Release form and composition
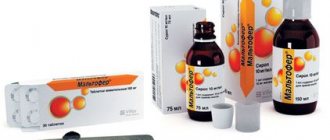
Maltofer is produced in the following dosage forms:
- Oral solution: dark brown (5 ml in glass bottles, 10 bottles in a cardboard box);
- Drops for oral administration: dark brown (30 ml in dark glass bottles with a dispenser, 1 bottle in a cardboard box);
- Syrup: dark brown (150 ml in dark glass bottles, 1 bottle in a cardboard box complete with a measuring cap);
- Chewable tablets: flat-cylindrical, scored, brown with white inclusions (10 pieces in blisters, 3 blisters in a cardboard box);
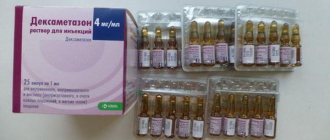
- Solution for injection: brown (2 ml in colorless glass ampoules, 5 ampoules in a cardboard box).
The composition of 1 ml of oral solution includes:
- Active substance: iron – 20 mg (in the form of iron (III) hydroxide polymaltosate);
- Auxiliary components: sucrose, 70% sorbitol solution, sodium methyl parahydroxybenzoate, sodium propyl parahydroxybenzoate, cream flavor, sodium hydroxide, purified water.
The composition of 1 ml (20 drops) drops for oral administration includes:
- Active substance: iron – 50 mg (in the form of iron (III) hydroxide polymaltosate);
- Excipients: sucrose, sodium methyl p-hydroxybenzoate, sodium propyl p-hydroxybenzoate, cream flavor, sodium hydroxide, purified water.
1 ml of syrup contains:
- Active substance: iron – 10 mg (in the form of iron (III) hydroxide polymaltosate);
- Excipients: sucrose, 70% sorbitol solution, methyl p-hydroxybenzoate, propyl p-hydroxybenzoate, 96% ethanol, cream flavor, sodium hydroxide, purified water.
1 chewable tablet contains:
- Active substance: iron – 103 mg (in the form of iron (III) hydroxide polymaltose);
- Auxiliary components: dextrates, macrogol 6000, purified talc, sodium cyclamate, vanillin, cocoa powder, chocolate flavor, microcrystalline cellulose.
The composition of 1 ml of solution for injection includes:
- Active substance: iron – 50 mg (in the form of iron (III) hydroxide polymaltosate);
- Auxiliary components: sodium hydroxide/hydrochloric acid, water for injection.
Indications for use
Maltofer in oral dosage forms (solution and drops for oral administration, chewable tablets, syrup) is prescribed for the following conditions/diseases:
- Latent and clinically pronounced iron deficiency (treatment);
- Iron deficiency in lactating and pregnant women, children and adolescents, adults (for example, the elderly and vegetarians), women of childbearing age (prevention).
Maltofer in the form of an injection solution is used in the treatment of iron deficiency in cases where it is impossible to take iron-containing drugs orally, as well as their ineffectiveness or lack of effectiveness in case of malabsorption, in patients who do not agree to regularly and long-term use of oral iron supplements and in patients with gastrointestinal disorders tract (for example, with ulcerative colitis), in which an exacerbation of the disease may occur when taking iron supplements orally.
Maltofer for injection is prescribed only in cases of iron deficiency confirmed by research (for example, determination of the level of hemoglobin, serum ferritin, number of red blood cells or hematocrit, as well as their parameters - the average content of hemoglobin in an erythrocyte, the average volume of an erythrocyte).
Drug interactions
Maltofer injection solution cannot be used in combination with iron preparations for oral use (their absorption from the gastrointestinal tract is reduced). In this regard, it is recommended to begin therapy with oral iron preparations no earlier than 7 days after the last administration of the solution.
When taken simultaneously with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (for example, enalapril), systemic adverse reactions that occur when using the injection solution may increase.
Contraindications
- Excess iron (hemosiderosis, hemochromatosis);
- Anemia not associated with iron deficiency (for example, impaired erythropoiesis, hemolytic anemia caused by a lack of vitamin B12 in the body, megaloblastic anemia, bone marrow hypoplasia);
- Impaired iron utilization (eg, thalassemia, sideroachrestic anemia, cutaneous porphyria tarda, lead anemia);
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Additional contraindications to the use of Maltofer in the form of an injection solution are:
- Infectious hepatitis;
- Osler-Rendu-Weber syndrome;
- Chronic polyarthritis;
- Uncontrolled hyperparathyroidism;
- Infectious kidney diseases (in acute cases);
- Bronchial asthma;
- Decompensated cirrhosis of the liver;
- Intravenous administration;
- First trimester of pregnancy.
When taking the drug orally, due to the need to prescribe smaller doses, Maltofer is recommended for premature children in the form of drops, for children under 12 years old - in the form of syrup.
The drug in the form of an injection solution is not recommended for use in children under 4 months of age (due to the lack of data on the safety and effectiveness of its use in this category of patients).
Analogues of Maltofer during pregnancy
In case of intolerance to the Maltofer composition, doctors prescribe similar drugs to pregnant women with a different composition, which have a milder effect on the body. Safer replacement drugs include Sorbifer and Durulex. In addition to the main constituent substances, the first preparation contains a small amount of ascorbic acid.
Reference! Scientists have found that ascorbic acid can improve the absorption of iron and prevent iron deficiency in the body.
Other proven analogues are the following drugs:
- Ferumbo;
- Aquaferrol;
- Hemojet;
- Ferrum Lek;
- Biofer;
- Ferroplex;
- Aktiferrin;
- Globiron-N.
Despite the similar composition of these drugs with Maltofer, they still have their side effects. Therefore, before purchasing and using this or that medicine, you should carefully read the instructions attached to it. It is best to consult a specialist about selecting the most suitable drug. Only a doctor, analyzing the patient’s medical history carefully, will be able to make the right choice and prescribe the necessary medicine.
Maltofer is prescribed quite often during pregnancy. This is due to the safety and fairly high effectiveness of the drug. Like any other medicine, this product has a number of contraindications and restrictions for use. To take Maltofer correctly, you must consult your gynecologist and carefully read the instructions included with it.
Especially for beremennost.net – Elena Kichak
Directions for use and dosage
Maltofer in the form of solution, drops, chewable tablets and syrup is taken orally during or immediately after meals.
Before taking the drops, solution and syrup can be mixed with soft drinks or vegetable or fruit juices. Chewable tablets can be swallowed whole or chewed.
The daily dose of the drug is determined by the degree of iron deficiency.
For iron deficiency anemia, the drug is prescribed in the following dosages:
- Premature babies: 1-2 drops of solution/kg;
- Children under 1 year: 25-50 mg of iron - 10-20 drops of solution or 2.5-5 ml of syrup;
- Children 1-12 years old: 50-100 mg of iron - 20-40 drops of solution or 5-10 ml of syrup;
- Children from 12 years old: 100-300 mg of iron – 40-120 drops of solution or 10-30 ml of syrup;
- Adults (including nursing women): 100-300 mg of iron – 40-120 drops of solution, 10-30 ml of syrup or 1-3 chewable tablets;
- Pregnant women: 200-300 mg of iron - 80-120 drops of solution, 20-30 ml of syrup or 2-3 chewable tablets.
For latent iron deficiency, Maltofer is prescribed:
- Children under 1 year: 15-25 mg of iron – 6-10 drops of solution;
- Children 1-12 years old: 25-50 mg of iron - 10-20 drops of solution or 2.5-5 ml of syrup;
- Children from 12 years old: 50-100 mg of iron - 20-40 drops of solution or 5-10 ml of syrup;
- Adults (including nursing women): 50-100 mg of iron – 20-40 drops of solution, 5-10 ml of syrup or 1 chewable tablet;
- Pregnant women: 100 mg of iron - 40 drops of solution, 10 ml of syrup or 1 chewable tablet.
For prophylaxis, the drug is prescribed in the following dosages:
- Children under 1 year: 15-25 mg of iron – 6-10 drops of solution;
- Children 1-12 years old: 25-50 mg of iron - 10-20 drops of solution or 2.5-5 ml of syrup;
- Children from 12 years old: 50-100 mg of iron - 20-40 drops of solution or 5-10 ml of syrup;
- Adults (including nursing women): 50-100 mg of iron – 20-40 drops of solution or 5-10 ml of syrup;
- Pregnant women: 100 mg of iron - 40 drops of solution, 10 ml of syrup or 1 chewable tablet.
The daily dose of Maltofer in the form of an oral solution can be taken all at once. When treating iron deficiency anemia, adults, children over 12 years of age and nursing mothers are prescribed 1 bottle 1-3 times a day, pregnant women - 2-3 times a day. To prevent iron deficiency and treat latent iron deficiency, adults (including nursing and pregnant women) and children over 12 years of age should take 1 bottle per day.
The duration of treatment for iron deficiency anemia (clinically pronounced iron deficiency) is 3-5 months (usually until hemoglobin levels normalize). After this, for several more months, taking Maltofer should be continued at a dose intended to treat latent iron deficiency, and for pregnant women in order to restore iron reserves - at least until childbirth.
The duration of therapy for latent iron deficiency is 1-2 months.
With clinically significant iron deficiency, replenishment of the necessary iron reserves and restoration of hemoglobin levels usually occurs within 2-3 months from the start of treatment.
Maltofer injection solution is administered intramuscularly.
Before the first use of the drug, a test should be carried out: adults are given 1/4-1/2 of the daily dose, children over 4 months – 1/2 of the daily dose. The remaining solution can be administered if no adverse reactions were noted within 15 minutes.
When performing an injection, it is necessary to ensure the availability of the funds necessary to provide assistance in the event of anaphylactic shock.
The dose of Maltofer is calculated individually using the following formula and adjusted according to the general iron deficiency: total iron deficiency (mg) = body weight (kg) × (normal Hb level - patient Hb level) (g/l) × 0.24 + iron reserves (mg).
With body weight less than 35 kg: normal Hb = 130 g/l (deposited iron = 15 mg/kg body weight).
With a body weight of more than 35 kg: normal Hb level = 150 g/l (deposited iron = 500 mg).
If the required dose is higher than the maximum daily dose, the administration of Maltofer should be fractional.
Adults are prescribed 1 ampoule daily; for children over 4 months, the dose is determined based on body weight.
The maximum permissible daily doses are (1 ml = 50 mg iron = 1/2 ampoule):
- Children up to 6 kg: 0.5 ml;
- Children 5-10 kg: 1 ml;
- Children 10-45 kg: 2 ml;
- Adults: 4 ml.
If there is no therapeutic response from hematological parameters after 7-14 days, the initial diagnosis should be reconsidered. The total dose of Maltofer per treatment course should not exceed the calculated number of ampoules.
The injection technique is important. Due to incorrect administration of the solution, pain and staining of the skin at the injection site may occur. Maltofer is injected into the upper outer quadrant of the gluteus maximus muscle. The lumen of the needle should be narrow, the length should be at least 5-6 cm. For adults with low weight and children, the needles should be thinner and shorter. After the injection, the patient should move around.
Causes of low hemoglobin in pregnant women
Determining the causes of decreased hemoglobin in an expectant mother helps speed up the process of normalizing indicators and establishing the correct diagnosis.
Often, a decrease in the concentration of red blood cells - cells that carry iron in the hemoglobin molecule - is called “physiological”, since it occurs due to an increase in blood volume in a woman’s body.
The amount of blood constantly increases, especially in the second and third trimester. This is due to the need to provide intrauterine nutrition to the baby. In this case, the body does not have enough time to produce a sufficient amount of hemoglobin.
It is noted that women with multiple pregnancies are more susceptible to anemia.
The underlying cause of anemia may be exacerbated by several other factors:
- insufficient intake of iron from food (unbalanced diet, diets, vegetarianism, etc.);
- lack of copper, vitamin B12, folic acid, as these microelements affect the absorption of iron;
- diseases of internal organs (gastritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, heart disease, hepatitis, etc.);
- repeated pregnancy occurring less than 3 years after the previous one;
- toxicosis;
- taking certain medications (Aminazin, Levomycetin, etc.).
If a woman does not have a decrease in hemoglobin, but she is at risk for its development, then Maltofer is prescribed during pregnancy as a prophylactic agent.
Side effects
When taking oral forms of Maltofer, it is very rarely possible to develop disorders of the digestive system, manifested as symptoms of irritation of the gastrointestinal tract (a feeling of fullness, pressure in the epigastric region, nausea, diarrhea or constipation). Also, during therapy, dark coloration of the stool is possible (this symptom is due to the release of unabsorbed iron and has no clinical significance).
When using Maltofer in the form of an injection solution, the following side effects may develop:
- Digestive system: rarely - vomiting, nausea (these side effects can be relieved with symptomatic therapy);
- Local reactions: pain, inflammation and staining of the skin at the injection site (if the technique of administering the drug is violated);
- Body as a whole: rarely - headaches, swollen lymph nodes, joint pain, malaise, fever; very rarely - anaphylactic or allergic reactions.
Overdose
Maltofer cannot be overdosed. The degree of iron absorption is selective. If a sufficient amount of the element is present in the body, the absorption rate is automatically reduced to minimum levels.
The greater the iron deficiency, the greater the amount taken is absorbed.
In clinical practice, it was confirmed that even when taking 2000 mg of iron per 1 kg of weight, death did not occur.
The likelihood of an overdose increases with intramuscular administration, but this form of Maltofer is not sold in our country.
special instructions
When prescribing Maltofer orally to patients with diabetes mellitus, it should be taken into account that 1 ml of oral drops contains 0.01 XE (bread units), 1 ml of syrup - 0.04 XE, 1 bottle of oral solution - 0.11 XE, 1 chewable tablet – 0.04 XE.
Maltofer does not stain tooth enamel.
Parenteral iron supplements can cause anaphylactic and allergic reactions. Patients at increased risk of developing such reactions include patients with bronchial asthma or patients with low serum iron-binding capacity and/or folic acid deficiency.
For moderately severe allergic reactions, antihistamines should be prescribed. If a severe anaphylactic reaction occurs, epinephrine (adrenaline) should be administered immediately. When administering Maltofer, the availability of funds for cardiopulmonary resuscitation should be ensured.
The drug is recommended to be administered with caution to patients with allergies, as well as renal and liver failure.
Parenteral use of Maltofer in children may have a negative effect on the course of the infectious process.
Side effects that develop in patients with cardiovascular disorders can aggravate the course of the underlying disease.
Before using Maltofer, ampoules should be inspected for damage and the presence of sediment. The solution for injection should be administered immediately after opening the ampoule.
Maltofer for injection should not be mixed with other medications.