Pharmacological properties of the drug Nacom
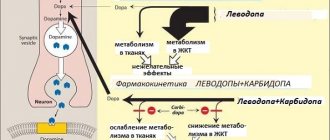
A combined antiparkinsonian drug containing carbidopa (an aromatic amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor) and levodopa (a metabolic precursor of dopamine). It is likely that the symptoms of Parkinson's disease are related to dopamine deficiency. Normally, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter and is produced in brain cells that control muscle activity. It is believed that movement disorders are a consequence of dopamine deficiency. Levodopa reduces the symptoms of Parkinson's disease by converting it into dopamine in the brain through decarboxylation. Carbidopa, which does not penetrate the BBB, prevents extracerebral decarboxylation of levodopa. This increases the amount of levodopa that enters the brain and is converted into dopamine, which leads to a decrease in the severity of Parkinson's disease symptoms in many patients. Levodopa is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. It is mainly converted into dopamine, adrenaline, norepinephrine and, ultimately, into hydroxyphenylacetic, homovanillic and vanylmandelic acids. 3-O-methyldopa is detected in blood plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. The half-life of levodopa from blood plasma is about 50 minutes. If carbidopa and levodopa are eliminated together, the half-life increases to 1.5 hours.
general information
Nakom is a popular antiparkinsonian drug. It is produced by a well-known pharmaceutical company from Slovenia in collaboration with a company from the USA.
Drug group, INN, application
The drug belongs to a large drug group - dopaminergic drugs. Such medications effectively eliminate the symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
The international nonproprietary name is the name of the active substance that is part of the drug and determines its effect on the body. This medicine contains 2 active ingredients, the main one being levodopa. Therefore, its INN is Levodopa in combination with a decarboxylase inhibitor.
Mechanism of action of antiparkinsonian drugs
The area of use of the drug is neurology. It is prescribed, as already mentioned, for primary or secondary parkinsonism.
Dosage form and cost
On pharmacy shelves the drug is presented in tablet form. All Nacom tablets have an oval, convex shape and are blue in color. They are placed in aluminum foil blisters of 10 pieces. In total, the cardboard box contains 100 tablets.
The retail price of a medicine depends on where it is purchased. Prices in different pharmacies in large Russian cities are shown in the table.
| Name of medicine (250/25 mg, No. 100) | Name of pharmacy and city | Cost in rubles |
| On whom | DIALOGUE, Moscow | 1318 |
| On whom | Laboratory of beauty and health, Moscow | 1410 |
| On whom | ZdravCity, Moscow | 1478 |
| On whom | 24-hour pharmacy "Roxana", St. Petersburg | 1590 |
| On whom | BALTIKA-MED, St. Petersburg | 1570 |
| On whom | GORZDRAV, St. Petersburg and region | 1441 |
| On whom | Online pharmacy 36.6, Moscow and region | 1410 |
| On whom | Online pharmacy 36.6, St. Petersburg and Leningrad region | 1433 |
The drug is released only with a special doctor's prescription. In many pharmacies it must be pre-ordered by phone or online.
Use of the drug Nakom
The dosage regimen is set individually depending on the severity of the disease, concomitant pathology and response to treatment. Usually the initial dose is 1/2 t of Nacom tablet 1 or 2 times a day after meals. To achieve an optimal response to treatment, the dose can be increased by gradually adding 1/2 t of tablet every day or every other day. For most patients, 3–6 tablets of the drug per day are enough. The daily dose should not exceed 8 tablets. For patients taking other antiparkinsonian drugs simultaneously with Nakom, dose adjustment may be required. To achieve optimal effect, it is better to take the drug daily without taking breaks.
Release form and composition
Nakom is produced in the form of tablets: biconvex, oval, with a notch on one side, blue with beige and individual dark blue inclusions (in blisters of 10 pcs.; 10 blisters in a box).
1 tablet contains:
- Active ingredients: levodopa – 0.25 g, carbidopa – 0.025 g;
- Auxiliary components: magnesium stearate, indigotin E132 (blue dye), corn starch, pregelatinized starch, microcrystalline cellulose.
Side effects of the drug Nacom
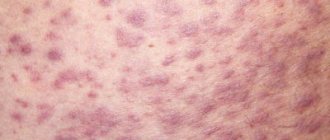
The side effects that occur during treatment with Nacom disappear when the dose is reduced or during treatment. The development of dyskinesia is most often noted. Often (more than 2%) - nausea, hallucinations, confusion, dizziness, chorea, dry mouth. Rarely (1–2%) - sleep disturbances, dystonia, drowsiness, insomnia, depression, asthenia, vomiting, anorexia. With a frequency of 0.5–1% - headache, lethargy and disinhibition, constipation, loss of orientation, paresthesia, shortness of breath, fatigue, orthostatic reactions, palpitations, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, muscle spasms, movement disorders and extrapyramidal reactions, decreased mental abilities, chest pain, diarrhea, weight loss, agitation, a state of pathological fear, frequent falls, impaired walking and blurred vision. Other side effects that have been reported in connection with the use of levodopa or its combinations: from the nervous system - ataxia, numbness, hand tremors, muscle twitching, tonic blepharospasm, trismus, activation of latent Bernard-Horner syndrome; euphoria, paranoid ideas, transient psychosis, dementia; from the gastrointestinal tract - a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, sialorrhea, dysphagia, bruxism, hiccups, gastrointestinal bleeding, flatulence, a burning sensation of the tongue, the development of duodenal ulcers; from the cardiovascular system - arterial hypotension, phlebitis; on the skin side - hyperemia, sweating, dark discoloration of sweat, hair loss; from the genitourinary system - urinary retention, urinary incontinence, dark colored urine, priapism; from the blood system - leukopenia, hemolytic and non-hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis; from the senses - diplopia, mydriasis, oculomotor crisis; others - general weakness, malaise, hoarseness, hot flashes, agitation, dyspnea, hypertension (arterial hypertension), phlebitis, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, malignant melanoma. In some cases, seizures developed, but a causal relationship with the use of levodopa or its combination with carbidopa has not been established. The use of the drug may cause changes in the following laboratory parameters: ALP, ALT, AST, LDH, bilirubin, blood urea nitrogen, protein-bound iodine, Coombs reaction.
Analogs
There are many antiparkinsonian drugs on the pharmacy market. Nak can be replaced by its structural analogues, which have a similar composition and mechanism of action. The most famous of them:
Carbidopa and Levodopa-Teva. Remedy from Israel. Available in the form of tablets for oral administration. It is an effective remedy, but it is quite difficult to buy in Russian pharmacies.- Duodopa. A German drug based on levodopa and carbidopa, which is available in the form of an intestinal gel. It is administered using a duodenal tube into the small intestine. Used in late stages of parkinsonism.
- Sindopa. An Indian generic, one tablet of which contains an increased amount of carbidopa (100 mg per 250 mg of levodopa).
- Tremonorm. An affordable Israeli product, which is available in tablet form. This medicine is widely popular.
All these drugs are available only with a doctor's prescription. He also determines the dosage and duration of therapy.
Special instructions for the use of the drug Nacom
Patients who were taking levodopa before prescribing Nacom should stop taking it at least 8 hours before starting treatment with Nacom (in the case of using long-acting forms of levodopa, stop taking it at least 12 hours). Patients who have previously been treated with levodopa may develop dyskinesia, since carbidopa promotes the penetration of large amounts of levodopa into the brain and, thereby, the formation of large amounts of dopamine. The occurrence of dyskinesia requires a reduction in the dose of the drug. Nacom, like other levodopa drugs, can cause involuntary movements and mental disorders. It is assumed that such reactions are due to an increase in dopamine concentrations in the brain after the use of levodopa. It may be necessary to reduce the dose of the drug. Careful monitoring of patients is necessary to identify their symptoms of depression with accompanying suicidal intentions. Patients with psychosis (including a history) require special monitoring. Nacom should be administered with caution to patients with severe cardiovascular or pulmonary disease, asthma, kidney, liver, or endocrine disease, or a history of ulcers or seizures. Caution should be exercised when prescribing the drug to patients who have recently suffered a myocardial infarction, especially in the presence of arrhythmia. In such patients, it is necessary to monitor the cardiovascular system, especially during the period of establishing the initial dose. Patients with chronic open-angle glaucoma should be prescribed Nacom with caution, with constant monitoring of intraocular pressure and careful monitoring of its changes during treatment. When the drug is suddenly stopped, a symptom complex resembling neuroleptic malignant syndrome occurs. It includes muscle rigidity, hyperthermia, mental disorders and increased serum CPK activity. Careful monitoring of the condition of patients whose dose is reduced or discontinued is necessary, especially if the patient is simultaneously taking antipsychotics. Nacom is not recommended for the treatment of drug-induced extrapyramidal disorders. During long-term treatment, it is recommended to periodically monitor the functions of the liver, kidneys, cardiovascular and hematopoietic systems. When treating with carbidopa preparations with levodopa, deviations in the results of various laboratory parameters may be observed - liver tests, alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST, bilirubin, a test for the presence of blood in the urine and the Coombs test. Carbidopa preparations with levodopa may give a false-positive reaction to ketone bodies in the urine if an indicator tape is used to determine ketonuria. This reaction will not change after boiling urine samples. False-positive results can be obtained when using the glucose oxidase method for determining glycosuria. The effect of the drug on the course of pregnancy has not been established; in animal experiments, levodopa and its combination with carbidopa caused malformations of internal organs and skeleton. Therefore, when prescribing the drug to women of childbearing age, the expected therapeutic effect should be compared with the possible risk to the fetus. It is not known whether carbidopa passes into breast milk. Since many drugs pass into breast milk and may cause adverse reactions in infants, a decision should be made to discontinue breastfeeding/use of the drug, taking into account the importance of treatment for the mother. Safety for use in infants and adolescents has not been established and is therefore not recommended for use in patients under 18 years of age. The drug may affect psychophysical abilities. Individual response to treatment may vary. Some side effects observed during treatment with NACOM may affect the ability to drive a car or use machinery.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- Angle-closure glaucoma;
- Melanoma suspected or established;
- Skin diseases of unknown etiology;
- Concomitant therapy with non-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors (their use should be discontinued 14 days before starting treatment with levodopa);
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Relative (must be used with extreme caution as there is a possibility of complications):
- Open angle glaucoma;
- Severe liver failure;
- Severe renal failure;
- Decompensated diseases of the endocrine system, including diabetes mellitus;
- Erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (due to the risk of bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract);
- Convulsive seizures (history), including epileptic seizures;
- Severe diseases of the respiratory system, including bronchial asthma;
- Severe diseases of the cardiovascular system, including myocardial infarction with cardiac arrhythmias (history), heart failure.
Drug interactions Nakom
Antihypertensive drugs. In patients taking antihypertensive drugs, the simultaneous use of a combination of levodopa and a decarboxylase inhibitor caused the development of symptomatic orthostatic hypotension, therefore, at the beginning of treatment with Nakom, a dose adjustment of the antihypertensive drug may be necessary. Antidepressants. There are several reports of adverse reactions, including hypertension (arterial hypertension) and dyskinesia, caused by the concomitant use of tricyclic antidepressants and levodopa with carbidopa (for patients taking MAO inhibitors). Other drugs. Phenothiazines and butyrophenones may reduce the therapeutic effect of levodopa. Papaverine and diphenine can lead to a decrease in the antiparkinsonian effect of Nakoma. Patients taking these drugs simultaneously with Nakom require constant medical supervision (to detect a decrease in the therapeutic effect).
Cost of treatment for Parkinson's disease in Moscow
The Neurology Clinic, part of the Yusupov Hospital, is a place where every person with Parkinson’s disease, regardless of the severity of the pathological process, receives quality treatment.
The Yusupov Hospital implements comprehensive programs for this disease, including consultations with leading specialists, drawing up a treatment program, placing the patient in a comfortable ward and various therapeutic measures. As part of drug therapy, patients are prescribed Nak in combination with various drugs; patient reviews indicate its effectiveness.
The cost of treating Parkinson's disease when choosing a comprehensive program is lower than when ordering services separately. The Yusupov Hospital cares about patients, and therefore provides them with complete and reliable information about the price of treatment and the scope of activities.