Pharmacological effect
The drug has disinfecting, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and regenerating effects. It is active against staphylococci, gram-negative intestinal, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus, gonorrhea, salmonella, streptococci. The product easily penetrates deep into tissues, transports chloramphenicol and sulfadimethoxin.
Due to its high dehydration activity, within 2-3 days Levosin eliminates peripheral edema and cleanses the wound of purulent-necrotic contents. Methyluracil accelerates wound healing and stimulates cellular defense factors. Trimecaine anesthetizes, has a stronger and longer-lasting effect than Novocaine, is low-toxic, and does not irritate the skin. Levosin does not accumulate.
Levosin
Levosin (chloramphenicol + sulfadimethoxin + methyluracil + trimecaine) is a combined domestic drug for external use, which has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and necrolytic effects and is used to accelerate the healing of purulent wounds affected by mixed microflora, incl. burns and hard-to-heal ulcers. The problem of treating diseases of purulent-inflammatory origin has been occupying the minds of surgeons for many years. The reason for this is the steady and progressive increase in the number of complications, including deaths. The prevalence of purulent-septic complications is associated with the dynamic change of various infectious agents, and all this occurs against the background of total antibacterial therapy. An aggravating factor in the development of severe purulent-inflammatory infections is the coherence in the action of pathogenic microorganisms, in other words, their synergy. Increasingly, entire microbial associations are involved in infection. The active development of aerobic bacteria, which intensively consume oxygen, creates fertile soil for the dominance of anaerobes. The result of such an undesirable symbiosis is a severe purulent-inflammatory process, which could not be caused by one weakly pathogenic species of microbes. The problem of effective local impact on infectious and inflammatory foci, as noted above, has not lost any of its relevance today, rather the opposite. One of the most effective remedies in this regard is Levosin ointment. This domestic drug can, with good reason, be considered a fundamentally new drug, completely devoid of any auxiliary components, since all the substances included in its composition take an active part in the formation of the therapeutic effect. The possibility of developing levosin was caused by the rapid development in the 50-60s of the last century of a new direction in science - biological pharmacy. Within the framework of this direction, the very definition of the concept of “medicine” was, in fact, revised and an active study of production factors that determine the therapeutic effectiveness of drugs was launched.
Already the first results of clinical trials of levosin were very promising. All clinical centers announced that the ointment under study has a multi-vector effect on all the main etiopathological links of inflammation, while exhibiting a pronounced antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect. The drug significantly shortened the healing time of infected wounds and improved the overall prognosis. It is curious that the drug almost immediately came to the attention of military surgeons, who drew attention to the effectiveness of levosin in extreme conditions and in cases of total destruction of the population: the drug was able to localize a purulent-inflammatory focus in the wound for 1-2 days, thereby providing much-needed temporary “backlash” before primary surgical treatment. Levosin confirmed all these numerous advances during the war in Afghanistan, the earthquake in Armenia and in many other extreme situations. Levosin is effective against infections caused by both gram-positive and gram-negative representatives of pathogenic and opportunistic microflora. The ointment easily penetrates into the deepest layers of the skin, transferring its main antibacterial “weapons” - chloramphenicol and sulfadimethoxine - to the place of their direct action. Due to its high hydration activity, the drug in the shortest possible time (no more than 2-3 days) eliminates the swelling adjacent to the source of inflammation and washes out the accumulated purulent-necrotic contents from the wound. Methyluracil, which is part of levosin, promotes rapid wound healing and activates tissue protective factors. Trimecaine, another active component of the drug, is a local anesthetic that is superior in its analgesic activity to novocaine and acts for a longer period of time. In conclusion, it should be noted that levosin is almost completely devoid of locally irritating properties and does not accumulate in the body.
Instructions for use
Levosin ointment is used in traumatology to heal wounds in which purulent exudate has accumulated. The drug should be used exclusively as prescribed by a doctor after conducting a series of laboratory tests. The fact is that wounds can be infected with microorganisms against which Levosin is powerless. Its use will not speed up the patient’s recovery, but will increase the severity of clinical manifestations.
Patients often ask dermatologists whether Levosin is an antibiotic or not. It contains chloramphenicol, which has bactericidal properties. This determines whether the ointment belongs to antibacterial drugs.
Indications and contraindications
The main indication for use of Levosin is infectious and inflammatory skin diseases. The ointment is prescribed regardless of the origin of the pathological process. The drug is included in therapeutic regimens for infections of burns, cuts, frostbite, and cracks.
It is also recommended for healing skin damaged as a result of exposure to internal negative factors. For example, Levosin accelerates tissue regeneration in diabetic feet and ulcers that form due to venous stagnation of blood.
We recommend
Oflomelid ointment is an effective remedy for the treatment of burns and ulcers.
An antibacterial agent is used after open surgery. After stitches are placed, they can become infected with pathogenic bacteria. In such cases, the inflammatory process quickly develops, accompanied by tissue suppuration. Patients after surgery are prescribed Levosin in combination with antiseptic solutions.
The ointment has only one contraindication - individual intolerance to its constituent components.
Directions for use and doses
To treat minor skin lesions, it is enough to apply a thin layer of Levosin to the surface of the wound. This is relevant for thermal or radiation burns of the 1st degree, frostbite, cuts, cracks.
In the treatment of deep wounds with necrotic masses, the application of breathable dressings is practiced. To do this, spread the ointment evenly on a sterile bandage or napkin and apply it to the affected skin. The bandage is fixed with adhesive tape. The duration of the treatment procedure is 4-5 hours.
In a hospital setting, the drug is injected with a syringe into pathological lesions after mechanical cleansing of the wound. Therapy continues for 14-20 days until all clinical manifestations disappear completely.
Side effects and special instructions
Do not use the drug in high dosages so that the wound quickly cleanses. Active ingredients in high concentrations often provoke local allergic reactions. The skin becomes even more swollen and red, and a small itchy rash appears on it. You should wash off the product and apply any antihistamine gel - Fenistil, Gistan, La-Cri.
It is necessary to consult a doctor when the first signs of tissue necrosis appear. The pathological process is clinically manifested in redness and swelling of the wound edges, pain on palpation. The doctor will perform an external examination, determine the method of use of the drug, the duration of the therapeutic course and dosage.
The use of Levosin in the treatment of pregnant women is undesirable. The doctor prescribes ointment in exceptional cases when safer means do not have the desired effect.
Analogues of the drug
The product can be replaced with drugs with the same properties and composition or with other active substances. Analogues include:
- Fastin - ointment based on benzocaine, furacilin, syntomycin;
- Acerbine - ointment containing malic, salicylic, benzoic acids;
- Mephenate – ointment based on mephenamine, vinylin;
- Gentaxan is a powder for preparing a solution containing gentamicin, tryptophan, methoxane, zinc sulfate heptahydrate;
- Levomekol is an ointment based on chloramphenicol, methyluracil.
Reviews
Margarita, Bryansk
The instructions for Levosin contain a description of all possible treatment methods. Healing bandages with ointment helped me after a severe burn with boiling water. The wound healed quickly, and the pain disappeared almost immediately after applying the drug.
Alexander, Voronezh
The mother had a deep wound on her leg due to diabetes. The endocrinologist recommended frequent dressings with Levosin and treating the edges with Chlorhexidine solution. I didn’t expect these cheap drugs to help so quickly.
Read further:
Dioxidin ointment: instructions for use, recommendations for use for burns, analogues and reviews
Levomycetin ointment: instructions for use, prices, review of analogues and reviews
Oflomelid ointment: detailed instructions and recommendations for use, composition, review of analogues and reviews
Iruksol ointment: instructions and recommendations for use, composition, review of analogues and reviews
Rescuer ointment (balm): instructions and indications for use for various skin lesions, composition, analogues and reviews
Levosin ointment (review) from 50 rub.
Overall
4.8
- Efficiency
- Price
- Safety
- Availability
Pros
- Price
- Efficiency
- Convenient tube
- Wide spectrum of action
- Smell
- Consistency
Cons
- Short shelf life
Analogs
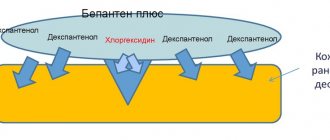
Current analogues of Levosin are Fastin, Levomekol, Sulfargin, Argosulfan (instructions), Bepanten Plus. Vishnevsky's liniment and Ichthyol ointment have a wound-healing effect. Substitutes are also Vulnuzan and Karotolin.