The main thing is to have an abortion in the first trimester, since the law in most countries where abortion is allowed, it can be performed at the request of the woman only up to the 12th week. After this period, social or medical grounds are needed, such as rape or abnormalities in fetal development. Similar rules apply in Russia, Ukraine and most European countries.
To make everything easier and safer, it is better to have an abortion as early as possible, but first the pregnancy must be confirmed. Transvaginal ultrasound is usually able to see the ovum a few days after the missed period, which corresponds to approximately 2.5-3 weeks after conception. But since official documents use the obstetric period to count the duration of pregnancy (from the first day of the last menstruation), this is approximately 4.5-6 weeks, according to this calculation.
The main methods of early termination of pregnancy (medical abortion and vacuum aspiration) can technically be used after the 3rd week, starting from the last menstrual period. But often the clinic may recommend waiting until 5-6 weeks until the pregnancy is confirmed by ultrasound.
Mini-abortion: let’s define the concept
Abortion is the artificial termination of pregnancy, which is carried out at the request of a woman up to 12 weeks, and later (up to 22 weeks) for social and medical reasons. A mini-abortion is the surgical removal of the fertilized egg in the early stages of gestation through vacuum aspiration (suction).
To carry out the procedure, the medical institution must have a special device - a vacuum excoleator or so-called suction, under the influence of which negative pressure is created in the uterine cavity, and the fertilized egg is peeled off from the uterine wall without much effort on the part of the doctor. Vacuum aspiration in the early stages of gestation is based on the fact that up to 6 weeks, the chorionic villi (future placenta) have not yet grown deep enough into the muscular layer of the uterus, and removing the embryo is not difficult.
How to do a medical abortion
Under no circumstances take any medications without a gynecologist's prescription.
Medical abortion must be carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor. So, you suspected you were pregnant and firmly decided that you wanted to get rid of it.
First you need to visit a gynecologist. The doctor will conduct an examination, find out when you had your period (this is important, since a medical abortion can be done if less than 7 weeks have passed since the start of your last menstruation) and will necessarily send you for an ultrasound to confirm the fact of pregnancy and exclude its ectopic variant. .
If everything is in order, you will receive two tablets (note that you cannot buy them yourself at the pharmacy - these are strictly prescription drugs) along with detailed instructions on how to take them.
The first contains mifepristone. It blocks the production of progesterone, a hormone that is responsible for the development of the lining of the uterus (endometrium). The endometrium becomes thinner, the fertilized egg cannot stay in it and begins to flake off. In addition, mifepristone causes the uterus to contract more actively, pushing out the egg, and softens its cervix to facilitate its passage out.
The second drug is based on misoprostol. It is taken 24–48 hours after mifepristone, when the effect of the first active substance gains strength. Misoprostol additionally stimulates the uterus, and the fertilized egg, along with the dead endometrium, is pushed out.
This process is similar to menstruation. Only more abundant: the uterus does not get rid of a tiny egg, but from a fertilized egg that has developed for several weeks.
Since both drugs affect hormonal levels and can cause serious bleeding, the tablets should only be taken under medical supervision. You may be asked to stay at the clinic for a couple of hours after taking each pill, and then, if everything goes well, you will be sent home.
You will then need to return to the hospital in 7-10 days to have another ultrasound to make sure the abortion is complete.
Dates
As the name implies, when performing a mini-abortion, the pregnancy period is quite short. When contacting a gynecologist with a request for a procedure, the doctor will ask about the number of days during which the due menstruation has not occurred (that is, delayed menstruation).
You can perform a mini-abortion if there is a delay of up to 21 days, but it is optimal to perform this manipulation on the 14th – 15th day of absence of menstruation, since if vacuum aspiration is performed earlier, you may simply “not notice” and not remove the fertilized egg, and later the risk of complications increases .
“At what weeks can aspiration be performed?” - the woman is interested. According to the delay of menstruation, from three weeks of pregnancy. Again, a new question arises: “Until when?” Mini-abortion is performed up to 5, maximum (with the consent of the doctor) up to 6 weeks of gestation.
Late pregnancy termination
The period from the 12th week (3 months) from the moment of the last menstruation is considered late for termination of pregnancy. It is by this time that the placenta is formed from the chorion, the villi connecting the fertilized egg to the uterus. Now the word “fetus” is used instead of embryo.
Previously used methods such as medical abortion or vacuum aspiration are no longer effective at such periods, and therefore are not used. The only way to terminate an unwanted pregnancy is surgical or instrumental abortion.
The legislation establishes that late abortion is possible only on the basis of the conclusion of a medical commission. A gynecologist cannot perform an abortion solely on the basis of a patient’s request. Surgical abortion is resorted to under certain circumstances:
- Medical indications. These include serious problems with a woman’s health (heart disease, leukemia, oncology, absence of a kidney, liver damage). A commission of different medical specialists assesses the possible risk and gives the woman a referral for an abortion.
- Medical and genetic. They relate to serious developmental pathologies identified in the baby (Down syndrome, abnormalities in organ development, genetic mutations).
- Social indications. These include pregnancy resulting from rape, large families, divorce).
In essence, late abortion is already an artificial birth. It is performed under anesthesia, the patient remains in the hospital for several days. There are several methods of surgical abortion:
- Caesarean section can be transabdominal (when the abdominal wall is cut) and vaginal. The method is used in extreme cases (fetal suppuration, gynecological pathologies in women), and often ends with the removal of the uterus or fallopian tubes. With a vaginal caesarean section there is a risk of bladder injury.
- Introduction of hypertonic drugs into the amniotic fluid. A certain amount of amniotic fluid is removed from the woman using a thin needle, and then the same amount of solution is injected. The woman's labor is stimulated, and a miscarriage occurs within 24 hours.
- Use of prostaglandins. They are injected intravenously or into the amniotic fluid and cause a natural miscarriage.
All these methods are very dangerous and morally traumatic, because you already have to get rid of an already formed child - he has arms, legs, and a head. It's painful, unpleasant and offensive. Therefore, you need to think about abortion in case of an unwanted pregnancy in advance, without delay. And it is best to do it with medication, without surgical intervention.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Indications for mini-abortion
There are no special indications for this procedure. The leading and sufficient indication is the woman’s desire to terminate the pregnancy (in Russia, medical termination of an unplanned pregnancy at will is carried out up to 12 weeks). In addition, there are a number of indications for termination in the early stages of gestation (if, of course, the timing allows):
- frozen pregnancy;
- anembryony;
- bearing a fetus poses a threat to a woman’s health and life (diabetes mellitus, severe liver and kidney pathology, malignant tumors, etc.);
- history of rubella, influenza and other infections during pregnancy;
- social indications (rape, stay in prison, etc.).
Vacuum aspiration is used not only to terminate short-term pregnancies, but also to solve other gynecological problems:
- the need for an endometrial biopsy;
- remnants of the fertilized egg after pharmacological or surgical abortion;
- retention of parts of the placenta after childbirth or cesarean section;
- menstrual irregularities (bleeding);
- accumulation of blood (hematometra) or serous fluid (serozometra) in the uterine cavity;
- incomplete spontaneous abortion.
What to do after an abortion?
The menstrual cycle after an abortion is restored within 4-5 weeks. It is important to take care of yourself during this period to avoid negative consequences if possible. Here are some guidelines to consider:
- Do not use tampons and abstain from sex during the first week after an abortion.
- Take all medications as prescribed by your doctor, including antibiotics.
- If you are hospitalized for any reason within 30 days after an abortion, inform the doctors about the fact of termination of pregnancy.
- If two weeks after the abortion you do not feel normal, contact the clinic.
- A pregnancy test is not effective for some time after an abortion because pregnancy hormones are still present in the body.
- When traveling on a bus, train or car, try to periodically walk or stretch (at least while sitting).
- Drink enough fluids, watch your diet, and avoid alcohol and drugs for 48 hours after the procedure. Do not smoke, do strenuous exercise, or lift heavy objects for 3-4 days.
( 3 ratings, average: 2.67 out of 5)
Contraindications for the procedure
Since a mini-abortion is an invasive procedure and is considered a minor surgical operation, it has the same contraindications for its implementation as surgical termination of pregnancy:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- fever;
- infectious process of any localization (including “colds” on the lips);
- acute or exacerbation of chronic diseases of organs located in the pelvis;
- blood clotting disorder;
- Less than six months have passed since the previous termination of pregnancy.
In addition, vacuum mini-abortion is not performed and has its own specific contraindications:
- pregnancy exceeds 5 weeks (confirmed by ultrasound);
- malformations of the uterus;
- tumors of the uterus, due to which its cavity is deformed.
How to choose an abortion clinic
Today, surgical abortion is offered in many clinics, and not just in antenatal clinics, as before. This allows women to choose a medical facility that employs the best specialists, has the best reviews, reasonable prices, or simply the most convenient location.
And to make this task easier and faster, there is the “Your Doctor” website. It contains information about many Moscow clinics. Among the proposed options, you can choose the most suitable one, and then call the indicated numbers to find out more detailed information or simply make an appointment at a convenient time through the form on the website.
Publication date: 2019-04-24
Useful information on the topic:
- Calling a gynecologist to your home
- Consultation with a gynecologist
- HCG tests
- Ultrasound during pregnancy
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted diseases
- Fetal ultrasound
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Ultrasound during pregnancy
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Discharge in women
Examination before manipulation
Before undergoing a mini-abortion, a woman must undergo the following examination:
- medical examination in a gynecological chair (clarification of probable signs of pregnancy: cyanosis and softening of the cervix, enlarged and softened uterus);
- taking smears from the vagina, cervical canal and urethra, determining the degree of vaginal cleanliness;
- pregnancy test and mandatory ultrasound with a vaginal probe to exclude ectopic pregnancy;
- if necessary, testing for sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, ureaplasmosis and others);
- general blood and urine tests;
- blood for syphilis, hepatitis B and C, HIV infection.
In some clinics, the patient may be sent for a consultation with a therapist, blood donation for biochemistry, determination of blood clotting, group and Rh factor (this examination is not mandatory and is not approved by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation).
Contraindications
There is the following list of contraindications for performing a vacuum abortion:
- acute infections in the body, which increases the likelihood of infection of the genital tract and related complications associated with it;
- ectopic pregnancy that cannot be terminated with a vacuum abortion;
- poor blood clotting;
- unconfirmed pregnancy;
- if 6 months have not passed since the last birth;
- a period of more than 6 weeks, which significantly complicates the procedure for detachment of the fetus and its removal from the uterus.
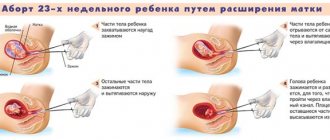
Mini-abortion technique
Almost all women are interested in the question: “How is a mini-abortion done?” The manipulation is usually performed on an outpatient basis and under local anesthesia. If desired, the patient may require general anesthesia, although this is not entirely justified. The woman is informed of the need to prepare for the procedure the day before:
- shave the hair in the pubic area - it contributes to the spread of infection and makes it difficult to perform an abortion
- take a shower
- when performing the procedure under general anesthesia, they warn about the prohibition of eating and drinking on the day of the abortion).
The woman is placed on a gynecological chair, and after treating the external genitalia with antiseptic solutions, a Simps gynecological speculum (spoon-shaped speculum or “spoon”) is inserted into the vagina. The cervix and vaginal walls are also treated with an alcohol solution of an antiseptic (iodine, chlorhexidine).
The cervix is then fixed with bullet forceps (forceps with long, thin, sharp teeth at the ends) to straighten the angle between the cervix and the body of the uterus. The uterine cavity is measured with a uterine probe, which allows you to determine its length and position of the uterus (deviated anteriorly or posteriorly, to the right or left).
A plastic tube with a diameter of 5, maximum 12 mm is attached to the vacuum excoleator, which is inserted into the uterine cavity through the cervical canal without first dilating it. The doctor makes rotational and back-and-forth movements along all the walls of the uterus, trying to find and remove the fertilized egg (the suction of the contents of the uterus is clearly visible through the translucent plastic tube, and the passage of chorionic tissue through the cannula indicates the removal of the fertilized egg).
After completion of the procedure, the cervix and vaginal walls are re-treated with an antiseptic solution and the woman is placed on a couch with ice in the lower abdomen for 30 to 40 minutes. Within a couple of hours after the mini-abortion, the patient returns to normal life. The entire manipulation takes 5, maximum 10 minutes.
Local anesthesia is carried out after fixing the cervix with bullet forceps, while solutions of local anesthetics (lidocaine, dicaine) are injected into the lateral vaults of the vagina with a syringe.
How is a vacuum abortion performed?
The operation is carried out using an electric vacuum pump, which extracts all its contents from the cavity of the reproductive organ.
The procedure is absolutely painless if it is performed under general anesthesia. If local anesthesia is chosen, the woman may feel tolerable nagging pain in the lower abdomen. The pump creates negative pressure or vacuum in the uterus, causing the fertilized egg to peel off and be expelled.
The vascular network of the uterus is practically not damaged during vacuum aspiration. Also, special dilators are not used for the cervix, which allows maintaining its integrity.
That is, a mini-abortion significantly reduces the risk of developing cervical insufficiency, which prevents pregnancy in the future.
Preparatory stage
Before having an abortion, a woman should consult a gynecologist. During the examination, the doctor determines the duration of pregnancy and prescribes the necessary examination. Typically it includes:
- general urine and blood tests;
- microflora smear;
- Ultrasound examination;
- blood tests for HIV, hepatitis and syphilis.
The tests listed are mandatory and, first of all, they show whether the patient has any contraindications to abortion.
Carrying out the operation
After completing the preparatory stage, the day of the operation is set. Abortion should only be carried out within the walls of a medical institution under the guidance of qualified specialists.
To perform aspiration, the patient sits in a gynecological chair, her legs are fixed in stirrups. The external genitalia are treated with an antiseptic. If a woman has never given birth, the doctor dilates the cervix with a special instrument.
For women who have given birth, this point is skipped. For local anesthesia, an injection of the drug is given into the cervix. During general anesthesia, the woman receives medicine into a vein and falls asleep for a short time. After the end of the anesthesia stage, the procedure itself begins.
The doctor inserts the tip of an electric vacuum pump - a cannula - into the uterus and turns on the device. Negative pressure is created in the cavity of the reproductive organ. The gynecologist carefully moves the cannula along the walls of the uterus, trying to achieve precise contact with the mucous membrane.
At this moment, the fertilized egg peels off and exits through a tube into a special container. After all the fruiting tissue is removed from the uterine cavity, it begins to actively contract. Once the tip of the pump is removed from the uterus, contractions will no longer be felt.
Some women complain of nausea, weakness and sweating during an abortion. For such a procedure, all this is a variant of the norm. Read more about the consequences of abortion →
Benefits of mini-abortion
Termination of pregnancy in the early stages using vacuum aspiration has many positive aspects compared to surgical abortion at a later date:
- the short period of interruption practically does not cause psychological trauma to the woman;
- Both local and general anesthesia can be used;
- short duration of manipulation (maximum 10 minutes);
- does not require curettage of the uterine cavity, which is not only very painful, but also traumatic;
- due to the use of a flexible plastic cannula, the risk of damage to the uterine cavity and cervix is reduced (the risk of uterine perforation and the development of isthmic-cervical insufficiency is minimal);
- shorter recovery period;
- There is virtually no risk of developing infertility;
- rapid restoration of the menstrual cycle.
Possible complications and consequences
The most dangerous and formidable complication of abortion is uterine perforation. Perforation can be caused not only by a novice doctor, but also by an experienced surgeon, because the mini-abortion procedure is done blindly.
Incomplete abortion is also no less dangerous for the female body. That is, particles of the fertilized egg or placenta remain in the uterine cavity. This manifests itself as pain in the lower abdomen and heavy bleeding.
As a result of incomplete contractility and spasm of the cervix, blood clots accumulate in the uterine cavity, this is called a hematometra. It is expressed by acute pain in the lower abdomen without bleeding.
This complication is manifested by the following symptoms: pain in the lower abdomen, nausea and vomiting. The doctor will prescribe another vacuum aspiration procedure and treatment with special medications.
The pregnancy may turn out to be ectopic, and if the doctor is not convinced that the fetus is located in the womb, a mini-abortion will not bring any benefit. The ectopic pregnancy will continue to develop. Pain in the lower abdomen and pain during sexual intercourse are signs of an ectopic pregnancy.
The most dangerous consequence of abortion is infertility. According to statistics, 40-50% of women who terminate an unwanted pregnancy cannot have children. The long-term consequences of abortion are: menstrual irregularities, ectopic pregnancy, uterine fibroids, and the development of endometriosis.
Discharge and menstrual cycle after mini-abortion
After a mini-abortion, spotting will definitely appear. In the first few days, the bleeding will be slight and spotting, and only on days 3–5 will it become more intense and is characterized by the woman as moderate. Most abortion clinic “clients” mistake such bleeding for menstruation, which is absolutely wrong. Increased discharge within a specified period is associated only with hormonal changes in the body after forced termination of pregnancy and the response of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system to a sharp drop in the level of progesterone in the blood.
In order for menstruation to occur after termination of pregnancy, the body requires at least a month; it is during this time that the proliferative and secretory transformation of the endometrium will occur (that is, it will grow and be ready for desquamation - rejection).
Therefore, the first menstruation after a mini-abortion should be expected no earlier than 28–35 days (depending on the length of the menstrual cycle, if the cycle is 32 days, then menstruation will occur 32 days later, counting from the day of the abortion). The complete restoration of the menstrual cycle (regularity and the appearance of ovulation) in nulliparous women is reported after 7–9 months, and in women who have given birth after 3–4. Of course, a number of factors influence the restoration of the cycle:
- the presence of gynecological and somatic diseases;
- term of termination of pregnancy (the shorter, the less impact on hormonal levels);
- number of pregnancies and births in history;
- patient's age;
- the nature of the menstrual cycle before the interruption (regular or not).
Spontaneous abortion
Such an abortion can occur without any intervention and against the woman’s wishes. Most experts believe that 14 to 18% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage. About a third of pregnancies end in miscarriage before the woman even knows about her situation. Most miscarriages occur in the first three months of pregnancy and only 1% occur after the 20th week.
Miscarriages occur twice as often in women over 35 years of age. About 35% of miscarriages are caused by chromosome defects. The rest are mainly a medical problem: a weak cervix, uterine defects (double uterus), uterine infections (sexually transmitted diseases), fibroids, other various neoplasms, scar tissue (consequences of abortions and curettage), effects of radiation, poor diet, exposure to toxic substances on one of the parents, smoking, alcohol abuse and a number of medications (including hormonal contraceptives and intrauterine devices), hormonal disorders and problems with the immune system.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Thrush on the eve of embryo transfer
As a result of contraction of the uterus, a gradual detachment of the fertilized egg from the uterus occurs, and the blood vessels of the decidua are damaged. Bleeding occurs, which can be of varying intensity. Under the influence of contractions, the cervical canal of the uterus opens and the fertilized egg is expelled in whole or in parts. Sometimes uterine contractions are preceded by the death of the child (frozen pregnancy).
Possible complications
The risk of complications and consequences after a mini-abortion is practically zero, but, of course, the possibility of their occurrence cannot be excluded (see consequences of abortion). And, of course, the greater the number of vacuum aspirations in the history, the higher the likelihood of complications.
Perforation of the uterus
Puncture of the uterus during vacuum aspiration is quite rare, since metal instruments that can damage the uterus are not used (with the exception of a probe). This is a complication that occurs during the procedure and is characterized by a sudden sharp “dagger” pain.
Inflammation of the uterus and/or appendages or exacerbation of chronic processes
As a rule, this complication occurs 4–5 days after the procedure and is associated either with violations of aseptic rules and neglect of the examination, or with the woman’s violation of the rules of behavior in the postoperative period.
Hormonal disbalance
Hormonal disorders occur especially often in young nulliparous women, which is associated with hormonal changes after termination of pregnancy. Hormonal imbalance can lead to ovarian dysfunction, menstrual cycle disorders and even infertility.
Incomplete removal of the embryo
Since abortion is a “blind” operation, the possibility of not removing the entire fertilized egg cannot be ruled out, which leads to bleeding and the development of a placental polyp and requires curettage of the uterine cavity.
Progressive pregnancy
If vacuum aspiration is performed too early, there is a high probability that the fertilized egg will not be detached from the uterine wall and, as a result, further progression of pregnancy.
Hematometer
In nulliparous women, the cervical canal is quite narrow, which is fraught with blockage by a blood clot and accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity - Hematometra. If there is no effect from drug therapy, artificial dilation of the cervical canal is performed, followed by curettage.
What you need to know before deciding to have a medical abortion
This is not a harmless procedure.
It is advisable to have an abortion before 6–7 weeks
The maximum Medical Management of First‑Trimester Abortion - ACOG period until which a medical abortion can be performed is 9 weeks from the first day of the last menstruation. The key word here is maximum.
The longer the pregnancy, the larger the size of the fertilized egg and the endometrium in which it is immersed. This means that “menstruation” can be much heavier and more painful than usual. In addition, the effectiveness of the procedure depends on the duration:
- if less than 42 days have passed since the first day of the last menstruation, the probability of a successful abortion is 96–98%;
- from 43 to 49 days - 91–95%;
- over 49 days - less than 85%.
Additional factor: when the pregnancy is more than 49 days, the risk of complications increases (more on them below). Therefore, most clinics prefer to work with patients whose last menstrual period has been less than 7 weeks.
Medical abortion is not performed at less than 4 weeks.
This is due to the need to confirm the pregnancy using an ultrasound and find out if it is ectopic.
Even the most sensitive transvaginal test, in which a probe is inserted directly into the vagina, can detect the fertilized egg in the uterus only after it reaches a size of about 2 mm. This approximately corresponds to a period of 4 weeks.
Until an ultrasound is performed and its results are received, a self-respecting clinic will refuse to perform an abortion.
The procedure is not carried out on the day of treatment
Based on the two points above, it is clear that time is limited. A woman has only 2–3 weeks to establish pregnancy, decide on an abortion and carry it out. And during this period, one more nuance must be included: medical abortion, as a rule, is not performed on the day of treatment.
A good gynecologist will send you to think for a few days. It will give you a chance to cope with emotions and, perhaps, still maintain the pregnancy.
Medical abortion takes longer than vacuum or surgical abortion
Classic instrumental types of abortion have their disadvantages, such as the need for anesthesia. But there are also advantages.
If you come for a surgical or vacuum abortion, you clearly know when it will begin and end. As a rule, the procedure takes no more than an hour and a half, including all the necessary preparation and time to recover from anesthesia. In most cases, patients do not feel pain, do not suffer from heavy bleeding, do not experience problems with well-being and can try to forget about the abortion the very next day.
The medication option is different. You will constantly remember about it for at least several days - the interval between taking the pills and the entire period of subsequent bleeding until the second ultrasound. There may also be problems with well-being.
Be prepared for side effects
Taking Mifepristone is often accompanied by unpleasant side effects:
- nausea and vomiting;
- abdominal cramps;
- diarrhea;
- dizziness and headache;
- weakness;
- temperature rise.
This means that your energy, performance, and concentration will decrease. Or perhaps you don’t want to leave the house at all. Take this fact into account when planning your time.
Medical abortion can be painful
Although bleeding with this type of abortion resembles menstrual bleeding, it is more difficult to tolerate. It is often accompanied by severe cramps in the lower abdomen.
Sometimes this pain can be relieved by taking an over-the-counter pain reliever, such as ibuprofen. But more powerful prescription medications may be required. Be sure to discuss this issue with your doctor.
Possible serious complications
First of all, in the form of excessive uterine bleeding. This can be defined, for example, like this: you have to change two or more maxi pads per hour for 2 hours in a row. If this is your case, consult a gynecologist. Or, if the bleeding frightens you with profuseness, call an ambulance immediately.
You should also seek help from a doctor if heavy bleeding does not decrease in intensity within 2-3 days.
Fortunately, such complications are quite rare: statistics show that they occur in less than 1% of women.
You may still have to undergo a surgical abortion
Medicines do not provide a 100% guarantee of termination of pregnancy.
It may happen that the fertilized egg does not come out and the pregnancy continues to develop. This situation is called incomplete abortion. In this case, the remnants of the fertilized egg and the dead endometrium will have to be removed surgically.
There are contraindications for medical abortion
A good clinic will refuse the procedure if the patient:
- pregnancy over 70 days (10 weeks);
- ectopic pregnancy;
- inflammatory or infectious diseases of the genital organs;
- uterine fibroids;
- liver or kidney failure;
- diabetes;
- an intrauterine device is installed;
- there is any diagnosis for which she regularly takes corticosteroids;
- pregnancy occurred while using hormonal contraceptives.
Your doctor will tell you more about contraindications.
You will have to be more active in protecting yourself
There is data from Conception rates after abortion with methotrexate and misoprostol that those who have undergone a medical abortion experience pregnancy in the next year more often than the average for other women. This happens even if the woman does not plan to become a mother.
Scientists warn of an increased risk of another unwanted pregnancy after a medical abortion and ask for more active use of contraception.
If you nevertheless decide to have a child, a medical abortion performed a month or two before the onset of a new pregnancy will not become an obstacle: it does not in any way affect the health of the unborn baby.
Recommendations after the procedure
After undergoing a mini-abortion procedure, a woman must follow simple rules (see rehabilitation after an abortion):
- exclude sexual activity for 2 weeks (optimally 4 weeks);
- resolve the issue of contraception (oral hormonal pills are recommended, which the doctor selects for the patient at the appointment even before the manipulation);
- avoid pregnancy for at least six months;
- control check with a gynecologist and ultrasound after 10 days;
- do not overheat (exclude visiting the bathhouse, sauna and taking a bath);
- avoid hypothermia;
- If pain occurs after the procedure, consult a doctor immediately;
- immediately after vacuum aspiration, start taking water pepper tincture (reducing) and antibiotics (according to indications);
- If subjective signs of pregnancy persist (nausea and vomiting, breast engorgement), visit a gynecologist as soon as possible.
Author:
Sozinova Anna Vladimirovna obstetrician-gynecologist
How early do doctors allow abortion?
Technically, abortion can be done as early as 3-4 weeks into pregnancy, if it is confirmed. Modern pregnancy tests and analyzes make it possible to find out about it so early. But abortion is often done after the pregnancy can be seen on an ultrasound, which is about 5-6 weeks.
Clinics and doctors differ on how soon you can have an abortion in the first trimester - usually 5-6 weeks after your last period (obstetric period). At this time, today in most developed countries, medical abortion (taking pills) is increasingly used, which can be performed up to 9 weeks.
If we are talking about vacuum aspiration, then it is best to use it at 8-12 weeks of pregnancy. Before this, the gestational sac (fertilized egg) is so small that it can be missed, and later the procedure becomes more complex.
Sometimes, for various reasons, it happens that a woman decides to have an abortion later. In such cases, it is worth considering how this will affect your health, and also take into account the regulations regarding abortion.
Classic abortion
Classical curettage is often used, although it cannot be called gentle abortion.
Some patients do not have the opportunity to pay for gentle vacuum or pharmaceutical abortion procedures, so they are forced to agree to surgical intervention. How to have a surgical abortion? It is carried out starting from 7 weeks. The inside of the uterus is scraped out using a curette. The procedure is performed under local intravenous anesthesia. Such an abortion often causes complications such as heavy bleeding, inflammation, infections, a painful recovery period and infertility. Therefore, if an abortion is inevitable, then it is better to do it using a vacuum or medication method.
Timing and abortive methods
Termination of pregnancy in the early stages involves the removal from the uterus of an embryo that has not reached 12 weeks of age. If abortive manipulations are performed at 12-22 weeks, then this is a late termination. If the decision to have an abortion in the early stages of pregnancy is finally made, then you must immediately contact a gynecologist. The specialist will conduct an examination, confirm the fact of conception and its timing, take a smear and prescribe the necessary laboratory tests. If any infection is detected, mandatory treatment will be required, only then will it be possible to perform an abortion at a short term.
A visit to the gynecologist should be made immediately after discovering an interesting situation. As soon as menstrual delay is detected, do not delay, contact us in its first days. The sooner you contact a specialist, the more gentle the abortion will be at an early stage. Perhaps everything can be managed only with the help of medication or vacuum interruption, which have a lot of advantages and do not involve surgical manipulation. There are three abortive options: medical, vacuum and surgical. All of them are used today in gynecological practice in accordance with the specific timing and condition of the patient.
Medication interruption
In the first week of conception, the resulting embryo has not yet had time to form close connections with the uterine endometrium, so its removal will be much easier than in a later period. Special abortifacient tablets have been created that interfere with the favorable course of pregnancy and interrupt it. The most famous among them are:
- Mifegin. Successfully used by Russian gynecologists. The components of the medication block uterine receptors, which provokes spontaneous miscarriage and embryo release. Experts note that the abortive effect when using Mifegin is achieved in almost 99% of cases.
- Mifepristone. Used up to 8 weeks. The active components of the tablets produce a nerve impulse block, resulting in termination of pregnancy at an early stage. Within a couple of hours after taking the pills, the patient will feel the onset of contractions. When undergoing a medical abortion, women are recommended to remain under medical supervision.
- There are a large number of drugs on the market
Metholian. The drug provokes detachment of the embryo from the uterine wall, causing a natural miscarriage.
- Postinor. The drug is usually used as an emergency contraceptive, but is often used for artificial abortion. But, according to statistics, Postinor does not give a 100% result.
- Epostan. Abortion at an early stage is often carried out with the help of this drug, which reduces enzymatic and hormonal activity. Using Epostan in the first weeks, patients get rid of unwanted conception in approximately 80% of cases.
Positive and negative aspects of the procedure
The medical abortion method is the safest for patients; it is carried out only if the pregnancy is in the early stages before reaching 8 weeks, i.e. up to 63 days of gestation. The desired abortive effect is achieved in approximately 96% of patients, depending on the drug used, which is considered an undoubted advantage of this technique. The patient does not experience such strong painful sensations, and the contractive contractions of the uterus during the release of the fertilized egg are comparable in intensity to traditional discomfort during menstruation.
In addition, early-stage medical abortion does not have the risks associated with surgical abortion, and also eliminates the possibility of HIV or blood contamination. The procedure does not affect fertility functions in any way and can be performed on the day the pregnant woman applies. Medical abortion in the early stages is easier for patients to perceive psychologically, while surgical intervention often ends in severe stressful experiences.
But such an abortion event also has its negative sides. Rejection of the fertilized egg is accompanied by painful sensations similar to premenstrual syndrome and pain during menstruation itself. Also, after the embryo is removed, the woman will have to deal with prolonged bleeding, similar to menstrual flow. Sometimes problems arise when choosing a low-quality abortifacient drug or violating the recommended dosage.
How is it carried out?
A similar procedure occurs with the participation of a specialist
It is impossible to carry out such an interruption on your own, since the risk of sudden bleeding and an inadequate individual reaction of the body to taking the drug remains. Therefore, after taking the pills, the woman remains under medical supervision for several hours. An abortion at an early stage by medication is considered accomplished if heavy uterine bleeding begins. After about a couple of weeks, the patient undergoes a gynecological examination and ultrasound examination of the uterine cavity.
Contraindications
Pharmabort is one of the most gentle methods of interruption; it is relatively safe and does not require the use of surgical manipulations. Carrying out a pharmaceutical abortion in the first month of pregnancy is not suitable for every patient; it is contraindicated:
- In late gestation, starting from the second trimester, as well as during breastfeeding.
- If the pregnant woman is not yet 18 years old, because hormonal imbalance is likely to develop.
- Ladies who smoke, as there is a risk for cardiovascular activity.
- If you suspect ectopic implantation of the fertilized egg, under the influence of the pills, the fallopian tube may rupture, causing dangerous bleeding, which can be fatal.
- In the presence of hormonal abnormalities, pharmaboration is also contraindicated, since additional intake of hormones can lead to even greater hormonal imbalance. Also, this method of interruption should not be used in patients taking hormonal corticosteroid drugs or having an IUD.
- Genital organ pathologies such as fibroids and endometriosis, uterine scars or malignant tumors, fibrous tumor processes.
- Early termination of pregnancy is contraindicated in the presence of chronic pathological conditions such as hemophilia, adrenal insufficiency, kidney or liver failure, hemorrhagic syndromes or inflammatory pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular and pelvic inflammatory pathologies. In addition, pharmabortion is not done for asthma and tuberculosis lesions, severe extragenital diseases or hereditary porphyria.
In addition, it is necessary to exclude the presence of allergic reactions to abortifacient drugs. Therefore, abortion is performed with pharmaceutical drugs only as prescribed and under the supervision of a qualified gynecologist.
Consequences
Complications may arise later
How a particular patient’s pregnancy can be terminated should be decided only by a doctor, since even such a relatively safe termination as a pharmabortion can lead to undesirable consequences. Firstly, after taking abortive drugs, patients often experience irritability and constant fatigue, lack of appetite and sleep disturbances. Such conditions are caused by hormonal changes occurring in the patient’s body.
It is also impossible to exclude the absence of an effect, due to which the pregnancy will continue, but the health and usefulness of the fetus will be significantly impaired. After pharmaabortion, on the second day, side effects such as fever, inflammatory processes in the genital organs, ovarian dysfunction or menstrual irregularities, abnormal bleeding or chronic abdominal pain may occur.
Vacuum aspiration
An abortion can also be performed using another fairly common method - vacuum aspiration. In fact, the technique involves the use of surgical instruments, but is still considered a mini-abortion, and not a full-fledged surgical termination. It is used in situations where pharmaceutical abortions are contraindicated. The procedure is possible only during 4-6 weeks of pregnancy. At an earlier time, such a procedure is ineffective and impractical, and in the later months of pregnancy it is not able to provide a complete termination.
Advantages and disadvantages
Vacuum aspiration has many advantages. Firstly, such an interruption does not use methods of expanding the cervical tissue and does not cause severe damage to the uterine wall. Secondly, recovery after a mini-abortion lasts much less than after a classic surgical abortion. In addition, the risk of heavy bleeding is minimized.
A mini-abortion does not cause serious complications such as uterine perforation or serious hormonal imbalances. The procedure lasts about 10 minutes, is carried out without the use of anesthesia, and after it there is a rapid restoration of the monthly cycle.
But this abortive technique still has disadvantages.
- Expert opinion
Incomplete abortion, when gestation may be interrupted incompletely, i.e., part of the fertilized egg remains inside the uterine cavity. As a result, the procedure has to be repeated or curettage is performed.
- Vacuum aspiration is only available within 4-6 weeks, in extreme cases up to 7 weeks.
- Emotional stress conditions, unfortunately, are not excluded. But this is more a rule than a disadvantage, since with any method of interruption the patient experiences guilt and worries after what she did.
Progress of the procedure
Before a mini-abortion, tests and an ultrasound examination must be prescribed in order to maximally exclude the occurrence of possible complications. The procedure itself can be performed using either general anesthesia or local anesthesia. If the patient has not previously given birth, she is often given Misoprostol to relax the cervical muscles so that instruments can penetrate more easily.
A suction tube is inserted through the cervical canal, through which the fetus is removed. When the procedure is completed, the gynecologist must examine the removed tissue to ensure that all of the fertilized egg has been removed. An ultrasound is performed to confirm the absence of embryonic remains in the uterine body. The woman is monitored for another 1-4 hours, depending on the patient’s condition. If there are no complications, she is sent home.
Consequences
Vacuum aspiration can lead to a variety of complications. Already in the first days, infectious complications, heavy bleeding, incomplete abortion, and menstrual disorders may be detected. The procedure, according to the women who have gone through it, is not very pleasant, but quite tolerable. If it is performed under anesthesia, then painful discomfort is completely absent. But in general, the procedure does not cause particularly serious complications, so it is quite suitable as an effective and safe option for ending a pregnancy.
Urgent termination of pregnancy immediately after conception
It is possible to terminate a pregnancy immediately after conception. That is, in the period from several hours to several days after sexual intercourse. To terminate a pregnancy, you need to take 2 tablets of the drug Postinor 12 hours apart. If suddenly after taking the second one there was vomiting, in this case it is allowed to take the third tablet.
The first tablet should be taken as soon as possible. The drug will be most effective within the first 24 hours after intimacy; the probability of getting rid of an unwanted pregnancy is 95%. If 24 to 48 hours have passed, then the success rate is 85%.
If 48 to 72 hours have passed since conception, then in this situation the probability of successful termination of pregnancy is 59%. The drug acts in such a way that, with the help of a group of medications, it suppresses fertilization and ovulation
It is important to know that taking postinor is allowed only once during one menstrual cycle.