Sinusitis is an inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, which can be caused by a number of reasons. Therefore, if characteristic symptoms appear (long-lasting runny nose with thick mucus, headache, feeling of fullness in the infraorbital region), it is necessary to visit a doctor, undergo diagnostics and receive qualified recommendations. Ignoring the problem, symptomatic measures and self-medication can result in sinusitis becoming chronic.
In the vast majority of cases, this disease is bacterial in nature, therefore, antibiotics for sinusitis are the first-line drugs. However, systemic antimicrobial therapy is prescribed only in cases where the patient’s body cannot independently overcome the infection for a long time and there is a risk of severe complications. Bacteria from the maxillary sinuses can enter the lower respiratory tract through the bloodstream and cause bronchitis or even pneumonia. But the main danger is the proximity of the inflammation to the brain and the possibility of developing meningitis or encephalitis.
Symptoms of sinusitis in adults
Acute or chronic inflammation of the maxillary sinuses is characterized by certain symptoms:
- headache radiating to the teeth with increased pain in the evening;
- mucopurulent or purulent discharge from the nose or its outflow along the back wall of the nasopharynx;
- persistent nasal congestion with a characteristic “in-the-nose” tone of voice;
- decreased sense of smell on the side of the affected sinus;
- a feeling of squeezing and/or heaviness in the face with pain when pressing on the area of the maxillary sinuses (paranasal region, cheeks, brow ridges);
- general weakness, malaise and worsening symptoms of a viral infection a week after starting treatment.
Physiotherapy
To achieve maximum effect in the treatment of sinusitis, physiotherapy is used.
Electromagnetic waves of super high frequency have the greatest effect:
- Microwave therapy.
- UHF electric field.
- Low frequency pulse currents (amplipulse therapy, diadynamic therapy).
Ozokerite compresses are used with success in the complex treatment of sinusitis (10 - 20 per course of treatment).
Rice. 16. Using endoscopic surgery, mycetomas (photo on the left) or foreign bodies of odontogenic origin (tooth roots and filling material) are removed.
Main aspects of treatment of sinusitis
Treatment of this disease is carried out only when the diagnosis is clarified, which is determined on the basis of both a clinical examination of the patient and mandatory instrumental confirmation of the pathological process in the maxillary sinuses - computed tomography, ultrasound examination of the nasal cavity or radiography of the paranasal sinuses of the skull.
Correct, adequate and timely treatment of sinusitis in adults is considered to prevent their complicated course and the spread of the infectious process to nearby organs and systems:
- brain (with the development of meningitis, meningoencephalitis, brain abscesses, inflammation of the veins of the dura mater);
- organs of vision (eyeball and its appendages) with the emergence and progression of reactive edema of the tissue of the eyelids and/or orbit, purulent-inflammatory processes in the bone walls and soft tissues of the orbit, retrobulbar abscess and thrombosis of its veins;
- organ of hearing with the development of otitis, labyrinthitis and neuritis of the auditory nerve;
- spread of infection through the blood and lymphatic vessels to distant organs, causing infectious-allergic inflammatory reactions, myocarditis, nephritis, rheumatism of the heart and nervous system, osteomyelitis, hepatitis, trigeminal neuritis.
Traditional methods of treating an infectious-inflammatory process in the maxillary sinuses are based on individual complex drug therapy, which includes:
- antibiotics;
- mucolytics;
- decongestant and anti-inflammatory local medications;
- symptomatic treatment (analgesics, detoxification therapy, antihistamines);
- antiviral agents (if sinusitis develops against the background of a viral infection);
- restorative therapy (herbal adaptogens, vitamins, immunomodulators).
As well as rinsing the nasal cavity, physiotherapeutic procedures and puncture of the maxillary sinus if indicated.
Indications for the use of antibiotics for sinusitis
Antibiotic therapy for sinusitis today is prescribed by otolaryngologists quite often, but only if the cause of acute or protracted sinusitis is a bacterial infection. In this case, before starting treatment with antibacterial drugs, a bacteriological culture from the nose is performed to determine the sensitivity and resistance of pathogenic microorganisms that caused the inflammatory process.
Also, when choosing an antibacterial drug, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the patient, concomitant diseases, possible allergic reactions to antibiotics and other drugs so that the treatment of sinusitis with antibiotics is effective, with minimal risks to the health of patients and does not become a waste of money and time.
As a rule, at the initial stage of sinusitis without the presence of purulent discharge from the nose, a pronounced disturbance in the general well-being of the patient and persistent pain syndrome, otolaryngologists monitor the course of the disease and are in no hurry to immediately prescribe antibiotics or begin with the use of local complex medicines that also contain antibacterial components . These drugs include Bioparox, Isofra, Polydexa. But when there is abundant purulent discharge, persistent nasal congestion, pain in the maxillary sinuses and symptoms of intoxication (lethargy, fever, headache), which intensify, it is necessary to prescribe antibiotics orally or parenterally. Most often, antibacterial drugs from the group of penicillins, macrolides and cephalosporins are used to treat sinusitis. In severe forms and protracted course of acute sinusitis, antibiotics from the group of fluoroquinolones and, less commonly, aminoglycosides are prescribed.
Rinsing the nose and preparing drops
If the patient's condition is not critical, you should not treat sinusitis with antibiotics and buy expensive drugs. Folk remedies for sinusitis must be used very often during the treatment process, but they act very gently on the body and treat purulent sinusitis without causing even more discomfort.
To treat a runny nose, you can drip peach oil into the nose for children and adults. Read about it here.
Do you know why you can’t get monta wet? Read about this at the link -.
An effective treatment for hemorrhoids are preparations based on Witch Hazel - read the article “Witch Hazel - suppositories for hemorrhoids and cosmetics.”
Here are effective and simple mixtures for rinsing the nasopharynx:
- In a glass of warm water, dissolve a teaspoon of sea or table salt and 15 drops of propolis infusion.
- The simplest and most accessible solution: 0.5 tsp. salt and 0.5 tsp. soda It is better if the salt is sea salt, but regular salt will do.
It is important that the medicine gets into the maxillary sinuses not only during rinsing, but remains there for as long as possible. To do this, the nose is constantly instilled. But nasal drops for sinusitis differ from the usual ones that treat a runny nose. And they can also be prepared at home.
- Grate the potatoes and onions and separate the juice. Add 2 tbsp. l. honey The mixture should be stored in the refrigerator, but warmed up slightly before use. This composition makes breathing easier very quickly.
- Chop a small onion and 3 cloves of garlic as best you can. Fill with vegetable oil. These are very effective drops, but they must be infused for a whole week, so you need to prepare the remedy at the first suspicion of sinusitis.
- Just honey drops work great too. Dissolve a spoonful of honey in the same amount of warm water and drop it into your nose several times a day.
- You can drop menthol oil into your nose, and also lubricate the area around your nose with it if it is irritated from frequent nose blowing. But only oil is suitable for this; it cannot be replaced with alcohol tincture.
Return to content
When is it not appropriate to take antibiotics?
To determine the need to prescribe antibiotics for the development of sinusitis, it is necessary to determine the cause of sinusitis and/or its causative agent due to the fact that antibacterial therapy in the presence of certain provoking factors can not only become an ineffective method, but also aggravate inflammation, as well as provoke a protracted course of the disease and slow down the healing process.
This occurs:
- with sinusitis of allergic origin;
- for acute sinusitis caused by a viral infection;
- in case of chronic sinusitis, which develops as a result of viral-fungal associations or fungal etiology - in this case, taking broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs will exacerbate the process and can cause dysbiosis of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses.
For mild viral sinusitis, the most effective treatment methods are nasal lavage in combination with inhalations, mucolytics and immunotherapy.
It is important to remember that the prescription of therapy for the treatment of sinusitis, as well as other types of sinusitis, is prescribed only by a specialist, is complex and individual, taking into account the characteristics of the patient (age, concomitant diseases, allergic reactions), the microflora that caused the inflammatory process and the immunological reactivity of the body.
Taking antibiotics quite often does not leave its mark on the body and is used only in cases of extreme necessity, and pronounced negative side reactions can occur when the dose and frequency of taking these medications is exceeded as a result of self-medication or when they are used uncontrolled. Also, all antibiotics, to a greater or lesser extent, suppress the immune system of patients and can provoke changes in the normal microflora of the intestines, vagina, mouth and the development or progression of dysbiosis and fungal diseases. In all these pathological processes, they manifest themselves in the form of an unpleasant taste in the mouth, aphthous stomatitis, stomach and intestinal disorders with diarrhea of varying severity and symptoms of vaginal fungal infections (thrush).
How to properly warm up
Treatment of sinusitis at home is much more effective if you constantly warm it up. The therapeutic-warming procedure for sinusitis is extremely simple.
- You can use a regular heating pad. Wrap it in a towel and apply it to the affected side several times a day.
- Warming up with wax or paraffin works great. Melt the candle until it is soft and does not burn your skin. Apply a thick layer to the nose, frontal and maxillary cavities and keep until completely cool. It will be easy to remove the hardened composition.
- You can use freshly boiled eggs as a warmer. They need to be applied to the bridge of the nose and held until they cool down.
- Pour 30 g of bay leaves into a glass of boiling water and let it cool slightly in the water. Wrap a couple of sheets in a napkin moistened with the broth, apply it to your face, place a towel on top and breathe in the air with the laurel aroma. As soon as the compress has cooled, apply a new one of the same type - warm it up until the water in the bowl has cooled completely.
Attention! This procedure is effective only for occasional sinusitis. Do not try to treat chronic sinusitis with heating, this will greatly aggravate the problem.
Return to content
Features in the treatment of sinusitis with antibiotics
1. Antibiotics should be taken only after consulting an ENT doctor (upon clarifying the diagnosis) and in accordance with his recommendations - doses, frequency and duration of use. You should not stop taking these medications when the first symptoms of improvement appear or when symptoms completely disappear due to a possible relapse of the disease.
2. An important aspect of the effectiveness of antibacterial drugs is the discharge of purulent discharge from the nasal sinuses, which is achieved by the combined use of vasoconstrictors and decongestants, mucolytic drugs (to thin out viscous mucus) and rinsing the nasal cavity with antiseptic solutions.
3. To prevent dysbiosis and the addition of a fungal infection, the joint administration of probiotics is necessary.
4. The use of the latest technologies for the treatment of sinusitis as prescribed by an otolaryngologist - a special catheter for the paranasal sinuses "YAMIK", laser therapy and the herbal homeopathic drug Sinuforte, which cleanse the maxillary sinuses and increase local immunity.
Other folk remedies
- Chewing honey zabrus. Zabrus is a mixture of honey and beeswax, which contains propolis. Honey and propolis have anti-inflammatory properties, strengthen the immune system and facilitate the removal of pus. Chewing wax is an additional massage of the palate and maxillary sinuses.
- Special massage. Lightly and often tap the bridge of your nose with your knuckles, then massage in a circular motion, with light pressure, into the skin at the base of the eyebrows, in the corners of the eyes, in the area of the hump and at the base of the wings of the nose.
- Vinegar fumes. Place a piece of bread soaked in a weak vinegar solution on a hot frying pan. Carry out inhalation, inhaling the resulting vapors for a couple of minutes. Be careful! The vinegar should be weak and the procedure should be short.
- Honey compress. Mix honey and medical alcohol in a 1:1 ratio. Before going to bed, thickly lubricate the skin around the sore area with this mixture, then pull a warm hat over your face so that there is a passage for air, and go to bed. Overnight, the honey will be completely absorbed into the skin, and the symptoms of sinusitis will noticeably weaken.
Return to content
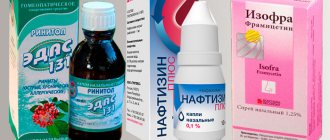
The most effective antibiotic drops and sprays
Topical antibacterial medications include nasal drops or nasal sprays containing antibiotics. The most widely used today are Isofra, Polydexa and Bioparox.
Polydexa
Polydexa is a modern complex drug for the effective treatment of purulent complications in otolaryngology, including sinusitis (sinusitis, ethmoiditis and frontal sinusitis) of microbial etiology. This drug has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect with significant inhibition and/or destruction of bacterial microflora and purulent complications are completely cured.
The effectiveness of this local antibacterial drug is determined by its composition:
- two antibacterial drugs – neomycin and polymyxin, which activate each other’s actions;
- dexamethasone is a hormonal anti-inflammatory component;
- phenylephrine is a vasoconstrictor drug (anticongestant) from the group of alpha-adrenomimetic drugs.
Polydexa has an antimicrobial and bactericidal effect with a strong anti-inflammatory effect for the local treatment of sinusitis.
It is important to remember that the need to use this antibiotic-containing drug can only be decided by the attending otolaryngologist after examination and with a confirmed diagnosis of sinusitis.
Absolute contraindications to the use of Polydex nasal drops are:
- children under 2 years of age;
- increased individual sensitivity to one of the main components (neomycin, polymyxin and dexamethasone) or excipients of this drug;
- suspicion of angle-closure glaucoma;
- simultaneous use of this drug with monoamine oxidase inhibitors;
- viral diseases of the nasopharynx;
- period of pregnancy or while breastfeeding;
- albuminuria syndrome in severe kidney disease.
The prescription of Polydexa for the treatment of sinusitis in professional athletes often causes positive reactions in doping tests.
Polydex is prescribed with extreme caution when used simultaneously with attenuated live vaccines BCG and BCG-M (anti-tuberculosis) and polio, which is associated with a high risk of developing these dangerous diseases against the background of generalization of the infection, therefore vaccination is transferred and carried out only after the patient has been completely cured. Also, Polydex is not used with aminoglycoside antibiotics, which have a pronounced ototoxic effect, especially with combined complications such as otitis or labyrinthitis.
Polydexa has a complex composition and its independent use is strictly prohibited - treatment with this drug can only be started after examination by an ENT doctor, family doctor, internist and pediatrician and under mandatory dynamic observation with individual doses, frequency of administration and duration of therapy, concomitant diseases and immunological reactivity of the patient's body.
In severe cases, local use of Polydex is combined with oral antibiotics or their parenteral administration.
Bioparox
Bioparox is currently a new generation drug, which is considered quite effective if there are indications for its local use in the form of severe infectious and inflammatory diseases of the nose - sinusitis.
This antibacterial drug is available in the form of an aerosol (spray) for local use in the nasopharynx (with two nozzles - for the nose and throat separately). Bioparox is available in 20 ml bottles containing 400 doses of the drug. The active ingredient in the spray is the topical antibiotic fusafungin. The effective therapeutic effect of this drug is based on a double effect, which consists of the simultaneous antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects of fusafungin. It is active against staphylococci, group A streptococci, pneumococci, some strains of nonseria and anaerobes, as well as mycoplasma and fungi of the genus Candida, which in most cases are the causative agents of both secondary sinusitis (when pathogenic microflora is attached to the background of viral and colds), and and primary sinusitis, which develop with the activation of the own microflora of the nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses against the background of a decrease in the local immune reactivity of the mucous membranes or with the progression of concomitant infectious and allergic processes in the body.
When used correctly, Bioparox, in the form of tiny particles, actively penetrates deep into the walls of the nasopharynx and sinuses, relieving swelling and inflammation of the mucous membranes, improving the outflow of mucus from the nose and causing the death of pathogens of the infectious process. At the same time, Bioparox has minimal systemic effects and is found in blood plasma in small quantities. But at the same time, it is used with caution during pregnancy and lactation - in these conditions, even a small amount of fusafungine in the blood can have a general adverse effect on the fetus and infant.
It is also important to remember that Bioparox for sinusitis in the form of monotherapy can be effective only at the beginning of the disease, when the inflammatory process is catarrhal in nature. Acute purulent sinusitis and its protracted forms are difficult to treat with Bioparox alone; complex therapy is used, which is prescribed by a specialist. Self-medication in this case can lead to the progression of the disease, the addition of other catarrhal or purulent inflammations, the development of resistance of pathogenic microflora, dysbacteriosis or the layering of a fungal infection, which significantly complicates the cure and can lead to the transition of sinusitis to a chronic form.
Adverse reactions when using Bioparox occur rarely, but can manifest themselves in the form of local allergic reactions on the skin and mucous membranes, which manifest themselves in the form of an allergic rash or swelling, discomfort in the paranasal sinuses, burning and redness of the nasopharyngeal mucosa. Less commonly, an allergic reaction manifests itself in the form of bronchospasm and angioedema.
Isofra
Isofra nasal spray is an antibacterial drug that contains framycetin sulfate, an aminoglycoside antibiotic.
Isofra is produced in the form of a nasal aerosol and is used in the form of intranasal injections using a nebulizer, as a result of which the antibacterial agent is sprayed and absorbed into the mucous membrane of the nasal passages and the uniform distribution of microparticles of the active substance framycetin sulfate with the penetration of the antibiotic even into hard-to-reach areas of the paranasal sinuses during sinusitis .
This drug is often prescribed as part of combination therapy in the treatment of bacterial sinusitis caused by Haemophileus influenza, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae in the absence of violation of the integrity of the walls of the paranasal sinuses and nasal septum, which is an important condition that is taken into account when prescribing Isofra. The drug is strictly contraindicated for use when washing the maxillary sinuses during puncture. Isofra is ineffective in the treatment of infectious and inflammatory processes caused by S. pneumoniae, S. maltopilia and B.cepacia, like most antibiotics from the aminoglycoside group.
It is important to remember that this drug is an antibacterial drug for the treatment of purulent, mucopurulent or catarrhal complications of a viral infection in the form of sinusitis (sinusitis, ethmoiditis and frontal sinusitis). The effectiveness of these drugs can be determined only after an antibiogram as a result of bacteriological cultures of the nasal cavity and sinuses with determination of the pathogenic pathogen and its sensitivity to the antibiotic.
Untimely and/or incorrect use of this drug will, at best, be ineffective (provided the microflora is resistant), but can lead to a complicated course of sinusitis and negative effects on the body as a whole when taken simultaneously with incompatible drugs (ototoxic antibiotics, MAO inhibitors, antiarrhythmic drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). And also cause the development of dysbacteriosis, layers of fungal infection, congenital anomalies of the fetus when used during pregnancy, aggravation of concomitant somatic pathology (with vasculitis, severe diseases of the blood, kidneys or liver).
It is important to remember that even topical antibiotics are prescribed only by a specialist, and self-medication in this case does more harm than good in most cases.
How to relieve pain
Analgesics are used to reduce pain and inflammation during sinusitis. Drugs from the group of non-narcotic analgesics have proven themselves well: Paracetamol and Ibuprofen and their analogues. Stronger drugs are sold in pharmacies only with a doctor's prescription.
Before using painkillers, you must carefully read the instructions. Like any drugs, medicinal substances in this group have side effects - they cause allergies, irritate the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, and have a toxic effect on the liver and blood. In people under 20 years of age, pain medications can cause acute hepatic encephalopathy (Reye's syndrome).
Rice. 9. Medicines for pain relief. The active ingredients are paracetamol (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil).
Strictly follow the instructions for use of the drugs. Do not use painkillers for more than 10 days!
The most effective systemic antibiotics
Oral or parenteral prescription of antibiotics as part of complex therapy is carried out:
- with acute catarrhal sinusitis with a pronounced clinical picture and progression of the process;
- with profuse mucopurulent or purulent discharge from the nose with severe nasal congestion;
- with severe pain syndrome, which is manifested by persistent headache and pain syndrome in the projection of the maxillary sinuses, upper jaw, cheeks, brow ridges;
- in the presence of intoxication syndrome;
- with prolonged course of sinusitis;
- with multiple purulent complications in the form of sinusitis, otitis, labyrinthitis, reactive edema of the tissue of the eyelids and/or orbit, periostitis of the upper jaw, odontogenic sinusitis (as a result of complicated caries of the upper teeth), associations of microbial flora (several pathogens);
- or a combination of several of the above aspects.
Most often, antibacterial drugs from the group of cephalosporins, penicillins, macrolides and fluoroquinolones are used to treat sinusitis.
Penicillin antibiotics
(Amoxicillin, Flemoxin Solutab, Hiconcil, Flemoklav Solutab and protected amoxicillins - Amoxiclav and Augmentin).
Penicillin antibiotics - for sinusitis, aminopenicillins are more often used, which are today the best antibacterial drugs for the treatment of infectious and inflammatory pathological processes in the paranasal sinuses:
- they have fewer side effects;
- easy to carry;
- aminopenicillins are effective against gram-positive cocci (staphylo-, pneumo- and enterococci) and less effective against streptococci. Also, these drugs are highly effective against gram-negative microorganisms of the intestinal group (Shigella, Salmonella, Escherichia coli) and Haemophilus influenzae.
But in the presence of a severe inflammatory process caused by penicillin-resistant infections (staphylococci, gonococci, Haemophilus influenzae producing beta-lactamases), they may be ineffective, and therefore protected aminopenicillins are used in combination with clavulonic acid (Amoxiclav) or sulbactam ( Augmentin).
Any of these drugs is prescribed only by the attending physician, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the course of the disease.
Drugs from the aminopenicillin group are low-toxic antibiotics, but sometimes adverse reactions may occur:
- allergic manifestations (skin rash, bronchospasm, angioedema or anaphylactic shock);
- disturbances of water and electrolyte balance (hypokalemia or hypernatremia);
- hematological reactions (anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia);
- vascular complications;
- increased activity of liver transaminases;
- neurotoxicity (tremor, convulsions, severe headache);
- psychopathic reactions (increased anxiety, sleep disturbances).
Cephalosporins
(Cefuroxime, Cefixime, Ceftibuten, Zinnat, Ospexin, Cefutil, Cefotaxime, Cefix, Cedex)
This group of antibiotics is prescribed orally and parenterally for severe inflammation and/or when other antimicrobial agents are ineffective.
The pharmacological effect of all cephalosporin antibiotics is bactericidal. The basis of their therapeutic action is the inhibition of metabolic processes in the cell wall of the pathogen, as a result of which lysis of bacteria occurs under the influence of intracellular osmotic pressure and the death of microorganisms.
Due to their high bactericidal activity, these antibiotics are used in complex treatment regimens for sinusitis in adults and children in outpatient settings and in hospitals.
The most common side effects observed with the use of cephalosporins are allergic (urticaria, erythema multiforme, angioedema), hematological reactions and effects on the digestive tract (abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, pseudomembranous colitis).
Injections
The answer to the question of what antibiotics are prescribed for sinusitis for intramuscular administration is also ambiguous. The range of drugs includes Ceftriaxone, Cefazolin, Amoxiclav. All these medications are used for inflammatory processes characterized by severe disease. The course of injections does not exceed 7 days, and can be extended only in exceptional cases.
Despite numerous studies, the statement about which antibiotic is better - in tablets or administered intramuscularly - remains controversial to this day.
Injections, unlike pills, have virtually no effect on the gastrointestinal tract, but they also have a number of contraindications and side effects.
After a course of injections, the doctor may additionally prescribe pills to maintain the therapeutic effect.