and breastfeeding women. This medicine has many side effects.
Take the drug orally, regardless of food intake. You need to take the whole tablet, since it contains the optimal therapeutic dose. You can take no more than 10 tablets per day.
Pharmacokinetics of the drug
This group of drugs quickly spreads throughout the body through the digestive system. The truth is that only 20-30% of the substance taken from the dose is absorbed in the body.
In addition, it must be remembered that undigested food slows down the absorption process.
When taking tablets within one or two hours, this substance dissolves in the body and only 3% of it enters the human brain. In addition, during this period the drug settles in the body.
It comes out hard. For example, 75% is excreted by the kidneys in 8 hours, and only 35% of the drug is excreted through the intestines in just 7 hours.
Similar drugs
There are cases when the use of levodopa is not possible. In such a situation, analogs based on the mechanism of action help. The most popular of them:
Midantan. A drug based on amantadine, which has antiparkinsonian and at the same time antiviral effects. It is also used to successfully treat neuralgic diseases caused by herpes zoster. Available in tablet form for internal use. Inexpensive and effective medicine.- Pronoran. This drug contains piribedil, which is a dopamine agonist. Prescribed for intolerance to levodopa. In pharmacies it is presented in the form of extended-release tablets.
- Newpro. An antiparkinsonian medicine that comes in the form of a transdermal patch. Contains the active substance rotigotine.
Can also be used:
- Madopar.
- Azilect.
- I won.
- Sindopa.
- Mendylex.
- Midantan.
- PC-Merz.
Only the attending physician can prescribe this or that analogue. He also selects the dosage regimen and determines the duration of the therapeutic course.
Analogs
The following analogs of the drug Levodopa exist :
- Stalevo (1780-2259 rubles);
- Nakom (1377-1526 rubles);
- Madopar GSS “125” (763-850 rubles);
- Madopar “125” (482-706 rubles);
- Madopar “250” (1300-1497 rubles);
- Madopar fast-acting tablets (dispersible) “125” (803-844 rubles);
- Madopar (482-741 rubles);
- Tremonorm (648-708 rubles);
- Tidomet forte (633-699 rubles);
- Striaton (about 106 rubles).
There are also drugs that rarely appear on sale - Sindopa, Carbidopa/Levodopa, Duellin, Sinemet, Sinemet SR, Isikom, Credanil 25/250, Zymox.
In general, all these drugs have an identical effect, but the active substance, levodopa, is much less in them, but this does not affect the manifestations of side effects.
In addition, the disadvantage is the cost of these drugs in comparison with Levodopa.
Signs of overdose
Taking increased doses of the drug Levodopa/Benserazide, synonyms of which will be presented below, can cause symptoms such as nausea, arrhythmia, involuntary movements of a pathological nature, insomnia, vomiting, and confusion. It should also be noted that the development of such signs may be delayed due to delayed absorption of the drug from the gastrointestinal tract.
To treat the described conditions, symptomatic therapy is carried out (antiarrhythmic drugs, respiratory analeptics and neuroleptics are prescribed), and vital functions of the body are also regularly monitored.