What organs are located on the left side of the abdominal cavity?
The content of the article
The abdominal cavity consists of 9 parts and is divided into 3 sections:
- Epigastrium
. The epigastrium itself is located directly above the navel. On the right is the subcostal region. - Mesogastrium
. Consists of the peri-umbilical and right lateral regions. - Hypogastrium
. Includes the suprapubic and right iliac region.
Due to the different anatomical structure, pain of the same nature and intensity, localized in the same place, in men and women indicates different diseases.
The following organs are located in the area of the left hypochondrium:
- spleen
- left kidney (from the back)
- 3/4 stomach
- pancreas
- left adrenal gland
- left ureter
- small intestine (loops)
- part of the large intestine
- left half of the diaphragm (muscle-tendon formation separating the peritoneum and sternum).
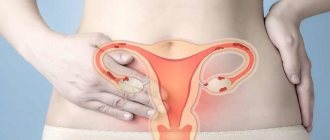
Men and women have anatomical differences in the organs located in the left half of the pelvis. So, in men there is a prostate gland - a tubular-alveolar organ that produces a secretion that maintains an optimal environment for the life of sperm. In women, the uterus is located on the left side of the abdomen, behind it is the left ovary and next to it is the fallopian tube. Depending on the location and nature of the pain, you can determine which organ is in trouble.
Sometimes pain is not associated with pathology in the development of internal organs. But in any case, the problem cannot be left unresolved. It is necessary to undergo a detailed examination to confirm or exclude the presence of the disease.
Causes
Spleen
There can be many reasons for illness of this organ.
It should be noted that the spleen is one of the most important organs of the hematopoietic system, where the process of recycling waste red blood cells occurs, and also provides one of the main links of the immune system.
Normally, the tragacanth parenchyma is devoid of pain receptors, and pain can only occur in the organ capsule.
The causes leading to pain in the lower abdomen can be divided into several groups:
- immunological;
- inflammatory;
- malignant;
- traumatic.
Pain that occurs in a woman after any mechanical impact, injury, blow, fall, etc. most often it is acute, accompanied by rare pain, it can radiate over the entire surface of the abdomen, and is also accompanied by signs of hemorrhagic shock due to the rich blood supply to the organ.
The pain in this case is dull, most often of a slight diffuse nature. It occurs due to general inflammation of the tissue or the formation of an encapsulated purulent focus.
Malignant causes of pain are more often associated with leukemia, the pain varies depending on the stages, in the chronic course it is predominantly dull and aching, and in the acute case it is more pronounced. In addition to pain, there may be an increase in body temperature, the appearance of intoxication, etc.
Intestines
This type of pathology is quite common and it is with it that differential diagnosis is carried out in gynecological practice. After all, many women throughout their lives may come to the doctor with complaints of pain in the lower abdomen, and it should be noted that they are most often localized on the left.
Considering the anatomical structure of the body, it should be noted that in this area the woman has the sigmoid colon.
This is one of the sections of the large intestine that is most often affected by pathology, and there can be many reasons for the development of pain in the lower abdomen localized on the left.
The average age at which women come can be different; for inflammatory diseases of the sigmoid colon it is 25 - 35 years, while for other pathologies it is predominantly an elderly age of 60 - 80 years.
Causes and symptoms:
- Of great differential importance is the fact that from the moment of menopause, a woman less often develops pathologies on the left ovaries, the risk of adnexitis is very low, there is only a possibility of a malignant lesion. In this case, the pain is characterized by a predominantly aching character, radiating to the back, rarely when it is an acute pain. In this case, you should pay attention to the woman’s stool. The pain in this case is dull, localized on the left, but it is not too widespread, nor does it radiate.
- In acute inflammatory diseases in the intestines, the pain can be acute, not associated with stool, but also localized in the lower abdomen and mainly on the left. Women facing this problem are quite young, as well as a large number of nervous factors that lead to constant stress. Diseases that characterize these pains include Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis or other infectious causes.
- In some cases, a woman associates the appearance of pain with some factors , for example, traveling to exotic countries or eating foods unusual for the diet of the area. Changes in stool are present in most cases, most often they tend to become more frequent.
- A fairly common pain in the left lower abdomen is intestinal dysbiosis. In this case, in addition to pain, there is bloating, a feeling of heaviness, abnormal bowel movements, and the pain is diffuse in nature.
- In rare cases, other parts of the intestine may be affected, but the pain will not be localized below, but somewhat higher , which immediately alerts the gynecologist and he will recommend examination by other specialists.
Reproductive system
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes
A disease that is also found under the term salpingitis. It occurs in women at any age, but most often it is 20-35 years old.
The most common cause of this pathology is infection. It can be caused by sexually transmitted infections, or opportunistic flora, which begins to appear with reduced immunity.
In this case, the main way of transmitting or provoking the disease is promiscuity.
If the process is left unattended and not treated in time, this leads to the development of adhesions, space-occupying formations, transition to chronic or infertility.
Symptoms:
- The pain occurs both at complete rest and intensifies with movement, and can radiate to the lower back or side.
- Accompanied by a deterioration in general condition, an increase in body temperature, and in some cases, vomiting and dizziness.
- Also, the pain is diffuse in nature, usually accompanied by discharge from the genital tract, which is pathological in nature, white in color with a green or yellow tint, as well as an unpleasant odor.
- In most cases, damage to the bladder is also associated, which is manifested by cutting, pain, as well as an imperative urge to have sex.
Rupture or twisting of an ovarian cyst
This is a condition in gynecology that is not inflammatory, but is considered acute. This is due to the fact that it usually arises spontaneously. This condition can be preceded by the development of cysts in the ovarian area and their sizes can be quite large.
This pathology can manifest itself at any age, but mainly in girls aged 18 to 30 years.
Symptoms:
The disease manifests itself as acute pain in the lower abdomen , the character can be either aching or severely acute.- The woman is forced to take the position in which relief occurs. This is a lying position with your knees brought to your stomach, this reduces the pressure on the affected area and causes slight relief.
- The pain can be so acute that it disrupts the process of palpation due to tension in the abdominal muscles.
- In addition to pain in the lower abdomen or diffuse nature, there is also a sign of painful shock or hemorrhagic shock.
- You may notice confusion, decreased blood pressure , increased heart rate, and cold, clammy sweat on the surface of the body.
- Some women experience involuntary urination or bowel movements due to pain .
As it progresses, the degree of pain covered will depend on the severity of the torsion. So, with minor pain, there is simply the development of pain in the lower abdomen on the right or left, which the woman is able to tolerate, but with complete torsion, the symptoms of pain are so pronounced that the woman cannot restrain it.
Endometriosis
This is one of the common problems in modern gynecology and this is due to the fact that at present the cause of its occurrence has not yet been precisely confirmed. There are many theories at various levels, but none have yet been proven definitively.
This pathology occurs in women of reproductive age, this is especially important, since the disease is hormonal-dependent and its development is associated with the monthly cycle. Therefore, this pathology should not occur in women during menopause.
The main symptom of endometriosis is pain, which is localized mainly in the lower abdomen when pressed.
It should be noted that there are many variants of the disease and course:
- If it is adenomyosis, i.e. endometriosis of the body of the uterus , then the pain can be localized in the lower abdomen along the midline, and if there is a deviation of the organ in one direction or another, it can be on the left and right. The lesions can be localized on the intestines, ligaments, behind the uterine space, bladder, etc. The nature of pain when the body of the uterus is damaged is quite typical; it is an aching pain that intensifies in the period before menstruation. Its appearance occurs mainly in 3-4 days. There may simply be a dull nature of the pain, as well as a nagging one. In addition, intensification occurs during sexual intercourse; women often describe this condition as pain in the entire lower abdomen. At the same time, it is not possible to clearly name the localization. The appearance of spotting brown discharge is noted a few days before and after menstruation. The nature of menstruation also changes; it is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, as well as greater volume and duration.
- With the development of an endometrioid cyst in the ovarian area, the pain is also localized in the lower abdomen, in this case coming from the side on which the ovary is affected. It should be noted that most often it is the left ovary that is affected, i.e. the pain occurs more on the left. There are other options for the development of endometriosis. Among them there is an external one, in which other organs are involved in the pathological process. With ovarian cysts, the pain will have a slightly different character. Small sizes may be accompanied by almost imperceptible periodic aching pain, but larger cysts or multiple formations are accompanied by severe stabbing or aching pain, occurring clearly on the right or left side of the lower abdomen. External endometriosis is accompanied by pain under such conditions, but the pain can be localized clearly in the lower abdomen on the right or left. Such a disease very often leads to the development of infertility; it requires mandatory treatment and monitoring by a specialist.
Adnexit
This is an inflammatory disease of the Don reproductive system, which is characterized by damage to the ovaries.
This pathology occurs in women at any age, but most often it is reproductive, with an age period of maximum occurrence from 18 to 30 years.
In this case, the main cause of this inflammation is an infectious factor, predominantly of a bacterial nature.
This can be both opportunistic flora and bacteria that are absolute pathogens, these include gonococci, chlamydia, trichomonas, etc.
Infection occurs both sexually, but also when exposed to provoking factors that contribute to a decrease in immunity.
Symptoms:
- The main symptom of ovarian inflammation is pain in the lower abdomen on the right or left, depending on the location of the process.
- Its character can be sharp or aching. Basically, they do not depend on any conditions, but can intensify after sexual intercourse or fast walking.
- They are also accompanied by signs of intoxication of the body, an increase in body temperature.
There is a possibility of the process spreading to other organs and tissues. When a process or suppuration occurs for the first time, the pain is acute, localized in the lower abdomen on both the right and left, and palpation is very difficult. A bilateral process with severe pain may also occur, which is also associated with damage to the fallopian tubes and uterus.
Ectopic pregnancy
This is a dangerous pathological condition that develops in women of reproductive age. Most often, this process can develop after inflammatory or adhesive processes in the pelvic area.
Ectopic pregnancy is preceded by pathologies such as salpingitis, salpingoophoritis, pelvioperitonitis, etc.
Occurs against the background of delayed menstruation. It should be noted that there are two stages of the process: undisturbed and disturbed pregnancy.
It can occur in various areas, the most common location being the fallopian tubes, it can be the ovaries, cervix, or abdominal cavity.
Symptoms:
It manifests itself as a pain syndrome that occurs in the lower abdomen on the right or left.- With an undisturbed process, the pain is often dull and aching, which gradually intensifies.
- Palpation and sexual intercourse, as well as physical activity, cause pain.
- At rest, there is usually no pain.
- There may be no other symptoms; sometimes a woman may notice the appearance of a menstrual-like reaction, which is manifested by spotting bloody discharge from the genital tract according to the duration and time of the corresponding menstruation. The disrupted process is manifested by pain in the lower abdomen on the right or left; in some cases, the pain is diffuse in nature, which can be difficult to accurately determine the location; this picture depends on the stage of pregnancy.
- The pain occurs at rest and does not decrease under other conditions.
- There are no signs of intoxication or inflammation; body temperature is usually normal.
- Hemorrhagic syndrome may appear, accompanied by pallor of the skin, the appearance of cold sticky sweat, and increased heart rate.
- In addition to pain, a woman may notice indirect signs of pregnancy, such as engorgement of the mammary glands, toxicosis, etc. Upon examination, the uterus will not correspond to the expected period of pregnancy.
Allen-Masters syndrome
This disease is currently a fairly rare pathology that occurs in gynecology, but it should be remembered because in some cases this may lead to incorrect diagnosis and subsequent treatment. Very often this disease is confused with endometriosis due to the nature of the pain.
This pathology occurs most often in women aged 25 - 35 years, and accordingly, if the diagnosis is incorrect, then the woman suffers from it even at a later age. This age group is primarily associated with the main factor that leads to pain, most often pathological childbirth.
This syndrome occurs due to rapid labor or improper management of the second and third periods, which is accompanied by too much pressure on the uterus or its excessive stretching and lowering. As a result, the broad ligament of the uterus, which is the main supporting mechanism, ruptures.
Symptoms:
- A woman experiences severe pain, which occurs mainly after childbirth , it intensifies in a standing position, and the main pain occurs on the side where the tear occurred.
- If at the initial stages the pain is quite sharp, then it becomes dull and can be nagging . The woman notes an increase in pain when standing, long walking, and it will descend deep into the lower sections, both on the left and on the right.
- Strengthening occurs before the previous menstruation , which is why many doctors confuse this pathology with endometriosis. The nature of menstruation does not change in any way, except for the pain of the first two days.
Causes of pain in the right hypochondrium
Pain in the left side or lower abdomen on the left side indicates diseases of the organs and more. Urology ranks first among the causes of pain, followed by gynecology and gastroenterology. In some cases, pain is in no way related to anatomical pathologies. Among the reasons that cause pain in the left half of the body may be the following:
- Lymphocytic leukemia or myeloid leukemia
. This is a collection of malignant atypical cells in the blood. The center of pain is located in the spleen, because the organ produces blood cells and also stores reserve cells, including cancer cells. Although lympho- and myeloid leukemia are diseases of hematopoiesis, they affect the spleen as a depot that stores a third of all platelets. Problems with this organ are clearly detected by ultrasound of the spleen. - Purulent arthritis of the left hip joint
. Pathogenic bacteria enter the joint cavity due to injury or damage to the walls (abscess), resulting in acute inflammation and pus accumulating inside the joint. The pain radiates (gives) to the left side of the abdomen. - Inflammation of the lymph nodes of the left half of the abdomen.
Caused by the entry of streptococci and staphylococci into the blood. The source of inflammation is an internal organ (stomach, spleen, kidney), and pathogenic bacteria enter the lymph nodes through the outflow of blood. You can check your stomach with a stomach ultrasound. - Abdominal aortic aneurysm.
This is an atherosclerotic lesion of the vessel supplying blood to the organs of the left half of the abdomen. Leads to aortic rupture and death. - Acute mesenteric ischemia
. Characterized by acute pain around the navel. It is complemented by a decrease in peristalsis and a sharp increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood. - Abdominal pain with depression.
Depression is accompanied by increased anxiety and increased levels of norepinephrine and cortisol. They cause spasms of smooth muscles, including the intestines. The person experiences symptoms characteristic of indigestion. Moreover, this is not associated with eating low-quality food. Abdominal pain cannot be relieved by medications because it is psychosomatic in nature. - A severe and prolonged cough
also causes abdominal pain. This is due to the increased load on the abdominals, which not everyone has trained and strong. Frequently coughing, the patient strains the muscles, they stretch and put pressure on the diaphragm, causing dull pain. It goes away on its own after the cough is cured.
Prevention of lower abdominal pain
Preventive measures:
- Lifestyle changes.
- It is necessary to regularly visit specialists and at the first pathological symptoms it is worth starting to diagnose it and treat it in a timely manner.
- In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to the quality of sexual life , casual sexual intercourse should be avoided, as well as the lack of protective equipment with people who have not been tested for sexually transmitted infections.
- Maintain personal hygiene measures , especially when traveling.
- Monitoring the state of immunity , regular nutrition, adequate sleep, prevention of respiratory and other types of infections.
Causes of abdominal pain on the left: pathologies of internal organs
Sometimes the causes of pain under the left rib are actually diseases in various organs.
Spleen diseases
Heart attack (disturbance of blood circulation of the vessels penetrating the organ); torsion of the pedicle (the pedicle through which the arteries and veins supplying the spleen with blood passes is twisted, resulting in tissue necrosis and intoxication); abscess due to infection; rupture of the spleen leads to the formation of connective tissue, and if it is injured, peritonitis and splenomegaly occur (enlargement of the spleen due to autoimmune and hematopoietic diseases); spleen cyst (formed after the completion of an abscess); benign and malignant neoplasms.
Intestinal diseases
Diseases of the small intestine
: malabsorption (inability of the intestinal walls to absorb some component (fructose, lactose); celiac disease (inability to tolerate gluten contained in cereals);
Colon diseases
: Hirschsprung's disease (lack of nerve endings in some parts of the intestine); Crohn's disease (inflammation of the colon); ulcerative colitis (inflammation of the large intestine); irritable bowel syndrome (caused by stress, which releases adrenaline, causing smooth muscle contraction); diverticulosis - protrusion of the intestinal walls outward; intestinal polyps that interfere with water absorption; atony (impaired intestinal motility); malignant tumors, intestinal infections. You can check the organ with an ultrasound of the intestines.
Diseases of the left kidney
Abscess (purulent inflammation), pyelonephritis (bacterial inflammation), cysts, kidney stones, echinococcosis (presence of helminths in the kidney), hydroureteronephrosis (enlargement of the renal pelvis with impaired urine outflow); tuberculosis (drying) of the kidney, malignant tumor. If these diseases are suspected, an ultrasound of the kidneys is performed.
Gynecological diseases
- Endometriosis (proliferation of epithelial cells lining the inner surface of the uterus); adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages);
- salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes);
- parametritis (inflammation of uterine tissue);
- Allen-Masters syndrome (rupture of the uterine ligaments during childbirth or an accident);
- ovarian adhesions (fusion of the ovary and fallopian tube);
- ectopic pregnancy in the left fallopian tube;
- cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix);
- rectal-uterine cavities (proliferation of endometriotic nodules into the walls of the rectum.
Pathologies are detected by ultrasound of the ovaries, ultrasound of the appendages and other methods.
Pathologies of the genital organs in men
Varicocele (impaired blood flow in the testicles); dropsy of the ovary (accumulation of excess fluid); testicular torsion with pinched nerves and blood vessels, epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis). Here you will need to undergo an ultrasound of the scrotum and testicles.
Characteristics of pain in diseases of the urinary organs
Urinary diseases occur in cases of pathology of the kidneys, bladder, and ureter. The localization we are studying includes local pain in the ureter caused by its stretching and radiating pain from the left kidney.
Pyelonephritis
Inflammation of internal structures (pelvis, calyces) caused by infection. It begins suddenly with high fever, vomiting, chills, pain in the lower back on the left, radiating to the left side of the abdomen. Impaired urination, pain, and urinary retention occur. Pulsating pain is an unfavorable sign indicating the formation of an abscess in the kidney.
In the chronic course, exacerbations are milder, but with the same symptoms. As a result, scars appear in place of the inflamed tissue, the kidney becomes deformed and loses function. Kidney failure occurs when the second healthy kidney stops working hard to compensate for the diseased organ. The disease is treated by urologists with antibacterial agents, diuretics, and, if necessary, by opening the suppuration or resection of part of the kidney.
Urolithiasis disease
Often accompanied by inflammation of the urinary tract and metabolic disorders. It is caused by the loss of crystalline sediment in the urine, its settling in the pelvis and gluing into stones. The most common compositions are phosphates, oxalates, and urates.
The stone causes a disruption in the process of urine outflow, so stagnation and distension form in the higher-lying sections. The movement of a stone along the ureter explains why the lower abdomen hurts. Clinically, after intense shaking or running, the patient experiences an attack of renal colic.
The pain is very intense in nature, cutting. Localized in the lower back or to the left of the navel. Acute urinary retention occurs. The duration of the attack is up to several hours. For emergency care, painkillers and antispasmodics are administered. Frequent recurrence of attacks is an indication for surgical removal of the stone.
What does pain in the left side of the abdomen indicate?
Based on the nature of the pain and the location of the source of pain, you can determine the cause of the disease even before going to the doctor.
| Nature of pain | Cause | Additional symptoms |
| Dull aching pain | Gynecological diseases (endometriosis, fibroids, ovarian cysts, inflammatory processes) | Increased body temperature, pain during sex, menstrual irregularities, spotting |
| Nagging pain | Pathology of the pelvic organs (inflammation of the scrotum in men, strangulation of the inguinal hernia, sprain of the inguinal ligaments) | Lymph nodes become enlarged, diarrhea, vomiting are observed, body temperature rises |
| Sharp unbearable pain | Rupture of the ovary, dilatation of the bladder or renal pelvis, passage of stones in the urinary tract | Distension of the intestines, bloating, gases. |
| Stitching pain | Kidney and intestinal diseases, cyst rupture, inflammation of the ureter | Shooting pain in the lower back, increased gas formation, constipation |
Classification of pain
It should also be remembered that pain in the lower abdomen can be different.
Therefore, it should be remembered that its character is of great importance in making a diagnosis:
- Aching. Pain is characteristic mainly of inflammatory pathologies.
- Stabbing. This can be either an acute inflammatory process or a pathology associated with a space-occupying formation.
- Sharp. In this case, pain in the lower abdomen occurs due to non-inflammatory diseases. These include ectopic pregnancy, cyst rupture, etc.
- Bursting. This type of pain is characteristic of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract or one of the stages of the inflammatory process.
What tests should be taken for pain in the left side of the abdomen?
If there are complaints of pain in the left side of the abdomen, the doctor sends the patient to undergo the most important tests, the results of which will show a complete picture of the condition of the body.
General blood analysis
- A low hemoglobin level indicates internal bleeding and impaired absorption of nutrients in the intestine. Too high hemoglobin indicates intestinal obstruction, tumors in the kidneys and stomach;
- An increase in red blood cells indicates inflammation and dehydration, a decrease indicates internal bleeding;
- A high level of leukocytes is characteristic of an infectious disease of the gastrointestinal tract, a low level is characteristic of typhoid fever;
- An increase in platelets is typical with malignant tumors and splenic rupture, a decrease with infections;
- An increase in ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is observed in cancer, inflammation and infections;
Blood chemistry
Blood biochemistry determines:
- Alanine aminotransferase (AlAT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), enzymes found in different organs. An increase in ALT and AST indicates pathology of the kidneys, liver, and kidneys. Liver tests are the most important method for diagnosing metabolic disorders.
- Urea is released in large quantities in case of pyelonephritis, other pathologies of the kidneys and bladder, decrease - in case of liver dysfunction;
- Creatine characterizes kidney function. Elevated creatine levels are typical for acute renal failure;
- Glucose increases in diabetes mellitus, which causes other problems;
- Total protein changes indicators in cancer;
- Protein albumin decreases in kidney diseases, intestinal diseases, and oncology.
General urine analysis
Urinalysis shows:
- An increase in acidity is observed with infections of the genitourinary system, chronic renal failure, a decrease is observed with dehydration;
- Color changes: Bright orange and brown colors are characteristic of kidney disease;
- An increase in protein and glucose in the urine is typical for kidney disease;
- A high level of leukocytes indicates inflammation (cystitis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis);
- Epithelial cells are also seen in kidney problems.
Treatment
The choice of tactics will directly depend on the identified pathology:
- If there is pathology on the part of the spleen, the decision is made by a hematologist. In this case, it can be medicinal, surgical or a combination.
- In case of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, much attention is paid to the etiological factor, since the pathology can be surgical, therapeutic or infectious in nature.
- With a disease such as endometriosis, pain in the lower abdomen can be eliminated in several ways. The main and initial one is medicinal; in this case, hormonal agents are selected that have an anti-estrogenic effect. If they are ineffective, surgical methods can be used.
- For inflammatory lesions, the choice depends on the type of pathology; antibacterial agents are most often prescribed, as well as detoxification and anti-inflammatory agents. To restore the body's defenses, immunostimulants and immunomodulators are used. Great importance is given to taking vitamins. Antibiotics are selected based on the sensitivity of the microorganism to them.
- In case of acute surgical pathology, as well as ectopic pregnancy, surgical treatment is used. The extent of the operation will directly depend on the woman’s condition, as well as the amount of damage. In some cases, it may be necessary to completely remove the organ, as well as install systems for washing cavities prone to inflammation.
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity for pain in the abdomen on the left
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity is very effective and eloquent. It reveals the following pathologies:
- presence of free fluid in the abdominal cavity
- mesadenitis (enlarged lymph nodes)
- aortic aneurysm dissection
- tumor in the kidney
- stones in the kidneys
- kidney cyst
- abscess, peritonitis
- enlarged spleen
- tumors.
In addition to ultrasound, endoscopic research methods are very popular in identifying the causes of pain in the left half of the abdomen. Such an examination is prescribed if an ultrasound scan shows pathology and the diagnosis needs to be confirmed.
Which doctor should I contact?
Considering that many diseases can cause pain in the lower abdomen on the left side, it is initially recommended to consult a therapist. He will definitely conduct an examination, prescribe laboratory tests and instrumental examinations.
Based on the data obtained, a referral to a specialist will be given:
- If the causes of pain are associated with intestinal pathologies, then a gastroenterologist will be involved in treatment. The most common pathologies are inflammation of the sigmoid colon and irritable bowel syndrome.
- When an injury, hernia or abscess is confirmed, the help of a surgeon will be needed. Often surgery is required when problems arise with the spleen or tumor formations are detected.
- If pathologies of the kidneys and other organs of the urinary system occur, you may need the help of a urologist or nephrologist. Most often, the need for treatment by a specialist arises with the development of cystitis.
- All female diseases associated with the development of pathologies of the female reproductive system will be treated by a gynecologist.
- If prostatitis is confirmed, men will be given a referral to a proctologist.
It is important to understand that timely diagnosis and progressive treatment methods provide high guarantees of successful treatment of all diseases that provoke pain on the left side of the abdomen. Therefore, when the left stomach hurts, it is recommended not to start taking painkillers, but to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Endoscopic examination methods
These include:
- FGDS
(fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy). This method is popularly called “swallowing the probe.” With its help, esophagitis (inflammation of the walls of the esophagus), polyps and tumors of the stomach, reflux disease (impaired passage of food), gastritis (inflammation of the walls of the stomach), duodenitis (inflammation of the intestinal walls), stomach and duodenal ulcers, bleeding are detected. - X-ray diagnostics.
Detects perforated ulcer, pneumatosis (accumulation of gases), intestinal obstruction, megacolon (thickening of the intestinal walls), rupture of the spleen. - Colonoscopy
(examination of the rectum through the anus). Detects cancer, polyps and intestinal tumors, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, proctitis (inflammation of the rectum). - MRI
(magnetic resonance imaging). Gives a complete picture of the condition of internal organs. - Retrograde cholangiopancreatography
is a combination of fluoroscopic and endoscopic methods. Used to collect material for biopsy. Helps with complicated forms of pancreatitis, in which it is difficult to examine the bile ducts due to the enlargement of the organ. It also detects the localization of stones in the kidneys and urinary tract. - Laparotomy and laparoscopy
. These are similar methods, only with laparotomy large incisions are made in the abdominal cavity, and with laparoscopy they are very small. Using a laparoscope (a flexible optical tube with a camera at the end), you can see injuries to internal organs, tumors of the abdominal organs, inflammation of the lymph nodes, stomach and duodenal ulcers, and splenic rupture.
Colon
Irritable bowel syndrome is associated with the colon. Until now, the origin of this disease remains unclear. Both women and men suffer from it. In women, exacerbations coincide with changes in hormonal levels and menstruation. Symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome are stool upset and flatulence. As a rule, this disease may indicate serious pathological changes in the body. These include nonspecific ulcerative colitis, malignant and benign tumors, diabetes mellitus, hormonal disorders, acute intestinal infections with subsequent dysbacteriosis. The patient’s condition can be stabilized with the help of special medication and a special diet. In this case, the symptoms subside and the disease may go away completely.
When such problems arise, it is important to know which doctor to contact. If there is a sharp pain in the left side of the lower abdomen, help will often be provided by a gastroenterologist. After all, the problem may also be Hirschsprung's disease. This is a hereditary disease that mainly affects representatives of the stronger half of humanity. It occurs when there are no areas of innervation in the colon. In addition to pain in the left side, symptoms include bloating, constipation and increased gas production. Hirschsprung's disease can only be cured through surgery. Parts of the colon that lack nerve endings are simply removed.
An inflammatory disease of the large intestine that is accompanied by such pain is Crohn's disease. According to the ICD 10 code, this disease is classified as a deviation from the norm identified during clinical and laboratory tests. In this case, a specific part of the intestine hurts, which turned out to be susceptible to the inflammatory process. This is a complex disease that necessarily requires both surgical and conservative treatment. The whole problem is that it is often disguised as other ailments; making a correct diagnosis turns out to be very difficult. According to ICD 10 code, Crohn's disease is classified as regional enteritis.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis can also create problems. This is a polyetiological inflammatory disease, accompanied by morphological changes that occur in the large intestine. It is believed that its key cause lies in malfunctions of the immune system and hereditary factors. The pain in this case is paroxysmal with varying intensity.
Sharp discomfort may occur due to colon polyps, which are benign formations. They are accompanied by stool disorder, when constipation can be replaced by diarrhea, which threatens complete dehydration of the body. On the left side, pain occurs when polyps affect the descending part of the colon.
How is left-sided pelvic pain treated?
Painful sensations can be relieved at home. To do this, take antispasmodic and painkillers. In most cases, this helps for a while, after which the discomfort returns.
A specialized doctor should identify the cause of pain and select therapy. Restoring blood circulation, eliminating the source of inflammation or tumor will relieve abdominal pain and accompanying symptoms.
Self-administered pain relief can be harmful in some cases. Antispasmodics can “blur” the clinical picture and provoke referred pain, which significantly complicates diagnosis.
If there is discomfort in the abdomen of any location, the help of a doctor is necessary. Pain is the main symptom of a disease that needs to be found and cured. Sometimes pain appears in an advanced situation when surgical help is required. Ignoring the problem leads to a significant deterioration in well-being, aggravation of pathological processes and can cost the patient his life.