Unpleasant sensations in the heel indicate the consequences of an injury or the presence of a disease. The massive part of the foot is designed to bear heavy loads and perform a shock-absorbing function for the spine. This is facilitated by its anatomy and dense fat deposits. The structure of the ankle contains many nerve endings, vessels, and tendons. The spongy structure of the bone increases the risk of various types of damage. Their result is a sore heel and it hurts to step with every step.
Heel pain - what could it be?
Pain in the heel is caused by various reasons and is accompanied by specific symptoms. What diseases may pain indicate:
- If discomfort appears directly in the center of the heel and is accompanied by numbness on the side of the sole, the pathology is called Morton's neuroma . It is caused by compression of nerve endings
- Sharp discomfort after rest that occurs from heel to toe is a manifestation of plantar fasciitis . This is not a spur, as diseases are often confused. Pain appears in the bottom of the foot and covers the leg right up to the heel.
- Pain in the back of the heel, if there is no spur, signals calcaneal apophysitis - inflammation of the heel bone. Occurs in adolescents and is associated with inflammation of ossification foci.
- If the heel hurts on the side on the inside, this signals flatfoot , which is caused by hallux valgus . The arch of the foot drops, so the load on the inner side provokes a dull pain. It often occurs after a long walk or when you stand for a long time and load your leg statically.
- Discomfort in the center of the heel, accompanied by swelling, indicates Achilles bursitis . Inflammation of the synovial bursa is combined with inflammation of the Achilles tendon. When pressing on the heel joint, a sharp pain is felt.
- If discomfort appears from the back of the heel, but shoots into the shin, the legs ache, doctors suspect spinal osteochondrosis . A person spares his back and distributes body weight incorrectly; the heel suffers first of all.
- Unpleasant sensations at the back of the foot, if a lump (inflamed or not) is noticeable on the surface above the heel, speaks of Haglund's disease. A painful growth, a bone, forms on the back of the foot, accompanied by inflammation and the appearance of osteophytes.
- If there is discomfort on the outside of the heel while walking, the cause is inflammation in the tendons. This process is called tenosynovitis and affects the entire foot, right down to the toes.
Diagnosis of diseases using instrumental and laboratory methods
At the first stage of the examination, a visual examination is carried out, palpation of the affected part of the foot, and a questioning of the patient. Special medical equipment is then required to detect changes in the heel. The third stage is a laboratory blood test (may precede hardware diagnostics).
Diagnosis of plantar fasciitis
Involves X-ray examination and computed tomography. A preliminary examination by a doctor is aimed at checking the sensitivity and tone of the ankle muscles, reflexes, and coordination of movements. MRI provides the most information.
Diagnosis of heel spurs
All calcium build-ups and painful areas are easily detected by compacted tissues at the initial appointment with a specialist. It is almost impossible to feel them, therefore, together with the inflamed tendons, they are visible only on an x-ray. The diagnosis is confirmed by everyday observations. There is unbearable pain after changing body position, morning stiffness in the joint, and increasing discomfort when walking.
Of the diagnostic methods, X-ray and laboratory tests have the proper level of information. It is important for the doctor to rule out other heel diseases (Reiter's syndrome, ankylosing spondylitis).
Diagnosis of calcaneal apophysitis in adolescents
A medical examination is of utmost importance. All assumptions are supported by the results of complex radiation imaging methods - MRI, ultrasound. The patient then undergoes laboratory diagnostics. X-ray examination in this case is useless.
Diagnosis of Achillodynia
The soft tissues and muscles around the heel bone at the junction of the Achilles tendon are examined using ultrasound and MRI. X-ray measures are characterized by lower diagnostic value. At the discretion of the doctor, additional puncture of the synovial cavity may be required, followed by analysis of a sample of the material.
Diagnosis of achillobursitis
First of all, the patient undergoes an X-ray examination, which reveals the effects of trauma and bone destruction from rheumatoid arthritis. Your doctor will then order laboratory tests. A blood test can detect gout. Puncture and taking the contents of the tendon bursa confirms or denies the presence of viral bursitis.
Diagnosis of nerve compression
Nerve compression can be complicated by diabetes mellitus and central nervous system damage. To determine the diagnosis, a blood glucose test is performed. Additionally, instrumental techniques are used:
- MRI and ultrasound reveal inflammation, tumors affecting the nerves.
- Electroneuromyography (ENMG) determines the quality of transmission of signals from muscle fibers to nerve endings.
- X-rays reveal calcium deposits and bone deformation.
Nerve compression is also determined independently. Sitting on the edge of a chair and placing a moderately heavy load on your knee, you can feel pain at the bottom of the ankle. This confirms the presence of neurological disorders.
Causes of heel pain when walking
Sore heel.
External causes of heel pain do not lie in pathologies of the foot, but can be somatic, that is, associated with a general disease of the body. In this case, the heel hurts when walking and even at rest.
The following diseases lead to heel pain:
- diabetes;
- calcium deficiency in the body;
- metabolic disorders;
- lack of vitamins;
- fungal infection of the skin surface;
- gastritis.
With the listed pathologies, discomfort in the legs is a symptom, a secondary manifestation that is worth paying attention to. After diagnosis, treatment is directed directly to the underlying disease.
Causes
The intensity and location of pain directly depends on the cause of its occurrence. There are natural sources of the problem and those caused by inflammatory processes in the heel zone. The first group of factors is associated with the activation of static load on the sole. Then pain rarely occurs at rest. The second group of reasons is caused by a disorder of the endocrine system or immunity. This creates favorable conditions for infection of the soft tissues of the foot by various microorganisms.
Uncomfortable shoes
When everyday shoes do not correspond to the actual size of the foot - they are tight, narrow, pressing - pain occurs when walking. This unpleasant symptom is more often observed in women due to the need to use heels.
In order not to overload the lower part of the ankle and prevent its subsequent inflammation, it is recommended to follow simple rules:
- Do not wear shoes with flat soles or excessively high heels for a long time (maximum height – 7 cm).
- Avoid low-quality materials that can put excessive pressure on the leg or rub the skin.
- Avoid excessive abrasion of the sole, especially if you have flat feet.
- Choose shoes with arch support, preferably on an orthopedic basis.
In some cases, it is possible to achieve comfortable wearing of shoes with the help of special insoles that fix the foot in the optimal position.
Excess weight
Excess weight significantly increases pressure on the legs. The ankle joint is especially affected. It is necessary to alleviate the situation with proper nutrition, physical activity and systematic foot massage. The diet should include foods containing proteins, vitamins, and microelements. Every day you should burn more calories than you consume. Morning jogging, swimming, cycling, fitness, and athletics help improve metabolism and burn excess fat.
Excessive stress on the legs due to lifestyle
The need for long-term walking or standing increases the total load on the heel area. A person with a sedentary lifestyle who decides to sharply increase physical activity will encounter physiological errors. Its manifestations are pain in the longitudinal arch of the foot, corns, and calluses. It is necessary to increase pressure on the feet gradually, especially for people with a thin layer of subcutaneous fat on the plantar surface.
Calcaneal bursitis
It is an inflammation of part of the joint - the synovial bursa. A distinction is made between posterior calcaneal bursitis and Albert's disease - achillobursitis. Potential reasons:
- Using tight shoes that rub the heel and increase the load on it.
- Various injuries affecting the posterior talofibular ligament.
- Development of bone spurs on the lower leg (Haglund deformity). One of the symptoms of the disease is a visual increase in the size of the heel.
- Flat feet, club feet.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, other autoimmune diseases.
The pain in both types of disorders is localized behind the heel, where its protruding part connects to the Achilles tendon.
Plantar fasciitis
It is a consequence of damage or inflammation of the plantar fascia, which is responsible for connecting the heel bone to the foot. An additional function of the anatomical structure is to provide the ability to fully move.
Risk factors for developing plantar fasciitis include:
- Excess weight, metabolic disorders, hormonal imbalance.
- Pregnancy, during which a woman actively gains weight, changes her usual gait pattern.
- Staying on your feet for a long time is typical for workers in relevant professions and athletes - track and field athletes, skateboarders.
Most often, the disease manifests itself after 40 years, when the muscle corset weakens and an age-related decrease in activity occurs.
Arthritis, arthrosis
At the initial stage, degenerative-inflammatory processes develop without signs of pain. Changes in the condition of bone tissue are detected during an x-ray examination. Arthritis of the 2nd and 3rd degrees is manifested by severe pain, especially when walking. Additional symptoms are swelling of the leg, redness, and a significant increase in the size of the ankle.
Deformation of the feet is inevitable. Therefore, the intensity of symptoms is reduced immediately - with drug treatment or a course of physiotherapy. It is important to prevent loss of the ability to move independently.
Heel Spitz
It is a wart on the skin surface of the heel area. It causes an unpleasant sensation and difficulty walking. The plantar spitz is a source of pain, burning, itching. Treatment methods include surgery and drug therapy.
Osteoporosis
Characterized by bone fragility due to a decrease in their density. With stage 2 or more of the disease, the area to the right or left of the calcaneofibular ligament is of concern. Adults over 37 years of age are susceptible to pathology. The main factor in pathogenesis is the leaching of micronutrients from bone tissue. The development of the phenomenon is facilitated by:
- Poor food.
- Bad habits.
- Early menopause, late menstruation.
- Long-term breastfeeding.
Along with the pain syndrome, the phenomena of osteoporosis are detected in scoliosis and decreased growth of the body. The disorder can also be detected when the healing of fractures takes an unnaturally long time. Therapy is based on following a proper diet and taking medications that stimulate bone regeneration.
Why does your heel hurt after sleep?
If the heel hurts very much in the morning or after sleep, when the leg has been at rest for some time, then doctors speak with almost one hundred percent certainty about plantar fasciitis. It is associated with stretching of plantar fascia fibers and aseptic inflammation.
Only the right or left leg, or both at once, is affected. During the night, the foot rests, the fibers contract slightly, but when you first step on the surface, a sharp pain appears in the foot. During the day, discomfort usually subsides, and in the evening it appears again, but most of all it bothers a person at rest in the morning.
Prevention
You can prevent pain by following these rules:
- Wear high-quality comfortable shoes with medium heels (no higher than 5 cm).
- Maintain proper physical activity and avoid long walks.
- Adhere to the principles of a balanced diet.
- Control your weight.
It is necessary to follow safety rules and avoid situations that could cause foot injury.
Pain inside the heel in some cases signals the need to make changes to your lifestyle or daily routine, but sometimes you will need to seek medical help to solve the health problem. If your heel hurts, treatment begins only after a comprehensive examination and clarification of the cause of the pain.
Diagnosis: which doctor to go to
What to do if your heels hurt, a specialist will tell you. The disease is diagnosed by doctors of different profiles. Traditionally, patients consult an orthopedist , but examination will also be required:
- neurologist;
- traumatologist;
- rheumatologist;
- surgeon
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor will not only collect a thorough history and ask about the patient’s complaints, but will also prescribe additional diagnostic tests:
- X-ray;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- densitometry;
- blood and urine tests.
Based on the results obtained, they find out why the heel hurts when walking, what the reasons are, and prescribe treatment for the pathology.
Diagnostic measures
OBC, OAM, and blood biochemistry are mandatory. If we are talking about inflammation, there will be an increased ESR, an increase in leukocytes, and a decrease in hemoglobin. Biochemistry will show the level of inflammatory proteins, the presence of uric acid, etc. If reactive arthritis is suspected, a scraping may be taken from the urethra. Tuberculosis will be determined by an x-ray of the lungs and a puncture biopsy.
For osteomyelitis, a biopsy is also performed. For bursitis, I perform a puncture of the synovial bursa. Oncology can be determined by tumor markers, ultrasound, MRI, and osteoporosis by densitometry. However, the most important and most common diagnostic method remains an x-ray of the ankle in two projections.
Treatment of severe heel pain
To treat severe heel pain, you must consult a doctor, since not all diseases can be treated at home with conservative methods.
If non-surgical treatment is possible, the doctor will prescribe ointments, compresses, exercises and massage to relieve pain . Injecting some medications directly into the heel joint, such as a heel spur block, will require a clinic visit.
Injection of anesthetic into the heel.
Folk remedies for heel pain are also used. For Haglund's disease, achillobursitis and other pathologies at a late stage of development, surgical treatment is required to help get rid of a heel spur or other defect.
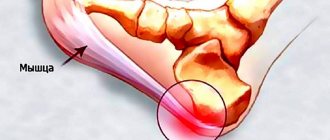
Structures susceptible to inflammation
The calcaneus is an irregularly shaped formation with the following sections:
- lower (plantar);
- posterior (includes the tubercle to which the Achilles tendon is attached);
- internal and external side;
- the upper part is adjacent to the talus, which takes part in the formation of the heel joint.
Each of these departments can undergo traumatic, inflammatory or destructive changes, which is accompanied by severe pain in the heel area.
The pathology of the considered element of the musculoskeletal system provokes unpleasant sensations in the following formations:
- ligament, muscle and tendon fibers;
- cartilage tissue;
- synovial membranes;
- skin layers and fiber;
- peripheral nerves;
- vessels.
Pathological processes bring a lot of concern, since this part of the body takes on most of the load while walking.
Treatment of heel diseases at home
After consultation, the doctor will recommend how to treat heel diseases at home. Most patients cannot do without the use of ointments, as they relieve pain well. An effective pain reliever is aspirin with iodine. Compresses with Dimexide on the heel will also help relieve swelling, relieve discomfort in the foot and stop the inflammatory process.
Ointments
Ointments for the treatment of heel pain contain an anti-inflammatory component. Non-steroidal drugs are usually prescribed:
- Ibuprofen;
- Naproxen;
- Movalis.
Ointment for heel pain should be applied to the feet 2-3 times a day. After a few days, the pain and swelling disappear. Read about the best ointments for spurs in a separate article.
Folk remedies
An effective folk remedy for heel pain is cinquefoil tincture. A tablespoon of the product is diluted in one-third of a glass of water and drunk three times a day for three weeks.
Tincture of cinquefoil for the treatment of heels.
Another effective remedy for pain is three crushed aspirin tablets, mixed with iodine to form an ointment. The application is made directly to the heel area and insulated overnight. It is possible to cure the disease in a few days. You can also use folk remedies for spurs.
Exercises
Exercise is an important step in the treatment of heel diseases. Classes will help not only to activate blood circulation inside the foot, but also to develop range of motion and stretch the plantar fascia.
It is useful to do them with a ball or special massagers. Do the exercises several times a day. At the same time, the doctor will recommend wearing an orthosis to ensure a stable effect from the exercises.
Video: 5 effective exercises for heel pain.
Massage
In the absence of contraindications, doctors recommend self-massage of the sore heel and teach basic movements. As a rule, when massaging and treating spurs at home, warming creams and ointments with an anti-inflammatory effect are used. First, the foot is stroked from top to bottom, grasping the shin. Then massage the area under the fingers in a circular motion and, increasing intensity, gradually move to the heel.
If professional intervention is necessary, the patient will be prescribed a massage course of 10 sessions, performed by a chiropractor.
Principles of treatment
Treatment can be medicinal or non-medicinal: herbal medicine, physiotherapy, exercise therapy, etc. If there is no effect, surgical intervention is practiced.
So, if the heel of your left foot hurts, how to treat it? Conservative therapy involves taking NSAIDs locally and orally, analgesics, cytostatics, and gold preparations (for systemic diseases). If the disease is inflammatory in nature, antibacterial therapy is required. To improve microcirculation and tissue regeneration, angioprotectors are used - Actovegin, Tivortin.
We must not forget about periodic intake of vitamins and minerals. For constant pain, blockades with Diprospan and Lidocaine, etc. are prescribed. For calluses, special patches with acids (lactic, salicylic) are used.
For bursitis, it is recommended to apply a special splint and rest; less often, a puncture of the joint is performed to wash the bursa.
For gout, medications that help reduce the amount of uric acid, such as Thiopurinol, are usually prescribed.
In case of injury, it is necessary to immobilize the foot. If your heel tendon is sprained, you will need a compression bandage. If a rupture occurs, surgery is indicated.
How to relieve pain and inflammation of the heel bone
The inflammatory process in the heel bone becomes the main source of pain. It is very important to stop inflammation to eliminate discomfort. Traditional medications are heel patches, hormonal or non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs. They are produced in tablets and intra-articular injections. Among the tablets, Chondrocerin and Ibuprofen are effective.
An excellent effect is achieved by introducing hydrocortisone into the joint cavity. Hormonal injections are not recommended for those who have atrophic processes in tissues, since hormones enhance destructive processes and can even provoke necrosis.
Diagnostics
To detect the cause of pain in the heel area, it is necessary to collect anamnesis, evaluate the clinical picture and conduct a set of additional examinations.
If the patient experiences pain in other joints and legs, a systemic disease must be assumed. With such a pathology, not only the musculoskeletal system is affected, but also the internal organs.
Anamnestic data allows you to diagnose an injury, the nature of which is detailed with the help of additional examinations.
Laboratory diagnostics
To clarify the diagnosis of heel diseases, clinical and biochemical blood tests are prescribed. The following laboratory data are required:
- general analysis of peripheral blood (an increase in the number of leukocytes and erythrocyte sedimentation rate indicates an inflammatory process in the body);
- biochemical analysis for rheumatic tests (helps to identify systemic damage to the musculoskeletal system due to the rheumatic process);
- Testing the amount of uric acid in the blood helps diagnose or rule out gout.
If you suspect the development of a neoplasm, which can compress nerves and blood vessels and cause heel pain, it is necessary to test for a malignant process using tumor markers.
To confirm the bacterial nature of the disease caused by infections of the genitourinary system or digestive tract, scraping of the urethra or bacteriological analysis of stool may be required.
A biopsy of the affected bone is necessary to diagnose osteomyelitis or tuberculous lesions of the heel.
Instrumental diagnostics
A history of traumatic injury necessarily requires an x-ray examination of bone structures. This method allows you to identify cracks and fractures of the heel bone; it is also indispensable if a tumor of a malignant or benign nature is suspected. A CT scan or MRI is needed to confirm ligament and tendon rupture.
Bone scintigraphy and ultrasound make it possible to diagnose fistulas, areas of necrosis and metastases.
Densitometry determines bone density. This study is necessary for older people to confirm or rule out osteoporosis.
Surgical treatment
Surgical intervention is practiced in the treatment of heel spurs if there is no effect of drug therapy. The plantar fascia is excised and part of the bone, spur or sequestrum is removed. The operation can be performed endoscopically or openly.
For fractures in the heel area, a cast is required for 1.5 months. Mobility only with the help of crutches. The forefoot can be loaded only one month after the cast is removed. The rehabilitation period includes exercise therapy, massage, and physiotherapy.
If recovery is slow, the patient wears an orthosis in the form of a boot, which reduces the load on the bone, prevents muscle atrophy, and reduces swelling. The recovery period generally takes 3 months. Even if movements are difficult, doctors recommend working out the leg from the first days of rehabilitation.
Fighting cracked heels
For heel pain treatment to be effective and efficient, it is necessary to eliminate the underlying cause that caused this discomfort. And if the discomfort was caused by the appearance of cracks, then a compress of cabbage leaves will help. The feet are pre-steamed and generously lubricated with lard or pork fat. After this, the leaves need to be mashed a little so that they release the juice, and apply to the heels for 20 minutes.
Chopped onions mixed with milk accelerate the healing of cracks and thereby relieve heel pain. Such lotions must be done twice a day. If you want to get rid of cracks as quickly as possible and forget about unbearable discomfort, then you can use compresses based on lemon juice combined with grated raw potatoes. This procedure must be repeated every two hours.
Prunes boiled in milk can give a positive result. Boiled warm dried fruits are applied to the sore heel for 40 minutes, after which the feet are rinsed with water. Such an unusual treatment at home and in familiar conditions will indeed help eliminate pain.
Prunes boiled in milk have a therapeutic effect on cracked heels
Egg yolks mixed with a small amount of honey can reduce pain and speed up the healing of cracks. The heels are coated with this mixture, and after five hours the feet are washed with water. Fat sour cream with honey has a similar effect, which is applied to the affected area for one hour and then washed off.