One of the modern gentle methods of stopping the development of an unwanted pregnancy in the early stages is medical abortion with mifegin. What kind of drug is this and what is its effect on the body?
For many years, research on the creation of contraceptives - pills effective in inducing miscarriage - has been carried out by scientists from different countries. The result of a long search was “Mifegin”® (synonyms: Myfegyne, mifepristone, RU-486) - a synthetic steroid drug with antiprogesterone activity, created in laboratories in France in 1980. Therefore, Mifegin is also called the “French pill”.
Deadlines
Medical abortion (up to 22 weeks) is performed using medications (mifepristone, pencrofton) that provoke a miscarriage.
- Up to 9 weeks (63 days of delay in menstruation), it is possible to carry out medical interruption on an outpatient basis;
- From 9 weeks - only in the hospital.
At the request of the woman, abortion is carried out only up to 12 weeks.
In the late period from 12 to 22 weeks, termination of pregnancy is carried out strictly if there are medical or social indications.
Medical abortion is performed on an outpatient basis for up to 9 weeks of pregnancy and provided that the pregnancy proceeds without complications.
During pregnancy from 9 to 12 weeks and above, medical termination of pregnancy is carried out only in a hospital. The effectiveness of drugs during this period is slightly reduced (the shorter the period, the more effective the drugs).
The procedure is performed using a drug called mifepristone (mifegin), which reduces the effect of progesterone, which is the main hormone of pregnancy, and is used in conjunction with prostaglandins - these are drugs that can increase uterine contractions and help reject the fertilized egg.
Misoprostol is a drug that causes contractions of the uterus and expulsion of the fertilized egg.
This drug and its analogues contain prostaglandins - substances that cause rejection and expulsion of the dead embryo. Under their influence, the uterine muscles contract and the embryo comes out.
The dosage of the drug is selected depending on the week in which the abortion pills are performed, the number of fetuses and the individual characteristics of the woman. It can be 400 or 800 mcg - two or four tablets.
Misoprostol has analogs (generics) that have the same effect and are effective in terminating pregnancy:
- Cytotec,
a drug produced by the American company Pfizer. - Mirolut,
produced by a chemical and pharmaceutical company in Obninsk. - Topogin
is a French drug produced by DELPHARM LILLE, SAS
There are also substances of the same group (prostaglandins) used to terminate pregnancy at longer periods. These are the drugs Enzaprost-F, Prostin F2-Alpha. Dinoprost. Late abortions are performed if the woman’s life is in danger or if fetal abnormalities are detected.
Contraindications
- Large uterine fibroids (many nodes or a node larger than 4 cm and deforms the uterine cavity, there is a possible risk of bleeding);
- Allergic reaction to drugs included in the abortion regimen;
- Suspicion of ectopic pregnancy;
- Anemia, in which the hemoglobin level is less than 100 g/l;
- Hormone-dependent tumors;
- Hepatic, renal, adrenal insufficiency and some severe extragenital diseases (hereditary porphyria, severe bronchial asthma, glaucoma);
- Smoking over the age of 35 years + long-term use of COCs and pregnancy arising from COCs (the risk of thrombosis increases, drug interruption can be used only after an additional study of the coagulating properties of the blood).
If pregnancy occurs due to an intrauterine device, the IUD should first be removed, and then it is also possible to use medical termination of pregnancy.
When using a medication regimen, you cannot breastfeed, so this method of abortion is not suitable for a nursing mother.
An alternative to medical abortion is vacuum aspiration.
How is a medical abortion performed?
The medical abortion procedure includes four visits to the gynecologist.
The abortion itself occurs in two stages: the first dose of the drug and a day or two later - the second dose. Bleeding occurs in the second stage and begins within 3-4 hours after taking the tablet.
After two weeks, a follow-up appointment with a gynecologist is required.
Visits to the gynecologist:
- 1 visit: consultation and referral for tests;
- Visit 2: taking the drug;
- 3rd visit, after 1-2 days: re-administration of the drug;
- 4 visit, no earlier than 14 days later: control visit
Standard tests before abortion
- general blood and urine analysis,
- blood group and rhesus,
- smears for purity and oncocytology,
- testing for HIV infection,
- hepatitis B and C and syphilis.
First appointment with a gynecologist
At the first appointment with a gynecologist regarding an unwanted pregnancy, a woman receives advice about available methods of termination, receives referrals for examination and psychological consultation.
Before the procedure begins, an ultrasound examination is mandatory, which serves as the basis for prescribing an abortion and as a method for excluding ectopic pregnancy.
If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, the patient is prescribed a blood test for hCG twice with an interval of several days (the increase in the pregnancy hormone over several days differs in the normal course of pregnancy and in an ectopic or frozen pregnancy).
If the examination reveals an inflammatory type of smear or bakvaginosis, then medical abortion is carried out in the usual way with the simultaneous administration of antibacterial drugs as prescribed by the doctor.
Carrying out an abortion requires the prescription of antibacterial drugs:
- In patients without risk factors for infection, examined for the presence of chlamydia: to prevent inflammatory complications, once a day of the procedure.
- In patients with identified chlamydial or other infection, as well as in the presence of risk factors for the addition of inflammatory complications (with bakvaginosis earlier in the smear): a course of 7-10 days.
Second appointment
At the second appointment with the gynecologist, the patient comes with a decision to have an abortion and signs an informed consent for medical termination.
The patient is given 1 dose of drugs: first, the drug mifepristone, which has an antiprogesterone effect, is used. Progesterone is a pregnancy hormone, and when it is blocked by the drug, a signal for termination occurs and the cervix prepares for miscarriage.
When using 1 tablet for 1 day, there are no significant changes in the woman’s well-being. There may be a slight nagging pain in the lower abdomen, scanty bleeding, and sometimes nausea.
Important! If the mother is Rh-negative and the partner is Rh-positive, it is also recommended to use an injection of a dose of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin to prevent Rh incompatibility with the child during the next desired pregnancy.
Third visit to the gynecologist
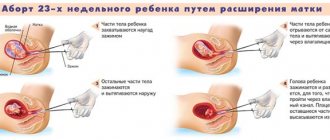
At the third appointment with the gynecologist, after 24-48 hours, the patient is given the second part of the tablets, which directly cause uterine contractions and miscarriage through the prepared dilated cervix. At different times, the dosage of drugs and the method of administration differ (tablets can be taken orally, placed under the tongue, or inserted vaginally).
In 95% of patients, bleeding begins within three to four hours after taking the drugs.
Women almost always develop symptoms that the doctor warns about in advance:
- Cramping pain in the lower abdomen, which each woman experiences differently, depending on her pain threshold. For pain relief, the patient can take a tablet of no-shpa, baralgin or ibuprofen. A miscarriage will occur a few hours after the contractions begin.
- Heavy bleeding during a miscarriage (more and heavier than normal menstruation). True bleeding occurs rarely, in 0.2-1% of cases. A woman should be alerted to such a volume of blood loss that two sanitary pads of the maximum size are thoroughly saturated with blood within an hour, and this is repeated for the second hour. In this case, the patient must call an ambulance, which will take her to the gynecological hospital. In the hospital, if bleeding develops, vacuum aspiration of the uterine cavity is performed.
- An increase in temperature to 38.5 (common and a common side reaction to the interruption pill). You should go to the hospital if the temperature rises for more than 4 hours, with chills.
- Diarrhea (observed in more than half of cases, also a side effect of drugs).
Usually bleeding stops completely after 7-9 days. The longer the pregnancy, the heavier the bleeding. In some cases, brown spotting persists until the next menstruation, which can be considered normal.
Fourth technique
4th appointment with the gynecologist - control. The patient is examined on a gynecological chair, and a control ultrasound of the pelvic organs is assessed. An ultrasound is recommended to be performed 2 weeks after a miscarriage. By this time, the cavity and size of the uterus are reduced. Within 2 weeks after the abortion, the patient can take herbal preparations to contract the uterus: royal collection, infusion of water pepper.
Diagnosis before taking the first abortifacient drug
Ultrasound before medical abortion
Before medical termination of pregnancy, a woman must undergo mandatory diagnostics:
- detailed survey and examination by a gynecologist;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- blood test for hCG;
- smear examination for flora and oncocytology;
- general blood analysis.
If a woman suffers from allergies, additional allergy tests may be prescribed. Patients with an unstable menstrual cycle are recommended to undergo an extensive hormonal profile study. It is also important to exclude Rh conflict between mother and fetus.
After a medical abortion
After medical termination of pregnancy, the patient is prohibited from sex for 3 weeks. A ban on sexual activity is associated with an increased risk of infection due to the increased vulnerability of the inner surface of the uterus.
If you want to protect yourself in the future with oral contraceptives, a woman should take 1 tablet from the package on the first day after a miscarriage.
Menstruation usually begins 3-4 weeks after the procedure and is no different from normal. Slightly more abundant or scanty discharge is allowed, as well as less intense nagging pain during the first menstruation after medical abortion. Typically, such disorders occur after a procedure performed over a period of more than 6 weeks.
If the patient decides to take oral contraceptives, the cycle will be set in accordance with their dosage regimen.
It is recommended to optimally plan a new pregnancy 6 months after an abortion. However, every woman’s body is individual, so it is strongly recommended to discuss this issue with a gynecologist.
"Mifepristone"
The first step uses drugs containing mifepristone, which is a synthetic steroidal antigestagen.
"Mifepristone", "Miropriston" (), "Pencrofton" (), "Mifeprex" (manufacturer - Moscow Pharmaceutical Factory) are Russian-made drugs, one tablet of which contains 200 mg of active substance. To terminate a pregnancy, the doctor prescribes 600 mg once, in three tablets. The drug is taken an hour after meals. The taste is neutral. After taking the tablets, you must be under medical supervision for at least two hours to avoid the development of severe side effects and to eliminate unwanted symptoms in a timely manner. Many women at this time complained of nausea, single vomiting, weakness, changes in blood pressure, dizziness, discomfort and pain in the lower abdomen. Most note the disappearance of side symptoms on the second day.
Possible consequences
- uterine bleeding requiring instrumental evacuation of the uterus in a hospital (vacuum aspiration of the uterine cavity) and the use of uterine contractions;
- incomplete abortion (remnants of the fertilized egg are also removed using vacuum aspiration of the uterine cavity in a hospital);
- infectious complications (the risk of their development is less than 1% of cases);
- progression of pregnancy in a situation where rejection of the fertilized egg has not occurred.
If medical abortion is ineffective and pregnancy progresses, the patient is offered to terminate the pregnancy using vacuum aspiration.
There have been no large-scale studies on the teratogenic effect of drugs for medical abortion on the fetus, but 14 cases of fetal defects developing after using this regimen are known. If the patient suddenly changes her mind and decides to carry an advanced pregnancy, she should be warned about these known cases.
Preparation for the procedure
When you first visit a gynecologist, you need to conduct a general examination, a bimanual examination on a chair and in mirrors, and vaginal smears are taken. Blood pressure, pulse, and respiratory rate are also measured. Next, the woman is sent for an ultrasound to determine the exact day of gestation, the condition of the uterus, and the fertilized egg.
Referrals are given for blood, urine, glucose, and ECG tests. A coagulogram is prescribed if there is a history of problems with the blood coagulation system. Additional examination methods may be needed, the need for which is determined by the doctor.
Advantages of the method
- high efficiency of the method (95-98%);
- eliminates surgical intervention, injury to the uterine mucosa and damage to myometrial vessels;
- with medication interruption, a gentle, non-traumatic dilation of the cervix occurs;
- Medical abortion makes it possible to avoid general anesthesia;
- Medical termination is not a surgical procedure, so the risk of ascending infectious complications is very low (less than 1%);
- the risk of long-term consequences for the patient’s reproductive health is reduced, which is especially important for first-time pregnant women;
- Psychologically, it is easier for a woman to endure a medical interruption than a surgical operation under anesthesia.
Sources:
- Medical termination of pregnancy. Clinical recommendations (treatment protocol). — Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2015.