Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The substance increases the level of NO2 ( nitric oxide ) in endothelium . The drug acts as a venous and arterial dilator . Reduces the need for oxygen in the heart muscle, reduces the overall tension of the walls of the ventricles of the heart. Isosorbide dinitrate reduces the load on the heart, dilates the coronary arteries, redistributes coronary blood flow to an area with insufficient oxygen supply, and reduces blood pressure on the walls of blood vessels in the pulmonary circulation.
The drug, as a rule, does not affect the heart rate; sometimes it slightly increases heart rate. Under the influence of the substance, cerebral vessels dilate and pulmonary vascular resistance changes.
After taking the tablets, the medicine is quickly and completely absorbed. The biological availability of the product is no more than 22%. When used sublingually, the bioavailability is 60%. The degree of binding to blood plasma proteins is no more than 30%.
The effect of taking sublingual tablets occurs after 3 minutes, from oral tablets - after 15-40 minutes. When sprayed onto the oral mucosa, the antianginal effect develops within 30 seconds and lasts up to 2 hours.
After injection of the drug, it is half eliminated from the body after 20 minutes; when administered sublingually, the half-life is one hour, when taking tablets - 4 hours. The substance is metabolized in the liver, forming active metabolites: isosorbide-5-mononitrate, isosorbide-2-mononitrate . Metabolites are eliminated by renal glomerular filtration.
Long-term use of the medicine may lead to the development of tolerance.
Analogs
If you have to take Isosorbide dinitrate for certain reasons, it can be replaced with another remedy.
Structural
Among the drugs with isosorbide dinitrate as an active component, the following are noted:
Isoket. A vasolitic drug that helps relieve the symptoms of angina pectoris. Available in the form of a spray and solution for injection, which allows you to provide the patient with faster assistance. Cost – from 325 to 950 rubles.- Nitrosorbide. The most popular structural analogue of Isosorbide dinitrate. It comes in the form of tablets to be taken with water. It is popular among patients suffering from coronary heart disease and quickly relieves angina attacks. It has the most affordable price - from 25 rubles.
- Cardiket. An excellent drug that quickly relieves the symptoms of angina pectoris. Available in tablet form, 20, 40, 60 mg. Cost from 67 rub.
Thanks to the many forms of the drug, each patient can choose the right one and provide immediate assistance even in the absence of doctors or before the ambulance arrives.
Preparations based on another active ingredient
Analogs belonging to other groups include
Monocinque. A drug produced by a German company. The active ingredient is isosorbide mononitrate. It is highly effective and is intended for the prevention and treatment of angina pectoris, CHF, and recovery after a heart attack. Cost – from 147 rubles.- Molsidomin. The active ingredient is molsidomine. It is produced in tablet form (2 and 4 mg of molsidomine). Used to relieve and prevent angina. The average price is from 85 rubles.
- Nitroglycerine. A drug from the group of nitrates based on nitroglycerin. Helps quickly relieve the unpleasant symptoms of angina pectoris, and also helps prevent attacks. Most often used as emergency aid. May cause headaches as a side effect and is not recommended for long-term use as it may be addictive. Cost – from 50 rubles.
You should take medications only on the recommendation of a doctor. Self-medication can lead to serious consequences.
Indications for use
The medicine is prescribed orally, buccally and sublingually:
- for relief and prevention of angina ;
- during rehabilitation treatment after myocardial infarction ;
- as part of complex treatment of chronic heart failure ;
- for certain forms of pulmonary hypertension ;
- as part of combination therapy for cor pulmonale.
The drug is used by inhalation:
- for the relief and prevention of angina pectoris ;
- in case of acute myocardial infarction , acute left ventricular failure ;
- as a prophylaxis or to treat spasm of the coronary arteries if a cardiac catheter is used.
The medicine is administered intravenously:
- in acute myocardial infarction ;
- for unstable angina ;
- patients with pulmonary edema .
It is also possible to use the substance cutaneously to prevent angina pectoris .
Instructions:
Clinical and pharmacological group
01.029 (Peripheral vasodilator. Antianginal drug)
pharmachologic effect
Peripheral vasodilator with a predominant effect on venous vessels. Antianginal agent. The mechanism of action is associated with the release of the active substance nitric oxide in the smooth muscles of blood vessels. Nitric oxide causes activation of guanylate cyclase and increases cGMP levels, which ultimately leads to smooth muscle relaxation. Under the influence of isosorbide dinitrate, arterioles and precapillary sphincters relax to a lesser extent than large arteries and veins. This is partly due to reflex reactions, as well as the less intense formation of nitric oxide from active substance molecules in the walls of arterioles.
The effect of isosorbide dinitrate is associated mainly with a decrease in myocardial oxygen demand due to a decrease in preload (dilatation of peripheral veins and a decrease in blood flow to the right atrium) and afterload (reduction in peripheral resistance), as well as with a direct coronary dilation effect. Promotes redistribution of coronary blood flow in areas with reduced blood supply.
Increases exercise tolerance in patients with coronary artery disease and angina pectoris. In heart failure, it helps to unload the myocardium by reducing preload. Reduces pressure in the pulmonary circulation.
Pharmacokinetics
When taken orally after absorption from the gastrointestinal tract, isosorbide dinitrate undergoes a “first pass” effect through the liver. Cmax in blood plasma is achieved after 1 hour. When administered buccally, isosorbide dinitrate is rapidly absorbed, Cmax of the active substance in plasma is achieved after 5-6 minutes.
Metabolized to form the active metabolite isosorbide-5-mononitrate, whose T1/2 is 5 hours, as well as isosorbide-2-mononitrate with a T1/2 of 2.5 hours.
T1/2 of isosorbide dinitrate, depending on the dosage form used, varies from 20 minutes to 4 hours. It is excreted by the kidneys and through the intestines.
Dosage
When taken orally, a single dose is 10-120 mg, frequency of administration is 1-5 times a day, depending on the indications and the dosage form used.
For sublingual or buccal use, a single dose is 5-10 mg, the frequency of administration depends on the indications and the patient’s response to treatment.
For inhalation use, 1-3 doses are injected into the oral cavity at intervals of about 30 seconds while holding the breath. For acute myocardial infarction and acute heart failure, the initial dose is 1-3 inhalations. If there is no improvement after 5 minutes, inhalations can be repeated subject to constant monitoring of blood pressure and heart rate. To prevent coronary spasm in case of catheterization, 1-2 doses should be administered immediately before the procedure.
When administered intravenously, the dosage regimen depends on the clinical situation and the dosage form used.
For cutaneous use, the initial dose is 1 g at night, before bedtime, and, if necessary, in the morning.
The duration of treatment is determined in each case individually.
Drug interactions
When used simultaneously with adsorbents, astringents and enveloping agents, the absorption of isosorbide dinitrate decreases.
With the simultaneous use of antihypertensive drugs, peripheral vasodilators, calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers, antipsychotics (neuroleptics), tricyclic antidepressants, PDE inhibitors, ethanol, the hypotensive effect may be enhanced.
When used simultaneously with anticholinergic drugs, memory and attention problems may occur in elderly patients.
When used simultaneously with sympathomimetic drugs, the antianginal effect of isosorbide dinitrate may be reduced.
When used simultaneously with dihydroergotamine, it is possible to increase the concentration and enhance the effect of dihydroergotamine.
When used simultaneously with norepinephrine, the therapeutic effect of norepinephrine decreases.
When used simultaneously with sildenafil, there is a risk of developing severe arterial hypotension and myocardial infarction.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
The use of isosorbide dinitrate during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding) is possible only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus or child.
Side effects
From the cardiovascular system: dizziness, headache, tachycardia, transient facial hyperemia, feeling of heat, arterial hypotension; in some cases - increased attacks of angina (paradoxical reaction).
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, a slight burning sensation of the tongue, dry mouth.
From the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: drowsiness, blurred vision; rarely - cerebral ischemia and collapse.
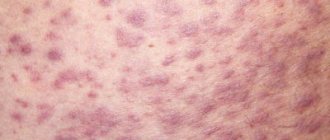
Allergic reactions: skin rash.
Indications
For oral, sublingual, buccal administration: relief and prevention of angina attacks, rehabilitation treatment after myocardial infarction. Chronic heart failure (as part of combination therapy), some forms of pulmonary hypertension, cor pulmonale (as part of combination therapy).
For inhalation use: relief and prevention of angina attacks; as an emergency medicine for acute myocardial infarction and acute left ventricular failure at the prehospital stage. Prevention and treatment of coronary artery spasm when using a cardiac catheter.
For intravenous administration: acute myocardial infarction, incl. complicated by acute left ventricular failure; unstable angina; pulmonary edema.
For cutaneous use: prevention of angina attacks.
Contraindications
Severe arterial hypotension (systolic blood pressure less than 100 mm Hg, diastolic blood pressure less than 60 mm Hg), collapse, shock, acute myocardial infarction with severe arterial hypotension, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, constrictive pericarditis, cardiac tamponade, toxic pulmonary edema , conditions accompanied by increased intracranial pressure (including hemorrhagic stroke, traumatic brain injury), angle-closure glaucoma, simultaneous use of sildenafil (PDE inhibitor), increased sensitivity to nitrates.
special instructions
Use with caution in patients with cerebrovascular accidents, aortic and/or mitral stenosis; in patients prone to orthostatic hypotension; in elderly patients. During treatment, especially in the case of a gradual increase in dose, monitoring of blood pressure and heart rate is necessary.
During the treatment period, avoid drinking alcohol.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
During the treatment period, it is not recommended to drive vehicles or engage in other potentially hazardous activities, because with regular use, isosorbide dinitrate reduces the ability to concentrate and the speed of psychomotor reactions.
Preparations containing ISOSORBIDE DINITRATE
• KARDIKET® tab. prolong. actions 40 mg: 20 or 50 pcs. • NITROSORBIDE tab. 10 mg: 10 pcs. • NITROSORBIDE tab. 10 mg: 50 pcs. • KARDIKET® tab. prolong. action 60 mg: 20 or 50 pcs. • ISACARDIN spray dosed 1.25 mg/1 dose: vial. 15 ml (300 doses) • NITROSORBIDE tab. 10 mg: 25 or 50 pcs. • NITROSORBIDE tab. 10 mg: 20, 30, 50 or 100 pcs. • ISACARDIN (ISACARDIN) concentrate for preparation. r-ra d/inf. 10 mg/10 ml: amp. 10 pieces. • NITROSORBIDE tab. 10 mg: 10, 20 or 50 pcs. • NITROSORBIDE tab. 20 mg: 50 pcs. • NITROSORBIDE tab. 10 mg: 50 and 100 pcs. • NITROSORBIDE tab. 10 mg: 10 pcs. • NITROSORBIDE tab. 10 mg: 25 or 50 pcs. • KARDIKET® caps. prolong. action 120 mg: 20 pcs. • KARDIKET® tab. prolong. actions of 20 mg: 20 or 50 pcs. • NITROSORBIDE tab. 10 mg: 10, 20, 30, 40 or 50 pcs. • KARDIKET® tab. prolong. action 60 mg: 20 or 50 pcs. • ISOLONG caps. prolong. action 40 mg: 20 or 1000 pcs. • ISOLONG caps. prolong. action 20 mg: 20 or 1000 pcs. • NITROSORBIDE tab. 10 mg: 10, 30, 50 and 30,000 pcs. • NITROSORBIDE tab. 10 mg: 10 or 50 pcs. • KARDIKET® tab. prolong. actions of 20 mg: 20 or 50 pcs. • ISOKET® spray dosed 1.25 mg/1 dose: vial. 15 ml (300 doses) • NITROSORBIDE tab. 20 mg: 10 pcs. • ISOKET® spray dosed 1.25 mg/1 dose: vial. 15 ml (300 doses) • KARDIKET® tab. prolong. actions 40 mg: 20 or 50 pcs. • DINISORB (DINISORB) concentrate for preparation. r-ra d/inf. 10 mg/10 ml: amp. 10 pieces. • NITROSORBIDE tab. 10 mg: 25 pcs. • NITROSORBIDE tab. 10 mg: 10 pcs. • ISOKET® (ISOKET) concentrate for preparation. r-ra d/inf. 10 mg/10 ml: amp. 10 pieces. • ISOKET® (ISOKET) concentrate for preparation. r-ra d/inf. 10 mg/10 ml: amp. 10 pieces. • NITROSORBIDE-RUSPHAR tab. 10 mg: 10, 20, 25, 30, 40 or 50 pcs.
Contraindications
Isosorbide dinitrate preparations are not recommended for use:
- with severe arterial hypotension ;
- patients in shock;
- during collapse ;
- patients with constrictive pericarditis ;
- with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy ;
- patients with TBI , hemorrhagic stroke or simply increased intracranial pressure ;
- in acute myocardial infarction with low blood pressure ;
- with cardiac tamponade ;
- patients with toxic pulmonary edema ;
- for angle-closure glaucoma ;
- if allergic to the active substance.
Release form and composition
The drug is available in the form of tablets, capsules, concentrate for preparing a solution for infusion, sublingual spray, films for gluing to the gums.
Isosorbide dinitrate tablets 10 mg, 20 mg, sold in packages of 20, 25 or 50 pcs.
Isosorbide dinitrate retard capsules are available in 20 pcs. packaged.
The concentrate for preparing a solution for infusion is sold in 5 ml ampoules, with each package containing 10 ampoules.
Bottles with a sublingual spray dispenser contain 300 doses of Isosorbide.
The active substance of Isosorbide dinitrate is isosorbide dinitrate. Tablets of the drug contain 10 mg or 20 mg of the active substance, retard capsules - 20, 40, 60, or 120 mg, concentrate for solution for infusion - 1 mg/1 ml, sublingual spray - 1.25 mg/dose.
Side effects
After taking the drug, the following may occur:
- headache, facial flushing blood pressure ;
- dizziness, tachycardia , hot flashes and fever;
- paradoxical increase in angina ;
- dryness of the oral mucosa, burning sensation on the tip of the tongue, nausea;
- allergic skin rashes;
- decreased visual acuity, weakness and drowsiness ;
- collapse , cerebral ischemia (very rare).
Isosorbide Dinitrate, instructions for use (Method and dosage)
The substance is taken sublingually, orally, inhalation, buccally, cutaneously, or intravenous injections of the drug.
Orally, as a rule, 10 to 120 mg of the drug is prescribed, divided into 1-5 doses per day.
For buccal and sublingual use, up to 10 mg of the substance can be taken at a time. The medicine is taken at different frequencies depending on the indications.
Inhalation of the drug involves injecting 1-3 doses into the oral cavity. Between injections it is necessary to make a gap of 30 seconds, holding your breath.
To provide first aid for acute myocardial infarction or heart failure, use 1 to 3 doses. If after 5 minutes there is no improvement in the patient’s condition, then you can take the medicine again.
As a prophylactic agent during catheterization , to avoid coronary spasm, 1-2 doses of the substance are used before catheterization .
Intravenous injections are performed by medical personnel, the dosage varies, depending on the indications and condition of the patient.
The product is applied to the skin at night, 1 gram. In case of urgent need, the daily intake can be increased to 2 grams.
The course of treatment is determined by the attending physician on an individual basis.
Comment
Even if the drug is used as prescribed by a specialist, it can change the patient's reactivity to such an extent that it impairs the ability to drive a car. Dizziness and fatigue may occur at the beginning of treatment or immediately after increasing the dose, as well as when drinking alcohol or switching to another medicine at the same time. The patient should be informed that if the above symptoms occur, he should stop driving vehicles.
Overdose
In case of overdose, the following symptoms occur: anoxia , collapse , fainting and dizziness , cyanosis of nails and lips, headaches, general weakness, bradycardia , shortness of breath , increased body temperature, convulsions , diarrhea , blurred vision, decreased intracranial pressure , nausea .
As first aid, it is recommended to perform gastric lavage and use symptomatic therapy. With the development of methemoglobinemia, a solution of methylene blue 1-2 mg per kg of the victim’s weight is administered intravenously.
Interaction
The substance enhances the effect and increases the plasma concentration of dihydroergotamine .
Anticholinergics lead to impairment of memory and attention, especially in older people.
When combining the drug with astringents, enveloping agents and adsorbents, the absorption capacity of isosorbide dinitrate decreases.
Simultaneous use of peripheral vasodilators, beta-blockers, antipsychotics, tricyclic antidepressants, antihypertensive drugs, calcium channel blockers, ethyl alcohol, PDE inhibitors enhances the hypotensive effect.
Sympathomimetics reduce the antianginal effect of the drug.
The medicine reduces the effect of norepinephrine .
When combined with sildenafil, myocardial infarction and a sharp decrease in blood pressure increases .
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Due to the lack of studies in pregnant women, according to the instructions for use, isosorbide dinitrate and drugs containing it should not be used during pregnancy, unless the doctor considers it absolutely necessary and will directly and constantly monitor the progress of treatment.
There have been reports of nitrates passing into breast milk and methemoglobinemia in children due to this reason. The extent to which isosorbidinitrate and its metabolites are excreted in milk has not been established, so caution should be exercised when using the drug in nursing women.
special instructions
Particular care should be taken when treating patients with mitral or aortic stenosis , prone to low blood pressure , elderly people, and with cerebral circulatory disorders.
While undergoing therapy with the drug, you should not drive a car or perform tasks that require high reaction speed and concentration.
To avoid the development of tolerance, it is recommended to take 4 day breaks for every 3-6 weeks of using the substance.
With a gradual increase in the dosage of the drug, it is necessary to monitor blood pressure and heart rate.
Reviews from doctors
Isosorbide dinitrate is most often prescribed for the prevention of angina pectoris and various heart disorders. The drug has many positive reviews from experts:
Nikolaev P.N. cardiologist: “Isosorbide dinitrate is an inexpensive drug that is available in several forms. Thanks to this, patients have the opportunity to independently provide first aid before doctors arrive and avoid serious consequences.”
Vasilyeva O.P., cardiologist: “Isosorbide dinitrate, unlike other drugs, can quickly relieve an attack of angina and prevent dangerous symptoms. The drug shows excellent results in the treatment of ischemia and arterial hypertension. It has fewer side effects than drugs with similar mechanisms of action.”
Preparations containing (Isosorbide Dinitrate analogues)
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Nitrospray
Nitroglycerine
Efox
Monosan
Nitromint
Pectrol
Isoket
Erinite
Cardiket
Sustak Forte
Nitrosorbide
Trade names of Isosorbide Dinitrate: Aerosonit, Isacardin, Iso Mak spray, Isolong, Cardiket, Nitrosorbide, Nitrosorbide tablets, Dinisorb, Iso Mak retard, Isoket, Isosorbide dinitrate, Cardix, Nitrosorbide-Rusfar, TD-spray Iso Mak .